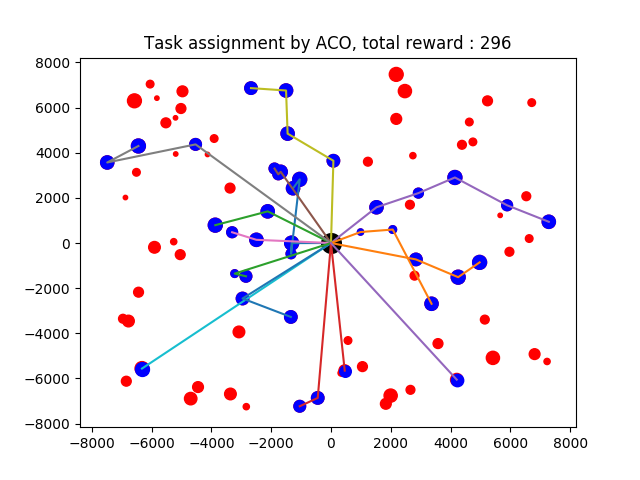
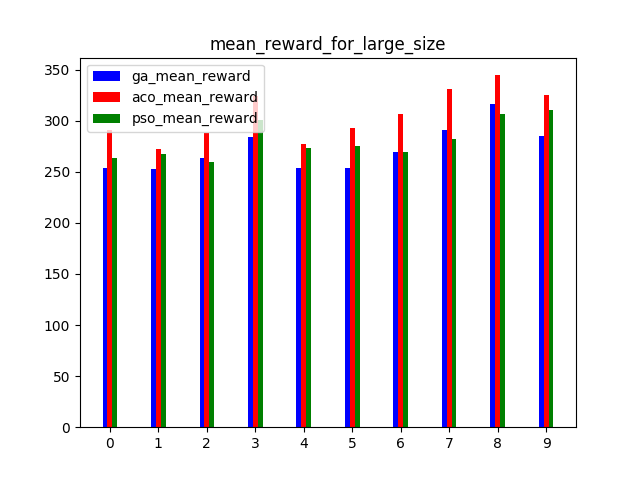
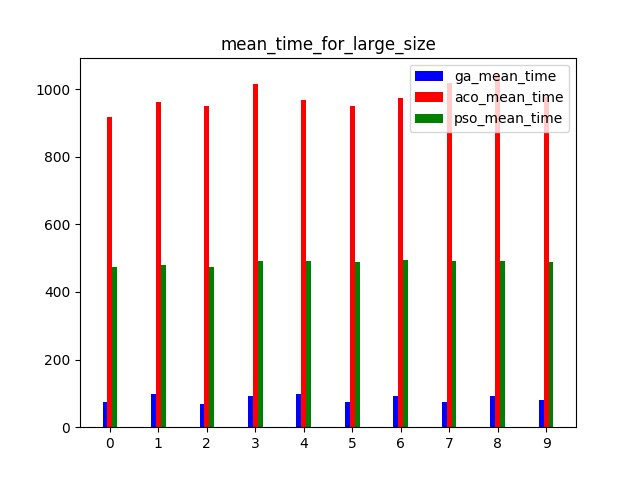
A benchmark for multi-UAV task assignment is presented in order to evaluate different algorithms. An extended Team Orienteering Problem is modeled for a kind of multi-UAV task assignment problem. Three intelligent algorithms, i.e., Genetic Algorithm, Ant Colony Optimization and Particle Swarm Optimization are implemented to solve the problem. A series of experiments with different settings are conducted to evaluate three algorithms. The modeled problem and the evaluation results constitute a benchmark, which can be used to evaluate other algorithms used for multi-UAV task assignment problems.
Please refer to the paper to see more detail.
Xiao, K., Lu, J., Nie, Y., Ma, L., Wang, X., Wang, G.: A Benchmark for Multi-UAV Task Assignment of an Extended Team Orienteering Problem. arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.00363 (2020)
Algorithm input includes vehicle number (scalar), speeds of vehicles (ga.py.
def __init__(self, vehicle_num, vehicles_speed, target_num, targets, time_lim)There should be a function called run() in the algorithm class, and the function should return task assignment plan(array, e.g. [[28, 19, 11], [25, 22, 7, 16, 17, 23], [21, 26, 12, 9, 6, 3], [5, 15, 1], [18, 20, 29]], each subset is a vehicle path) and computational time usage (scalar).
You can replace one algorithm below with another algorithm in evaluate.py, and then python evaluate.py. If you don't want to evaluate three algorithm together, you should modify the code properly( this is easy).
ga = GA(vehicle_num,env.vehicles_speed,target_num,env.targets,env.time_lim)
aco = ACO(vehicle_num,target_num,env.vehicles_speed,env.targets,env.time_lim)
pso = PSO(vehicle_num,target_num ,env.targets,env.vehicles_speed,env.time_lim)
ga_result=p.apply_async(ga.run)
aco_result=p.apply_async(aco.run)
pso_result=p.apply_async(pso.run)
p.close()
p.join()
ga_task_assignmet = ga_result.get()[0]
env.run(ga_task_assignmet,'GA',i+1,j+1)
re_ga[i].append((env.total_reward,ga_result.get()[1]))
env.reset()
aco_task_assignmet = aco_result.get()[0]
env.run(aco_task_assignmet,'ACO',i+1,j+1)
re_aco[i].append((env.total_reward,aco_result.get()[1]))
env.reset()
pso_task_assignmet = pso_result.get()[0]
env.run(pso_task_assignmet,'PSO',i+1,j+1)
re_pso[i].append((env.total_reward,pso_result.get()[1]))In Env() in evaluate.py, function step is used for reinforcement learning. Because this is still being developed, we cannot supply a demo. If your algorithm is reinforcement learning, you can try to train it with Env(). Your pull request and issue are welcome.