clang-tidy-cache is a command-line application which "wraps" invocations
of the clang-tidy static analysis tool and caches the results of successful
runs of clang-tidy. On subsequent invocations of clang-tidy on an unchanged
translation unit, the result is retrieved from the cache and clang-tidy
is not executed. For most C/C++ projects this allows to have static analysis
checks enabled without paying the cost of excessive build times when re-checking
the same unchanged source code.
clang-tidy-cache scans the command-line arguments passed to clang-tidy,
relevant clang-tidy configuration files, all source files being analyzed
and makes a hash uniquely identifying the invocation of clang-tidy.
Then it searches if its database contains that hash. If it does, clang-tidy-cache
returns immediately without invoking clang-tidy, otherwise clang-tidy
is executed and if it finishes without error, the hash is stored in the database.
clang-tidy-cache by default works as a standalone application and it stores
its hash database in a directory on the local file system. The location
is determined by the CTCACHE_DIR environment variable, by default it
is a sub-tree in the temporary directory. This means that the cache may
be cleared on reboot. If you want the cache to be persistent you need
to specify a path to a disk-backed file system directory.
clang-tidy-cache can also work in client/server mode where a dedicated
HTTP server (the clang-tidy-cache-server executable) can be used to store
and retrieve the cached hashes.
This mode is enabled by setting the CTCACHE_HOST (localhost by default)
and optionally CTCACHE_PORT (5000 by default) environment variables.
The most convenient way how to use clang-tidy-cache is to create a wrapper
shell script called clang-tidy in a directory which is listed
in the executable search path list, before the directory where the real
clang-tidy executable is located (on POSIX systems for example in /opt/bin),
The wrapper script typically contains something along these lines:
#!/bin/bash
REAL_CT=/full/path/to/clang-tidy
/path/to/clang-tidy-cache "${REAL_CT}" "${@}"You can also use the prepared wrapper script from the repository and adapt it to your needs.
Make sure to set write permissions properly to prevent tampering by unauthorized users!
The cache HTTP server can simply be run by executing clang-tidy-cache-server.
The server stores the hash database by default in the .cache/ subdirectory
of the home directory of the user under whose account it is executed.
This can be changed by a command-line option.
Invoke clang-tidy-cache-server with the --help argument to see all available
command-line options.
The systemd/ sub-directory also contains service file(s) that can be used
to run the server as a systemd service (for example on a RPi on the local
network).
The server can also be run in a Docker container.
The provided Dockerfile can be used to build the docker image.
docker build -t ctcache .The CTCACHE_PORT docker environment variable can be used to set the server
port number.
docker run -e CTCACHE_PORT=5000 -p "80:5000" -it --rm --name ctcache ctcacheIn order to make the saved cache data persistent in Docker, you can create
a volume and map it
to the /var/lib/ctcache directory:
docker volume create ctcache
docker run -p "80:5000" -v "ctcache:/var/lib/ctcache" -it --rm --name ctcache ctcacheThe client and server can be configured by setting the following environment variables:
| variable | client | server | description |
|---|---|---|---|
CTCACHE_CLANG_TIDY |
✓ | path to the clang-tidy executable |
|
CTCACHE_DISABLE |
✓ | disables cache, always runs clang-tidy |
|
CTCACHE_SKIP |
✓ | disables analysis altogether, returns OK | |
CTCACHE_STRIP |
✓ | list of strings stripped from inputs | |
CTCACHE_DUMP |
✓ | dumps all hash inputs into a file | |
CTCACHE_DIR |
✓ | the cache storage directory in local mode | |
CTCACHE_S3_BUCKET |
✓ | the S3 bucket to store cache remotely | |
CTCACHE_S3_FOLDER |
✓ | the prefix directory in S3, w/o leading and trailing / |
|
CTCACHE_S3_NO_CREDENTIALS |
✓ | if set, script won't try to put objects to S3 | |
CTCACHE_HOST |
✓ | ✓ | hostname or IP address of the server |
CTCACHE_PORT |
✓ | ✓ | listening port of the server |
CTCACHE_WEBROOT |
✓ | directory containin static server files |
The clang tidy cache's HTTP server also serves a couple of web pages
that are designed to be viewed in a browser.
The main one is the dashboard that can be accessed by visiting / or
/static/index.html at the server's site. For example if the server host name
is localhost and port is 5000 then the dashboard can be visited by
typing http://localhost:5000/ into the browser's address bar.
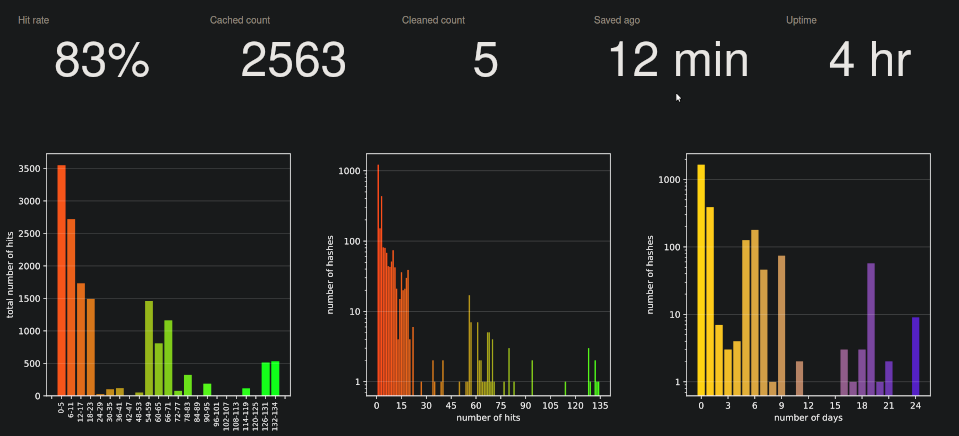
It displays basic information about the cache, like cache hit rate, number of cached hashes, uptime, etc. and some charts providing information about the current state of the server.
There is a presentation describing the motivation, implementation, deployment and configuration options, and some performance measurements in the doc subdirectory.