Keyword: iOS, Objective-C, MVVM, RAC, Redux
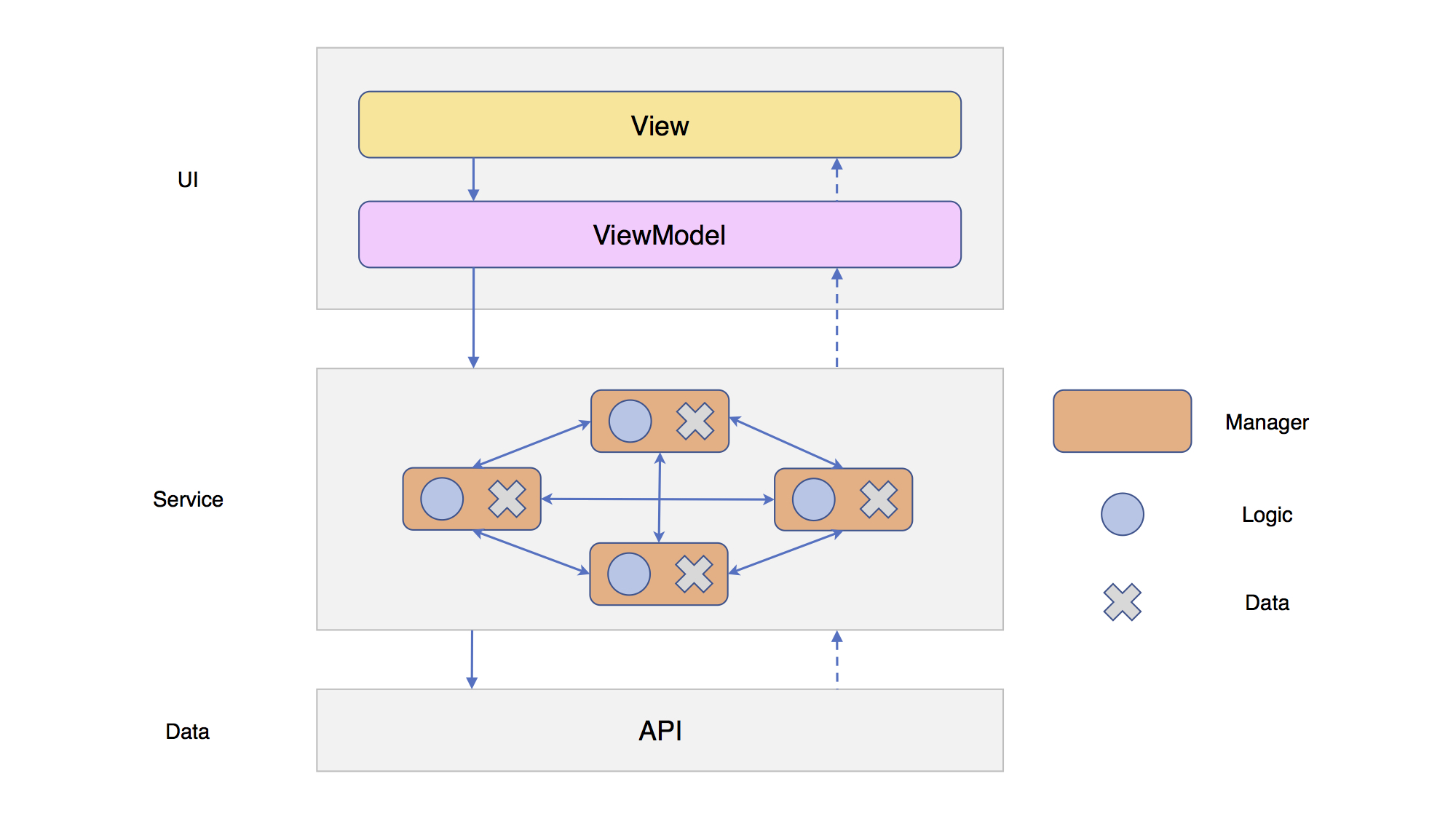
在这个架构中,UI层采用MVVM模式,Service层负责处理业务逻辑,Data层负责底层的网络请求等业务。
Service层中有多个Manager,每个Manager负责不同类型的业务逻辑,同时也会存储一些状态、数据。
Manager之间也会相互调用,以及访问各自的数据。
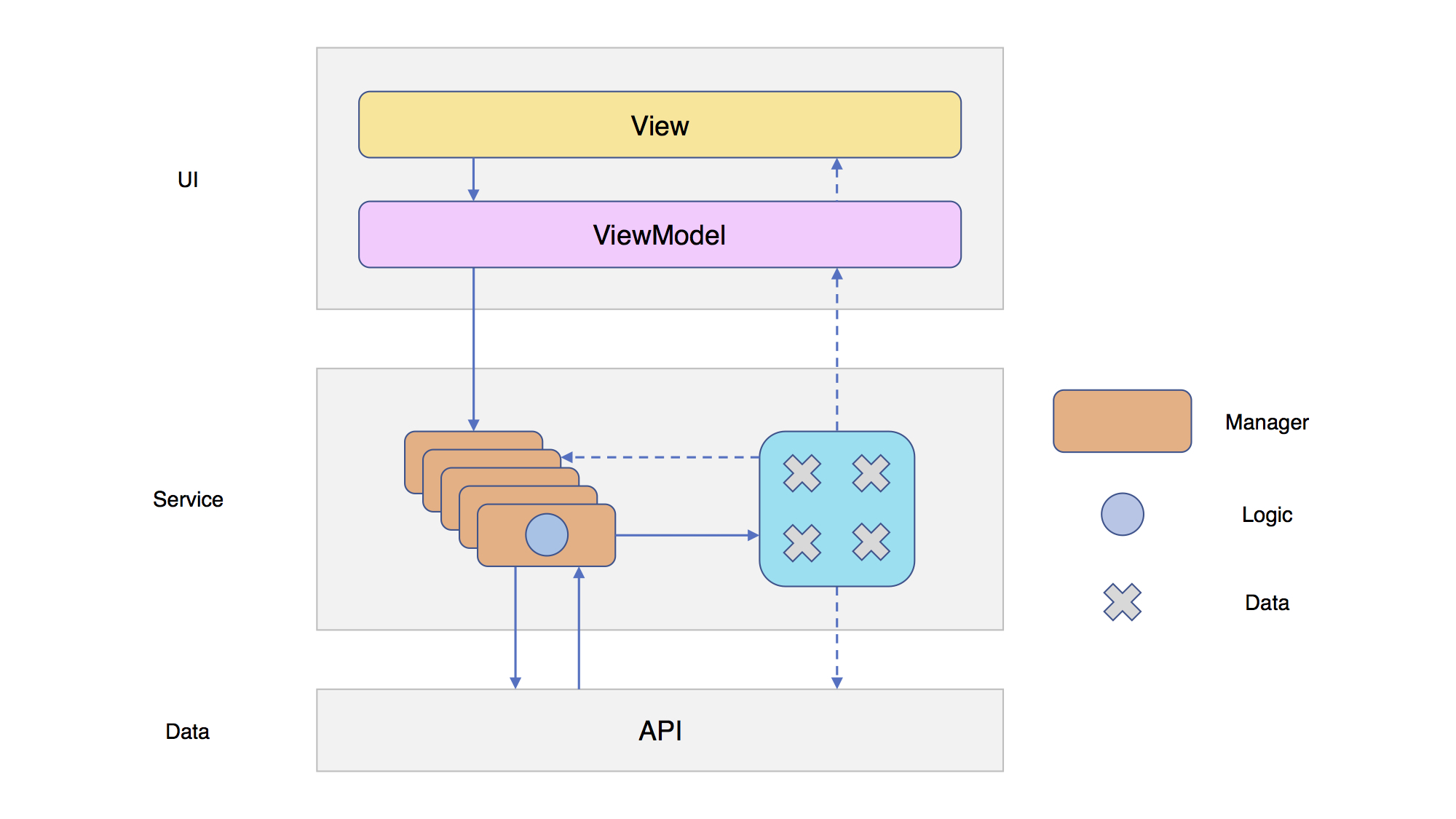
随着业务内容的不断增加,Manager之间的关系也会变得越来越复杂,数据的相互调用很容易发生错误。
理想的情况是将Manager中的业务逻辑与数据分离,这样即使Manager之间的关系有多么地复杂,也能够保证数据的高度独立性,不容易出现问题。
说到Redux,就不得不提Flux。Flux是由Facebook开发、用于构建客户端Web应用的一个架构,它的核心理念是“让数据单向流动”。利用Flux,我们可以非常方便地来管理和控制数据的流向。而Redux,可以将其看作以Flux为基础的一个演进版本。
在Swift语言中有ReSwift这样一个框架,它将Redux的**应用到了iOS开发中。
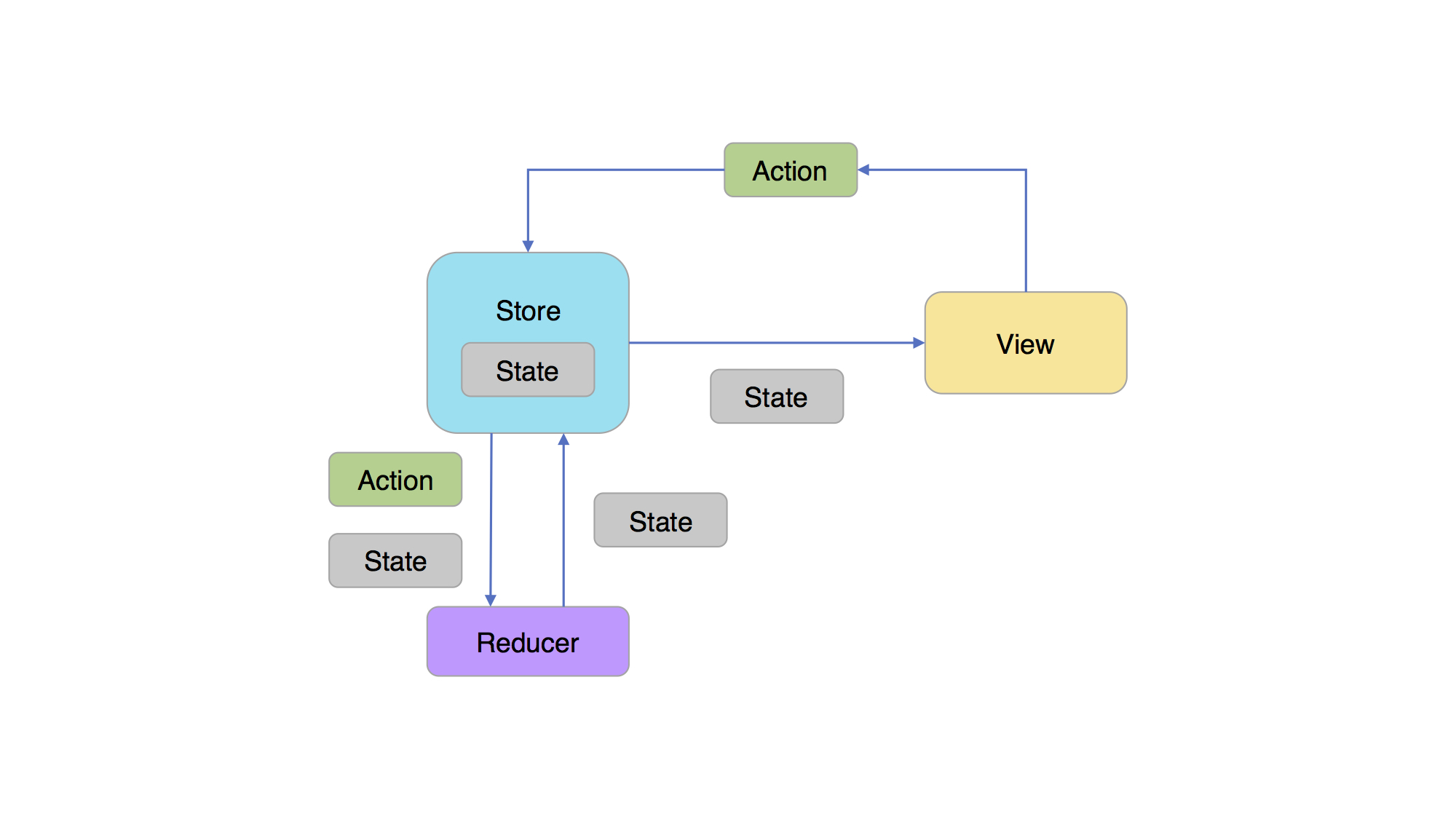
上图为ReSwift的主要架构
- View:UI,向用户展示的界面。
- Action:把数据传到Store的有效载荷,是Store中数据的唯一来源。它有可能是来自服务器的响应,或者是用户的输入。
- Store:负责存储、管理State,分配Action给Reducer。
- State:实际上是一种数据结构,而且是只读的,唯一能改变它的地方在Reducer。
- Reducer:负责更新State的地方
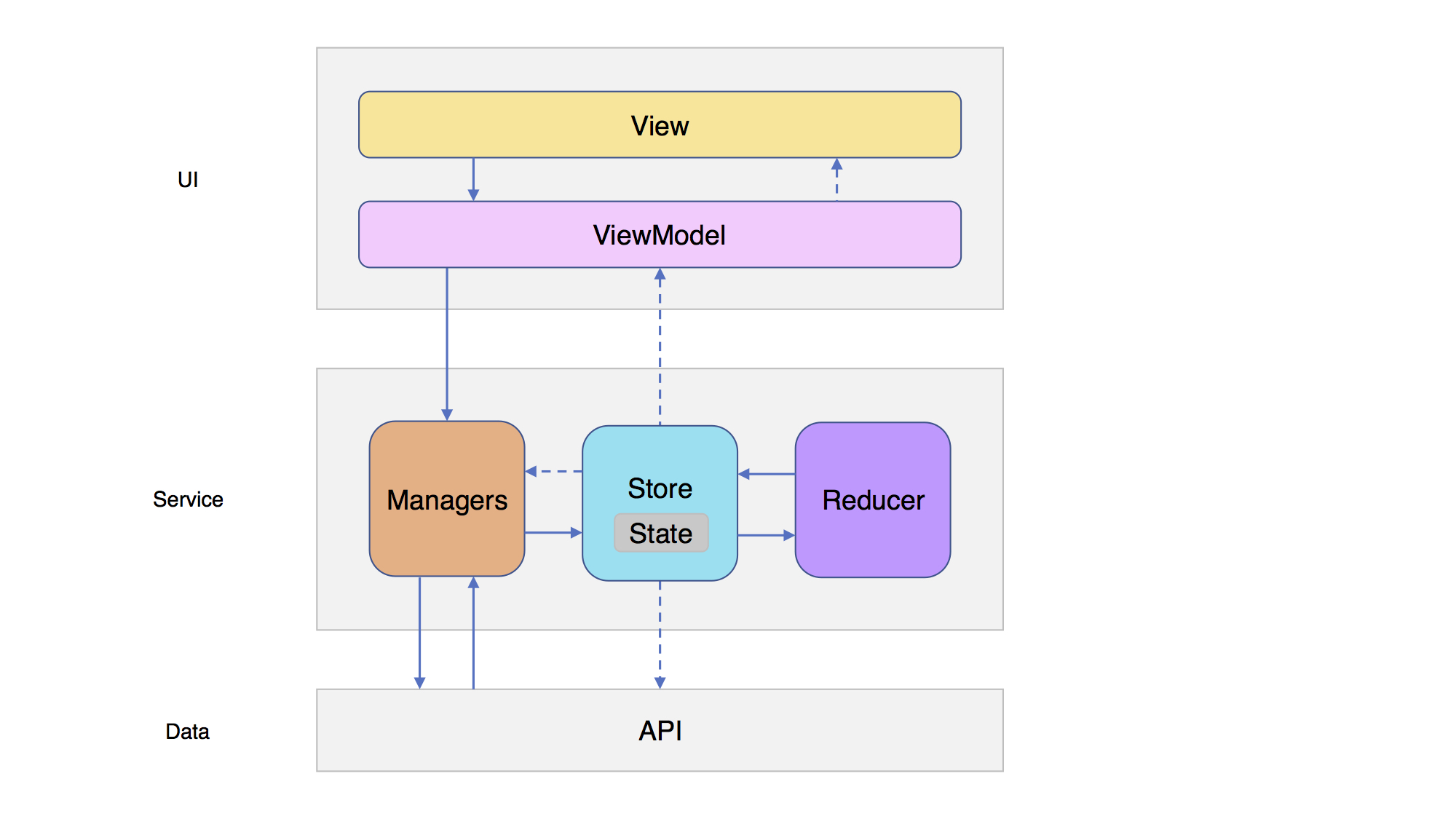
将ReSwift的View换成Manager,利用Redux的**,我们可以将Manager中原有的业务逻辑与数据分离。
Manager只负责逻辑业务,如何储存数据以及如何操作数据则全部交由Store去处理。
流程:
-
当Manager获取到数据或者数据需要改动的时候,会向Store发送一个Action,Action包含着对数据处理的方式以及数据本身(可空)。
-
Store收到来自Manager的Action后,会连同自身存储的State一并交给Reducer,Reducer会根据Action中的操作方式来对数据进行处理。
-
Store中的State被改变后,可以通过观察者模式来获取最新的数据。
Data层中的NumberGenerator负责生成随机数,模拟网络请求,返回数据。
Service层中的GeneratorManager负责获取随机数,OperateManager负责对数据进行增删操作。
UI层订阅Store中的数据,并将其显示给用户。
Action包含操作方式以及数据,其中数据可以为空。
Action.h
typedef NS_ENUM(NSInteger, ActionType) {
ActionTypeFetchNumber = 0,
ActionTypeAddNumber,
ActionTypeDeleteNumber
};
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN
@interface Action : NSObject
+ (instancetype)type:(ActionType)type payload:(nullable id)payload;
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) ActionType type;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly, nullable) id payload;
@end
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_END储存数据的载体。
State.h
@interface State : NSObject <NSCopying>
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSArray *numberArray;
@end根据业务的复杂程度,Reducer可以有多个,Store将会在Reducer的集合中历遍,以寻找对应能跟操作State的方法。
Reducer.h
@class State;
@class Action;
typedef void (^ReducerBlock)(State **, Action *);
@interface Reducer : NSObject
+ (NSArray *)reducerBlocks;
@endReducer.m
@implementation Reducer
+ (NSArray *)reducerBlocks {
return @[ [self actionReducer] ];
}
+ (ReducerBlock)actionReducer {
ReducerBlock block = ^(State **state, Action *action) {
State *newState = *state;
switch (action.type) {
case ActionTypeFetchNumber: {
newState.numberArray = action.payload;
break;
}
case ActionTypeAddNumber: {
NSMutableArray *temp;
temp = newState.numberArray ? [newState.numberArray mutableCopy] : [NSMutableArray array];
[temp insertObject:action.payload atIndex:0];
newState.numberArray = [temp copy];
break;
}
case ActionTypeDeleteNumber: {
NSMutableArray *temp;
if (newState.numberArray) {
temp = [newState.numberArray mutableCopy];
NSNumber *index = action.payload;
[temp removeObjectAtIndex:index.integerValue];
newState.numberArray = [temp copy];
}
break;
}
default:
break;
}
};
return block;
}
@endStore, 单例。
- 拥有一条串行队列保证每一时刻只有一个Action在执行。
- dispatch方法会把Action分发给Reducer。
- 分配任务给Reducer的时候,将会把当前的State复制一份,并将拷贝结果的地址作为参数传入,让Reducer直接在该地址上对数据进行操作,以提高性能。
注意,Reducer原有的定义为:
(previousState, action) => newState
传入旧的State,创建并返回新的State。
Store.h
@class Action;
@class RACSignal;
@interface Store : NSObject
+ (instancetype)sharedInstance;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) RACSignal *stateSignal;
- (void)dispatchAction:(Action *)action;
@endStore.m
@interface Store ()
@property (nonatomic, strong, readwrite) RACSignal *stateSignal;
@property (nonatomic, strong) dispatch_queue_t serialQueue;
@property (nonatomic, copy ) NSArray<ReducerBlock> *reducers;
@property (nonatomic, strong) State *state;
@end
@implementation Store
+ (instancetype)sharedInstance {
static Store *store;
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
store = [[Store alloc] init];
});
return store;
}
- (instancetype)init {
if (self = [super init]) {
_serialQueue = dispatch_queue_create("com.reduxObjc.queue", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL);
}
return self;
}
- (void)dispatchAction:(Action *)action {
dispatch_async(self.serialQueue, ^{
State *newState = [self.state copy];
for (ReducerBlock block in self.reducers) {
block(&newState, action);
}
self.state = newState;
});
}
#pragma mark - Lazy Loading
- (State *)state {
if (!_state) {
_state = [[State alloc] init];
}
return _state;
}
- (RACSignal *)stateSignal {
if (!_stateSignal) {
_stateSignal = RACObserve(self, state);
}
return _stateSignal;
}
- (NSArray<ReducerBlock> *)reducers {
if (!_reducers) {
_reducers = [Reducer reducerBlocks];
}
return _reducers;
}
@end以下为RAC版本
- (RACScheduler *)scheduler {
if (!_scheduler) {
_scheduler = [[RACTargetQueueScheduler alloc] initWithName:@"ReduxObjc" targetQueue:self.serialQueue];
}
return _scheduler;
}- (RACSignal *)dispatchSignal:(Action *)action {
return [RACSignal createSignal:^RACDisposable *(id<RACSubscriber> subscriber) {
return [self.scheduler schedule:^{
State *newState = [self.state copy];
for (ReducerBlock block in self.reducers) {
block(&newState, action);
}
self.state = newState;
[subscriber sendCompleted];
}];
}];
}优点:逻辑数据分离,结构清晰,易于维护,保证数据安全。
缺点:搭建略为麻烦,不适合小项目,性能较差。
对于一般简单的项目,并不需要使用这种方式来分离逻辑和数据,用了反而多此一举。但对于复杂的项目来说,值得一试。