Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis is one of the most popular problems in the globe due to its wide application in real-life situtations. Buying a new car, selecting appropriate supplier for a company, etc. can be defined as Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis problem. There are several methods to solve Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis problems yet the Ordinal Priority Approach (OPA) is one of the most recent MCDA methods.
The Ordinal Priority Approach is a novel Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis method which works based on the ordinal data. It can calculate the weights of experts, criteria, and alternatives at the same time. The OPA believes that human cannot provide precise values for comparing the experts, criteria, and alternatives. Therefore, using the preferences can be helpful to solve the problem. There are several types of solver for the Ordinal Priority Approach, including Web-Based, Excel-Based, Matlab-Based. However, we are going to implement the OPA into the LINGO software here. The important papers on the OPA can be found here. The LINGO software can be downloaded from here.
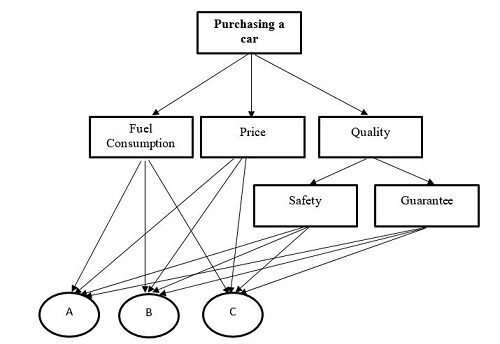
Here, we aim to buy a new car based on some pre-defined criteria. The decision problem is shown on the following figure:
The expert believes that the preference of the criteria are as follows:
P > S > G > F
Moreover, the expert suggested the following preference for each car in each criterion:
In criterion P : A > C > B
In criterion S : C > A > B
In criterion G : B > C > A
In criterion F : B > A > C
Since there is one expert, the problem is individual decision-making. Therefore, in the 1-Individual Decision-Making.lg4, we define the criteria, and alternatives as follows:
sets: Experts/E/:Experts_color,W_Experts; Criteria/G S P F/:W_Criteria; Alternatives/A B C/:W_Alternatives; Experts_Criteria(Experts,Criteria):Criteria_color; Experts_Criteria_Alternatives(Experts,Criteria,Alternatives):Alternatives_color,W; Experts_Alternatives(Experts,Alternatives); Criteria_Alternatives(Criteria,Alternatives); endsets
for your problem, you need to change the name or number of criteria and alternatives (bold values). There is no need to change other things in this part. Now, we are going to enter the input data regarding the criteria and alternatives. Since the problem is individual decision making, the preference of the expert should be defined as follows:
data: Experts_color= 1; enddata
After that, the preferences of the criteria should be defined as follows (The order of input data must be the same as the sets):
data: Experts_color= 1; Criteria_color= 3 2 1 4; enddata
Then, we should add the preferences of the alternatives as follows as well. Since we have four criteria, there are four rows. First row is related to criterion G.
data:
Experts_color= 1;
Criteria_color= 3 2 1 4;
Alternatives_color= 3 1 2
2 3 1
1 3 2
2 1 3;
enddata
Next, you need to update the number of the alternatives in the following codes (Bold values). Here, we have three alternatives, hence:
@FOR(Experts_Criteria(Ex,Cr): @for(Alternatives(r)|r#ne#3:Experts_color(Ex)*Criteria_color(Ex,Cr)*r*(W(Ex,Cr,Alternatives_color(Ex,Cr,r))-W(Ex,Cr,(Alternatives_color(Ex,Cr,r+1))))>=Z)); @FOR(Experts_Criteria(Ex,Cr): @for(Alternatives(r)|r#eq#3:Experts_color(Ex)*Criteria_color(Ex,Cr)*r*(W(Ex,Cr,Alternatives_color(Ex,Cr,r)))>=Z));
After that, if we solve the problem, the results will be obtained as follows:
W_EXPERTS( E) 1.000000 W_CRITERIA( G) 0.1600000 W_CRITERIA( S) 0.2400000 W_CRITERIA( P) 0.4800000 W_CRITERIA( F) 0.1200000 W_ALTERNATIVES( A) 0.4111111 W_ALTERNATIVES( B) 0.2511111 W_ALTERNATIVES( C) 0.3377778
Ataei, Y., Mahmoudi, A., Feylizadeh, M. R., & Li, D. F. (2020). Ordinal Priority Approach (OPA) in Multiple Attribute Decision-Making. Applied Soft Computing, 86, 105893.