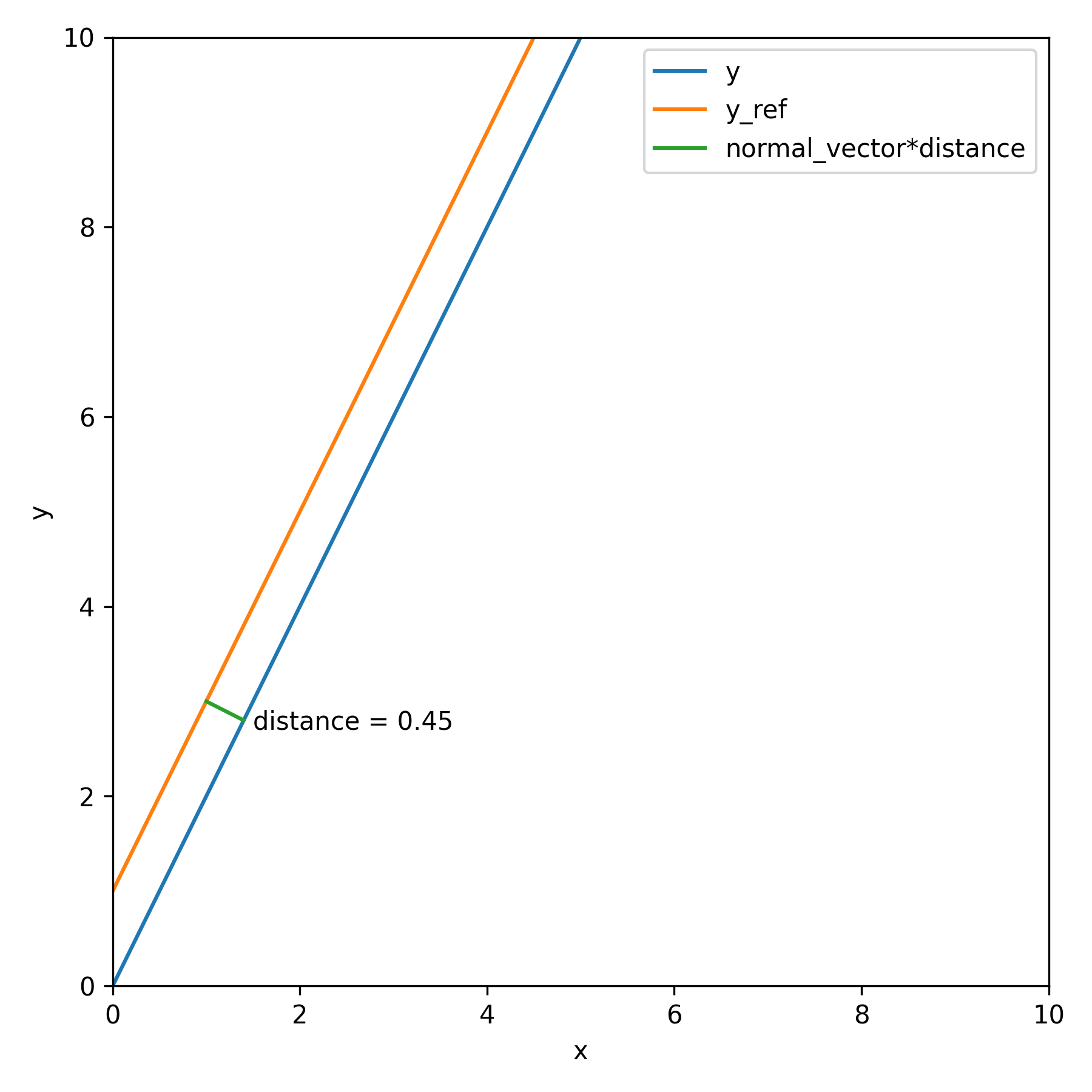
spdist is a simple metrics for comparing the distance between two given curves. The curves can be passed in as a numpy array with discrete values. It will interpolate between the values and calculate the minimum distance between each points in the curve and reference curve.
pip install spdistCurrently spdist has only one function spdist.
import spdist
import numpy as np
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y = 2*x
x_ref = x
y_ref = 2*x + 1
distance = spdist.spdist(x,y,x_ref,y_ref)
print(f"{distance}")Following example plot a straight line spdist function.
The normal vector is calculated as
The algorithm of the caculation is somewhat brute force and the time complexity is
distance = 0
for i in zip(x,y):
tmp_distance = 0
for j in zip(x_ref, y_ref):
if (x_ref == x_ref_next) and (y_ref == y_ref_next):
# point to point distance
tmp_distance = min(tmp_distance, ((x - x_ref)**2 + (y - y_ref)**2)**0.5)
continue
# point to line distance
# https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Distance_from_a_point_to_a_line#Line_defined_by_two_points
tmp_distance = min(tmp_distance, ((x_ref_next - x_ref) * (y_ref - y) - (x_ref - x) * (y_ref_next - y_ref)) / ((x_ref_next - x_ref)**2 + (y_ref_next - y_ref)**2)**0.5)
distance += tmp_distance
distance /= len(x)Although the algorithm itself is not optimized, the whole library is written in Rust Rust with parallel processing. (Thanks to Rust's borrow checker and rayon rayon, which is both great work.) Therefore, the calculation is fast enough.
This library was originally developed to calculate the distance between the measured spectra and the reference spectra of XAS. The metrics is useful to quantify and capture the features of the spectra.