- Introduction
- Requirements
- Installation
- Data persistence
- Configuring the dashboard
- Advanced Configuration
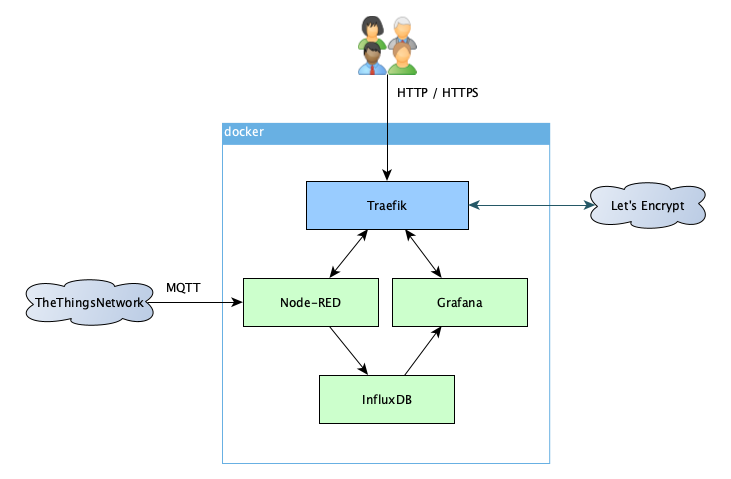
TTN Dashboard provides an easy to setup environment for displaying The Things Network application data on a Grafana dashboard.
This setup is based on Containers orchestrated by docker-compose.
It does not require a lot of resources and can run on a small Linux cloud instance or an ARM based device like a Raspberry Pi.
This project uses Traefik as Edge Router.
Previous version was using NGINX as reverse proxy, this is still available in the nginx branch of this repository, but it isn't maintained anymore.
The project uses the following container images:
- Traefik as Edge Router (only needed if you do not already run a Traefik instance on your host)
- Node-RED: user friendly interface to collect data from The Things Network, process it and store it into a database
- InfluxDB: Time series database to store the data
- Grafana: provides web-based dashboards from the stored data
You will need a Linux host with a container runtime (docker or podman), docker-compose and git installed.
Minimum required versions are:
docker: 17.06.0 or abovepodman: 3.0 or abovedocker-compose: 1.18.0 or above
However, for security reason, latest versions are strongly recommended.
If you want to expose your dashboard to the Internet, you will need domain names!
Traefik uses the domain name to route the requests to either Grafana or Node-RED; you will need two domain names pointing to your server -- e.g.: ttn-grafana.example.com and ttn-node.example.com.
If you don't have your own domain you can use a free service like Duck DNS.
For local/home usage (intranet) you can use a local DNS server or even the hosts file of your workstation.
-
Clone this repository and enter its directory:
git clone https://github.com/oracle/AmedeeBulle/ttn-dashboard.git cd ttn-dashboard -
Copy the
.env.distrfile to.envcp .env.distr .env
-
Customize the
.envfile to your needs, the following parameters are mandatory:- Host names
TTN_GRAFANA_HOST: the hostname to access the Grafana dashboard -- e.g.:ttn-grafana.example.comTTN_NODE_RED_HOST: the hostname to access the Node-RED interface -- e.g.:ttn-node.example.com
- InfluxDB
TTN_INFLUX_ADMIN_PASSWORD: administration passwordTTN_INFLUX_PASSWORD: password for the user with read/write access (used in Node-RED to insert data)TTN_INFLUX_READ_PASSWORD: password for the user with read-only access (used in Grafana to query the database)
- Grafana
TTN_GRAFANA_ADMIN_PASSWORD: password for the admin user (additional users are defined in Grafana itself)
- Node-RED
TTN_NODE_RED_CREDENTIALS: credentials to access the Node-RED instance.
- Traefik
- If you already run a Traefik container instance, set the network name, Entry Points and Certificate Resolver to match your existing configuration.
- Otherwise set
TRAEFIK_EMAIL, the email address used when requesting Let's Encrypt certificates.
- Host names
-
Building container images.
Thenode-redcontainer needs to be built to add theinfluxdbnodes:docker-compose build
docker network create traefik
-
If you don't already run a Traefik container instance, add
docker-compose-traefik.ymlto the stack and create thetraefikoverlay network:export COMPOSE_FILE=docker-compose.yml:docker-compose-traefik.yml docker network create traefik -
Start the containers (use Control-C to stop):
docker-compose up
The InfluxDB database will be created and initialized the first time the container runs.
You should be able to browse to your new Node-RED/Grafana setup using the specified domain names.
Basic docker-compose commands.
Start the containers (in detached mode):
docker-compose up -dView the log (use -f to follow log output):
docker-compose logs [-f]Stop (kill) the containers:
docker-compose killStop and destroy the containers:
docker-compose downIf you expose your setup to the Internet you should enable HTTPS to encrypt the traffic.
This will happen automatically once you add docker-compose-https.yml to the compose stack:
-
Stop the containers (if they already run)
docker-compose down
-
Set the
COMPOSE_FILEenvironment variable:# If you have a separate traefik container: export COMPOSE_FILE=docker-compose.yml:docker-compose-https.yml # Or with the traefik container from this repository export COMPOSE_FILE=docker-compose.yml:docker-compose-traefik.yml:docker-compose-https.yml
-
Restart the compose stack:
docker-compose up -d && docker-compose logs -f
It might take a couple of minutes to get the Let's Encrypt signed certificates in place, after which you can enjoy Secure HTTP!
Note that the HTTPS configuration is only possible if your server is exposed to the Internet (either directly or through NAT) as Let's Encrypt needs to authenticate the service (strictly speaking, Traefik also supports Let's Encrypt DNS-01 challenge, but you will have to update the Traefik configuration in docker-compose-traefik.yml)
Data (database, certificates, ...) is stored in docker named volumes and persists across container/system restart.
If you really want/need to delete the volumes and the associated data, run:
docker-compose down --volumesThis section covers the settings specific to this project; detailed instructions on how to use Node-RED and Grafana is outside the scope of this document.
See The Things Stack Node-RED Integration.
Configuration of the InfluxDB Server in the InfluxDB nodes:
Host: influxdbPort: 8086Database: same asTTN_INFLUX_DBparameter (default: ttn)Username: same asTTN_INFLUX_USERparameter (default: ttn-user)Password: same asTTN_INFLUX_PASSWORDparameterEnable secure (SSL/TLS) connection: unchecked
Create an InfluxDB data source (leave all fields not mentioned here to their default value):
URL:http://influxdb:8086Database: same asTTN_INFLUX_DBparameter (default: ttn)User: same asTTN_INFLUX_READ_USERparameter (default: ttn-read)Password: same asTTN_INFLUX_READ_PASSWORDparameter
The setup can be further customised (usernames, log level, ...) in the .env. It should be self-explanatory.
You can monitor your servers with collectd, and send the data to your InfluxDB instance
If you only want to monitor the dashboard host, perform the following easy steps:
-
Install collectd using your operating system package manager (
yum,apt, ...) -
On the collectd side, ensure the
networkplugin is enabled and configured -- E.g. in/etc/collectd.conf:... LoadPlugin network ... <Plugin network> # client setup: <Server "127.0.0.1" "25826"> SecurityLevel None </Server> ... </Plugin> ... -
Configure InfluxDB in the
.envconfiguration file:# Monitoring servers with collectd: TTN_INFLUXDB_COLLECTD_ENABLED=true # Database name for collectd (by default use the initial DB) TTN_INFLUX_COLLECTD_DB=ttn # Port to bind on: do NOT bind on your public interface! TTN_INFLUXDB_BIND_ADDRESS=127.0.0.1:25826 # Security level (none, sign, encrypt) TTN_INFLUXDB_COLLECTD_SECURITY_LEVEL=none -
Re-start collectd and the containers
If you want to monitor additional hosts (e.g. your gateways, ...), you will have to use the (private) IP of your server instead of the loopback interface.
It is also recommended to encrypt the collectd traffic.
-
Install collectd using your operating system package manager (
yum,apt, ...) -
On the collectd side, ensure the
networkplugin is enabled and configured -- E.g. in/etc/collectd.conf:... LoadPlugin network ... <Plugin network> # client setup: <Server "<YourServerPrivateIP>" "25826"> SecurityLevel Encrypt Username "<YourCollectdUser>" Password "<YourSecretPassword>" </Server> ... </Plugin> ... -
Configure InfluxDB in the
.envconfiguration file:# Monitoring servers with collectd: TTN_INFLUXDB_COLLECTD_ENABLED=true # Database name for collectd (by default use the initial DB) TTN_INFLUX_COLLECTD_DB=ttn # Port to bind on: do NOT bind on your public interface! TTN_INFLUXDB_BIND_ADDRESS=<YourServerPrivateIP>:25826 # Security level (none, sign, encrypt) TTN_INFLUXDB_COLLECTD_SECURITY_LEVEL=encrypt -
Create a file named
auth_filewith the username/password pair you specified in the/etc/collectd.conffile:<YourCollectdUser>:<YourSecretPassword> -
Copy that file into the
ttn_influxdbvolume$ # the actual volume name may vary depending on your configuration $ docker volume ls | grep ttn_influxdb local ttn-dashboard_ttn_influxdb $ # copy the file to the volume $ docker cp auth_file ttn-dashboard_ttn_influxdb:/etc/collectd/ -
Re-start collectd and the containers