Cloud computing ek aisi technology hai jisme computing services, jaise ki virtual machines, storage, databases, aur networking, internet ke through provide kiye jaate hain. Isme traditional IT infrastructure ke elements ko bhi shaamil kiya jata hai. Cloud services aaj kal Internet of Things (IoT), machine learning (ML), aur artificial intelligence (AI) jaise advanced technologies ko bhi include karte hain.
Iska matlab hai ki users ko apne local devices par necessary hardware aur software setup nahi karna padta, balki wo services ko remotely access kar sakte hain. Cloud computing ki madad se, users ko scalable aur flexible computing resources milte hain jinhe woh apne requirements ke hisab se use kar sakte hain, aur unhe sirf utni hi resources ke liye pay karna padta hai jitni unhe zarurat hoti hai.
Yeh approach cost-effective hota hai kyunki users ko apne infrastructure ko upgrade ya maintain karne ke liye kharcha nahi karna padta, aur unhe on-demand access milta hai advanced technologies jaise ki AI aur ML ka istemaal karne ke liye. Is tarah se, cloud computing ek modern aur efficient tareeka hai IT resources manage karne ka.
cloud computing ka upayog karke, users ko khud apne infrastructure ko upgrade ya maintain karne ke liye kharcha nahi karna padta. Traditional IT infrastructure mein, jab aapko apne servers, storage, aur networking equipment ko upgrade ya maintain karna hota hai, to isme considerable cost aur time lagta hai.
Cloud computing mein, aap third-party service providers ke through computing resources ka upayog karte hain. Iska matlab hai ki aapko khud servers kharidne ya maintain karne ki zarurat nahi hoti. Aap sirf woh resources use karte hain jo aapko zarurat hote hain, aur iske liye aapko provider ko pay karna hota hai.
Isse cost-effective hota hai kyunki aap only us amount ke liye pay karte hain jo aapne use kiya hai, aur aapko apne infrastructure ki scaling aur maintenance ki chinta nahi hoti. On-demand access ke karan, aap quickly aur flexibly advanced technologies jaise AI aur ML ka istemal kar sakte hain jab aapko zarurat ho.
Overall, cloud computing ek modern, efficient, aur cost-effective approach hai IT resources manage karne ka, jo traditional methods ke mukable mei adhik flexibility aur scalability provide karta hai.
##Internet of Things (IoT): Jab devices, jaise ki sensors aur smart gadgets, data generate karte hain aur ye data cloud computing ke through manage hota hai. Isse data ko ek central location se control kiya ja sakta hai aur ye system scalable hota hai, matlab ki aap as per requirement apne data ko badha ya ghataya ja sakte hain.
##Machine Learning (ML): Cloud services aise computational power aur resources provide karte hain jo machine learning models ko train karne aur deploy karne ke liye zaroori hote hain. Isse organizations ko apne infrastructure ko upgrade karne ki zarurat nahi hoti, aur wo machine learning ka faida utha sakte hain bina kisi bade infrastructure ke.
##Artificial Intelligence (AI): Cloud computing AI applications ke development aur deployment ko support karta hai. Ye computational resources, storage, aur tools provide karta hai jo AI ko seamlessly business processes aur services mein integrate karne mein madad karte hain.
Client/Server Computing: Before the emergence of cloud computing, there was client/server computing, where all software applications, data, and controls were centralized on the server. Users had to connect to the server to access specific data or run programs.
Distributed Computing: Following client/server computing, distributed computing came into play. In this model, computers were networked together and shared resources as needed.
Concept of Cloud Computing: Based on distributed computing, the concept of cloud computing emerged. The idea was to implement computing resources in a way that resembles a utility, much like water or electricity.
John McCarthy's Suggestion (1961): In 1961, John McCarthy suggested in a speech at MIT that computing could be sold as a utility. However, despite interest in the idea, the technology was not ready for it at that time.
Salesforce.com (1999): In 1999, Salesforce.com started delivering applications to users over the Internet, making the idea of computing as a utility a reality for enterprises.
Amazon Web Services (AWS, 2002): In 2002, Amazon launched Amazon Web Services (AWS), providing services such as storage, computation, and even human intelligence. The Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) was launched in 2006 as a truly commercial service open to everybody.
Google Apps (2009): In 2009, Google Apps entered the scene, offering cloud computing enterprise applications.
Microsoft Azure (2009): In the same year, Microsoft launched Windows Azure, marking its entry into the cloud computing space. Other major players like Oracle and HP also joined the evolution.
Mainstream Adoption: Today, cloud computing has become mainstream, with various companies, both early and late adopters, actively participating in the cloud computing ecosystem.
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1WIQXNJN-9jonRvpxcwyJUzgYsh88Dy43/view?usp=sharing
Cloud computing architecture is divided into the following two parts - • Front End • Back End-
Front End (फ्रंट एंड): Yeh client dwara istemal hota hai, jisme user interfaces aur applications hote hain jo cloud computing platforms tak pahunchne ke liye use hote hain. Jaise ki web browsers, tablets, mobile devices, etc.
-
Back End (बैक एंड): Yeh service provider dwara istemal hota hai, jisme saare resources hote hain jo cloud computing services provide karne ke liye chahiye hote hain. Jaise ki data storage, security mechanisms, virtual machines, servers, etc.
cloud models ka matlab hota hai ki kaise aap apne IT resources ko deploy karte hain. Teen main cloud models hote hain: private, public, aur hybrid.
Private cloud ek aisa cloud hai jo sirf ek hi organization ke liye hota hai. Isme company ko zyada control milta hai, lekin iska kharcha bhi zyada hota hai aur public cloud ke fayde kam hote hain. Private cloud apne datacenter par ho sakta hai ya fir kisi dedicated datacenter mein bhi hosakta hai.
- Security and Privacy: Private cloud users ko zyada security aur privacy milti hai.
- Better Performance: Isme better performance hoti hai, tezi aur zyada space capacity ke saath.
- On-Demand Resources: IT team ko on-demand IT resources allocate karne mein jaldi hoti hai.
- Full Control: Organization ko full control hota hai, kyun ki woh apne aap manage karta hai.
- Personalized Use: Ye un organizations ke liye suitable hai jo apne personal use ke liye alag cloud chahte hain aur unko apni data security se fikar hai.
- Skilled People Required: Isko operate karne ke liye skilled log chahiye hote hain.
- Limited Operations: Private cloud sirf organization ke andar accessible hota hai, bahar nahi.
- Not Suitable for High User Base: Ye un organizations ke liye suitable nahi hai jo zyada users ke saath kaam karte hain.
- Infrastructure and Manpower: Agar organization mein infrastructure nahi hai ya sufficient manpower nahi hai to private cloud suitable nahi hoga.
Public Cloud ek aisa cloud hota hai jo third-party cloud provider dwara banaya, control kiya, aur maintain kiya jata hai. Isme koi bhi jo cloud services kharidna chahe, woh resources ko access aur use kar sakta hai. Isme general public ke liye availability hoti hai, aur yeh public aur private clouds ke beech ka ek bada difference hai.
- Kam Cost: Public cloud private aur hybrid cloud se sasta hota hai.
- Maintenance-Free: Isme provider maintenance karta hai, toh aapko iski fikar nahi hoti.
- Integration Aasan: Public cloud ko integrate karna aasan hota hai, jisse flexibility milti hai.
- Location Independent: Kyunki services internet ke zariye milti hain, isliye location par koi restriction nahi hoti.
- Scalability: Computing resources ko zarurat ke mutabiq scale karne mein madad karta hai.
- Accessible to General Public: Public cloud ko general public bhi access kar sakti hai, isme user limit nahi hoti.
- Kam Security: Public cloud less secure hota hai kyun ki resources publically share hote hain.
- Performance Depends on Internet: Performance high-speed internet network par depend karta hai.
- Client Ka Data Control Nahi Hota: User ko apne data par full control nahi hoti, provider control karta hai.
Hybrid Cloud ek aisa computing environment hai jo public aur private dono clouds ka use ek interconnected environment mein karta hai. Isme private cloud temporary demand ke liye public cloud resources ka istemal karke surge kar sakta hai. Hybrid cloud extra security layer bhi provide karta hai, jisme users ko flexibility milti hai ki kaun se services ko public cloud mein rakhein aur kaun se private cloud infrastructure mein.
- Adhik Security: Hybrid cloud organizations ke liye suitable hai jo zyada security chahte hain.
- Quick Deployment: Naye products aur services ko jaldi deliver karne mein madad karta hai.
- Risk Kam Karne Ka Tarika: Risk ko kam karne mein madad karta hai.
- Flexible Resources: Public cloud ke wajah se flexible resources milte hain aur private cloud ke wajah se secure resources.
- Security Challenges: Private cloud ki tarah strong security nahi hoti.
- Complex Management: Do alag deployment models ko manage karna thoda complex ho sakta hai.
Community Cloud ek aisa cloud model hai jo kai organizations ke beech mein data aur services share karne ke liye banaya jata hai. Isme ek specific community ke group ke beech mein information exchange hota hai. Ye cloud ek ya ek se zyada organizations, third-party, ya unka combination dwara owned, managed, aur operated hota hai.
- Cost-Effective: Community cloud cost-effective hota hai kyun ki ise kai organizations share karte hain.
- Collaborative Security: Ye un organizations ke liye suitable hai jo collaborative cloud chahte hain, public cloud se adhik security ke saath.
- Better Security: Public cloud se behtar security provide karta hai.
- Collaborative Environment: Collaborative aur distributive environment provide karta hai.
- Shared Resources: Community cloud allow karta hai ki various organizations apne resources, infrastructure, aur capabilities ko share karein.
- Not Suitable for Every Organization: Har organization ke liye ye suitable nahi hota.
- Security Features Not as Good as Private Cloud: Security features private cloud ke comparison mein utne strong nahi hote.
- Not Suitable without Collaboration: Agar collaboration nahi hai to ye suitable nahi hota.
- Limited Storage and Bandwidth: Ek fixed amount ka data storage aur bandwidth community ke sabhi members ke beech mein share hota hai.
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1m-mr8loXtGJn8zzqtWY6pQTo9-gUptwN/view?usp=sharing
- IaaS ek cloud computing service model hai, jisme users ko virtualized computing infrastructure, jaise ki virtual machines, storage, aur networking, internet ke through provide ki jati hai. Ismein users ko infrastructure ka direct control hota hai, lekin physical hardware ki responsibilities service provider par hoti hain.
- Advantages : Pura control infrastructure par hota hai, scalability hai, aur pay-as-you-go model flexibility provide karta hai.
- Definition : PaaS ek cloud computing service model hai, jisme users ko ek ready-to-use platform milti hai jiska istemal karke woh applications develop aur run kar sakte hain, bina infrastructure ki detailed management kiye. Ismein users ko application development par focus karne mein madad milti hai.
- Advantages : Developers ko simplified environment milta hai, automatic scaling hoti hai, aur infrastructure management provider ki zimmedari hoti hai.
- Definition : SaaS ek cloud computing service model hai, jisme users ko internet ke through ready-to-use software milta hai, jaise email, office tools, ya collaboration applications. Ismein users ko installation aur maintenance ki chinta nahi hoti.
- Advantages : Turant access milta hai, managed services hote hain, aur users ko infrastructure ke upar kam worry hoti hai.
Describe the core architectural components of Azure such as Azure Regions and Region Pairs, Availability Zones, Azure Subscriptions, Management Groups, Resource Groups and Resources 🥴🥴
Azure Management Infrastructure ka matlab hai woh basic components ya tatva jo Microsoft Azure cloud platform mein hote hain aur jinka use resources ko organize, provision (taiyar karna), aur manage karne mein hota hai.
-
Azure Resources: Azure Resources woh basic units hain jo Azure platform mein use hote hain. Examples mein Virtual Machines (VMs), virtual networks, databases, cognitive services, aur bhi kuch aata hai. Essentially, jo bhi aap Azure mein create, provision, ya deploy karte hain, woh resource hota hai.
-
Resource Groups: Resource Groups containers hote hain jo Azure resources ko logical taur par organize karne mein help karte hain. Har resource ko ek resource group mein place karna zaroori hai. Ek resource group mein bahut se resources ho sakte hain, lekin har resource sirf ek hi resource group mein exist kar sakta hai. Resource groups ek tareeka provide karte hain ki actions ko ek saath apply karke resources ko manage kiya ja sake. Ye nested nahi hote, matlab ek resource group ko doosre ke andar nahi daala ja sakta.
-
Subscriptions: Subscriptions Azure mein ek logical unit of ownership aur billing ko represent karte hain. Ye Azure resources ke liye containers ka kaam karte hain aur inhen specific billing entities ke saath associate kiya ja sakta hai. Subscriptions allow karte hain users ko access, policies, aur costs ko manage karne mein. Ek subscription ke saath multiple resource groups associate kiye ja sakte hain.
-
Accounts: Azure Accounts woh user accounts hote hain jo Azure services aur resources tak pahunchne mein use hote hain. Ye subscriptions ke saath associate hote hain aur Azure environment mein resources ko manage karne mein important role play karte hain. Users ke accounts par unke responsibilities ke hisab se different roles aur permissions assign kiye ja sakte hain.
- Virtual Machine Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) ka use karke aap cloud mein VMs create aur use kar sakte hain. VMs infrastructure as a service (IaaS) provide karte hain, jisme ek virtualized server ka use hota hai aur ise kai tariko se istemal kiya ja sakta hai. Jaise ki ek physical computer mein, aap apne VM par chalne wale sabhi software ko customize kar sakte hain.
VMs ek ideal choice hai jab aapko yeh chahiye:
- Aapko operating system par poora control chahiye ho.
- Aapko apne custom software ko run karne ki zarurat ho.
Azure VM aapko virtualization ki flexibility deta hai bina physical hardware ko khareed kar aur maintain karne ke liye. Lekin, IaaS offering hone ke bawajood, aapko phir bhi VM par chalne wale software ko configure, update, aur maintain karna padta hai.
Azure Region ek aisi jagah hai jahan par Microsoft ne apne data centers set kiye hote hain. Har region apne aap mein ek alag set kiya gaya data centers ka group hai, jo ek specific geographical area mein hota hai. Har region apne power, cooling, aur networking ke liye independent hota hai, jisse data residency, compliance, aur fault tolerance ensure kiya ja sake.
For example, agar aapka business India mein hai aur aap apne data ko India mein hi store karna chahte hain taki woh local laws aur regulations ke mutabiq rahe, toh aap Azure ka ek India region choose kar sakte hain.
- Data Residency
- Resource Deployment
- Service Availability
- Availability Zones
Region Pair do aise regions ko represent karta hai jo ek hi geography mein hote hain. Inka use mainly data protection aur disaster recovery ke liye hota hai. Ye dono regions ek dusre se door hote hain taki agar ek region mein koi problem aati hai, toh dusra region uska backup provide kar sake.
For example, agar aapka data ek region mein hai, toh aap us data ka backup dusre region mein bhi rakh sakte hain. Jaise ki agar aap Azure Site Recovery ka use karte hain, toh aap ek region se dusre region mein apne data ko replicate kar sakte hain, jisse aapko disaster ki situation mein data loss nahi hoga.
- Region Pair
- Disaster Recovery
- Resiliency
- Data Replication
- Planned Maintenance
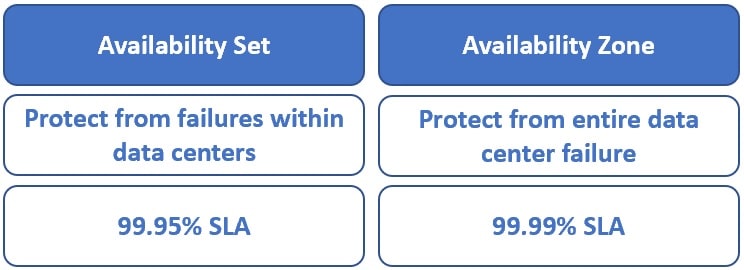
Availability Zone ek physical data center hota hai jo ek specific geographic area mein located hota hai. Har ek Availability Zone apne alag-alag power, cooling, aur networking se equipped hota hai, jisse agar ek Zone mein koi issue aata hai, toh dusre Zones kaam karna continue kar sakte hain.
Availability Set ek aisi setting hai jo cloud computing mein use hoti hai taki agar kisi server ya resource mein koi problem aaye, toh dusre resources kaam karte rahein. Isse hamara application hamesha up aur available rehta hai.
- Example Imagine a bank with multiple branches. Instead of keeping all customer data in one branch, they distribute it among different branches. If one branch faces an issue, others can still serve customers, ensuring continuous banking services.
- High Availability: Keeps your application running even if one part fails.
- Fault Tolerance: Reduces the risk of system failures affecting the entire application.
- Business Continuity: Ensures your services are available to users without interruption.
- Cost: Setting up and maintaining multiple instances can be more expensive.
- Complexity: Managing multiple instances and ensuring synchronization can be complex.
- Resource Utilization: Some resources may be underutilized if all instances are not running at full capacity.
-
Availability Set: Ye multiple VMs ko ek hi data center ke andar alag-alag physical servers par distribute karta hai. Agar data center mein kuch ho jaaye, toh Availability Set ensure karta hai ki application kaam karna jaari rakhe.
-
Availability Zones: Ye ek level up hai. Availability Zones alag-alag data centers ko indicate karte hain jo ek city ya region ke andar hote hain. Agar ek Availability Zone mein koi problem aati hai, to dusre Availability Zones ka use karke application ko up aur running rakha ja sakta hai.
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1YABcmqL0JwwQ_QEY-IwANNb82ZsvvJVu/view?usp=sharing
Azure Compute Services ek cloud computing platform hai jo Microsoft dwara provide kiya jata hai. Ismein aapko alag-alag types ke computing resources milte hain jo aap apne applications deploy, manage, aur scale karne ke liye istemal kar sakte hain. Ye resources include karte hain
- Virtual Machines (VMs): VMs ek virtualization technology ka ek mazboot udaharan hai. Inka mool uddeshya ek hi physical server ko multiple virtual servers mein batakar resources ka behtar istemal karna hai. Har VM ek dedicated environment pradan karta hai, jismein apna operating system, applications, aur resources hota hai. Isse har ek VM ek dusre se isolated hota hai, jisse security aur flexibility milti hai. VMs ki scalability ki baat karein toh, aap aasani se naye VMs deploy kar sakte hain, aur agar zarurat nahi hai toh unhe hibernate ya shutdown bhi kar sakte hain, jo operational cost kam karta hai.
-
Image (Chitra): Azure mein Virtual Machine create karne ke liye aapko kisi base operating system ya pre-configured image ka chayan karna hota hai. Jaise ki Windows Server ya Linux distributions.
-
Size (Size): VM ka size decide karta hai ki kitne CPU cores aur kitni RAM aapko chahiye. Jaise ki small, medium, large, aur extra-large.
-
Disk Storage (Disk Bhandar): VM ke liye storage ya disk space ka chayan karna hota hai. Ismein aap data aur operating system ke liye alag-alag disk attach kar sakte hain.
-
Networking (Network): VM ko Azure ke network se connect karne ke liye aapko virtual network, subnets, IP addresses, aur security groups ka configuration karna hota hai.
-
Availability Sets (Uplabdhi Samuha): Yeh ek group hota hai jismein aap multiple VMs ko include kar sakte hain, taki agar koi ek VM fail ho jaye to dusri VMs available rahein.
-
Extensions (Vistar): Extensions VM ke functionalities ko badhane aur customize karne ke liye use hote hain. Jaise ki antimalware extensions, custom script extensions, etc.
-
Lifecycle Management (Jivan Chakr Prabandhan): VM ke jivan chakr ko manage karna, jaise ki create, update, aur delete karna, ismein aata hai. Yeh operations VM ke management aur maintenance ke liye hote hain.
-
Azure App Service: Azure App Service PaaS ka ek prakar hai jismein aapko infrastructure management se chhutkara milta hai. Yeh developers ko allow karta hai apne applications ko code, deploy, aur scale karna. Ismein kai features shaamil hain jaise ki auto-scaling, high availability, aur automatic patching, jo aapke application ko robust banate hain. Aap apne applications ko multiple environments mein deploy kar sakte hain, jaise ki testing aur production, without worrying about underlying infrastructure.
-
Web Apps: You can create and host web applications in various programming languages such as .NET, Java, Node.js, Python, etc.
-
Mobile Apps: Azure App Service supports the development and hosting of mobile applications, providing backend services for mobile app scenarios.
-
API Apps: Developers can build and expose APIs using Azure API Apps, allowing easy integration with other services and systems.
-
Logic Apps: Integration with Azure Logic Apps allows you to create workflows and automate processes, enhancing the functionality of your applications.
-
Containers: Azure App Service supports containerized applications, allowing you to use Docker containers for deploying and scaling your apps.
-
Scaling: App Service provides automatic scaling based on demand, ensuring that your applications can handle varying workloads.
-
Continuous Deployment: Integration with Azure DevOps, GitHub, or other version control systems enables continuous deployment and delivery of your applications.
-
Security and Compliance: Azure App Service includes features for securing your applications, integrating with Azure Active Directory for authentication, and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
-
Monitoring and Diagnostics: App Service provides built-in monitoring tools, logging capabilities, and integration with Azure Application Insights for tracking and diagnosing issues.
-
Global Availability: You can deploy your applications in multiple regions around the world to improve availability and reduce latency for users in different geographic locations.
Azure Functions serverless computing ki visheshata hai, jismein developers ko apne code ki execution ke liye server ki chinta nahi hoti. Yeh microservices architecture mein kaam aata hai, jismein aap chhote functions likh kar unhe specific events par trigger kar sakte hain. Isse aap sirf woh resources use karte hain jo execution ke liye zaroori hote hain, jisse cost savings hoti hai.
AKS ek managed Kubernetes service hai, jo container orchestration ko asaan banata hai. Kubernetes ek open-source system hai jo containers ko deploy, scale, aur manage karta hai. AKS ke zariye aap complex applications ko efficiently aur dynamically handle kar sakte hain. Yeh service aapko control aur visibility provide karta hai over each container, aur aapko infrastructure management se mukt karta hai.
-
Azure Batch: Azure Batch ek distributed computing service hai jo high-performance computing ke liye design kiya gaya hai. Ismein aap multiple tasks ko define karke distribute kar sakte hain, jo parallel processing mein execute hote hain. Isse aap large-scale data processing, scientific simulations, aur rendering tasks ko efficiently aur scale par perform kar sakte hain. Batch aapko compute resources ki abstraction provide karta hai, jisse aap application logic par dhyan de sakte hain.
-
Azure Container Instances (ACI): ACI ek fast aur simple tareeka hai containerized applications ko run karne ka. Ismein aapko VMs ya clusters ki zarurat nahi hoti, aur aap containers ko bina orchestration ke seedha deploy kar sakte hain. ACI aapko granular control deta hai over resources, jisse aap specific requirements ke hisab se resources allocate kar sakte hain. Yeh on-demand nature se aata hai, jisse aapko jald hi applications deploy karne mein madad milti hai.
-
Azure Dedicated Host: Azure Dedicated Host ek dedicated physical server provide karta hai, jise sirf aapka control hota hai. Ismein aap VMs ko seedha host karte hain, lekin dedicated hardware resources provide kiye jate hain. Aap Dedicated Host ke zariye apne applications ko isolate environment mein run kar sakte hain, jo compliance aur security requirements ko meet karta hai. Ismein aapko flexibility milti hai apne VMs ke placement, sizing, aur configurations ke liye.
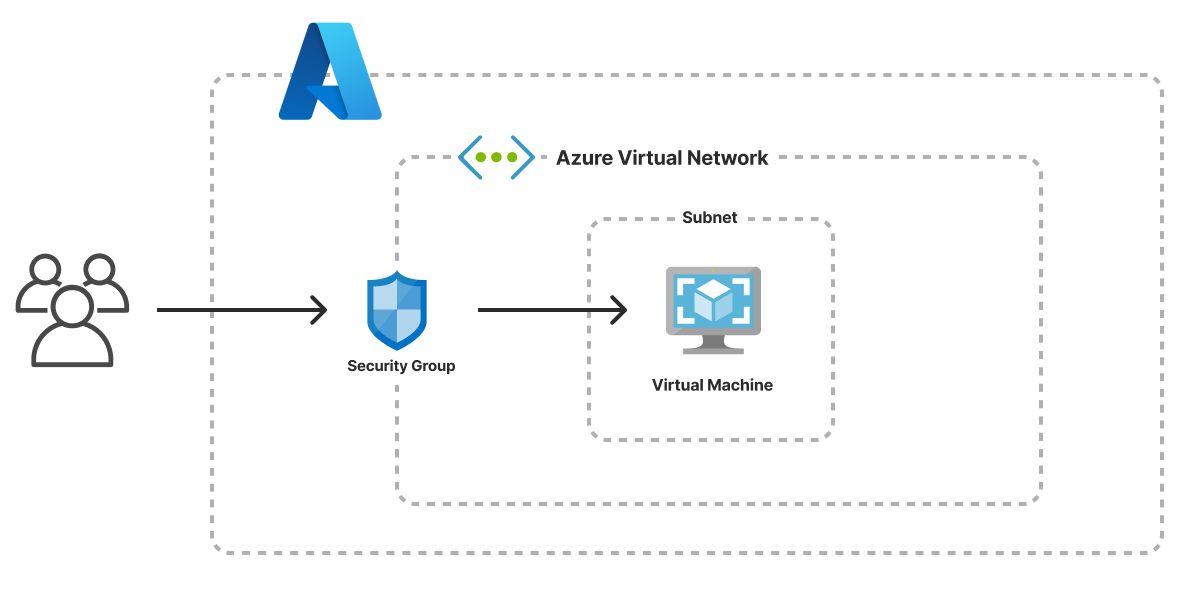
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) ek aisi service hai jo Microsoft Azure cloud platform par provide ki jaati hai, jisse aap ek virtual private network setup kar sakte hain apne cloud resources ke liye. Isme kuch key elements hote hain:
-
Subnets: VNet me aap apne resources ko organize karne ke liye alag-alag sub-networks, ya subnets, create kar sakte hain.
-
Virtual Network Gateway: Ye ek service hai jo on-premises network ko Azure VNet se connect karne ke liye use hoti hai, jisse aap hybrid network setup kar sakte hain.
-
A Virtual Network Gateway is a cloud-based, software-defined networking device that facilitates secure and encrypted communication between different networks, such as connecting an on-premises network to an Azure Virtual Network.
- Network Security Groups: Ye aapke VNet ke andar security ko manage karne ke liye use hota hai, jaise ki traffic ko allow or block karna.
- NSG ek firewall ki tarah kaam karta hai, jisse aap specific types of traffic ko allow ya block kar sakte hain, depending on your security requirements. Har NSG ke paas rules hote hain jo decide karte hain ki kis tarah ka traffic allow hoga aur kis tarah ka block. Yeh rules IP addresses, port numbers, aur protocols ko consider karte hain.
-
Azure DNS: Isse aap apne Azure resources ke liye DNS (Domain Name System) ko manage kar sakte hain.
-
Route Tables: Ye determine karte hain ki kis tarah ke traffic ko kahan bhejna hai aapke network ke andar.
-
Peering: Isse aap ek VNet ko doosre VNet ke sath connect kar sakte hain, jo ki resources ke behtar accessibility aur communication ko enable karta hai.
-
VPN Gateway: Ye aapko on-premises network ko secure VPN connection ke through Azure VNet se connect karne ki suvidha deta hai.
-
Azure Private Link: Ye aapko Azure services ko private network ke through access karne ki permission deta hai, jisse security aur privacy maintain hoti hai.
-
Service Endpoints: Ye aapko Azure services ke liye private IP addresses provide karta hai, jisse aap unhe VNet ke through hi access kar sakte hain.
-
Virtual Network TAP: Ye network traffic ko monitor karne aur analyze karne ke liye use hota hai.
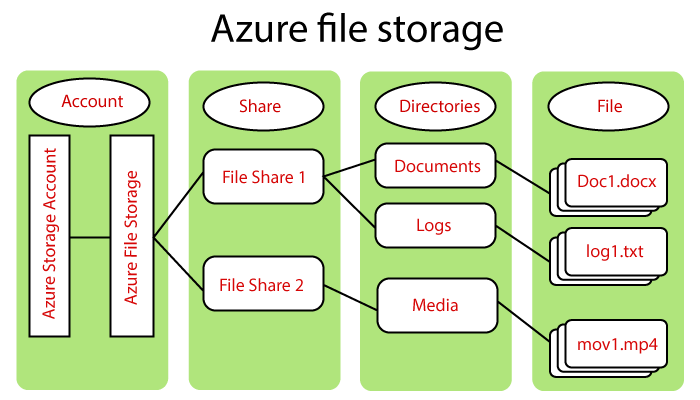
- Physical or Virtual Disks: Physical ya virtual disks ke through implement kiya ja sakta hai.
- File System Structure: File system structure ka use karta hai, jisme folders aur directories organize hote hain.
- Performance Types: Different performance types mein aata hai, including HDDs (Hard Disk Drives) aur SSDs (Solid-State Drives).
- Mounting to VMs: Directly virtual machines (VMs) se mount kiya ja sakta hai storage aur data access ke liye.
- Scalability: Vertical scaling ke liye individual disks ko upgrade karke ya horizontally by adding more disks se scalable hota hai.
- Data Persistence: Associated virtual machine stop hone par bhi data persist rehta hai, long-term storage ensure karta hai.
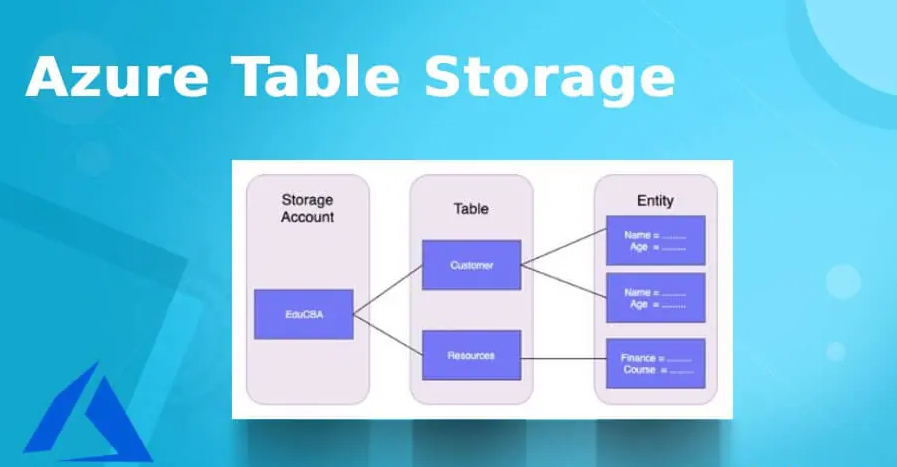
- Tabular Structure: Tables ek tabular data model ka use karte hain, jisme rows aur columns hote hain, structured data ke liye suitable hai.
- Partitioning and Indexing: Efficient data retrieval ke liye partitioning aur indexing ka support karta hai.
- Scalability: High scalability ke liye design kiya gaya hai, massive datasets ke storage aur retrieval ke liye.
- NoSQL Capabilities: NoSQL capabilities ko support karta hai, jisse data modeling mein flexibility aur schema-less design milti hai.
- Query Language: Query language ka use hota hai, often SQL-based, expressive aur powerful data queries ke liye.
- Global Distribution: Global distribution ke liye distribute kiya ja sakta hai, jisse performance aur reliability improve hoti hai.
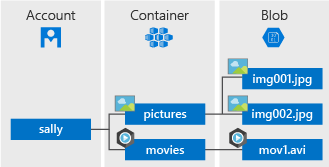
- Unstructured Data: Blob storage ka use kisi bhi tarah ke unstructured data jaise ki photos, videos, aur backups ke liye optimize kiya gaya hai.
- Tiered Storage: Yeh multiple access tiers (hot, cool, aur archive) support karta hai, jo data access patterns ke basis par costs ko optimize karne mein madad karta hai.
- Global Distribution: Data ko alag-alag geographical regions mein replicate karne ki capability provide karta hai, jisse availability aur performance improve hoti hai.
- Scalability: Data volumes badhne par seamless scaling ka option deta hai, isliye yeh large-scale applications ke liye suitable hai.
- Content Delivery: Content delivery networks (CDNs) ke saath integrate hota hai, jisse users ko efficient aur fast content delivery milti hai.
- Security Features: Yeh robust security features offer karta hai, jisme data ka encryption at rest aur in transit shaamil hai, jo data ki integrity ko ensure karte hain.
- Shared Access: Yeh multiple users ko allow karta hai concurrently shared files ko access aur collaborate karne ke liye, jisse yeh team collaboration ke liye suitable hai.
- Hierarchical Structure: Data ko hierarchical file system mein folders ke saath organize karta hai, jisse data management simplify hota hai.
- Scalability: Yeh moderate-sized data sets ke liye scalable hai, lekin extremely large datasets ke liye additional considerations ki zarurat ho sakti hai.
- Access Control: Folders aur files ke liye granular access control provide karta hai, taki permissions effectively manage ki ja sakein.
- Snapshot Capabilities: Specific points par data ke snapshots ya copies create karne ki capability deta hai, jo data recovery aur backup ke liye useful hoti hai.
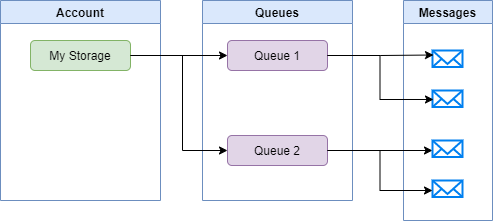
- Asynchronous Communication: Asynchronous communication ko facilitate karta hai, different components ya services ke beech mein.
- Message Priority: Message priority set karne ki capability hai, jisse critical tasks ya urgent messages ko handle kiya ja sake.
- Fault Tolerance: Fault tolerance ko enhance karta hai, allowing messages ko temporarily store karne ki permission deta hai.
- Scalability: Messages aur tasks ke badhne par horizontally scale hota hai.
- At-Least-Once Delivery: Reliable message delivery ensure karta hai, usually at-least-once delivery semantics ka use karta hai.
- Message Time-to-Live (TTL): Messages ke liye time-to-live set karne ki permission deta hai, jisse woh specific time ke baad automatically queue se remove ho jate hain.
Horizontal scaling ka matlab hai ki jab aap apne system ki capacity ko badhane ke liye aur servers ko add karte hain. Isme, aap apne existing infrastructure ke sath naye servers ko juda karke overall capacity ko badha sakte hain. Yeh tarika especially tab istemal hota hai jab aapke paas ek badi application hai jo bahut saare users ko handle kar rahi hai.
- Example: Maan lo aapke paas ek online shopping website hai. Jab festive season aata hai aur user traffic badh jata hai, toh aap horizontal scaling ka istemal karke apne servers ko aur add karke website ki performance ko maintain kar sakte ho.
Vertical Scaling:
Vertical scaling ka matlab hai ki aap apne existing server ki capacity ko badhate hain, jaise ki usmein more RAM, processing power, ya storage add karte hain. Isme, aap ek hi server ko upgrade karke uski capability ko enhance karte hain.
- Example (Udaharan): Agar aapka database server ek point par overload ho raha hai, toh aap vertical scaling ka istemal karke us server ko upgrade kar sakte hain, jisse woh zyada data handle kar sake.
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1NqRghzDqMbgsWIT3D_kaN3ysxLKcXP0P/view?usp=sharing
Locally Redundant Storage (LRS) ek aur storage option hai, lekin isme data ek hi data center mein three alag-alag replicas mein store hota hai. Jab aap data Azure Storage mein LRS ke saath store karte hain, toh yeh data ek hi data center ke andar teen alag-alag copies mein replicate hota hai. Agar kisi component mein koi issue aata hai, toh bhi doosre copies se data ko retrieve kiya ja sakta hai.
- Low-Cost Option: LRS ek cost-effective option hai, isme data ko ek hi data center mein store kiya jaata hai, jisse costs kam aate hain.
- Durability: LRS at least 11 nines (99.999999999%) durability offer karta hai, jo ki bhi ek saal ke liye hai. Lekin ZRS ke comparison mein thoda kam hai.
Zone-Redundant Storage (ZRS) ek storage service hai jo data ko three Azure availability zones mein synchronous taur par replicate karta hai. Iska mool uddeshya hai data ko ek zone unavailable hone par bhi accessible rakhna.
- Durability: ZRS at least 12 nines (99.9999999999%) durability provide karta hai, jo ek saal ke liye hai. Yeh data ko bahut zyada reliable banata hai.
- Accessibility: Agar koi zone unavailable ho jaaye, tab bhi aapka data accessible rehta hai, isse data ki high availability milti hai.
Definition (Varnan):
GRS ek Azure Storage Service hai jo data ko primary region se ek geographically distant secondary region mein replicate karta hai. Yeh redundancy provide karta hai taki agar primary region mein koi issue ho, toh data secondary region se recover kiya ja sake. Explanation (Samjhaayein):
Jab aap GRS use karte hain, toh aapki data initially ek primary region mein store hoti hai. Iske baad, yeh data ek dusre geographically distant region mein duplicate ho jata hai. Isse agar primary region mein kuch problem aata hai, toh aap apne data ko secondary region se retrieve kar sakte hain. Example (Udaharan):
Maan lijiye aapka primary data center New York mein hai. GRS ki madad se, aapki data automatically replicate hoti hai ek aur region, jaise London mein. Agar New York mein kisi natural disaster ya outage ki wajah se data loss ho jaata hai, toh aap London se apne data ko recover kar sakte hain. Geo-Zone-Redundant Storage (GZRS):
Definition (Varnan):
GZRS bhi ek Azure Storage Service hai, lekin isme data not only across regions but also within availability zones in the primary region replicate hota hai. Yeh ek aur layer of redundancy provide karta hai. Explanation (Samjhaayein):
GZRS mein, data ek primary region mein store hota hai, aur isme availability zones ke andar bhi replicate hota hai. Availability zones alag-alag physical locations hote hain with in the same Azure region, providing additional resilience. Example (Udaharan):
Agar aapka primary data center Mumbai mein hai, toh GZRS se, aapki data not only Singapore jaise kisi aur region mein duplicate hoti hai, balki Mumbai ke andar alag-alag availability zones mein bhi replicate hoti hai. Isse, agar kisi zone mein issue aata hai, toh baki zones se data recoverable rehta hai.
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1unD6nMzDxO7zWGZvFIGuetmLM_MIkbct/view?usp=sharing
- Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) ek cloud-based identity and access management service hai jo Microsoft dwara provide kiya jata hai. Iska mukhya uddeshya hai users ko alag-alag cloud applications aur services tak pahunchane ki suvidha pradan karna aur unhe secure tarike se authenticate karna. Azure AD mein users ke accounts create kiye jate hain jinhe unke organizations ke administrators manage karte hain. Har user ka ek unique username hota hai jise "user principal name (UPN)" kehte hain, aur unhe ek password ke saath login karne ki anumati hoti hai. Ismein groups ka upyog kiya jata hai users ko organize karne aur unhe alag-alag permissions aur access provide karne ke liye. Azure AD ke madhyam se, organizations apne users ko single sign-on (SSO) ki suvidha bhi pradan kar sakte hain, jisse users ko ek hi login ke jariye alag-alag applications aur services tak pahunchne ki anumati milti hai. Iske alawa, Azure AD ke security features unauthorized access se bachane aur overall security ko enhance karne mein madad karte hain.
-
IT administrators: IT administrators Azure AD ka istemal karte hain takay wo applications aur resources ko unke business ke mutabiq control kar sakein.
-
App developers: App developers Azure AD ka istemal karte hain takay wo apne banaye gaye applications mein functionality ko barha sakein, jaise ke SSO functionality ko shamil karna ya existing credentials ke saath app ko kaam karne mein madad karna.
-
Users: Users apni identities ko manage kar sakte hain aur self-service password reset jaise kaam bhi kar sakte hain.
-
Online service subscribers: Microsoft 365, Microsoft Office 365, Azure, aur Microsoft Dynamics CRM Online subscribers pehle se hi Azure AD ka istemal kar rahe hain apne accounts mein login karne ke liye.
-
Example Socho ki jab tum websites, email, ya online services mein sign-in karte ho, to kya kabhi tumhare phone par bheja gaya ek code enter karna pada hai? Agar haan, to tumne multifactor authentication ka istemal kiya hai sign-in ke liye.
-
Multifactor authentication tumhari identities ke liye additional security faraham karta hai kyunki ismein do ya zyada elements ka istemal hota hai authentication ke liye. Ye elements teen categories mein aate hain:
-
Kuch jo user jaanta hai – ye ek challenge question ho sakta hai.
-
Kuch jo user ke paas hai – ye user ke mobile phone par bheja gaya code ho sakta hai.
-
Kuch jo user hai – ye aam taur par koi biometric property hoti hai, jaise ki fingerprint ya face scan.
-
Multifactor authentication identity security ko badha kar credentials exposure ka asar kam karta hai (maslan, chori hue usernames aur passwords). Multifactor authentication ko enable karna chahiye jahan bhi mumkin ho kyunki ye security mein badi fawaid faraham karta hai.
- Ab single-factor authentication ke saath multifactor authentication ko compare karte hain. Single-factor authentication mein, ek hamla karne wala sirf ek username aur password ki zaroorat hoti hai authentication ke liye. Multifactor authentication ko enable karna chahiye kyunki ye security ko bada kar deta hai.
-
For example, agar aap Windows Hello for Business ka istemal karte hain, toh aap apne computer mein fingerprint ya facial recognition se login kar sakte hain, jiski madad se aapka identity verify hota hai. Yeh passwordless authentication ka ek example hai.
-
Real-life Example (Hinglish): Sochiye aap ek office mein kaam karte hain aur aapko rozana apne computer mein login karna hota hai. Agar aap passwordless authentication ka istemal karte hain, jaise ki Windows Hello for Business, toh aapko har baar apna password yaad rakhne ki zaroorat nahi hoti. Aap sirf apna fingerprint ya facial recognition ka istemal karke apne computer mein login kar sakte hain, jisse aapki security bhi hai aur aapko convenience bhi milti hai.
-
Cloud Computing Example (Hinglish): Cloud computing mein bhi passwordless authentication ka istemal hota hai. For example, agar aap Microsoft Azure ka istemal kar rahe hain aur aapko apne Azure account mein login karna hai, toh aap Microsoft Authenticator app ka istemal karke passwordless authentication ka fayda utha sakte hain. Ismein aapko ek code ya notification milta hai jise aap apne phone mein dekh kar apne Azure account mein login kar sakte hain, bina password ke. Yeh ek aur passwordless authentication ka example hai jo cloud computing mein istemal hota hai.