Turns a 17 minutes Nmap scan into 19 seconds.
Find all open ports fast with Rustscan, automatically pipe them into Nmap.
| Version 1.1.0 | Version 1.1.0 | Version 1.1.0 | Version 1.1.0 |
cargo install rustscan |
yay -S rustscan-bin |
brew tap brandonskerritt/rustscan && brew install rustscan |
Read the install guide |
- Find ports quickly using Rustscan (8 seconds at its fastest).
- Automatically runs
nmapon those ports. - Profit???
| Name | ⚡ Nmap with RustScan ⚡ | 🐢 Nmap 🐢 |
|---|---|---|
| Gif | 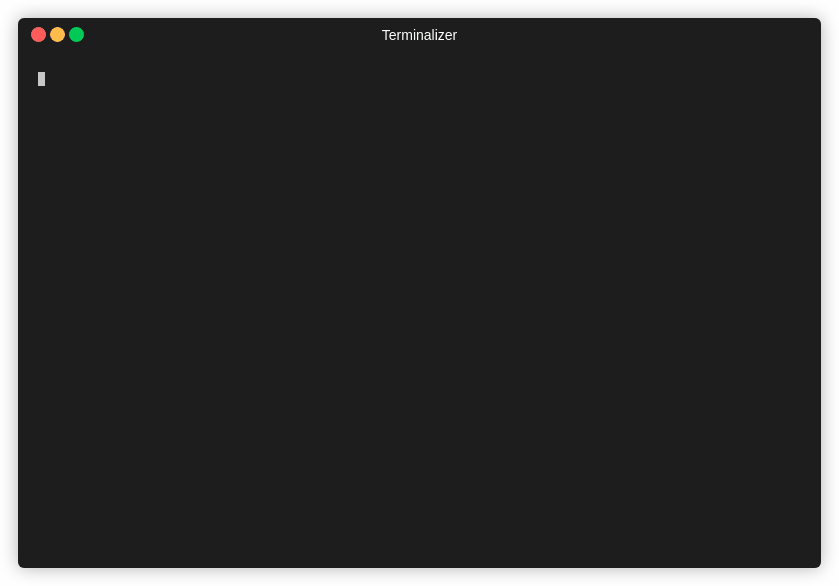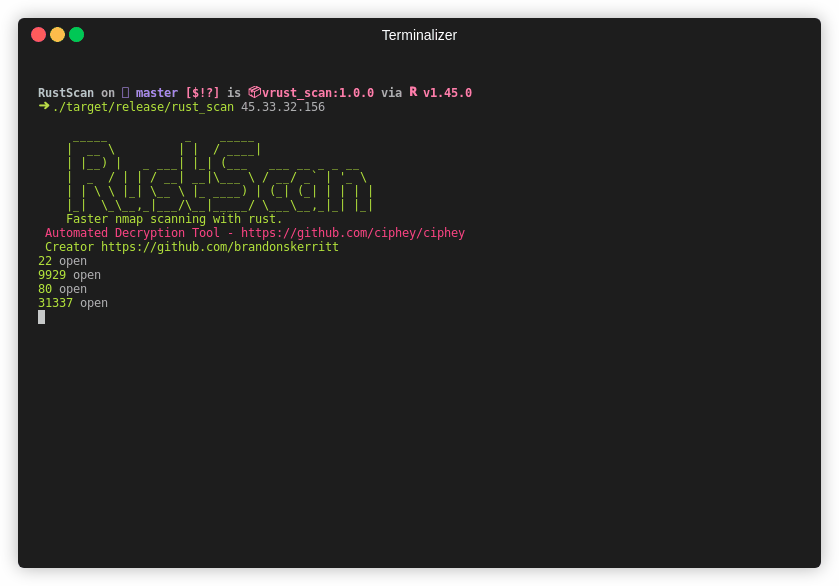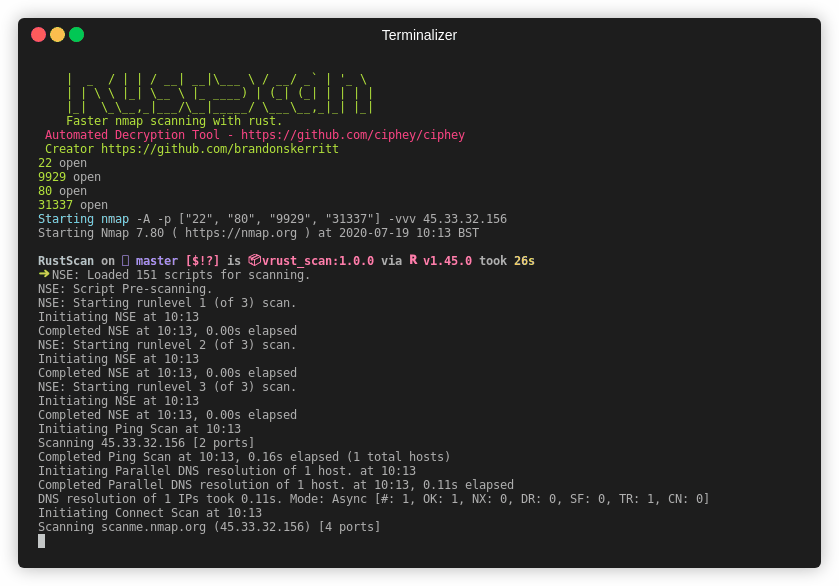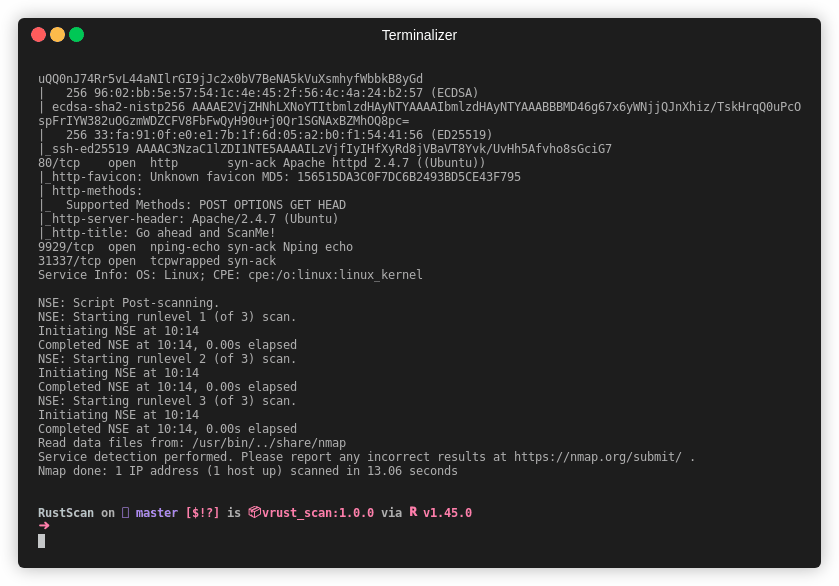 |
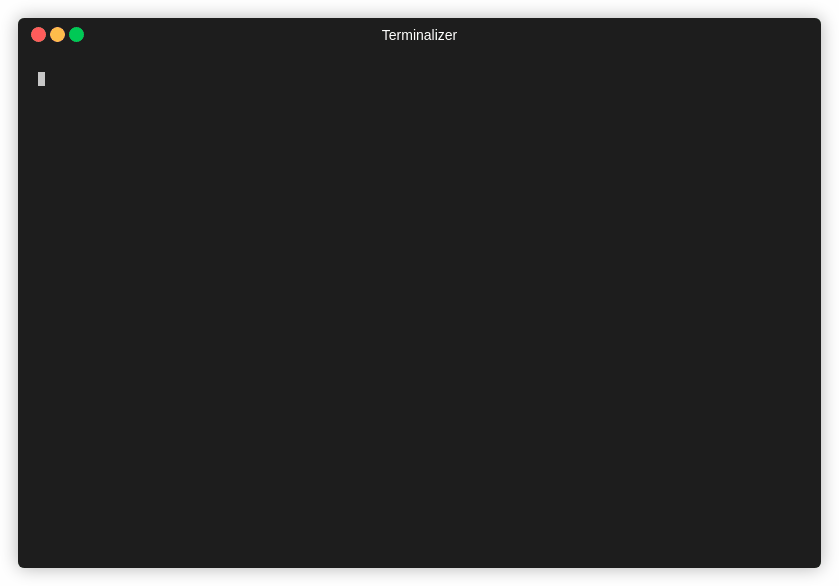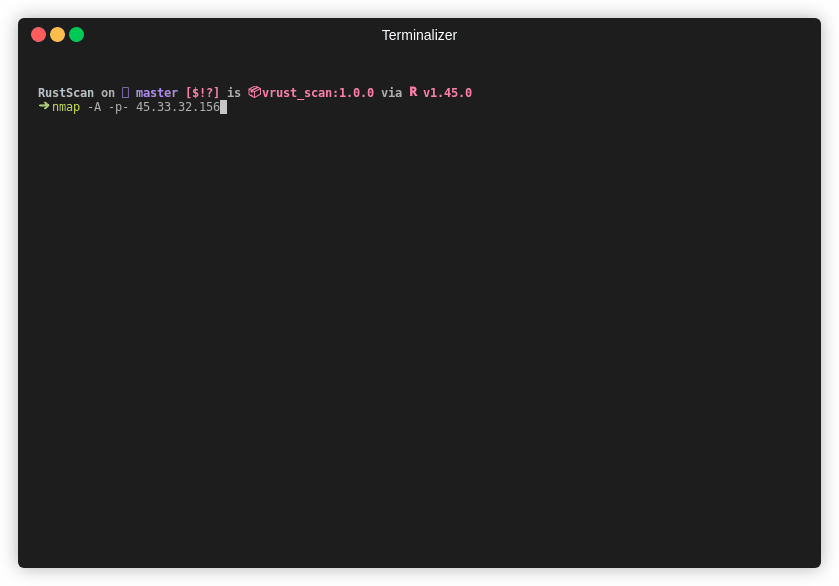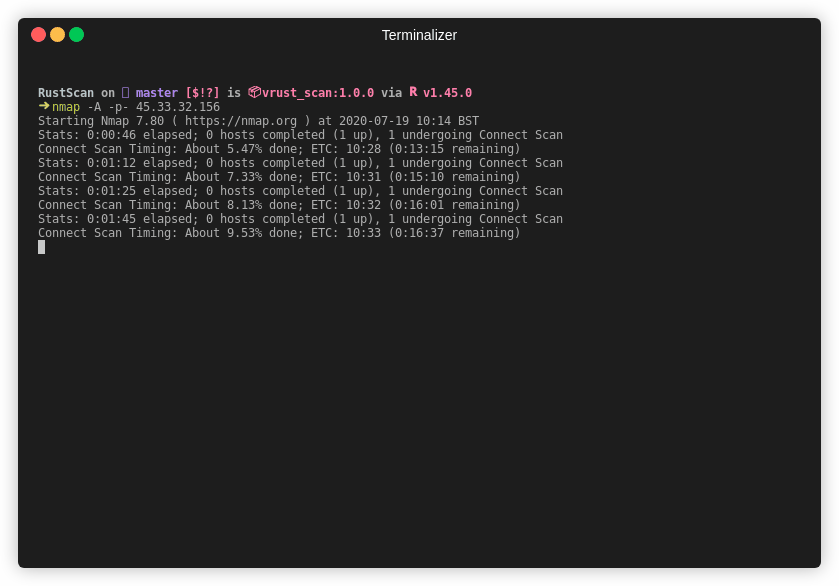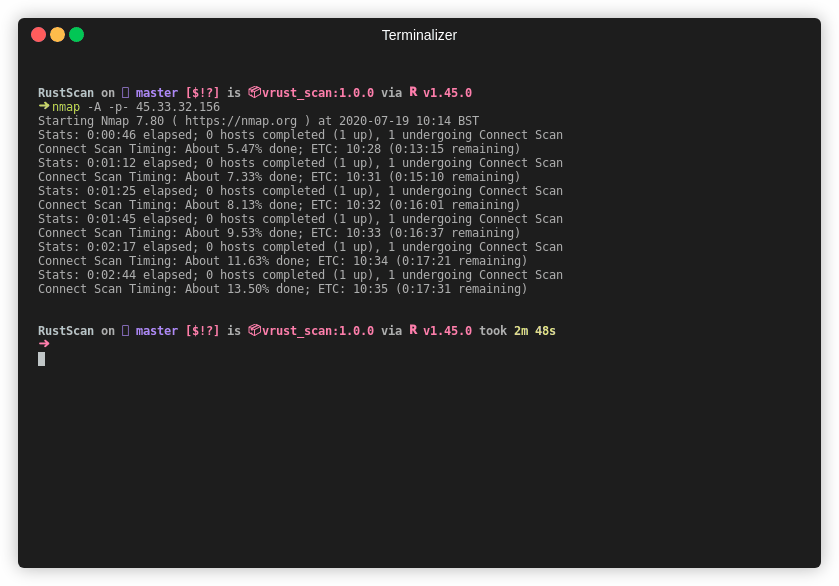 |
| Time | 39 seconds | 17 minutes and 41 seconds |
Note This is an older gif. RustScan's current top speed is 8 seconds for all 65k ports. This gif is 26 seconds.
RustScans only job is to reduce the friction between finding open ports and inputting them into nmap.
- Scans all 65k ports in 8 seconds (on 10k batch size).
- Saves you time by automatically piping it into Nmap. No more manual copying and pasting!
- Does one thing and does it well. Only purpose is to improve Nmap, not replace it!
- Let's you choose what Nmap commands to run, or uses the default.
Why spend time running fast scans and manually copying the ports, or waiting for a 20 minute scan to finish when you can just do all 65k ports in less than a minute?
RustScan running in 8 seconds and finding all open ports out of 65k.
| Name | RustScan | Nmap | Masscan |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fast | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Actually useful | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Realises it's not useful, and pipes the only useful data into the only useful port scanner | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
I think this would be a great port scanner on its own without Nmap!
No. If you want a fast port scanner, use Masscan.
I have this great idea for a script to get information on ports / hosts
Great. Contribute it to Nmap! :D
Not everyone has nmap installed....
If you're a pentester, then yes, you have Nmap installed.
I want to contribute!
Great! I'd love some help with this. Read the contributing.md file file for more information!
You need Nmap. If you have Kali Linux or Parrot OS installed, you already have Nmap. If not, follow the nmap install guide.
The easiest way to install RustScan is to use one of the packages provided for your system, such as HomeBrew or Yay for Arch Linux.
The most universal way is to use cargo, Rust's built in package manager (think Pip but for Rust). Follow this guide to installing Rust & Cargo.
If you face any issues at all, please leave a GitHub issue. I have only tested this on Linux, so there may be issues for Mac OS or Windows.
Download the .deb file from the releases page:
https://github.com/brandonskerritt/RustScan/releases
Run the commpand dpkg -i on the file. Note: sometimes you can double click the file to achieve the same result.
The .deb file only works on AMD64 CPUs. If yours is different (such as a Raspberry Pi) or the .deb file doesn't work, it is easy to build the .deb file yourself. Note: It is easier to install Rust and install via Cargo, then it is to build the .deb file. But this is just in case!
- Install Rust You can do this with
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | shwhich I took from the Rust website https://www.rust-lang.org/tools/install cargo install rustscanif you want the easiest method possible. Otherwise, to build the .deb filecargo install cargo-deb- Git clone this repo
git clone https://github.com/brandonskerritt/RustScan - cd RustScan (into the git cloned repo)
cd RustScan - Run
cargo deb - Your .deb file is now located in
target/releases/Debian/
Tap the brew:
brew tap brandonskerritt/rustscan
Install it:
brew install rustscan
- Git clone the repo.
- Install Rust. You can do this with
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | shwhich I took from the Rust website https://www.rust-lang.org/tools/install - cd into the Git repo, and run
cargo build --release - The binary is located at
target/release/rustscan - Symlink to the binary or something. Whatever you want!
rustscan -h
RustScan 1.2.0
Bee https://github.com/brandonskerritt
Fast Port Scanner built in Rust
USAGE:
rustscan [OPTIONS] <ip> [command]...
FLAGS:
-h, --help Prints help information
-V, --version Prints version information
OPTIONS:
-T, --timeout <T> The timeout before a port is assumed to be close. In MS. [default: 1500]
-b, --batch <b> Increases speed of scanning. The batch size for port scanning. Depends on your open file limit
of OS. If you do 65535 it will do every port at the same time. Although, your OS may not
support this. [default: 4500]
ARGS:
<ip> The IP address to scan
<command>... The Nmap arguments to run. To use the argument -A, end RustScan's args with '-- -A'. To run
EXAMPLE: 'rustscan -T 1500 127.0.0.1 -- -A -sC'. This argument auto runs nmap {your commands}
-vvv -p $PORTS
The format is rustscan -b 500 -T 1500 192.168.0.1 to scan 192.168.0.1 with 500 batch size with a timeout of 1500ms. The timeout is how long RustScan waits for a response until it assumes the port is closed.
The batch size determines how fast RustScan is. Set it to 65k, and it will scan all 65k ports at the same time. This means at at 65k batch size, RustScan will take TIMEOUT long to scan all ports. Essentially, if timeout is 1000ms, RustScan can scan in 1 second.
Your operating system may not support this, but it is worth it to play around and see where your open file limit is. Shortly I will be releasing a dockerised version with a much larger open file limit, so this will be possible.
This program, by default, scans 5000 ports at a time (5000 per second).
This may cause damage to a server, or may make it incredibly obvious you are scanning the server.
There are 2 ways to deal with this;
- Decrease batch size
rustscan -b 10will run 10 port scans for 1 second, and then another 10 for 1 second and so on. - Increase timeout
rustscan -T 5000will mean RustScan waits 5 seconds until it scans the next ports.
You can also use both of these at the same time, to make it as slow or as fast as you want. A fun favourite is 65535 batch size with 1 second timeout. Theoretically, this scans all 65535 ports in 1 second.
Please do not use this tool against sensitive servers. It is designed mainly for Capture the Flag events, not real world servers with sensitive data.
This is the most common error found in RustScan.
The open file limit is how many open sockets you can have at any given time.
This limit changes from OS to OS.
RustScan does not automatically create defaults (other than 5000) like Nmap does with their -T1, -T2 system.
By figuring out for yourself the optimal batch size, you will know that RustScan is the most optimised port scanner for your system.
There are 2 things you can do:
- Decrease batch size
- Increase open file limit
Decreasing batch size slows down the program, so as long as it isn't too drastic, this is a good option.
Run these 3 commands:
ulimit -a
ulimit -Hn
ulimit -Sn
They will give you an idea on the open file limit of your OS.
If it says "250", run rustscan -b 240 for a batch size of 240.
Increasing the open file limit increases speed, but poses danger. Although, opening more file sockets on the specified IP address may damage it.
To open more, set the ulimit to a higher number:
ulimit -n 5000
Mac OS Mac OS has, from what I can tell, a naturally very low open file descriptor limit. The limit for Ubuntu is 8800. The limit for Mac OS is 255!
In this case, I would say it is safe to increase the open file limit. As most Linux based OS' have limits in the thousands.
Although, if this breaks anything, please don't blame me.
Windows Subsystem for Linux Windows Subsystem for Linux does not support ulimt (see issue #39).
The best way is to use it on a host computer, in Docker, or in a VM that isn't WSL.
Automatic Ulimit updating We are currently working on automatic Ulimit updating. If it is too high, it will lower itself. If it is too low, it will suggest a higher Ulimit. Watch this issue for more.
To run your own nmap commands, end the RustScan command with -- -A where -- indicates "end of RustScan flags, please do not parse anything further" and any flags after that will be entered into nmap.
RustScan automatically runs nmap -vvv -p $PORTS $IP. To make it run -A, execute the command rustscan 127.0.0.1 -- -A.
Note: due to how Nmap behaves, sometimes you cannot SIGINT ctrl+c to end the scan and it acts like it is running in the background, but printing to STD::OUT. There is nothing I can do about this, unless I create a TTY shell for the sole purpose of running Nmap. Sorry 😓 I'll try to fix in an upcoming release. If any Rust experts want to help, please do!
- Batch size
This increases speed, by allowing us to process more at once. Something experimental I am working on is changing the open file limit. You can do this manually with ulimit -n 70000 and then running rustscan with -B 65535. This should scan all 65535 ports at the exact same time. But this is extremely experimental.
For non-experimental speed increases, slowly increase the batch size until it no longer gets open ports, or it breaks.
- Accuracy (and some speed)
To increase accuracy, the easiest way is to increase the timeout. The default is 1.5 seconds, by setting it to 4 seconds (4000) we are telling RustScan "if we do not hear back from a port in 4 seconds, assume it is closed".
Decreasing accuracy gives some speed bonus, but my testing found that batch size dramatically changed the speed whereas timeout did, but not so much.
Please read the contributing.md file
Ciphey is an automated decryption tool using artifical intelligence & natural language processing. Check it out here!
Thanks goes to these wonderful people (emoji key):
Brandon 🚇 |
SakiiR 💻 🐛 |
smackhack 🤔 💡 |
This project follows the all-contributors specification. Contributions of any kind welcome!