-
Class−- what is parent class vs derives class ?
- Parent Class (Base Class or Superclass): A parent class is the class that is extended or inherited by another class
// Parent class class Animal { public function makeSound() { } }
- Derived Class (Child Class or Subclass): A derived class is a class that extends or inherits from another class (the parent class)
// Derived class class Dog extends Animal { public function makeSound() { } }
Object−Member Variable− inside a class.Member function− inside a class
class Person { // Member variables (properties) private $result; // Member function public function add() { } }
-
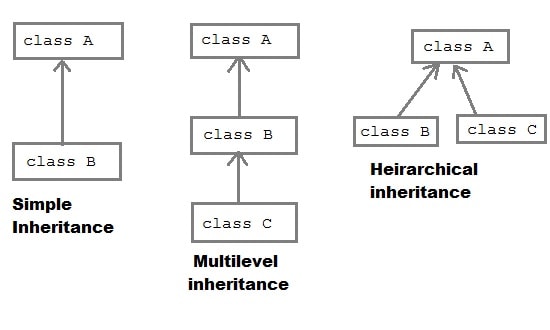
Inheritance− derives from another class. inherited class is defined by using theextendskeyword. - supports single inheritance- আপনার বাবা কখনো একসাথে দুজন হবে না এটাকে বলে ("OOP doesn’t allow multiple inheritance")
- আপনার দাদা -> বাবা -> আপনি... (Multi level)
- এখন একজন বাবার একাদিন সন্তান তো থাকতে পারে তাহলে? Inheritance 1 Inheritance 2
- Multiple - PHP OOP does not allow multiple inheritance
class class { // body } class class1 { // body } class class3 extends class class1 { // body }
- Multilevel inheritance - Allow only multilevel inheritance
class class1 { //Body of grand parent class } class class2 extends class1 { //Body Of parent class } class class3 extends class2 { //Body of child class }
- Single Inheritance
class Animal { // ... } class Dog extends Animal { // ... }
- Multilevel Inheritance
class Animal { // ... } class Dog extends Animal { // ... } class GermanShepherd extends Dog { // ... }
- Interface Inheritance (Implementation):
interface CanFly { public function fly(); } class Bird implements CanFly { public function fly() { // ... } }
- Trait Inheritance
trait Loggable { public function log($message) { // ... } } class Example { use Loggable; }
- Abstract Class Inheritance:
abstract class Shape { abstract public function calculateArea(); } class Circle extends Shape { public function calculateArea() { // ... } }
- Final Class or Method:
final class FinalClass { // ... } class SubClass extends FinalClass { // Error: Cannot extend final class // ... }
-
Parent class− -
Child class− -
Polymorphism− -
Overloading− -
Data Abstraction− সারসংক্ষেপ করা | - Abstraction is the any representation of data in which the implementation details are hidden (Data Representation refers to the form in which data is stored, processed, and transmitted) - Abstract classes and methods when the parent class has a named method, but need its child class to fill out the tasks. - abstract class is a class that contains at least one abstract method. - abstract method is a method that is declared, but not implemented in the code.abstract class ParentClass { abstract public function someMethod1(); abstract public function someMethod2($name, $color); abstract public function someMethod3() : string; }
// Parent class abstract class Bike { public $name; public function __construct($name) { $this->name = $name; } abstract public function intro() : string; } // Child classes class Yamaha extends Bike { public function intro() : string { return "I'm a $this->name!"; } } class splendor extends Bike { public function intro() : string { return "I'm a $this->name!"; } } class Vespa extends Bike { public function intro() : string { return "I'm a $this->name!"; } } // Create objects from the child classes $yamaha = new yamaha("Yamaha"); echo $yamaha->intro(); echo "<br>"; $splendor = new splendor("Splendor"); echo $splendor->intro(); echo "<br>"; $vespa = new vespa("Vespa"); echo $vespa->intro(); I'm a Yamaha! I'm a Splendor! I'm a Vespa!
-
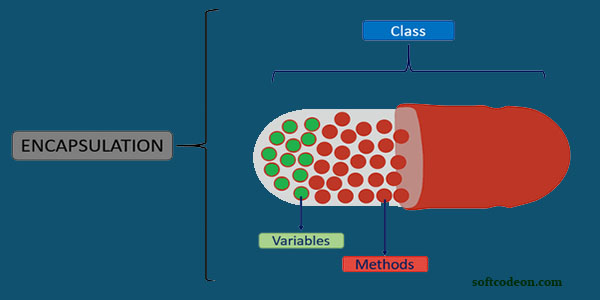
Encapsulation− Compressing or wrapping a bunch of data in a single unit. - Encapsulation the data is not accessed directly but it is accessed through the functions present inside the class. - In simpler words, attributes of the class are kept private and public getter and setter methods are provided to manipulate these attributes.- PHP Encapsulation?
- Data hiding
- Data abstraction
[Encapsulation]{https://softcodeon.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/Encapsulation-in-PHP-1.jpg}
- PHP Encapsulation?
-
Constructor−__construct- (magic method) that is automatically called when an object is instantiated from a class.class Car { // Properties private $brand; private $model; private $color; // Constructor public function __construct($brand, $model, $color = 'black') { $this->brand = $brand; $this->model = $model; $this->color = $color; echo "A new {$color} {$brand} {$model} is created!<br>"; } // Method to get information about the car public function getInfo() { return "{$this->color} {$this->brand} {$this->model}"; } } // Creating objects using the constructor $car1 = new Car("Toyota", "Camry"); $car2 = new Car("Ford", "Mustang", "red"); // Using the getInfo method echo $car1->getInfo(); // Outputs: black Toyota Camry echo $car2->getInfo(); // Outputs: red Ford Mustang
-
Chaining Constructors
class Animal { protected $name; public function __construct($name) { $this->name = $name; echo "Animal constructor called. Name: {$this->name}<br>"; } } class Dog extends Animal { private $breed; public function __construct($name, $breed) { // Call the parent class constructor parent::__construct($name); // Perform additional initialization for the Dog class $this->breed = $breed; echo "Dog constructor called. Breed: {$this->breed}<br>"; } } // Create an object of the Dog class $dog = new Dog("Buddy", "Golden Retriever");
Animal constructor called. Name: Buddy Dog constructor called. Breed: Golden Retriever
-
-
Destructor− -
Interfaces-```php // Implementing multiple interfaces interface CanRun { public function run(); } interface CanSwim { public function swim(); } class Tiger implements CanRun, CanSwim { /* Must implement run() and swim() */ public function run() { //... } public function swim() { //... } } ``` -
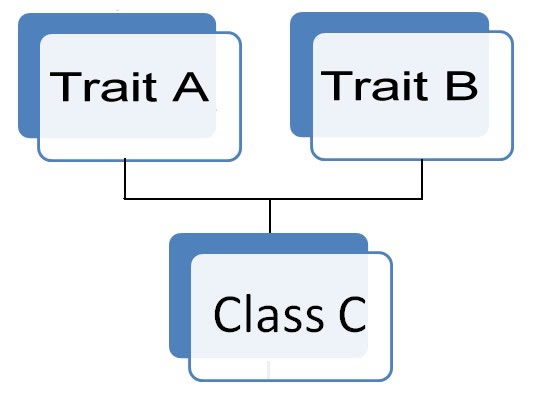
Traits- PHP only supports single inheritance: a child class can inherit only from one single parent. - if a class needs to inherit multiple behaviors? OOP traits solve this problem. Trait class: multiple behaviorstrait A { public function Hi() { echo 'Hi '; } } trait B { public function Users() { echo 'Bhumi '; } } class C { use A, B; public function Welcome() { echo 'Welcome'; } } $obj = new C(); $obj->Hi(); $obj->Users(); $obj->Welcome();
trait message1 { public function msg1() { echo "OOP is fun! "; } } trait message2 { public function msg2() { echo "OOP reduces code duplication!"; } } class Welcome { use message1, message2; } $obj = new Welcome(); $obj->msg1(); $obj->msg2();
trait Greeting{ public function sayHello() { echo 'Hello '; } abstract public function sayName(); } class MyGreeting { use Greeting; public function sayName() { echo ' Simone'; } } $g = new MyGreeting(); $g->sayHello() //Hello $g->sayName(); // Simone
class Base{ public function sayHello() { echo "Ciao "; } } trait Greeting{ public function sayHello() { echo "Hello "; } public function sayName() { echo 'Samuele'; } } class MyGreeting extends Base { use Greeting; public function sayName() { echo 'Simone'; } public function sayBaseHello() { echo parent::sayHello() . $this->sayName(); } } $g = new MyGreeting(); $g->sayHello() $g->sayName(); //Hello Simone $g->sayBaseHello(); //Ciao Simone
-
Static Methods- Static methods called directly - without creating instance of class -
Namespaces-PHP Namespaces are the way of encapsulating items so that same names can be reused without name conflicts. - Namespaces allows classes / functions / constants of same name be used in different contexts without any conflict- এনক্যাপসুলেশন অর্থ গোপনীয়তা। অন্য কোন অব্জেক্ট থেকে কোন ক্লাসের ডেটা লুকোনো বা সরাসরি ব্যবহার থেকে বিরত রাখা ই এনক্যাপসুলেশন। অর্থাৎ কোন ক্লাসের ডেটা বা মেথড কে প্রাইভেট করে রাখার প্রক্রিয়া-ই এনক্যাপসুলেশন ।
-
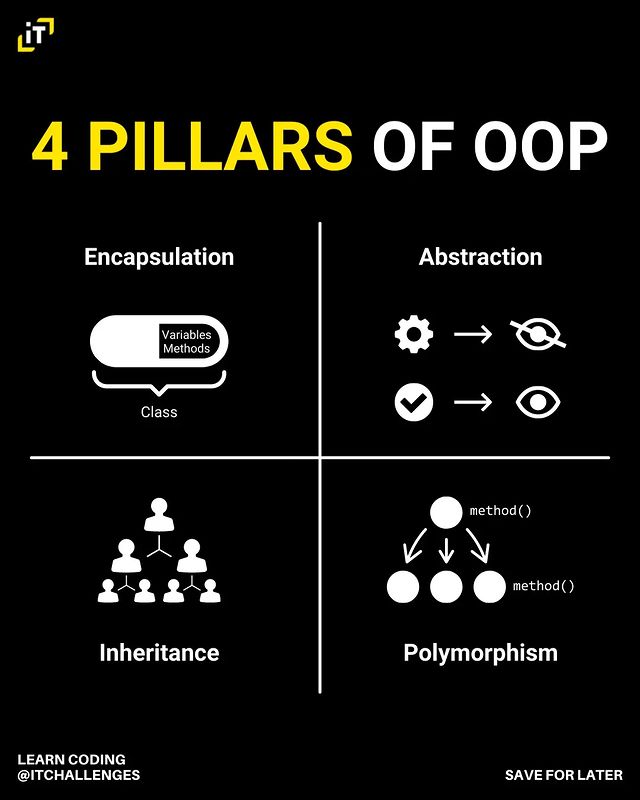
4 Pillars of OOP: i) Encapsulation ii) Abstraction iii) Inheritance iv) Polymorphism