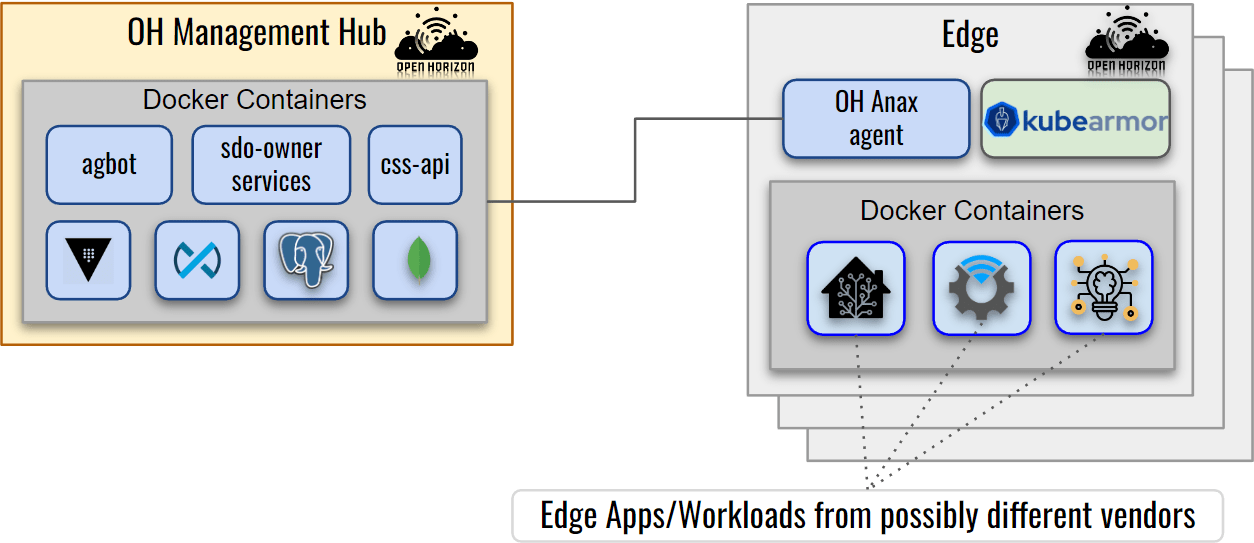
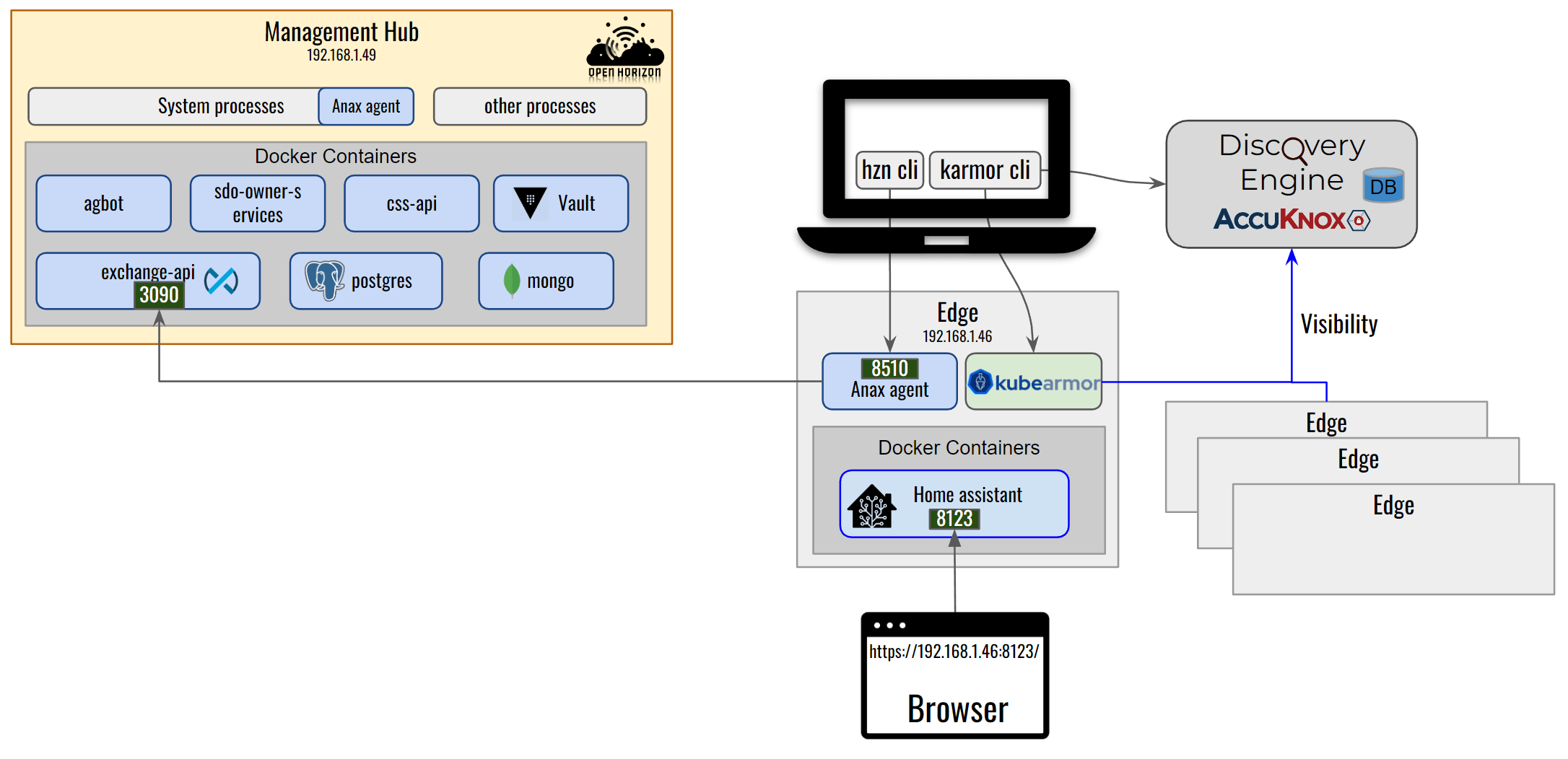
KubeArmor is a runtime security engine that can protect k8s-orchestrated, or pure containerized workloads as well as VM/Bare-Metal based workloads. Open Horizon deploys the edge workloads in either containerized mode or k8s orchestrated mode. The Open Horizon Edge Agent operates directly on the host as a systemd process.
KubeArmor running on the edge node provides visibility and protection for all the processes, files, or network operations in the containers as well as those running directly on the host.
Observability: KubeArmor can provide container-aware observability information about the operations happening:
- from Agent node to Management Hub (and vice-versa)
- between the containers and the agent edge node
- inside the containers running on the Agent node
Enforcement: KubeArmor can be used to apply security postures at the kernel level (using LSMs like AppArmor, BPF-LSM). It can protect both the host and workloads running on it by enforcing either some predefined security policies or automatically generated least permissive security policies (using Discovery Engine).
KubeArmor already supports k8s-orchestrated workloads and provides KVMService that allows orchestrating security policies to VMs for non-k8s environments. With v0.5.5 release, KubeArmor supports standalone un-orchestrated containers. KubeArmor in this mode supports both enforcement and observability of the host and the containers running on it.
Note This guide assumes both the Open Horizon Management Hub and Agent VM are running Ubuntu 20.04. We will first need to install Open Horizon Management Hub and Agent node components. For that please follow the Open Horizon setup guide. We also assume that Open Horizon Home Assistant service is running on the agent edge node.
Now we will run KubeArmor as a systemd process on the Open Horizon Agent VM
- KubeArmor Installation:
Note: For distributions other than Ubuntu/Debian i. Refer Installing BCC to install pre-requisites. ii. Download release tarball from KubeArmor releases
wget https://github.com/kubearmor/KubeArmor/releases/download/v0.9.0/kubearmor_0.9.0_linux-amd64.tar.gziii. Unpack the tarball to the root directory:
sudo tar --no-overwrite-dir -C / -xzf kubearmor_0.9.0_linux-amd64.tar.gz
-
Download the latest release of KubeArmor
wget https://github.com/kubearmor/KubeArmor/releases/download/v0.9.0/kubearmor_0.9.0_linux-amd64.deb
-
Install KubeArmor
sudo apt install ./kubearmor_0.9.0_linux-amd64.deb
Note that the above automatically installs
bpfcc-toolswith our package, but your distribution might have an older version of BCC. In case of errors, consider installingbccfrom source. -
Start KubeArmor
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl start kubearmor
-
To check KubeArmor running status
sudo journalctl -u kubearmor -f
- kArmor Installation:
Note kArmor should already be installed by the above KubeArmor installation. Check installation using
karmor version.
If kArmor is not installed run:
curl -sfL http://get.kubearmor.io/ | sudo sh -s -- -b /usr/local/bin- Discovery Engine Installation:
Note: For distributions other than Ubuntu/Debian i. Download release tarball from KubeArmor releases
wget https://github.com/accuknox/discovery-engine/releases/download/v0.6.3/knoxAutoPolicy_0.6.3_linux-amd64.tar.gzii. Unpack the tarball to the root directory:
sudo tar --no-overwrite-dir -C / -xzf knoxAutoPolicy_0.6.3_linux-amd64.tar.gz
Note: If you have previously installed discovery-engine, it's advised to restart the service: sudo systemctl restart knoxAutoPolicy
-
Download the latest release of Discovery Engine
wget https://github.com/accuknox/discovery-engine/releases/download/v0.6.3/knoxAutoPolicy_0.6.3_linux-amd64.deb
-
Install Discovery Engine
sudo apt install ./knoxAutoPolicy_0.6.3_linux-amd64.deb
-
Start Discovery Engine
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl start knoxAutoPolicy
-
To check Discovery Engine running status
sudo journalctl -u knoxAutoPolicy -f
-
To see alerts on policy violation, run:
karmor log
-
Now, let's apply a sample policy: block-secrets-access.yaml using:
karmor vm policy add block-secrets-access.yaml
block-secrets-access.yaml
apiVersion: security.kubearmor.com/v1
kind: KubeArmorPolicy
metadata:
name: block-certificates-access
spec:
severity: 10
message: "a critical file was accessed"
tags:
- WARNING
selector:
matchLabels:
kubearmor.io/container.name: homeassistant
process:
matchPaths:
- path: /usr/sbin/update-ca-certificates
file:
matchDirectories:
- dir: /usr/share/ca-certificates/
recursive: true
- dir: /etc/ssl/
recursive: true
action:
BlockNote: More predefined policies and auto-discovered policy can be found here: https://github.com/kubearmor/openhorizon-demo/tree/main/Open-Horizon/policies
Here, notice the field kubearmor.io/container.name: homeassistant homeassistant is the container name to which we want to apply the policy.
karmor log
HostName: knownymousagent-VirtualBox
NamespaceName: container_namespace
PodName: homeassistant
ContainerName: homeassistant
ContainerID: 77c3916a24f74915cd7d2eb51ff6a2425c3b4d6e72b805f735800d023d355338
Type: MatchedPolicy
PolicyName: block-certificates-access
Severity: 10
Message: a critical file was accessed
Source: /bin/bash
Resource: /usr/sbin/update-ca-certificates
Operation: Process
Action: Block
Data: syscall=SYS_EXECVE
Enforcer: AppArmor
Result: Permission denied
HostPID: 4922
HostPPID: 4912
PID: 116
PPID: 110
ParentProcessName: /bin/bash
ProcessName: /usr/sbin/update-ca-certificates
Tags: WARNINGAvailable filters
--logFilter <system|policy|all> - Filter to receive general system logs (system) or alerts on policy violation (policy) or both (all).
--logType <ContainerLog|HostLog> - Source of logs - ContainerLog: logs from containers or HostLog: logs from the host
--operation <Process|File|Network> - Type of logs based on process, file or network
--container - Specify container name to view container specific logs
This will create an AppArmor profile at /etc/apparmor.d/ with the name kubearmor_<containername> (kubearmor_homeassistant here) and will load the profile to AppArmor.
To run a container with KubeArmor enforcement using the AppArmor profile kubearmor_homeassistant, pass --security-opt apparmor=kubearmor_homeassistant with the docker run command or if using docker-compose add:security_opts: apparmor=kubearmor_homeassistant under the container name in the docker-compose.yaml.
karmor discover tool can be used to automatically generate security policies. The output of the command can be redirected to a yaml file
karmor discover --format yaml --labels "kubearmor.io/container.name=homeassistant" > discovered_policy.yamlThis yaml file can be applied to KubeArmor to provide the least permissive security posture for the homeassistant-service container.
To apply security policy discovered_policy.yaml
karmor vm policy add discovered_policy.yamlNote: Host security policies are identified by
kind: KubeArmorHostPolicyand Container security policies havekind: KubeArmorPolicy.
We will first stop the KubeArmor and Discovery Engine system service and then will uninstall the packages.
sudo systemctl stop kubearmor knoxAutoPolicy
sudo apt remove --purge kubearmor knoxautopolicy karmor