This project is a NNs converter between Keras and Caffe (in both directions) and it includes pruning functionalities in Keras.
keras-caffe_converter_optimizer
|-- src
| |-- op_kp_printer.cpp
| |-- conversion
| | |-- caffe2keras_converter.py
| | |-- keras2caffe_converter.py
| | |-- caffe2keras
| | | |-- create_nn_struct.py
| | | |-- caffe_weight_converter
| | | | |-- caffe_weight_converter.py
| | |-- keras2caffe
| | | |-- create_prototxt.py
| | | |-- k2c_1.py
| | | |-- k2c_2.py
| | |-- README.md
| |-- optimization
| | |-- simple_classifier.py
| | |-- retrain_resnet50_cifar10.py
| | |-- README.md
Caffe is known to be the most efficient framework for developing and deploying NNs. It's made to work with C++, a Python API exists, but it's still a bit uncomplete and not very well documented. Furthermore no pruning/optimization APIs are available.
Keras is one the most high level framework for NNs. It works with Python and it's the most approachable way to work with NNs, moreover there's a specific module for pruning: tensorflow_model_optimization.sparsity
This project allows you to convert NNs from Caffe to Keras and back, so it's possible to work with the most approachable and high level framework to later deploy your NNs in the most efficient one. It may also turn useful, for example, to manipulate NNs in Keras within a project that necessarily requires Caffe.
User instructions: see the apposite README.md
In src/optimization/ there are 2 demo scripts to test Keras' pruning functionalities.
simple_classifier.pycreates and prune a small custom model for image classification withFashion MNISTretrain_resnet50_cifar10.pyis an example of 'transfer learning' plus pruning. The script loads ResNet50 with imagenet weights, adapts the net to perform classifications onCIFAR10and implements pruning functionalities.
User instructions: see the apposite README.md
Conversion:
The models conversion has been tested with OpenPose. I created a C++ script (op_kp_printer.cpp) to be placed in openpose/examples/user_code/ to process the frames from a video input and write all the keypoints (code, name and coordinates) in a csv file. Then, giving that file as input to INDE_performance_test the following graphs were extracted:
The first one was generated using the original OpenPose's models:
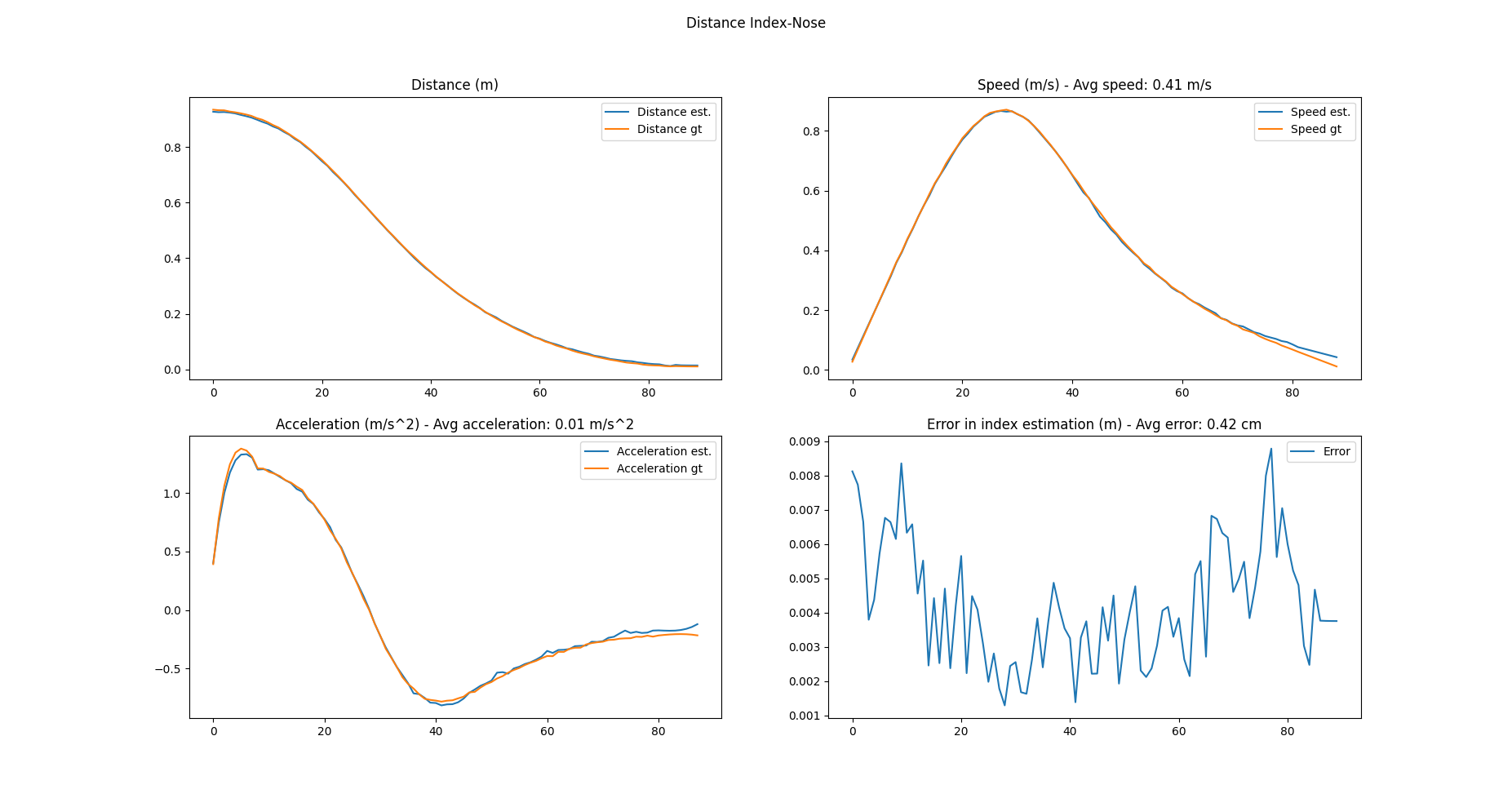 The second one with the same models converted from Caffe to Keras and back to Caffe:
The second one with the same models converted from Caffe to Keras and back to Caffe:
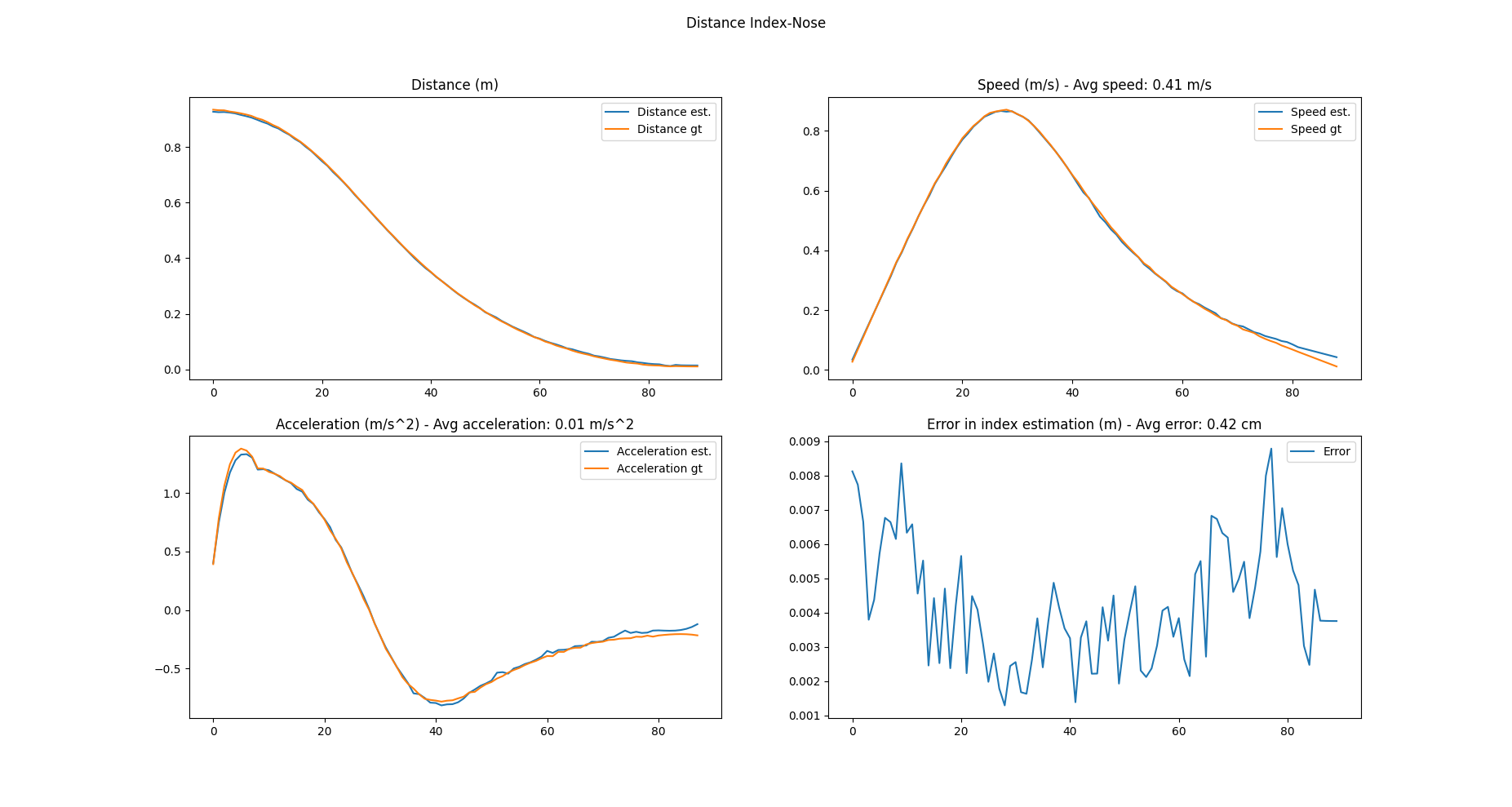 As it's possible to notice, they're basically identical, so the conversion back and forth does not introduce any error nor approximation.
As it's possible to notice, they're basically identical, so the conversion back and forth does not introduce any error nor approximation.
Pruning:
simple_classifier.py:
- Base model avarage accuracy: 0.8963 (89.63%)
- Pruned model avarage accuracy: 0.8945 (89.45%)
- Base model avarage evaluation time with 10000 samples: 0.6029 s
- Pruned model avarage evaluation time with 10000 samples: 0.2979 s
- Base model avarage accuracy: 0.8123 (81.23%)
- Pruned model avarage accuracy: 0.8001 (80.01%)
- Base model avarage evaluation time with 10000 samples: 5.2928 s
- Pruned model avarage evaluation time with 10000 samples: 4.2747 s

