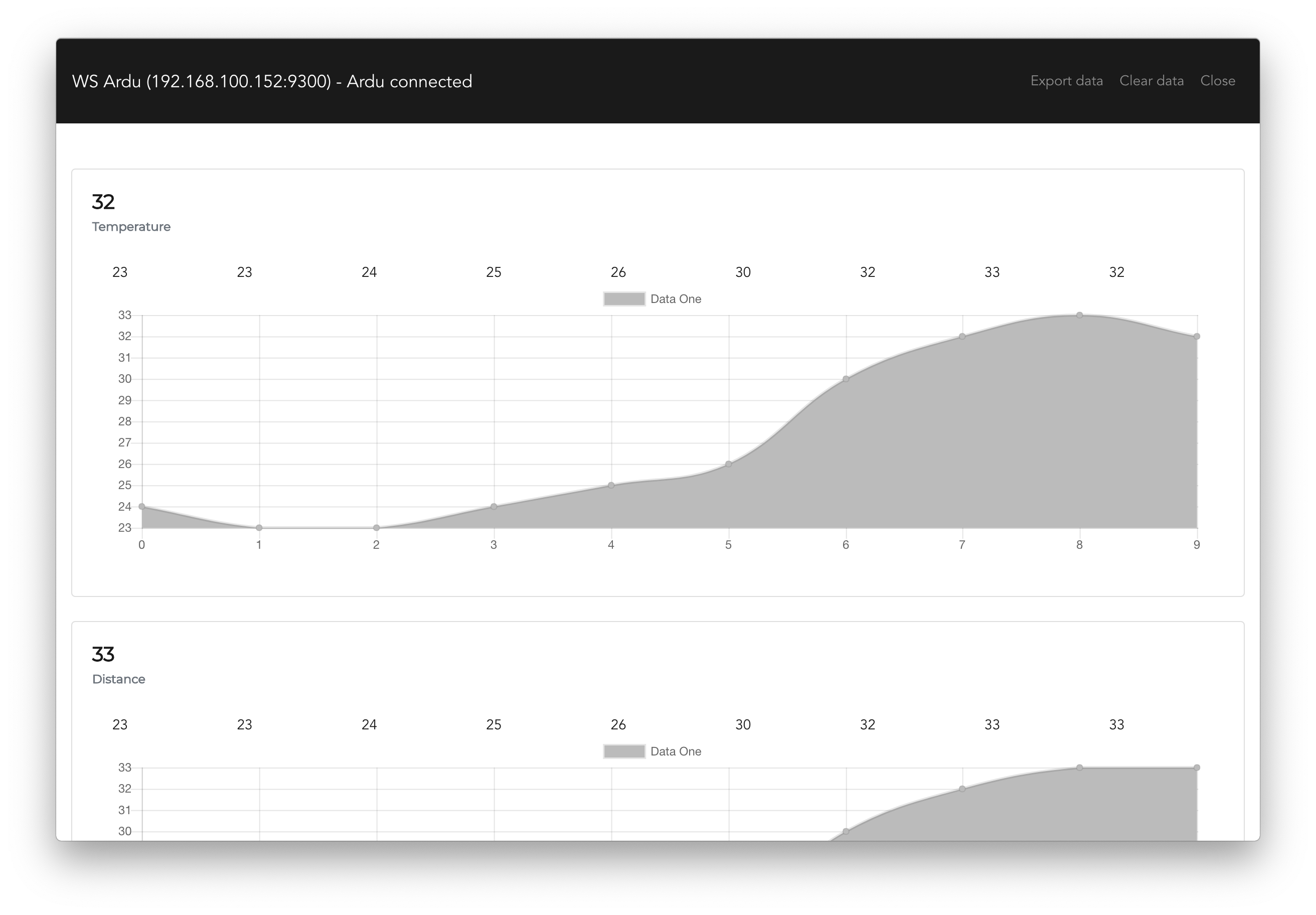
Starts a simple-websocket-server on port 9300 and logs data to app. You can export the whole data log to csv via the Export data button.
{
"t":string, // The sensor "type" or "alias"
"p":number // The value to be plotted/logged
}You may use any client device that has a Wifi antenna and is websocket enabled. Here is an example with Arduino:
#include <ArduinoHttpClient.h>
#include <WiFi101.h>
char serverAddress[] = "192.168.0.101"; // server address displayed on WS Ardu
int port = 9300;
WiFiClient wifi;
WebSocketClient client = WebSocketClient(wifi, serverAddress, port);
int status = WL_IDLE_STATUS;
int count = 0;
char ssid[] = "My Super Wifi Network";
char pass[] = "verysecretpassword";
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
while ( status != WL_CONNECTED) {
Serial.print("Attempting to connect to Network named: ");
Serial.println(ssid); // print the network name (SSID);
// Connect to WPA/WPA2 network:
status = WiFi.begin(ssid, pass);
}
// print the SSID of the network you're attached to:
Serial.print("SSID: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.SSID());
// print your WiFi shield's IP address:
IPAddress ip = WiFi.localIP();
Serial.print("IP Address: ");
Serial.println(ip);
Serial.println("starting WebSocket client");
client.begin();
}
void loop() {
float r1 = (float)rand() / (float)(RAND_MAX / 255.0f); //random value
float r2 = (float)rand() / (float)(RAND_MAX / 1024.0f); //random value
sendTelemetry("sensor1", r1);
sendTelemetry("sensor2", r2);
sendTelemetry("sensor3", r1);
sendTelemetry("sensor4", r1);
sendTelemetry("sensor5", r2);
sendTelemetry("sensor6", r1);
// simulate computing
delay(500);
}
int sendTelemetry(String sensor, float data) {
if (client.connected()) {
client.beginMessage(TYPE_TEXT);
client.print("{ \"t\":\"" + sensor + "\",\"p\": ");
client.print(data);
client.print("}");
client.endMessage();
}
}yarn install
yarn electron:serve
yarn electron:build
- Make data "time aware"
- Generate custom visualization for common sensors