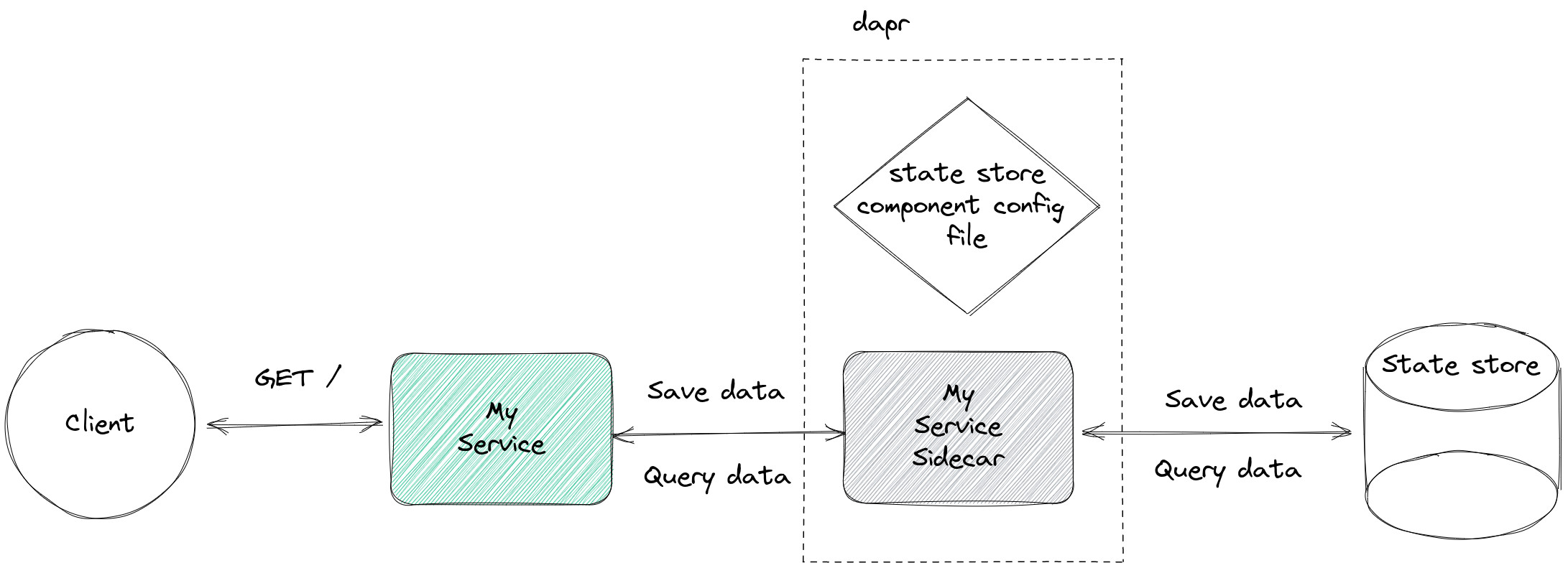
The following scenario is implemented here.
My service simply stores some data in a data store. But, it does not access the data store directly. Instead, it passes the data to its dapr sidecar and instructs it to store the data. Thus, dapr completely abstracts the underlying data store for My service.
- dapr CLI
- Java (Version >=17)
Install dapr on your system. This will start a redis docker container by default.
dapr init./gradlew buildFatJardapr run --app-id my-service --app-port 8080 --app-protocol http --dapr-http-port 3500 --components-path components/local/ -- java -cp build/libs/fat.jar com.example.MyServiceKtAs you can see, the dapr CLI is used to start up both, the dapr sidecar and the service.
curl http://localhost:8080dapr supports many data stores. A yaml config file specifies which concrete state store implementation is used for a project. This enables us to exchange the underlying state store implementation without making any code changes.
Each component has a specification (or spec) that it conforms to. Components are configured at design-time with a YAML file which is stored in either:
- A
components/localfolder within your solution, or - Globally in the
.daprfolder created when invokingdapr init.
In this project, the configuration file is placed inside the solution (components/local).