Jan 11, 2021
- First release of the project.
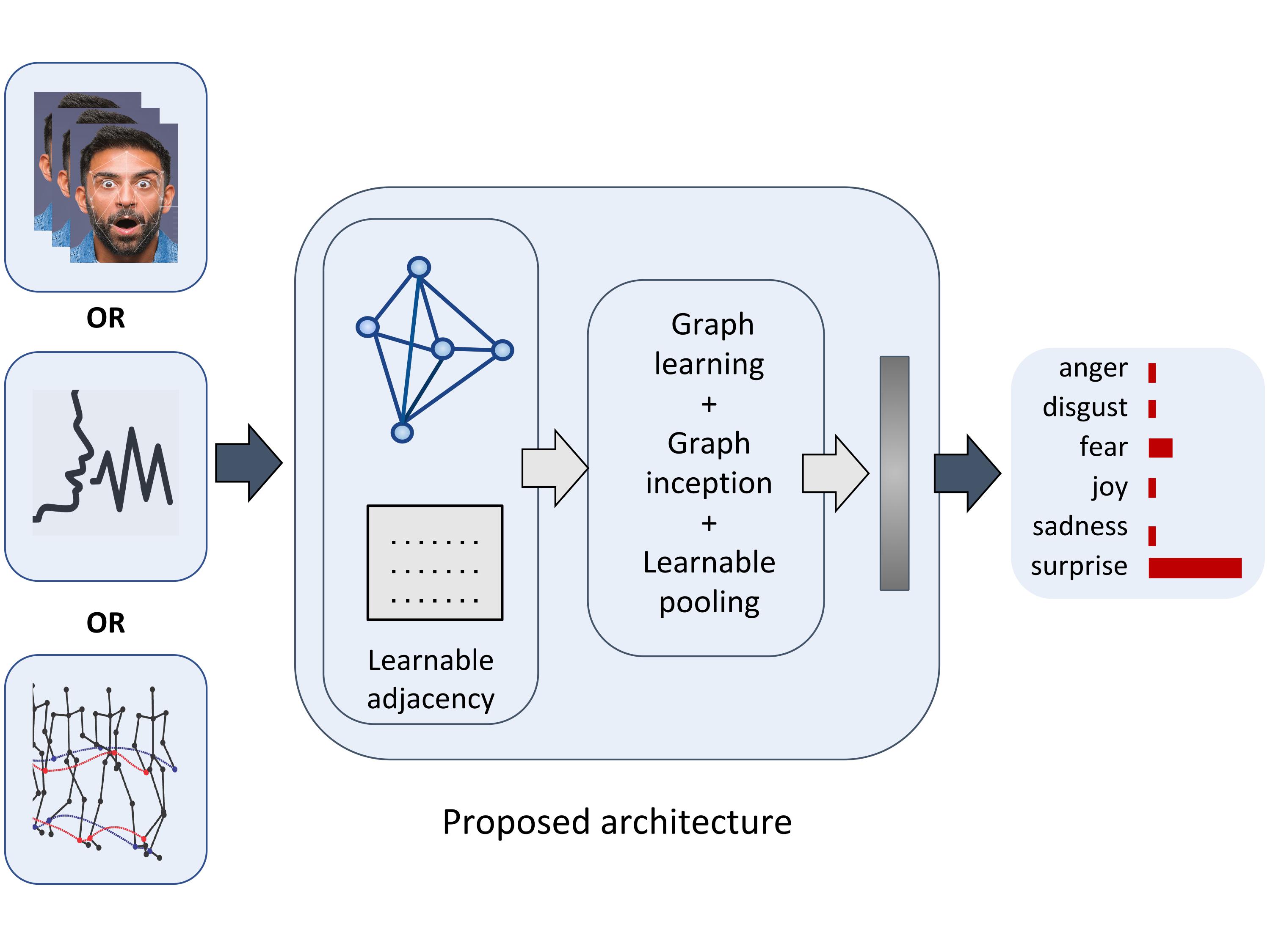
Figure: Qualitative results showing the node (frame) for a graph input that generated the strongest response in our network
In this project, we present the Learnable Graph Inception Network (L-GrIN) that jointly learns to recognize emotion and to identify the underlying graph structure in the dynamic data. Our architecture comprises multiple novel components: a new graph convolution operation, a graph inception layer, learnable adjacency, and a learnable pooling function that yields a graph-level embedding. We evaluate the proposed architecture on five benchmark emotion recognition databases spanning three different modalities (video, audio, motion capture), where each database captures one of the following emotional cues: facial expressions, speech and body gestures.
The code was successfully built and run with these versions:
pytorch-gpu 1.2.0
cudnn 7.6.4
cudatoolkit 10.0.130
opencv 3.4.2
scikit-learn 0.21.2
face_alignment 1.0.1 (for preprocessing)
Note: You can also create the environment I've tested with by importing environment.yml to conda.
The process for RML database is in preprocess directory. The process converts the database into one txt file including graph structure and node attributes.
Note: you can download the processed data from here and put in this directory:
/dataset/
Mine_Graph_RML/
Mine_Graph_RML.txt
You can train a simple model with main_Inception or the full model with main_Inception_learning_adj_pool
usage: main_Inception.py
optional arguments:
-h, --help Show this help message and exit
-device Which gpu to use if any
-batch_size Input batch size for training
-iters_per_epoch Number of iterations per each epoch
-epochs Number of epochs to train
-lr Learning rate
--num_layers Number of inception layers
--num_mlp_layers Number of layers for MLP in each inception layer
--hidden_dim Number of hidden units for MLP
--final_dropout Dropout for classifier layer
--Normalize Normalizing data
--patience Patience for early stopping
If you found this repo useful give me a star!
@article{shirian2020learnable,
title={Learnable Graph Inception Network for Emotion Recognition},
author={Shirian, Amir and Tripathi, Subarna and Guha, Tanaya},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2008.02661},
year={2020}
}