My solutions to Leetcode Top Interview Questions. Python is my language of choice 🐍.
Comments explaining each solution are in the corresponding solutions/something.py file.
You can click on Solution in each section to jump directly to the file.
<<<<<<:>~
- Easy
- Two Sum
- Roman to Integer
- Longest Common Prefix
- Valid Parentheses
- Merge Two Sorted Lists
- Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
- Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String
- Plus One
- sqrt(x)
- Climbing Stairs
- Merge Sorted Array
- Binary Tree In Order Traversal
- Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
- Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
- Pascal's Triangle
- Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
- Valid Palindrome
- Single Number
- Linked List Cycle
- Intersection of Two Linked Lists
- Majority Element
- Excel Sheet Column Number
- Reverse Bits
- Number of 1 Bits
- Happy Number
- Reverse Linked List
- Contains Duplicate
- Palindrome Linked List
- Valid Anagram
- Missing Number
- Move Zeroes
- Power of Three
- Reverse String
- Intersection of Two Arrays II
- First Unique Character in a String
- Fizz Buzz
- Medium
Two Sum is a problem in where you are given an array of integers nums and an integer target, then return indices of
the two numbers such that they add up to target.
You may assume that:
- Each input would have exactly one solution.
- You may not use the same element twice.
- You can return the answer in any order.
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: list[int], target: int) -> list[int]:
store = {}
for index, number in enumerate(nums):
if target - number in store:
return [store[target - number], index]
else:
store[number] = indexGiven a roman numeral, convert it to an integer.
Symbol Value
I 1
V 5
X 10
L 50
C 100
D 500
M 1000
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.answer = 0
def romanToInt(self, s: str) -> int:
chars = s
def add(number):
self.answer += number
# inelegantly replace all special cases with simplified versions. IV (4) becomes IIII (1,1,1,1) etc
chars = (
chars.replace("IV", "IIII")
.replace("IX", "VIIII")
.replace("XL", "XXXX")
.replace("XC", "LXXXX")
.replace("CD", "CCCC")
.replace("CM", "DCCCC")
)
# basically a switch statement to map each possible roam-nc numeral to an integer value and add it up
for char in chars:
match char:
case "I":
add(1)
case "V":
add(5)
case "X":
add(10)
case "L":
add(50)
case "C":
add(100)
case "D":
add(500)
case "M":
add(1000)
return self.answerWrite a function to find the longest common prefix string amongst an array of strings.
If there is no common prefix, return an empty string "".
class Solution:
def longestCommonPrefix(self, strs: list[str]) -> str:
length = min(len(i) for i in strs)
stack = set()
result = ""
for index in range(0, length):
for string in strs:
stack.add(string[index])
if len(stack) == 1:
result += stack.pop()
return resultGiven a string s containing just the characters (, ), {, }, [ and ], determine if the input string is
valid.
An input string is valid if:
- Open brackets must be closed by the same type of brackets.
- Open brackets must be closed in the correct order.
- Every close bracket has a corresponding open bracket of the same type.
class Solution:
def isValid(self, s: str) -> bool:
stack = ""
valid_brackets = ("()", "[]", "{}")
for char in s:
stack += char
if char in ")]}":
if stack[len(stack) - 2:] in valid_brackets:
stack = stack[:-2]
return len(stack) == 0You are given the heads of two sorted linked lists list1 and list2.
Merge the two lists in a one sorted list. The list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.
Return the head of the merged linked list.
# Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, list1: ListNode, list2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
dummy = ListNode(0)
new_list = dummy
while list1 is not None and list2 is not None:
if list1.val <= list2.val:
new_list.next = list1
list1 = list1.next
else:
new_list.next = list2
list2 = list2.next
new_list = new_list.next
if list1 is not None:
new_list.next = list1
else:
new_list.next = list2
return dummy.nextGiven an integer array nums sorted in non-decreasing order, remove the duplicates in-place such that each unique
appears only once. The relative order of the elements should be kept the same. Then return the number of unique elements
in nums.
Consider the number of unique elements of nums to be k, to get accepted, you need to do the following things:
- Change the array
numssuch that the firstkelements ofnumscontain the unique elements in the order they were - present in
numsinitially. The remaining elements of nums are not important as well as the size ofnums. - Return
k.
class Solution:
def removeDuplicates(self, nums):
nums[:] = sorted(set(nums))
return len(nums)Given two strings needle and haystack, return the index of the first occurrence of needle in haystack, or -1
if needle is not part of haystack.
class Solution:
def strStr(self, haystack: str, needle: str) -> int:
return haystack.find(needle)You are given a large integer represented as an integer array digits, where each digits[i] is the ith digit of
the integer. The digits are ordered from most significant to the least significant in left-to-right order. The large
integer does not contain any leading 0's.
Increment the large integer by one and return the resulting array of digits.
class Solution:
def plusOne(self, digits: list[int]) -> list[int]:
if digits[-1] == 9:
if len(digits) == 1:
return [1, 0]
return self.plusOne(digits[:-1]) + [0]
else:
digits[-1] += 1
return digitsGiven a non-negative integer x, return the square root of x rounded down to the nearest integer. The returned
integer should be non-negative as well.
You must not use any built-in exponent function or operator.
- For example, do not use
pow(x, 0.5)in c++ orx ** 0.5in python.
class Solution:
def mySqrt(self, x: int) -> int:
if x == 0:
return 0
last_guess = x / 2.0
while True:
guess = (last_guess + x / last_guess) / 2
if abs(guess - last_guess) < 0.000001:
return int(guess)
last_guess = guessYou are climbing a staircase. It takes n steps to reach the top.
Each time you can either climb 1 or 2 steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
class Solution:
def climbStairs(self, n: int) -> int:
if n <= 3:
return n
a = (1, 2)
for i in range(3, n + 1):
a = (a[1], a[0] + a[1])
return a[1]You are given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, sorted in non-decreasing order, and two integers m and n,
representing the number of elements in nums1 and nums2 respectively.
Merge nums1 and nums2 into a single array sorted in non-decreasing order.
The final sorted array should not be returned by the function, but instead be stored inside the array nums1.
To accommodate this, nums1 has a length of m + n, where the first m elements denote the elements that should be
merged, and the last n elements are set to 0 and should be ignored. nums2 has a length of n.
class Solution:
def merge(self, nums1: list[int], m: int, nums2: list[int], n: int) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify nums1 in-place instead.
"""
nums1[:] = sorted(nums1[:m] + nums2[:n])Given the root of a binary tree, return the inorder traversal of its nodes' values.
Example:
returns [1, 3, 2]
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
class Solution:
def inorderTraversal(self, root: [TreeNode]) -> list[int]:
res = []
stack = []
while True:
while root:
stack.append(root)
root = root.left
if not stack:
return res
node = stack.pop()
res.append(node.val)
root = node.rightGiven an integer array nums where the elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height-balanced search
tree.
from typing import Optional
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
class Solution:
def sortedArrayToBST(self, nums: list[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if not nums:
return None
middle = len(nums) // 2
root_node = TreeNode(nums[middle])
root_node.left = self.sortedArrayToBST(nums[:middle])
root_node.right = self.sortedArrayToBST(nums[middle + 1:])
return root_nodeGiven the root of a binary tree, return its maximum depth.
A binary tree's maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: [TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
return 1 + max(self.maxDepth(root.left), self.maxDepth(root.right))Given an integer numRows, return the first numRows of Pascal's triangle.
In Pascal's triangle, each number is the sum of the two numbers directly above it, as shown:
class Solution:
def generate(self, num_rows: int) -> list[list[int]]:
result = [[1]]
for x in range(num_rows - 1):
temp_list = [0] + result[-1] + [0]
next_row = []
for j in range(len(result[-1]) + 1):
next_row.append(temp_list[j] + temp_list[j + 1])
result.append(next_row)
return resultYou are given an array prices where prices[i] is the price of a given stock on the ith day.
You want to maximise your profit by choosing a single day to buy one stock and choosing a different day in the future to sell that stock.
Return the maximum profit you can achieve from this transaction. If you cannot achieve any profit, return 0.
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: list[int]) -> int:
max_profit = 0
min_purchase = prices[0]
for price in prices:
max_profit = max(max_profit, price - min_purchase)
min_purchase = min(min_purchase, price)
return max_profitA phrase is a palindrome if, after converting all uppercase letters into lowercase letters and removing all non-alphanumeric characters, it reads the same forward and backward. Alphanumeric characters include letters and numbers.
Given a string s, return true if it is a palindrome, or false otherwise.
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, s: str) -> bool:
s = ("".join(filter(str.isalnum, s))).lower()
return s == s[::-1]Given a non-empty array of integers nums, every element appears twice except for one. Find that single one.
You must implement a solution with a linear runtime complexity and use only constant extra space.
class Solution:
def singleNumber(self, nums: list[int]) -> int:
from collections import Counter
count = Counter(nums)
return [int(x) for x in count if count[x] != 2][0]Given head, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it.
There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the `next pointer.
Return true if there is a cycle in the linked list. Otherwise, return false.
from typing import Optional
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
seen: list[ListNode] = []
while head:
if head in seen:
return True
seen.append(head)
head = head.next
return FalseGiven the heads of two singly linked-lists headA and headB , return the node at which the two lists intersect.
If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return None.
from typing import Optional
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, head_a: ListNode, head_b: ListNode) -> Optional[ListNode]:
seen: set[ListNode] = set()
current = head_a
while current:
seen.add(current)
current = current.next
current = head_b
while current:
if current in seen:
return current
current = current.next
return NoneGiven an array nums of size n, return the majority element.
The majority element is the element that appears more than ⌊n / 2⌋ times. You may assume that the majority element
always exists in the array.
class Solution:
def majorityElement(self, nums: list[int]) -> int:
from collections import Counter
count = Counter(nums)
return [x for x in count if count[x] > len(nums) / 2][0]Given a string columnTitle that represents the column title as appears in an Excel sheet, return its corresponding
column number.
For example:
A -> 1
B -> 2
C -> 3
...
Z -> 26
AA -> 27
AB -> 28
...
class Solution:
def titleToNumber(self, column_title: str) -> int:
from string import ascii_uppercase
from collections import defaultdict
score = 0
letter_values = defaultdict()
for i, char in enumerate(ascii_uppercase):
letter_values[char] = i + 1
for i, char in enumerate(column_title[::-1]):
if i == 0:
score += letter_values[char]
else:
score += letter_values[char] * 26 ** i
return scoreReverse bits of a given 32 bits unsigned integer.
class Solution:
def reverseBits(self, n: int) -> int:
n = bin(n)[2:]
n = str(n).zfill(32)
n = n[::-1]
return int(n, 2)Write a function that takes the binary representation of an unsigned integer and returns the number of '1' bits it has (also known as the Hamming weight.)
class Solution:
def hammingWeight(self, n: int) -> int:
return bin(n).count("1")Write an algorithm to determine if a number n is happy.
A happy number is a number defined by the following process:
- Starting with any positive integer, replace the number by the summed squares of its digits.
- Repeat the process until the number equals 1 (where it will stay), or it loops endlessly in a cycle which does not include 1.
- Those numbers for which this process ends in 1 are happy.
Return true if n is a happy number, and false if not.
class Solution:
def sum_digits(self, number):
total = sum([int(n) ** 2 for n in str(number)])
if len(str(total)) == 1:
return total
else:
return self.sum_digits(total)
def isHappy(self, n: int) -> bool:
if self.sum_digits(n) in (1, 7):
return True
else:
return FalseGiven the head of a singly linked list, reverse the list, and return the reversed list.
from typing import Optional
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
prev = None
curr = head
while curr:
next_node = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next_node
return prevGiven an integer array nums, return true if any value appears at least twice in the array, and return false if
every element is distinct.
class Solution:
def containsDuplicate(self, nums: list[int]) -> bool:
seen = set()
for number in nums:
if number in seen:
return True
seen.add(number)
return FalseGiven the head of a singly linked list, return true if it is a palindrome or false otherwise.
from typing import Optional
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
if head is None:
return False
values = list()
while head is not None:
values.append(head.val)
head = head.next
if values == values[::-1]:
return True
else:
return FalseGiven two strings s and t, return trueif t is an anagram of s, and false otherwise.
class Solution:
def isAnagram(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool:
if sorted(s) == sorted(t):
return True
else:
return FalseGiven an array [nums] containing n distinct numbers in the range [0, n], return the only number in the range that
is missing from the array.
class Solution:
def missingNumber(self, nums: list[int]) -> int:
if nums == [0]:
return 1
for x in range(max(nums) + 1):
if x not in nums:
return x
return max(nums) + 1Given an integer array nums, move all 0's to the end of it while maintaining the relative order of the non-zero
elements.
Note that you must do this in-place without making a copy of the array.
class Solution:
def moveZeroes(self, nums: list[int]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead.
"""
number_of_zeroes = nums.count(0)
for x in range(number_of_zeroes):
nums.remove(0)
nums.append(0)Give an integer n, return true if it is a power of three. Otherwise, return false.
An integer n is a power of three if there exists an integer x such that n == 3x.
class Solution:
def isPowerOfThree(self, n: int) -> bool:
if n < 1:
return False
while n % 3 == 0:
n //= 3
return n == 1Write a function that reverses a string. The input string is given as an array of characters s.
You must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
class Solution:
def reverseString(self, s: list[str]) -> None:
s[:] = reversed(s)Given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, return an array of their intersection. Each element in the result must
appear as many times as it shows in both arrays, and you may return the result in any order.
class Solution:
def intersect(self, nums1: list[int], nums2: list[int]) -> list[int]:
from collections import Counter
counter1 = Counter(nums1)
counter2 = Counter(nums2)
result: list[int] = []
for key, value in counter1.items():
if key in counter2:
min_count = min(value, counter2[key])
result.extend([key] * min_count)
return resultGiven a string s, find the first non-repeating character in it and return its index. If it does not exist,
return -1.
class Solution:
def firstUniqChar(self, s: str) -> int:
for i, char in enumerate(s):
if s.count(char) == 1:
return i
return -1Given an integer n, return a string array answer (1-indexed) where:
answer[i] == "FizzBuzz"ifiis divisible by 3 and 5.answer[i] == "Fizz"ifiis divisible by 3.answer[i] == "Buzz"ifiis divisible by 5.answer[i] == i(as a string) if none of the above conditions are true.
class Solution:
def fizzBuzz(self, n: int) -> list[str]:
result = []
rules = {3: "Fizz", 5: "Buzz"}
for x in range(1, n + 1):
answer = ""
for key, value in rules.items():
if x % key == 0:
answer += value
result.append(answer or str(x))
return resultYou are given two strings s and t.
String t is generated by random shuffling string s and then add one more letter at a random position.
Return the letter that was added to t.
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order, and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
from typing import Optional
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(
self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]
) -> Optional[ListNode]:
t1_total = ""
t2_total = ""
node = l1
while node:
t1_total += str(node.val)
node = node.next
node = l2
while node:
t2_total += str(node.val)
node = node.next
result = list(str(int(t1_total[::-1]) + int(t2_total[::-1]))[::-1])
return lst2link(result)
def lst2link(lst):
cur = dummy = ListNode(0)
for e in lst:
cur.next = ListNode(e)
cur = cur.next
return dummy.nextGiven a string s, find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, string: str) -> int:
if len(string) == 1:
return 1
seen = set()
longest = 0
substring = ""
for i, char in enumerate(string):
for char2 in string[i:]:
if char2 not in seen:
seen.add(char2)
substring += char2
elif char2 in seen:
longest = max(longest, len(substring))
seen.clear()
substring = ""
break
return longestGiven a string s, return the longest palindromic substring in s.
class Solution:
def longestPalindrome(self, string: str) -> str:
length = len(string)
# if our string is already a palindrome, we know we cannot have the longest substring
if string == string[::-1] or length <= 1:
return string
# create our window pointers
left = 0
right = 1
longest = ""
while left + 1 < length:
# crete a window view using slices
current = string[left:right]
# if the window is a palindrome
if current == current[::-1]:
if len(current) > len(longest):
longest = current
# once the right pointer is at the end of the string,
# increment the left pointer by 1
# and set the right pointer to the left pointer position + 1
if right == length:
left += 1
right = left + 1
else:
right += 1
return longestGiven a signed 32-bit integer x, return x with its digits reversed.
If reversing x causes the value to go outside the signed 32-bit integer range [-231, 231 - 1], then return 0.
Assume the environment does not allow you to store 64-bit integers (signed or unsigned).
class Solution:
def reverse(self, number: int) -> int:
reverse: int = 0
negative: bool = number < 0
if negative:
number *= -1
while number > 0:
last_digit = number % 10
reverse = (reverse * 10) + last_digit
number = number // 10
if negative:
reverse = reverse * -1
# TODO: fix the -
if reverse > 2 ** 31 - 1 or reverse < -2 ** 32 or reverse == -2147483651:
return 0
return reverseImplement the myAtoi(string s) function,
which converts a string to a 32-bit signed integer (similar to C/C++'s atoi function).
from string import digits
class Solution:
def myAtoi(self, string: str) -> int:
string = string.strip()
prefix: str = ""
number_string = ""
found = False
if string[0] in ("-", "+"):
prefix = string[0]
string = string[1:]
for char in string:
if char in digits and not found:
found = True
if char not in digits and found:
return int(prefix + number_string)
elif found:
number_string += char
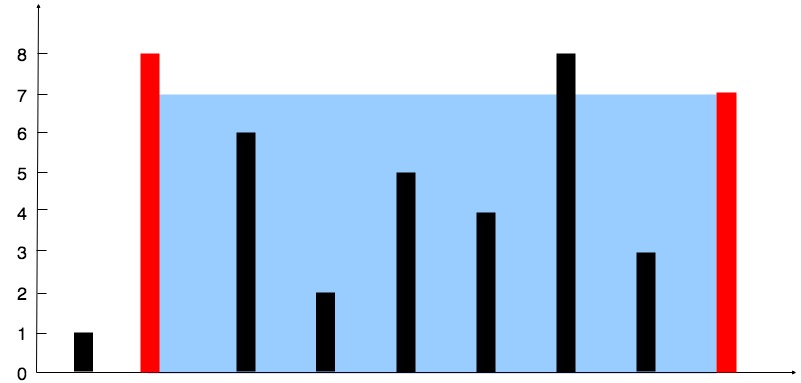
return int(prefix + number_string)You are given an integer array height of length n. There are n vertical lines drawn such that the two endpoints of
the ith line are (i, 0) and (i, height[i]).
Find two lines that together with the x-axis form a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Return the maximum amount of water a container can store.
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, height: list[int]) -> int:
left = 0
right = len(height) - 1
area: int = 0
while left < right:
area = max(area, (right - left) * min(height[left], height[right]))
if height[left] < height[right]:
left += 1
else:
right -= 1
return areaGiven an array nums with n objects colored red, white, or blue, sort them in-place so that objects of the same color
are adjacent, with the colors in the order red, white, and blue.
We will use the integers 0, 1, and 2 to represent the color red, white, and blue, respectively.
You must solve this problem without using the library's sort function.
class Solution:
def sortColors(self, nums: list[int]) -> None:
while True:
swapped = False
for i, _ in enumerate(nums):
if i < len(nums) - 1 and nums[i] > nums[i + 1]:
nums[i], nums[i + 1] = nums[i + 1], nums[i]
swapped = True
if not swapped:
break
print(nums)