The Aruba Cloud Driver is a plugin for Docker Machine which allows you to automate the provisioning of Docker hosts on Aruba Cloud Servers. The plugin is based on the Go Aruba Cloud SDK and Cloud API.
To acquire Aruba Cloud Cloud API credentials visit https://www.cloud.it.
- Docker Machine 0.9.0 or a newer version
Windows and Mac OS X users may install Docker Toolbox package that includes the latest version of the Docker Machine.
The latest version of the docker-machine-driver-arubacloud binary is available on the GithHub Releases page.
Download the tar archive and extract it into a directory residing in your PATH. Select the binary that corresponds to your OS and according to the file name prefix:
- Linux: docker-machine-driver-arubacloud-linux
- Windows: docker-machine-driver-arubacloud-windows
To extract and install the binary, Linux and Mac users can use the Terminal and the following commands:
sudo tar -C /usr/local/bin -xvzf docker-machine-driver-arubacloud*.tar.gzIf required, modify the permissions to make the plugin executable:
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-machine-driver-arubacloudWindows users may run the above commands without sudo in Docker Quickstart Terminal that is installed with Docker Toolbox.
Otherwise Windows users can extract the zip manually and add the plugin folder to the PATH environment variable.
Make sure you have installed Go and configured GOPATH properly.
To download the repository and build the driver run the following:
go get -d -u github.com/Arubacloud/docker-machine-driver-arubacloud
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/Arubacloud/docker-machine-driver-arubacloud
make buildTo use the driver run:
make installThis command will install the driver into /usr/local/bin.
Otherwise, set your PATH environment variable correctly. For example:
export PATH=$GOPATH/src/github.com/Arubacloud/docker-machine-driver-arubacloud/bin:$PATHIf you are running Windows, you may also need to install GNU Make, Bash shell and a few other Bash utilities available with Cygwin.
You may want to refer to the Docker Machine official documentation before using the driver.
Verify that Docker Machine can see the Aruba Cloud driver:
docker-machine create -d arubacloud --help--ac_username: Aruba Cloud username.--ac_password: Aruba Cloud password.--ac_admin_password: Virtual machine admin password.--ac_endpoint: Aruba Cloud Data Center (dc1,dc2,dc3,etc.).--ac_template: Virtual machine template.--ac_size: Size of the virtual machine.--ac_action: Type of action.--ac_ip: Specify an IP already purchased on Aruba Cloud (Valid only if ac_action="NewPro").--ac_ssh_key: Path of private key file. (Both private and public key must be in the same folder).
| CLI Option | Default Value | Environment Variable | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
--ac_username |
AC_USERNAME |
yes | |
--ac_password |
AC_PASSWORD |
yes | |
--ac_admin_password |
AC_ADMIN_PASSWORD |
yes | |
--ac_endpoint |
dc1 |
AC_ENDPOINT |
yes |
--ac_template |
ubuntu1604_x64_1_0 |
AC_TEMPLATE |
yes |
--ac_size |
Large |
AC_SIZE |
yes |
--ac_action |
NewSmart |
AC_ACTION |
yes |
--ac_ip |
AC_IP |
no |
Valid values for --ac_size are Small, Medium, Large, Extra Large.
####Size mapping for Pro machines
| Size | CPU | Ram (GB) | Disk Size (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|
Small |
1 | 1 | 20 |
Medium |
1 | 2 | 40 |
Large |
2 | 4 | 80 |
Extra Large |
4 | 8 | 160 |
Valid values for --ac_action are NewSmart, NewPro, Attach.
Available parameters for --ac_endpoint are shown in the next table.
| Parameter | Data Center Location |
|---|---|
dc1 |
Italy 1 |
dc2 |
Italy 2 |
dc3 |
Czech republic |
dc4 |
France |
dc5 |
Deutschland |
dc6 |
United Kingdom |
dc7 |
Italy 3 |
dc8 |
Poland |
Supported values for --ac_template are listed below.
| Parameter | OS |
|---|---|
debian8_x64_1_0 |
Debian 8 64bit |
ubuntu1604_x64_1_0 |
Ubuntu Server 16.04 LTS 64bit |
centos7_x64_1_0 |
CentOS 7.x 64bit |
docker-machine create --driver arubacloud \
--ac_username "ARU-XXXX" \
--ac_password "xxxxxxx" \
--ac_admin_password "yyyyyyyy" \
MyDockerHostName
docker-machine create --driver arubacloud \
--ac_username "ARU-XXXX" \
--ac_password "xxxxxxx" \
--ac_endpoint "dc1" \
--ac_template "ubuntu1404_x64_1_0" \
--ac_size "Large" \
--ac_admin_password "yyyyyyyy" \
--ac_action "NewSmart" \
MyDockerHostName
If you don't specify an IP Address a new one will be automatically purchased.
docker-machine create --driver arubacloud \
--ac_username "ARU-XXXX" \
--ac_password "xxxxxxx" \
--ac_endpoint "dc1" \
--ac_template "ubuntu1404_x64_1_0" \
--ac_size "Large" \
--ac_admin_password "yyyyyyyy" \
--ac_action "NewPro" \
MyDockerHostName
docker-machine create --driver arubacloud \
--ac_username "ARU-XXXX" \
--ac_password "xxxxxxx" \
--ac_endpoint "dc1" \
--ac_template "ubuntu1404_x64_1_0" \
--ac_size "Large" \
--ac_admin_password "yyyyyyyy" \
--ac_action "NewPro" \
--ac_ip "xx.xx.xx.xx" \
MyDockerHostName
Note:
- In order to attach to an existing machine, this machine must have been created with an SSH key.
- You must put private and public key in the same folder on the machine where docker-machine commands will be launched, and pass this folder as an argument (Eg. --ac_ssh_key="private_key_path").
- The name of the machine must be the same that is visible on Aruba Cloud Dashboard
docker-machine create --driver arubacloud \
--ac_username "ARU-XXXX" \
--ac_password "xxxxxxx" \
--ac_endpoint "dc1" \
--ac_action "Attach" \
--ac_ip "xx.xx.xx.xx" \
--ac_ssh_key "private_key_path" \
MyDockerExistingHostName
####View instances
Go to Aruba Cloud dashboard to view machine instances. Dashboard url is different depending on the selected endpoint:
| DC1 | DC2 | DC3 | DC4 | DC5 | DC6 |
|---|
####View instance list
docker-machine ls
NAME ACTIVE DRIVER STATE URL SWARM DOCKER ERRORS
MyDockerHostName * arubacloud Running tcp://10.254.4.232 v1.10.0
default - arubacloud Running tcp://10.254.4.231 v1.10.0
docker-machine ip MyDockerHostName
10.254.4.232
Verify Docker Engine is installed correctly by running docker commands.
Start with something basic like docker run hello-world, or for a more interesting test, run a Dockerized webserver on your new remote machine.
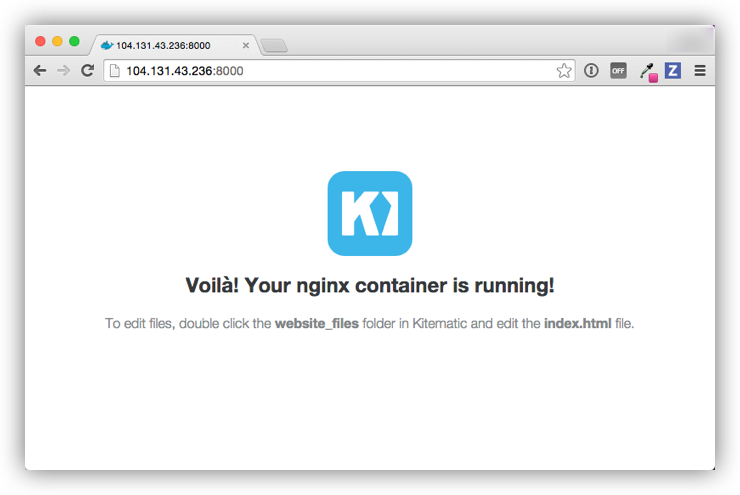
In this example, the -p option is used to expose port 80 from the nginx container and make it accessible on port 8000 of the host.
$ docker run -d -p 8000:80 --name webserver kitematic/hello-world-nginx
Unable to find image 'kitematic/hello-world-nginx:latest' locally
latest: Pulling from kitematic/hello-world-nginx
a285d7f063ea: Pull complete
2d7baf27389b: Pull complete
...
Digest: sha256:ec0ca6dcb034916784c988b4f2432716e2e92b995ac606e080c7a54b52b87066
Status: Downloaded newer image for kitematic/hello-world-nginx:latest
942dfb4a0eaae75bf26c9785ade4ff47ceb2ec2a152be82b9d7960e8b5777e65
In a web browser, go to http://<host_ip>:8000 to bring up the webserver home page. You got the <host_ip> from the output of the docker-machine ip command you ran in a previous step. Use the port you exposed in the docker run command.
docker-machine stop MyDockerHostName
docker-machine rm MyDockerHostName
About to remove MyDockerHostName
WARNING: This action will delete both local reference and remote instance.
Are you sure? (y/n): y
Successfully removed MyDockerHostName
This code is released under the Apache 2.0 License.
Copyright (c) 2017 Aruba Cloud