Fraudfinder - A comprehensive lab series on how to build a real-time fraud detection system on Google Cloud.
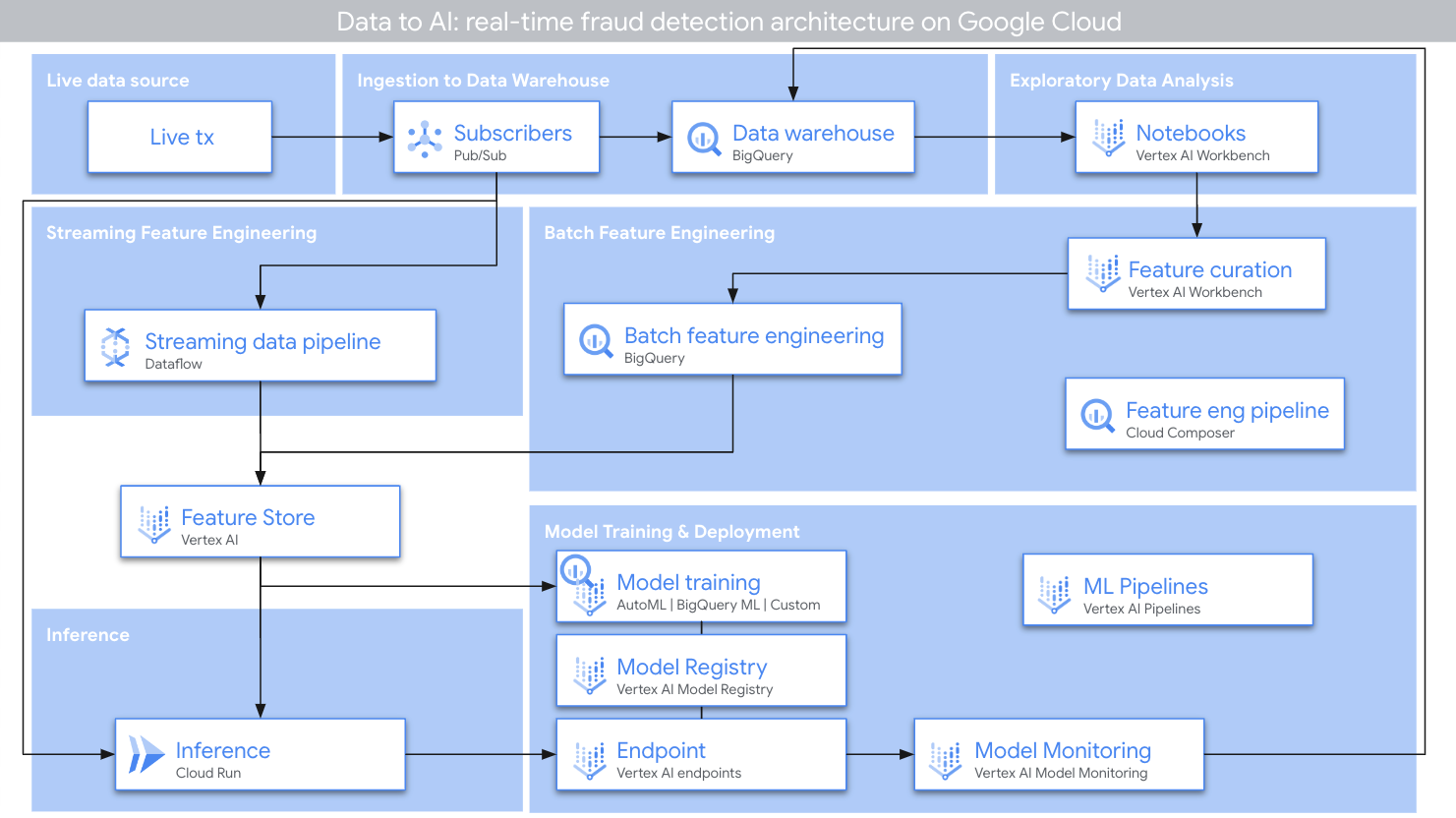
Fraudfinder FraudFinder is a golden Data to AI workshop to show an end-to-end architecture from raw data to MLOps, through the use case of real-time fraud detection. Fraudfinder is a series of labs to showcase the comprehensive Data to AI journey on Google Cloud, through the use case of real-time fraud detection. Throughout the Fraudfinder labs, you will learn how to read historical payment transactions data stored in a data warehouse, read from a live stream of new transactions, perform exploratory data analysis (EDA), do feature engineering, ingest features into a feature store, train a model using feature store, register your model in a model registry, evaluate your model, deploy your model to an endpoint, do real-time inference on your model with feature store, and monitor your model. Below you will find an image of the overall architecture:
This repo is organized across various notebooks as:
- 00_environment_setup.ipynb
- 01_exploratory_data_analysis.ipynb
- 02_feature_engineering_batch.ipynb
- 03_feature_engineering_streaming.ipynb
- bqml/
Before you begin, it is recommended to create a new Google Cloud project so that the activities from this lab do not interfere with other existing projects.
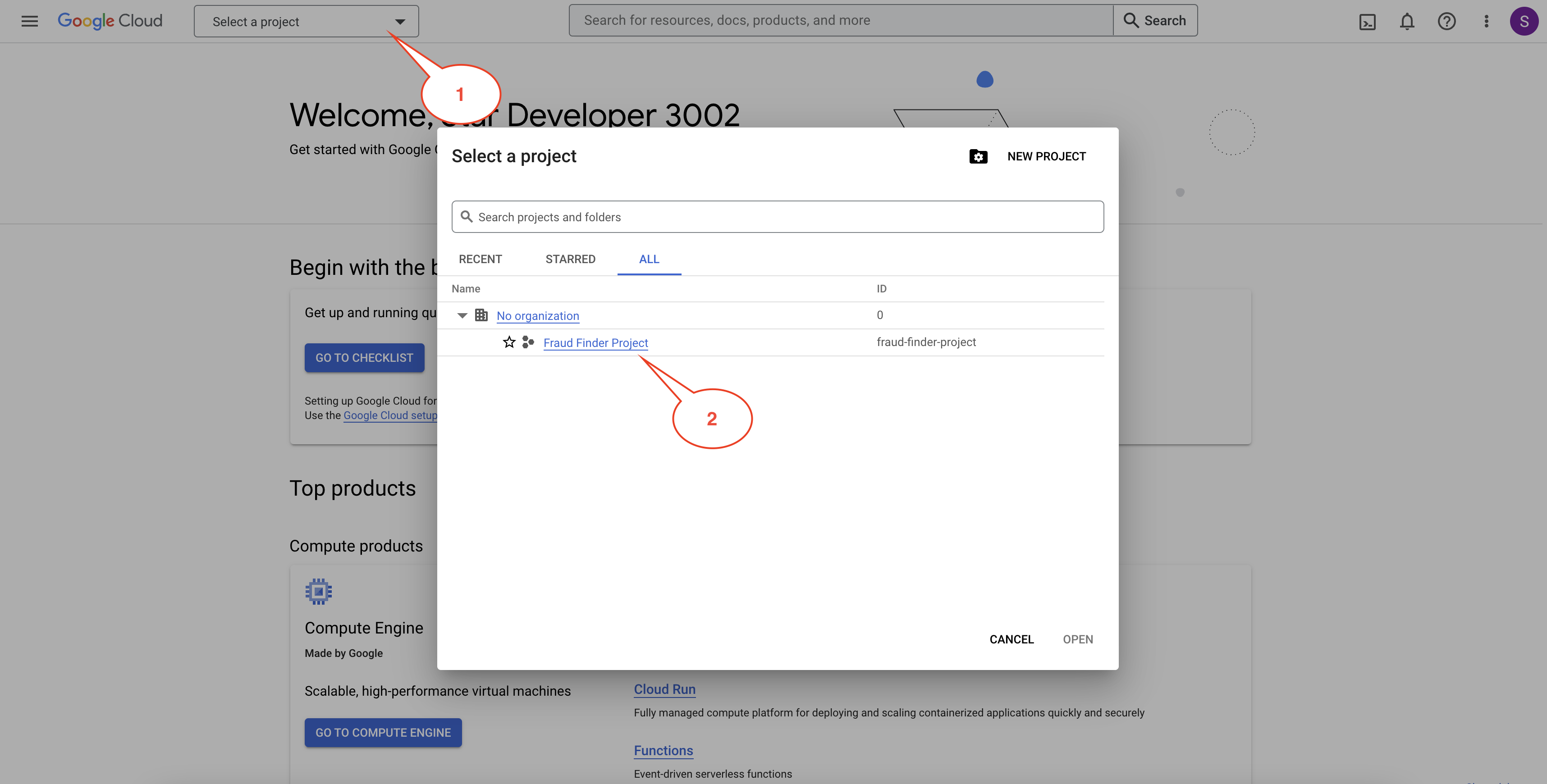
If you are using a provided temporary account, please just select an existing project that is pre-created before the event as shown in the image below.
It is not uncommon for the pre-created project in the provided temporary account to have a different name. Please check with the account provider if you need more clarifications on which project to choose.
If you are NOT using a temporary account, please create a new Google Cloud project and select that project. You may refer to the official documentation (Creating and Managing Projects) for detailed instructions.
To run the notebooks successfully, follow the steps below.
Please make sure that you have selected a Google Cloud project as shown below:
-
Activate Cloud Shell in your project by clicking the
Activate Cloud Shellbutton as shown in the image below.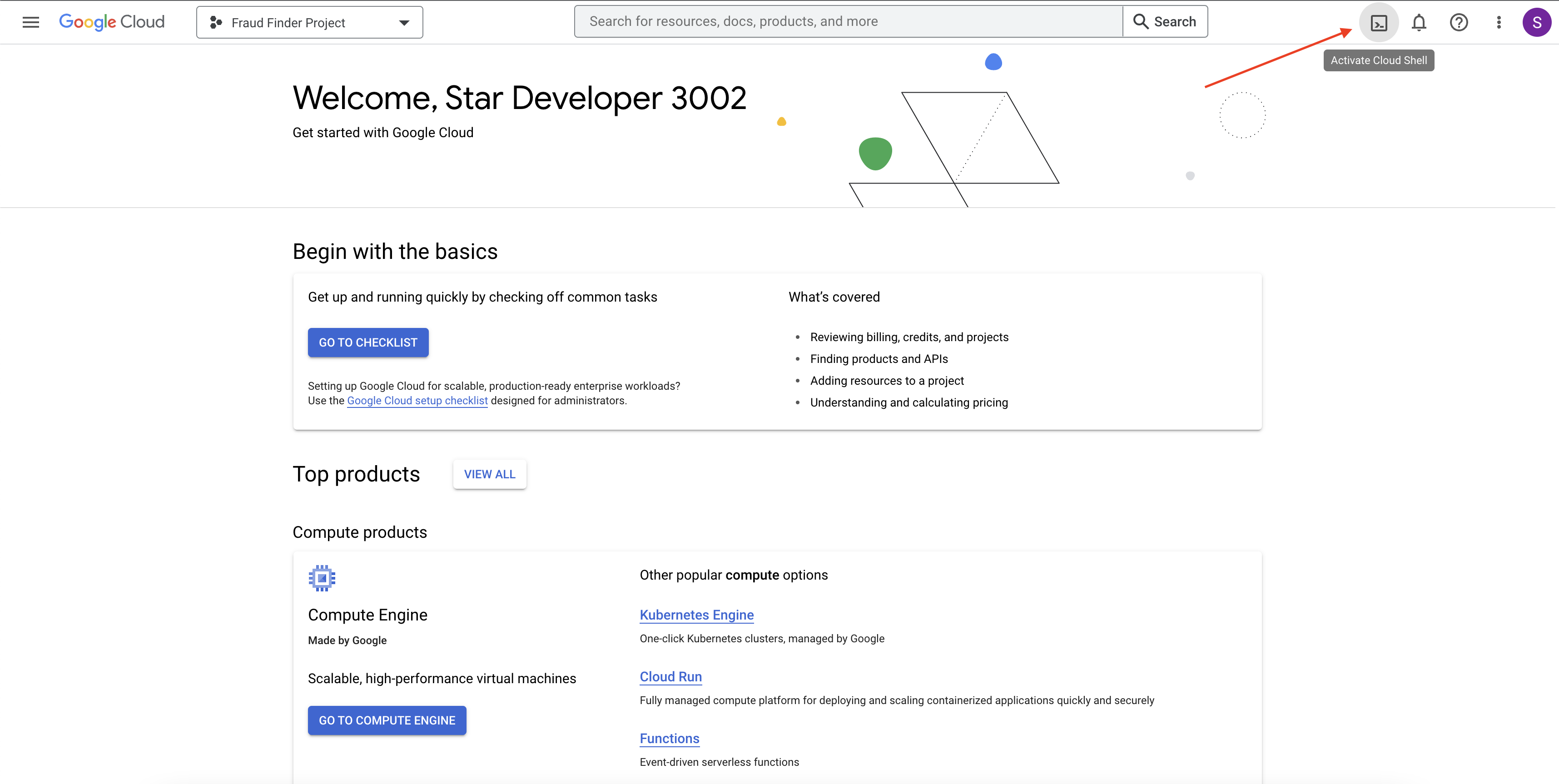
-
Once the Cloud Shell has activated, copy the following codes and execute them in the Cloud Shell to enable the necessary APIs, and create Pub/Sub subscriptions to read streaming transactions from public Pub/Sub topics.
-
Authorize the Cloud Shell if it prompts you to. Please note that this step may take a few minutes. You can navigate to the Pub/Sub console to verify the subscriptions.
gcloud services enable notebooks.googleapis.com gcloud services enable cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com gcloud services enable aiplatform.googleapis.com gcloud services enable pubsub.googleapis.com gcloud services enable run.googleapis.com gcloud services enable cloudbuild.googleapis.com gcloud services enable dataflow.googleapis.com gcloud services enable bigquery.googleapis.com gcloud services enable artifactregistry.googleapis.com gcloud services enable iam.googleapis.com gcloud pubsub subscriptions create "ff-tx-sub" --topic="ff-tx" --topic-project="cymbal-fraudfinder" gcloud pubsub subscriptions create "ff-tx-for-feat-eng-sub" --topic="ff-tx" --topic-project="cymbal-fraudfinder" gcloud pubsub subscriptions create "ff-txlabels-sub" --topic="ff-txlabels" --topic-project="cymbal-fraudfinder" # Run the following command to grant the Compute Engine default service account access to read and write pipeline artifacts in Google Cloud Storage. PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project) PROJECT_NUM=$(gcloud projects list --filter="$PROJECT_ID" --format="value(PROJECT_NUMBER)") gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \ --member="serviceAccount:${PROJECT_NUM}-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com"\ --role='roles/storage.admin' gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \ --member="serviceAccount:${PROJECT_NUM}@cloudbuild.gserviceaccount.com"\ --role='roles/aiplatform.admin' gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \ --member="serviceAccount:$PROJECT_NUM-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com"\ --role='roles/run.admin' gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \ --member="serviceAccount:$PROJECT_NUM-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com"\ --role='roles/resourcemanager.projectIamAdmin' gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \ --member="serviceAccount:service-${PROJECT_NUM}@gcp-sa-aiplatform-cc.iam.gserviceaccount.com"\ --role='roles/artifactregistry.writer' gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \ --member="serviceAccount:service-${PROJECT_NUM}@gcp-sa-aiplatform-cc.iam.gserviceaccount.com"\ --role='roles/storage.objectAdmin'
-
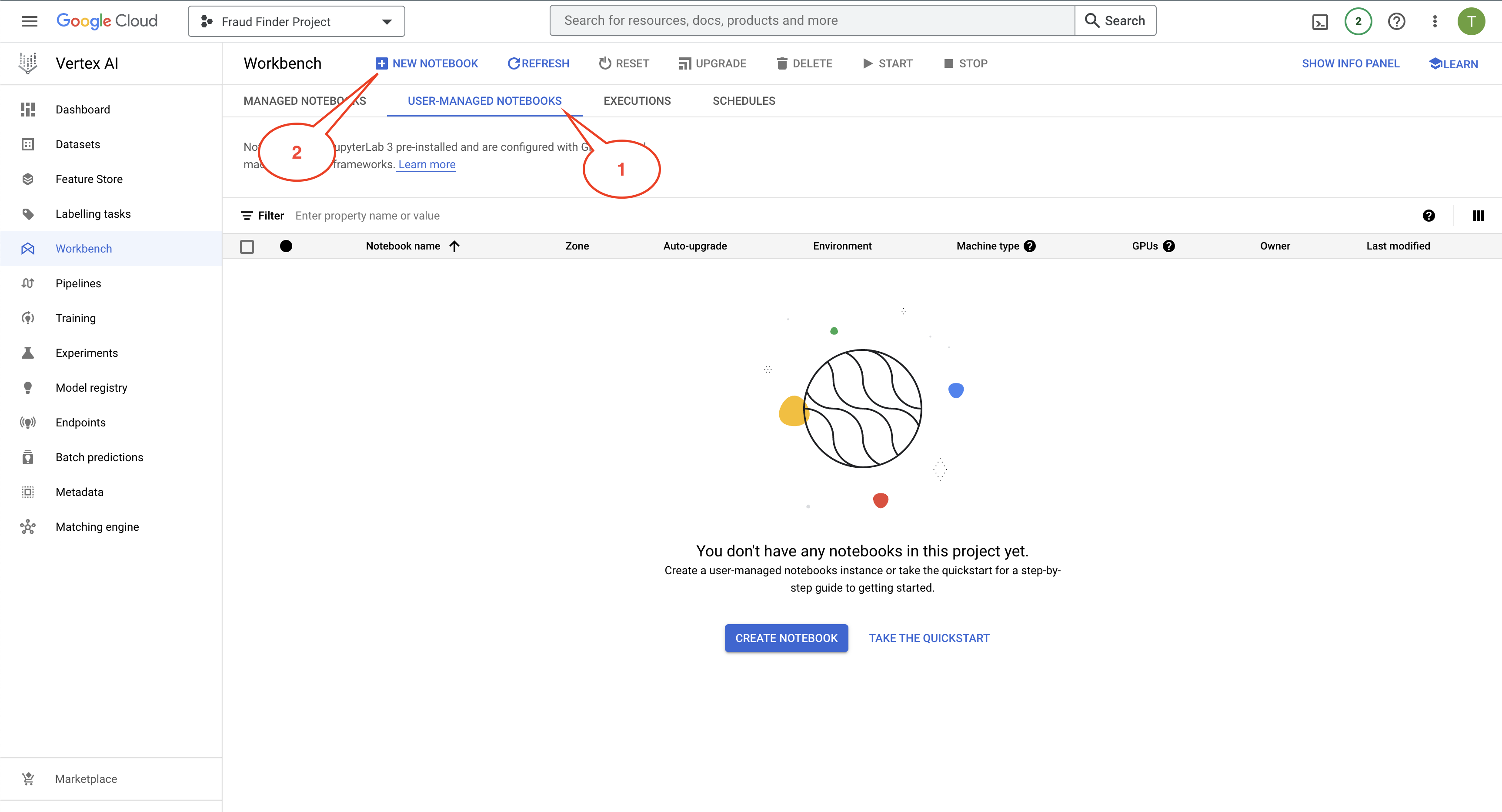
Browse to Vertex AI Workbench page, Click on "USER-MANAGED NOTEBOOKS" and Click on "+ NEW NOTEBOOK" as shown in the image below.
-
Please make sure you have selected the correct project when creating a new notebook. Upon clicking the "+ NEW NOTEBOOK", you will be presented with a list of notebook instance options. Select
Python 3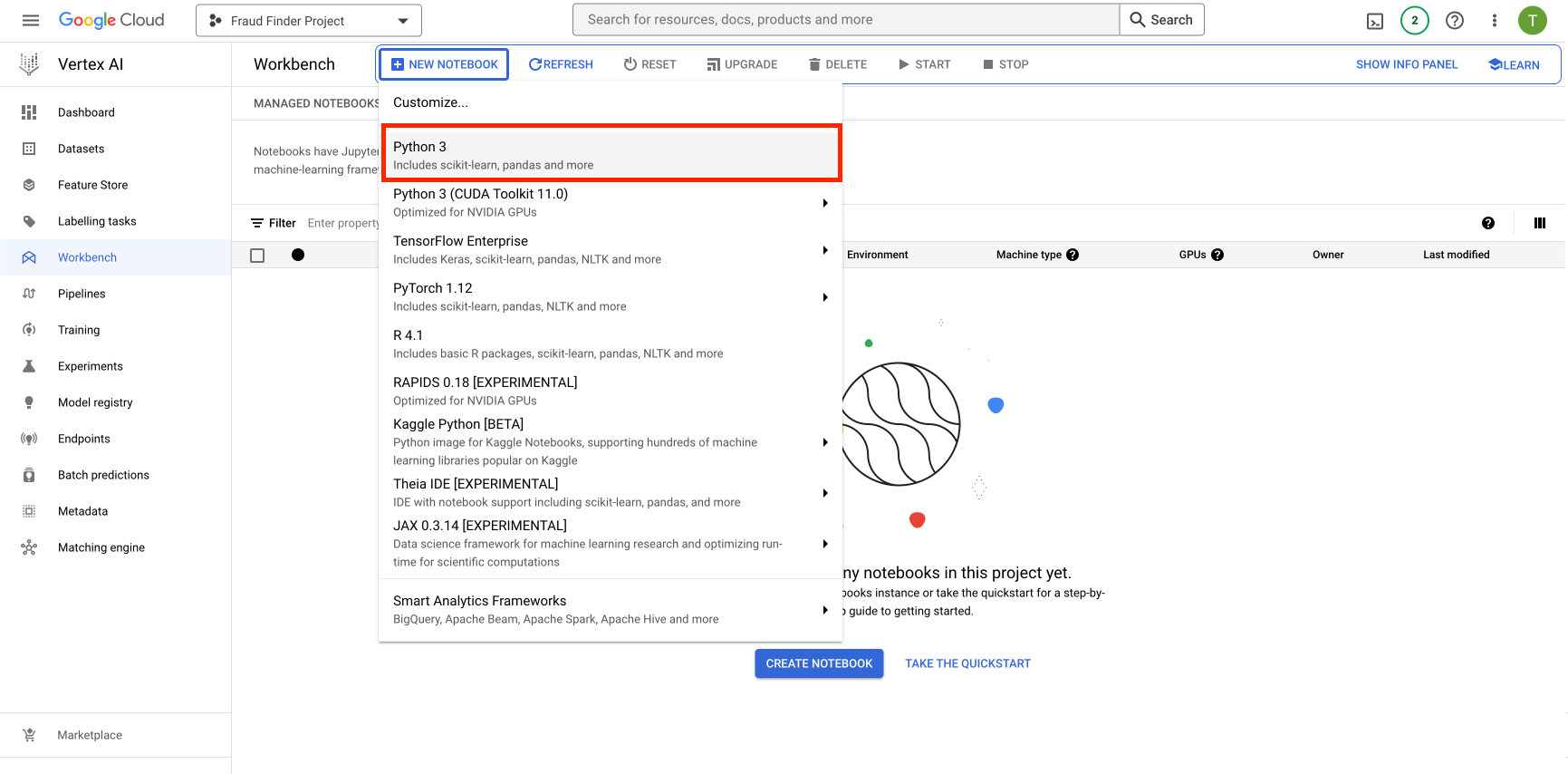
-
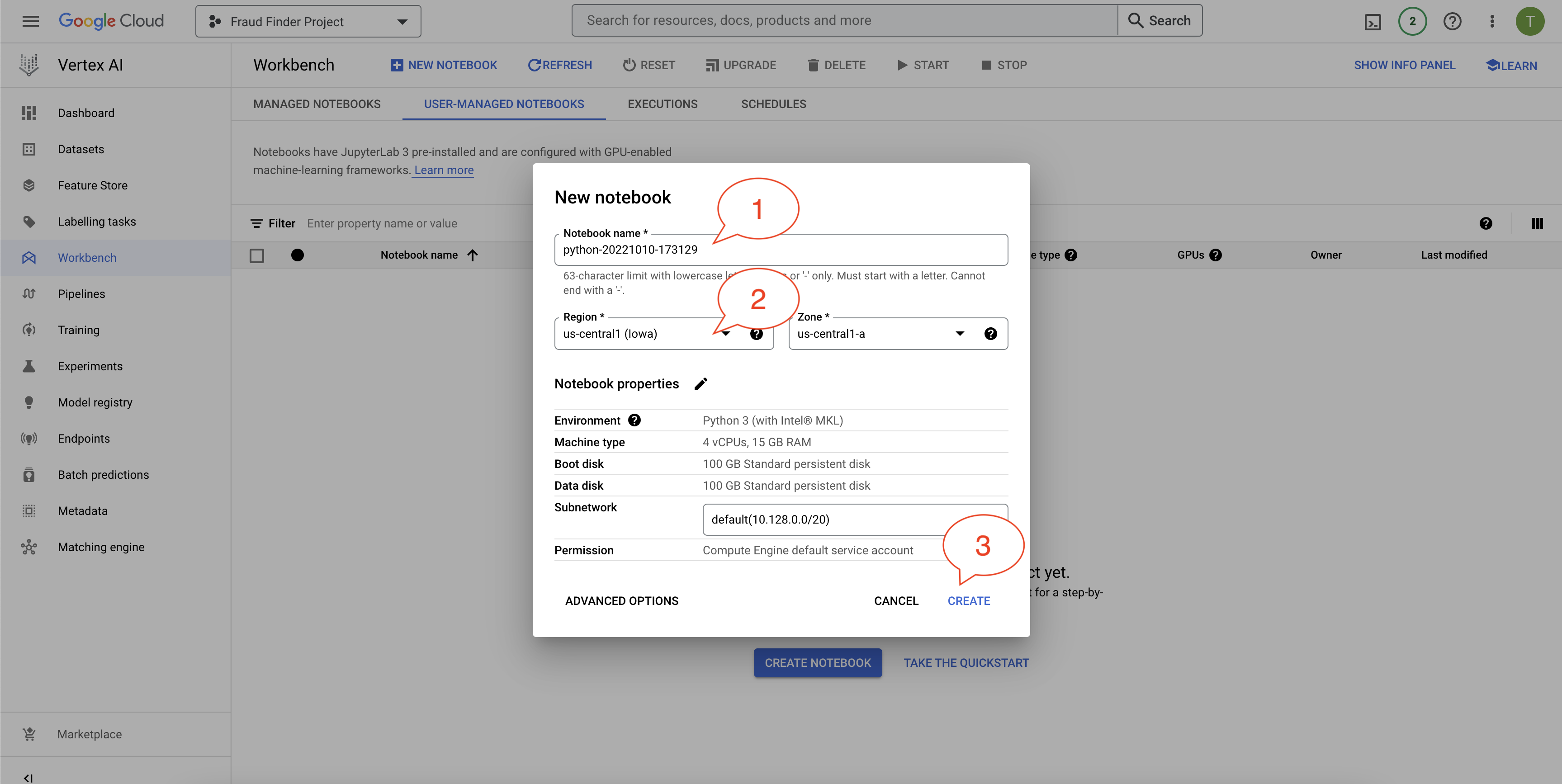
Pick a name (or leave it default), select a location, and then click "CREATE" to create the notebook instance.
-
The instance will be ready when you see a green tick and can click on "OPEN JUPYTERLAB" on the User-Managed Notebooks page. It may take a few minutes for the instance to be ready.
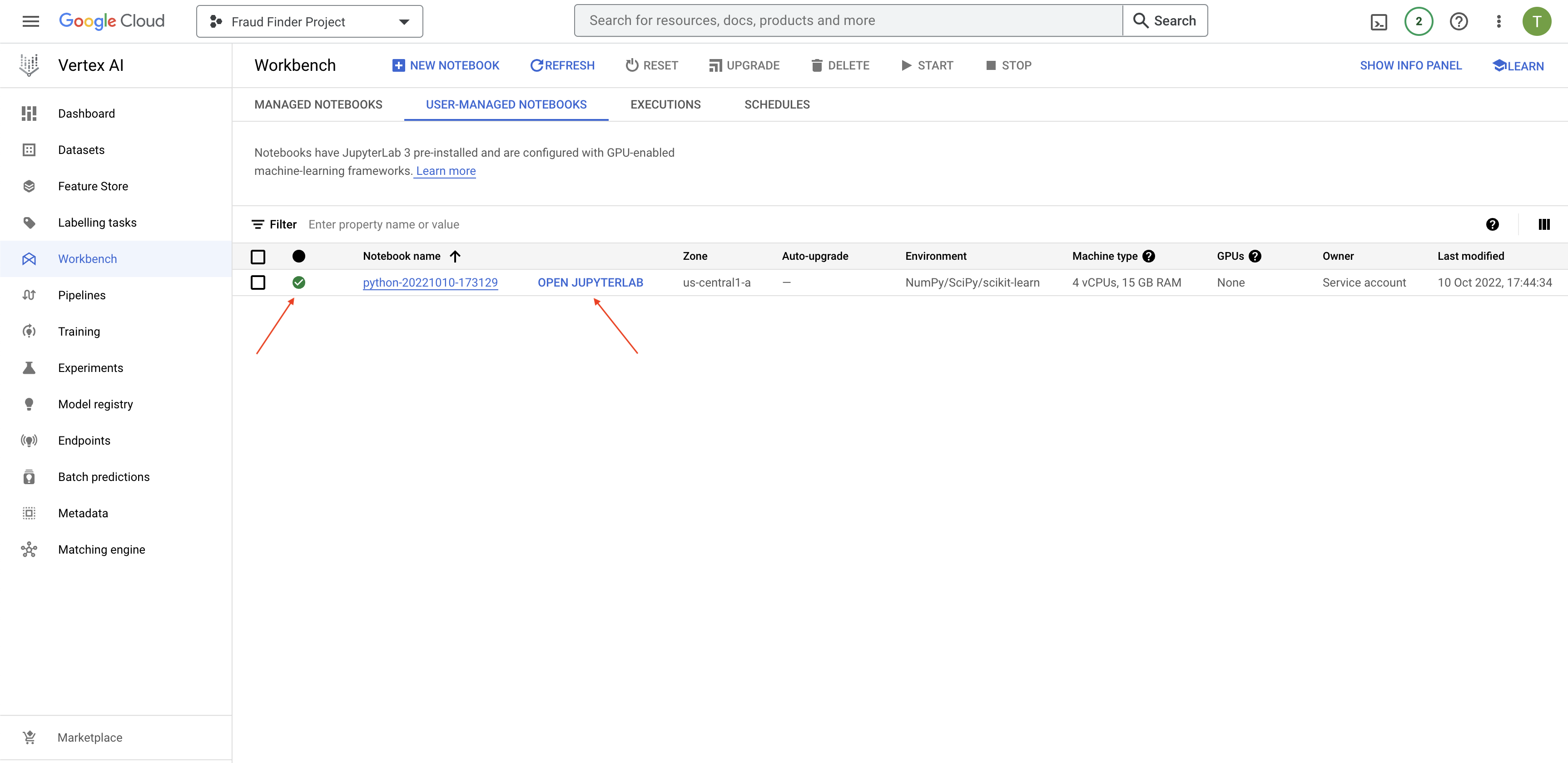
- Click on "OPEN JUPYTERLAB", which should launch your Managed Notebook in a new tab.
-
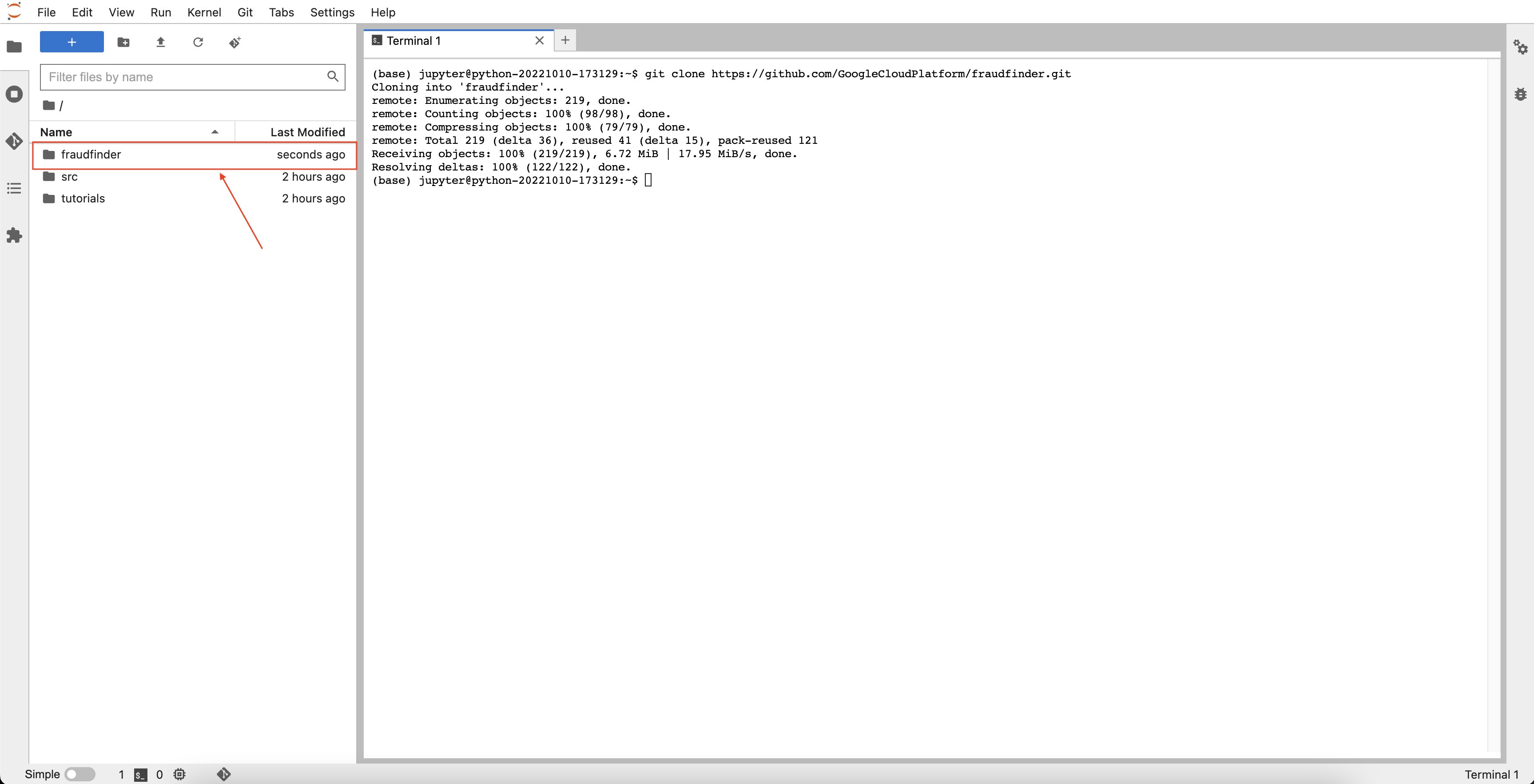
Run the following code to clone this repo:
git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/fraudfinder.git -
You can also navigate to the menu on the top left of the Jupyter Lab environment and click on Git > Clone a repository.
-
Once cloned, you should now see the fraudfinder folder in your main directory.