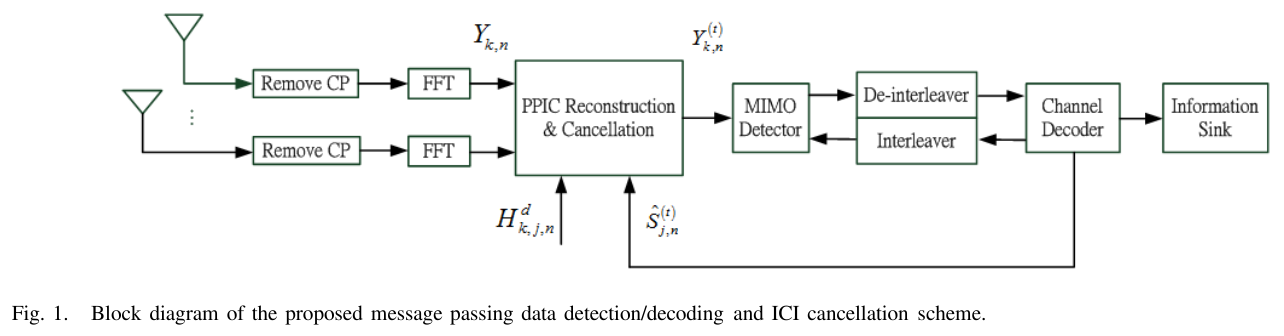
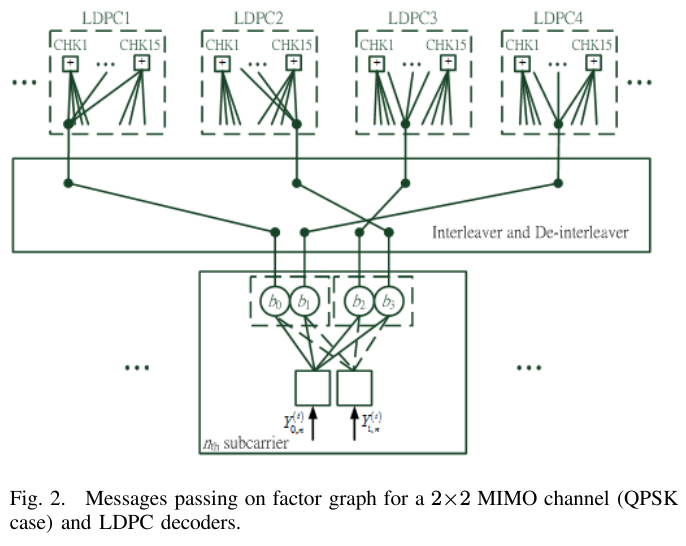
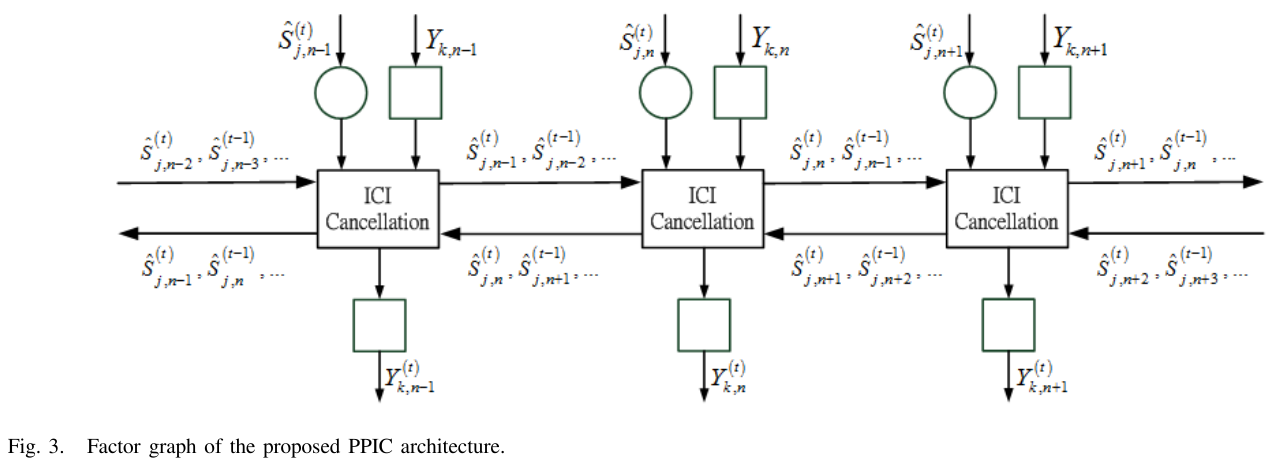
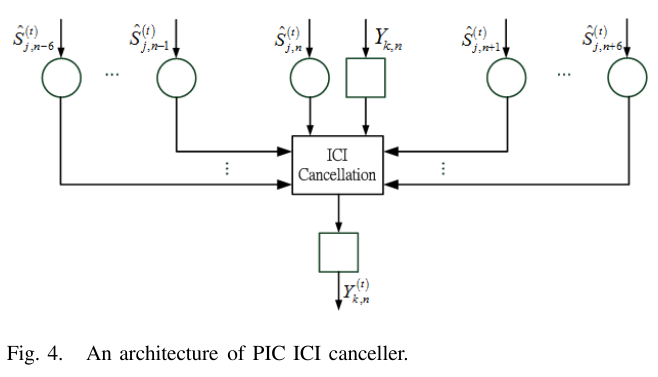
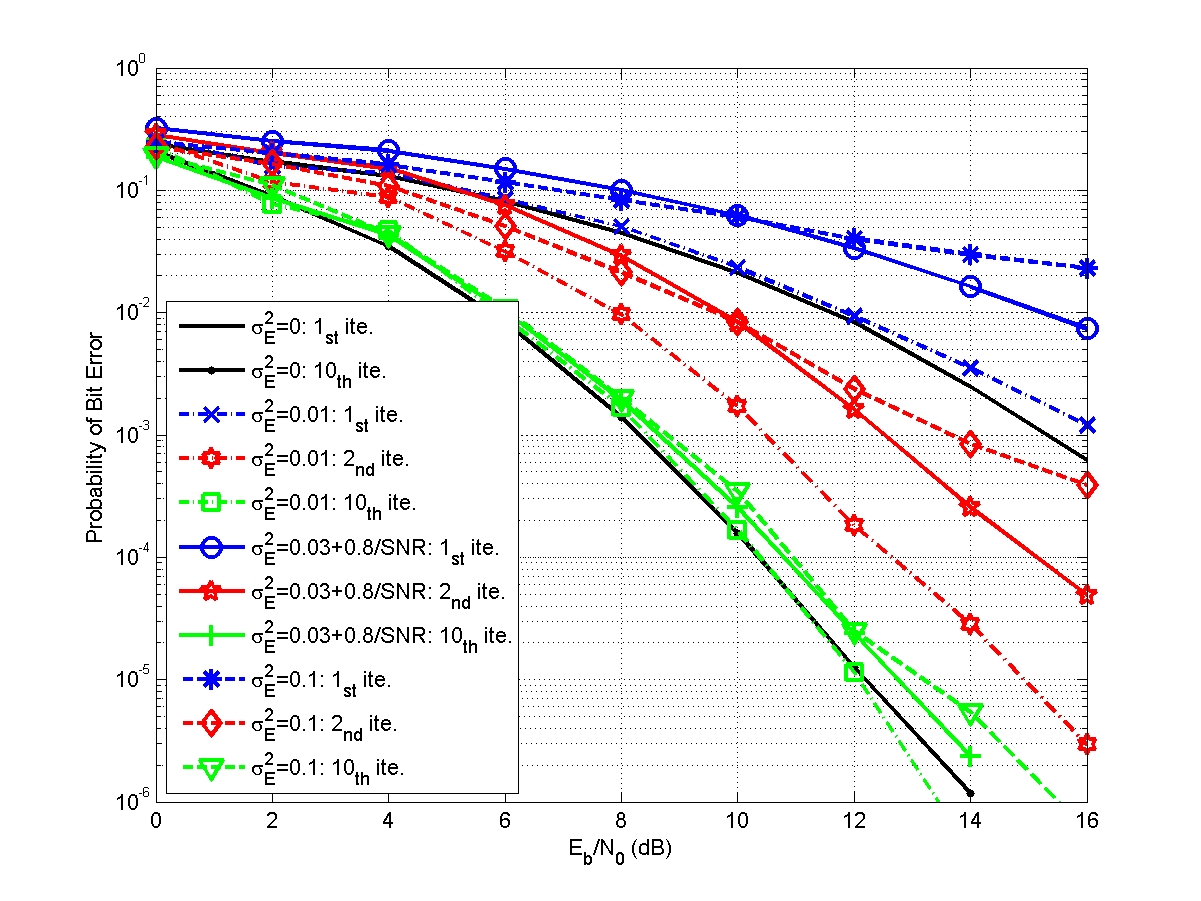
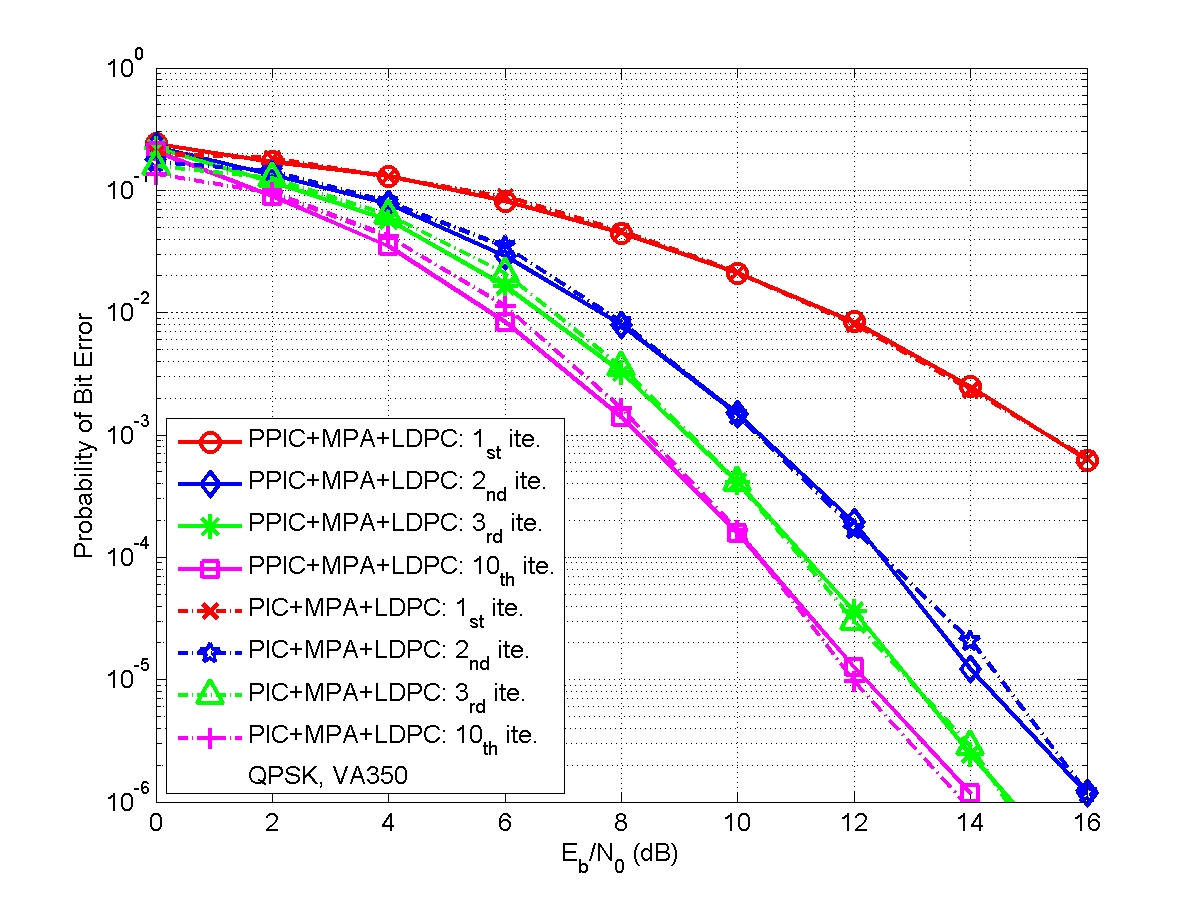
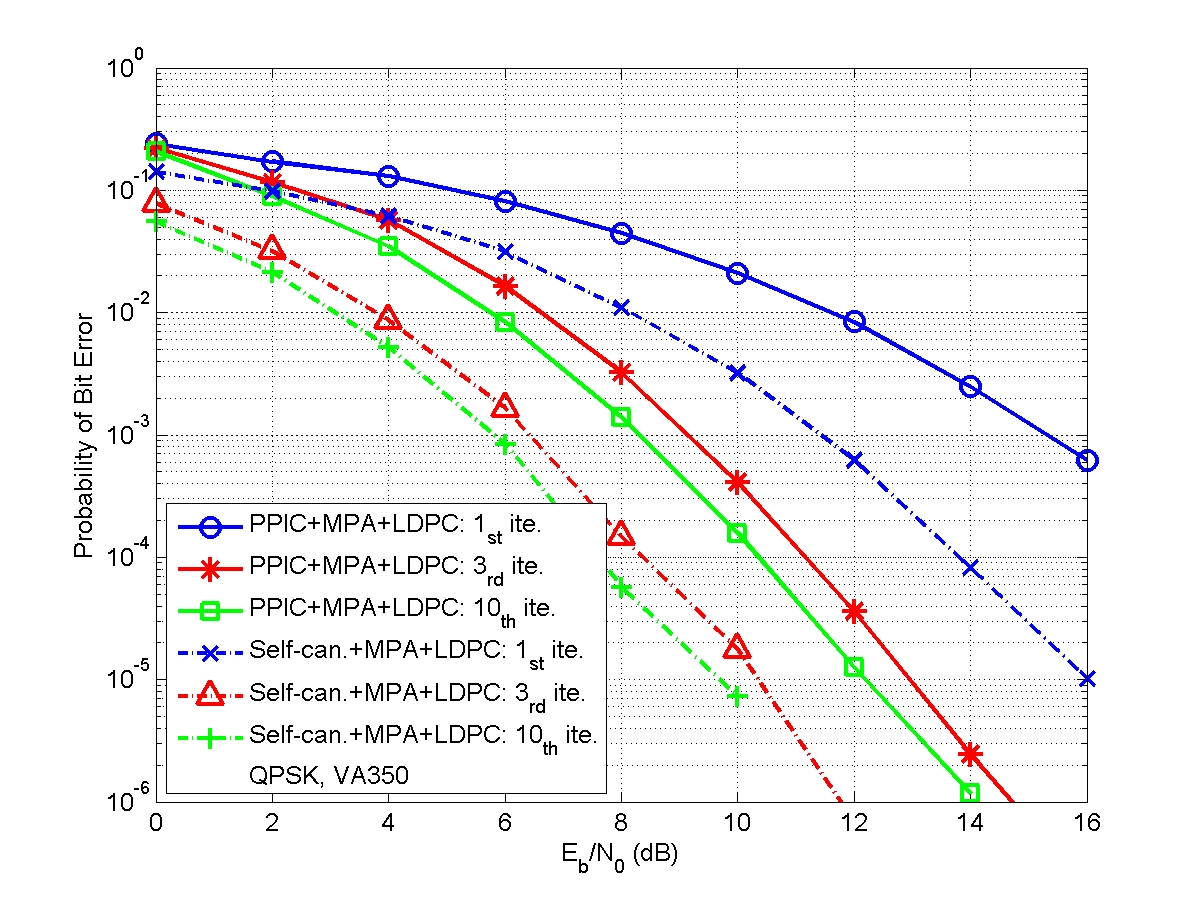
A joint design of message passing MIMO data detector/decoder with progressive parallel inter-carrier interference canceller (PPIC) based on factor graph for OFDM-based wireless communication systems is proposed. By exchanging messages both in space domain and frequency domain, the proposed algorithm can suppress inter-antenna interferences and cancel inter-carrier interferences iteratively and progressively. With a proper designed message passing schedule and random interleaver, the short cycle problem is solved. Computer simulations show that the performance of the proposed message passing MIMO detector outperforms MMSE-SIC MIMO detector. The performances of PPIC, both in perfect channel estimation and imperfect channel estimation cases, are compared with the standard PIC architecture and the ICI self-canceller. The proposed PPIC is superior to PIC both in computational complexity and system architecture. The parallel structure of PPIC is similar to a systolic array. The proposed algorithm potentially leads to a very-high-speed detector/decoder. It is very suitable for VLSI implementation and it is a potential candidate for data detection/decoding in future high data rate, high mobility, wireless MIMO-OFDM communication systems.
- Sum Product Rule
- Max Product Rule
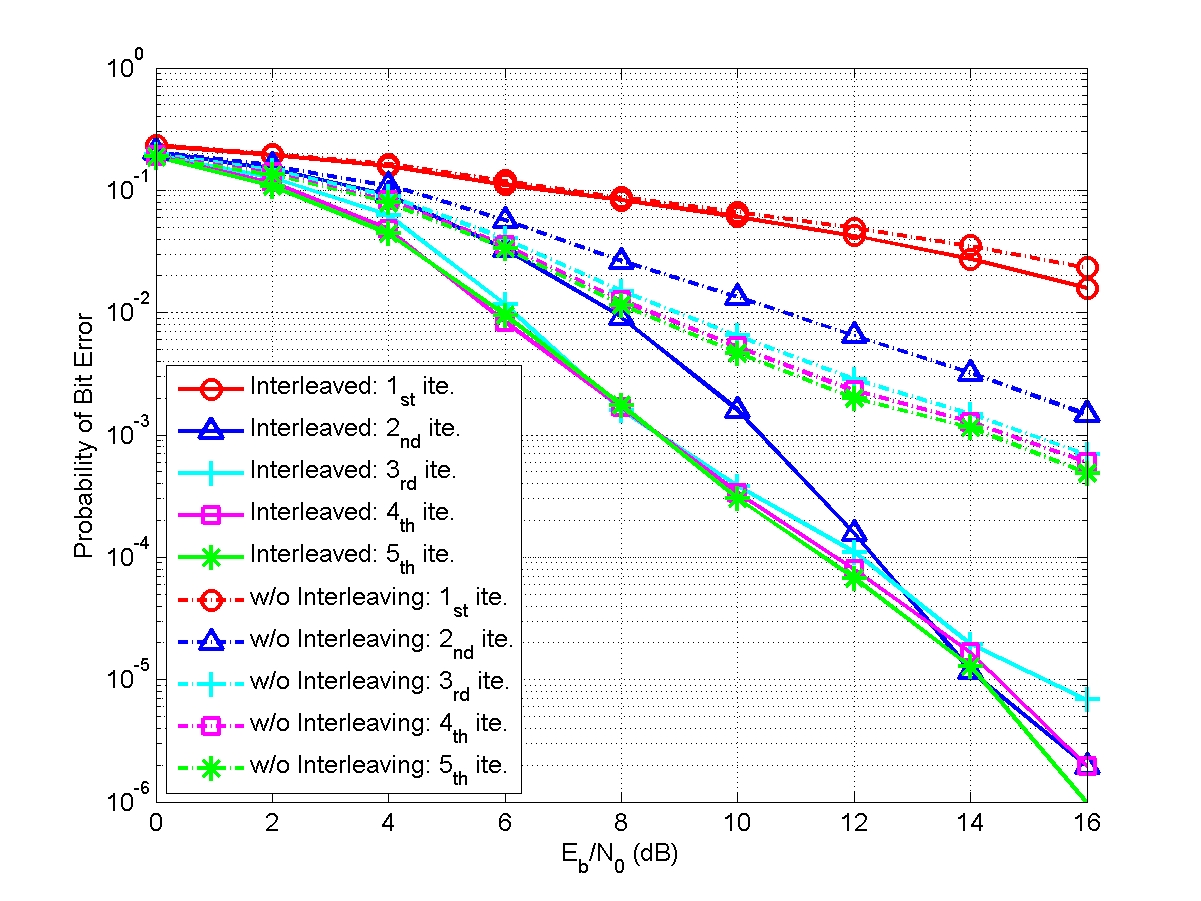
- MIMO Detector with progressive parallel ICI cancellation over multipath Rayleigh fading channel
- MAP MIMO detector and MMSE MIMO detector
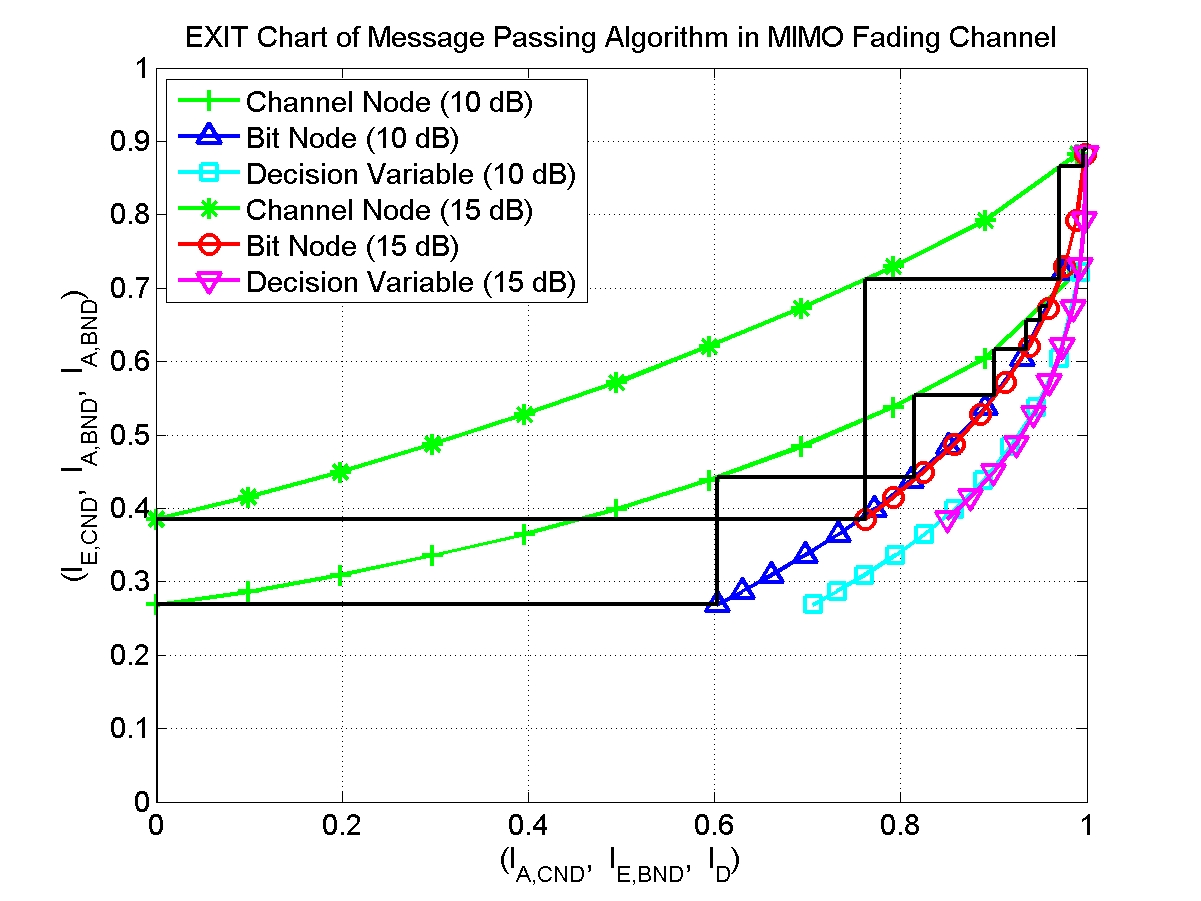
- EXIT chart (EXtrinsic Information Transfer chart) analysis
- EXIT chart