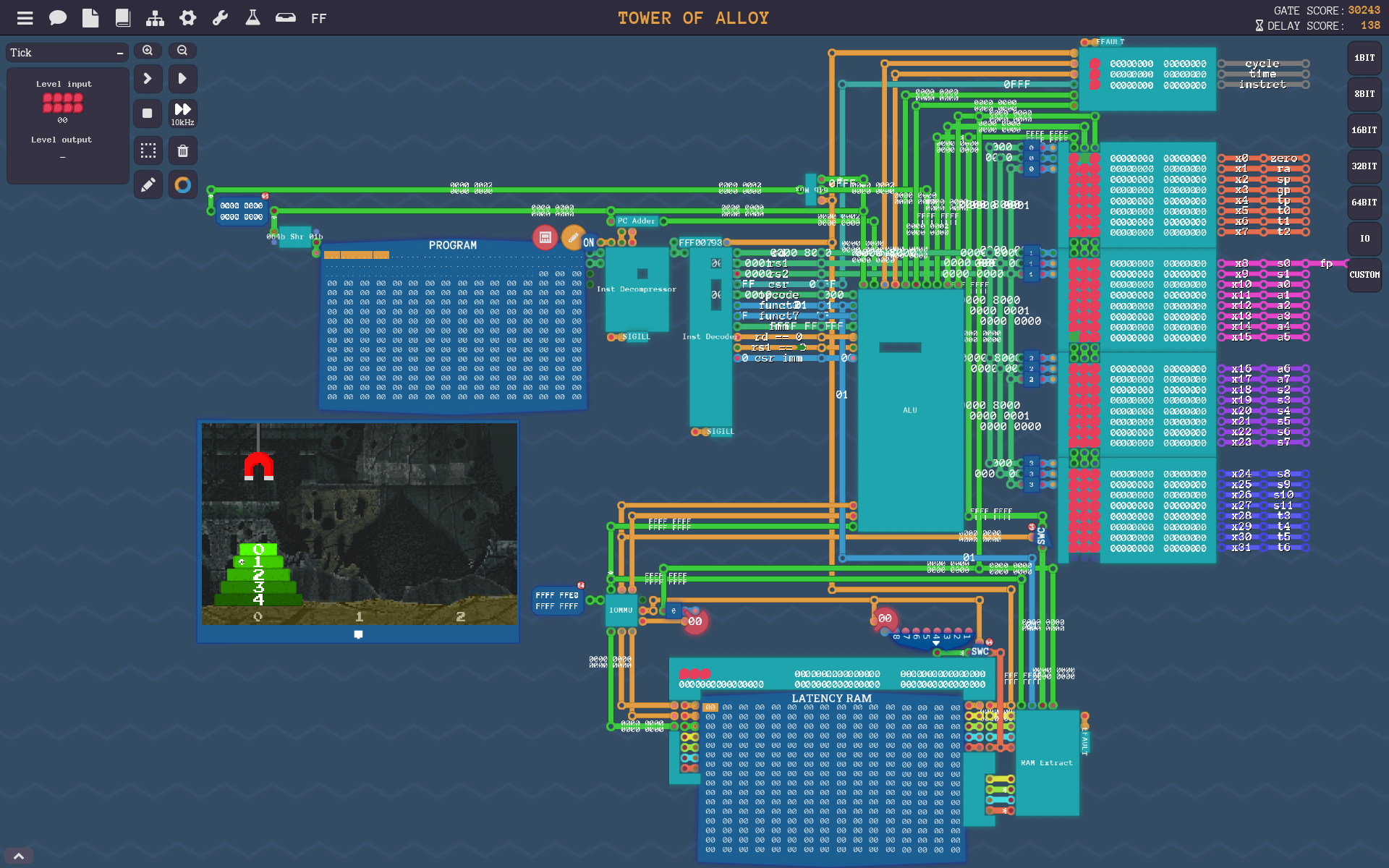
RISC-V assembler for an emulator I made in the game Turing Complete to learn about the ISA and have fun.
Video of the RISC-V emulator solving Towers of Alloy
The assembler only supports what the emulator implements. Per the unprivileged ISA spec version 20240411, the emulator supports:
-
RV32I 2.1 (32-bit integer register instructions)
-
RV64I 2.1 (64-bit integer register instructions)
-
Zicsr 2.0 (CSR instructions)
-
Zicntr 2.0 (cycle, time and instret CSRs)
-
Zicond 1.0.0 (conditional instructions for integer registers)
-
Zca 1.0.0 (compressed instructions for integer registers)
-
Zcb 1.0.0 (additional compressed instructions for integer registers)
-
Zba 1.0.0 (address generation instructions)
-
Zbb 1.0.0 (basic bit-manipulation instructions)
-
Zbs 1.0.0 (single-bit instructions)
Further extensions are not supported, notably instructions for hardware multiplication and division (M) and hardware floats (F, D).
Compressed instructions are supported in the sense that the assembler will encode regular instructions like add and lbu into the compressed form when compression is enabled. The mnemonics for the compressed instructions like c.add and c.lbu are not supported. Instructions that only exist in compressed instruction extensions like c.lwsp can be written as lwsp or c.lwsp.
The assembler also only partially implements the full syntax supported by GNU / LLVM (enough to make the gas tests compile), and notably does not support labels, symbolic constants or data sections. It does support the register mnemonics like ra and pseudo-instructions like j listed in the ASM manual (and older versions of the ISA spec before they were removed).
The assembler can be compiled as a freestanding binary that runs on the emulator. In this case the input file is read from the game's File Loader component, and the output is written to a memory address range that is expected to be present in a RAM linked to a Console.
make freestanding will compile the binary, make freestanding-install will install it along with the input file, and make freestanding-inspect will run llvm-objdump on the binary.
The tc/ directory contains solutions for some of the game's architecture puzzles using the emulator.
The *.S files contain the assembler programs. Running cargo run --bin riscv -- tc/foo.S will print the compiled program to stdout which can then be copy-pasted into the game's Program component. The component must have "Data width" set to "16 Bit". Running cargo run --bin riscv -- --compressed tc/foo.S will do the same but enable compressed instructions. Running cargo run --bin riscv -- --compressed=Zcb tc/foo.S will also enable compressed instructions from the Zcb extension.
The --save-breaker option will emit the output in the format used by the "save_breaker" branch's Assembler component instead. In this case, the Assembler must have its width set to "32".
The assembler does not consider whether the target architecture is 32-bit or 64-bit and will simply encode whatever instructions are given to it. This works fine because RV64I does not modify the behavior of RV32I instructions, except for two situations:
-
The pseudo-instructions
sext.b,sext.handzext.hshift the source register by different amounts on RV32I and RV64I. -
c.jalis only valid in RV32C; an RV64C implementation would interpret it asc.addiwinstead. Thusjalcannot be compressed intoc.jalon RV64C.
Therefore the assembler also has a --64 flag to explicitly set the target architecture to RV64I. When combined with the --compress flag it will instruct the assembler to not compress jal.
The *.c files contain equivalent C solutions that can be put in Compiler Explorer with compiler set to RISC-V (32-bits) gcc or RISC-V rv32gc clang or corresponding 64-bit version, and flags set to --std=c23 -Os -march=rv32id_zba_zbb_zbs_zicond or --std=c23 -Os -march=rv64id_zba_zbb_zbs_zicond. Note that the assembler programs are hand-written and will not exactly match the compiler's output.
The emulator has the Level Input and Level Output wired up to memory address 2^32 - 1, which is why the assembler programs refer to -1(zero) and the C programs refer to IO = (volatile uint8_t*)(intptr_t)-1;.
AGPL-3.0-only
riscv
https://github.com/Arnavion/riscv
Copyright 2024 Arnav Singh
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU Affero General Public License as
published by the Free Software Foundation, version 3 of the
License.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU Affero General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU Affero General Public License
along with this program. If not, see <https://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.