This is to keep track of changes to the dockerfile used to instantiate containers in which CSC Notebooks are run.
When creating the CSC Notebooks workspace and application, this repository can be directly referenced, see detailed instructions below.
-
Check out this repository
-
Adjust environment variables in
Dockerfile- Specifically, make sure that
AUTOGIS_SITE_COMMITis referencing a commit ofAutomating-GIS-processes/sitein which theci/environment.ymlhas been updated to list packages pinned to up-to-date versions (see the README there)
- Specifically, make sure that
-
Build the docker image:
docker build --network=host --tag autogis2022 ./
- Follow the instructions in CSC’s user manual
to upload the image to their docker registry.
- I used
autogisas<yourrahtiproject>,autogis2022as<yourimagename>, andv2022.1(andv2022.2...) as the version tag. Note that you have to create a Rahti project beforehand.
- I used
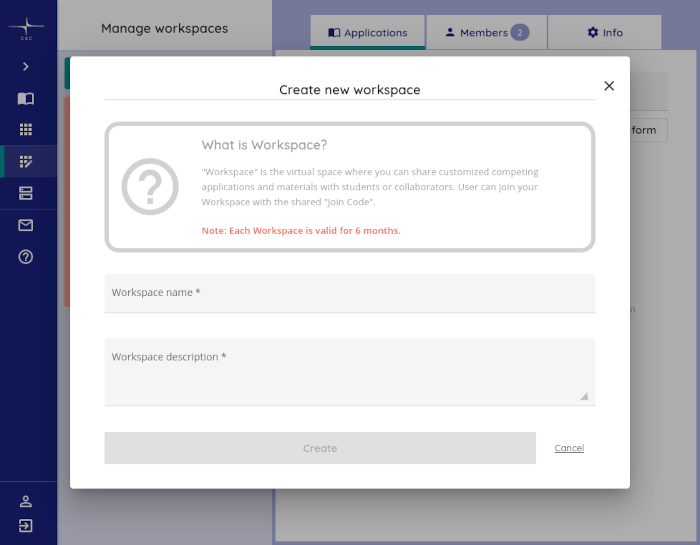
Log into https://notebooks.csc.fi/, navigate to ’Manage workspaces’, and choose ’Create new workspace’. Fill in the necessary details, and choose ’Create’.
As an example, for the 2022 iteration of the course, I entered the following information:
| workspace name | workspace description |
|---|---|
| Automating GIS processes 2, 2022 | ‘Automating GIS processes 2’ is a Masters’ level course at the Department of Geosciences and Geography, University of Helsinki. https://studies.helsinki.fi/courses/?searchText=GEOG-329-2 |
Note: CSC Notebook workspaces have a default lifetime of only 180 days. Be sure to create the workspace late enough so it lasts for the entire course.
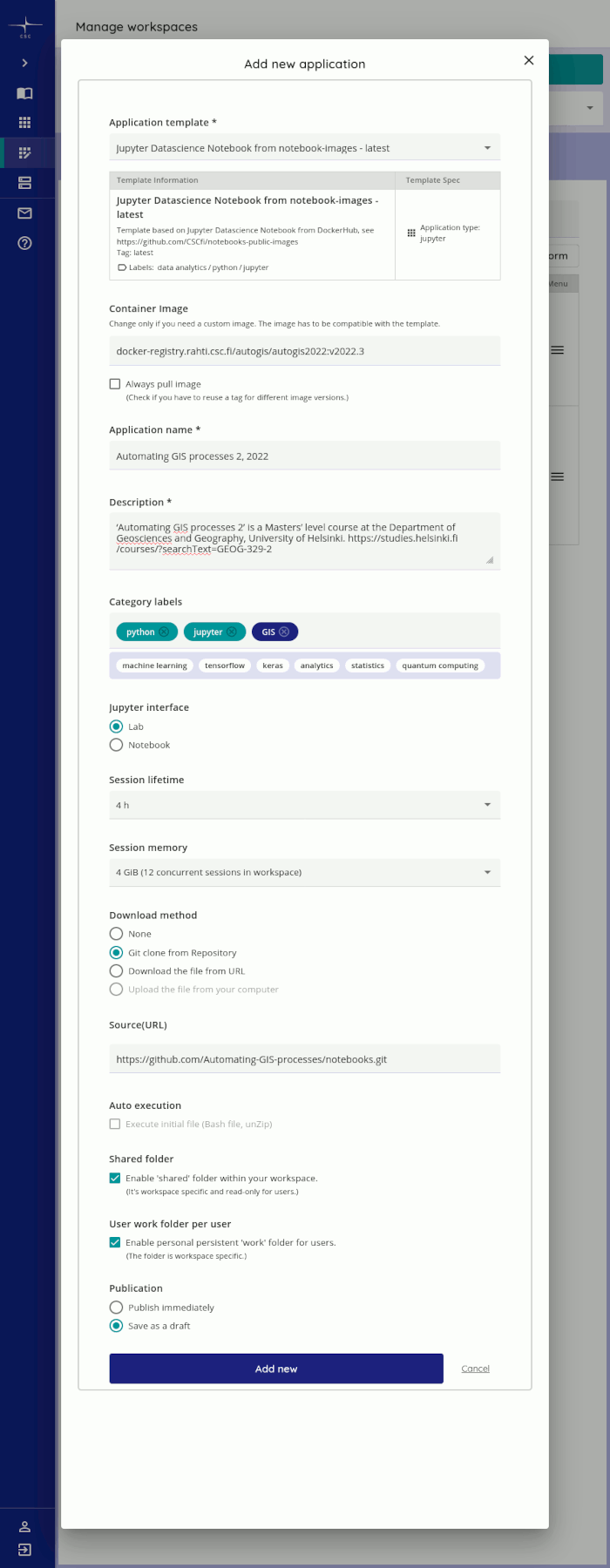
Navigate to ‘Manage workspaces’, then choose the newly created workspace in the left pane.
- On the right side, open the ’Applications’ tab and click ’+ Application’.
- Choose any of the available templates (we are using our custom image, anyways)
- Enter the resulting container image path and tag from step 2 (it should look something
like
docker-registry.rahti.csc.fi/autogis/autogis2022:v2022.1) - Enter a name and description (in 2022, I used the same values as for the workspace, see table above). Fiddle with the tags if you feel like it.
- Then, select ’Lab’ as the jupyter interface, a session lifetime appropriate for the course, and as much memory as you can per student (this can be increased upon request, if, e.g., accessibility calculations or other RAM-intensive analyses are carried out)
- Choose ‘Git clone from repository’ as a Download method, and add the URL of the
Automating-GIS-processes/notebooksas a Source (URL):https://github.com/Automating-GIS-processes/notebooks.git - Enable Shared folders and User work folders.