Inspired by tmuxinator and tmuxp.
Smug automates your tmux workflow. You can create a single configuration file, and Smug will create all the required windows and panes from it.
The configuration used in this GIF can be found here.
Download the latest version of Smug from the releases page and then run:
mkdir smug && tar -xzf smug_0.1.0_Darwin_x86_64.tar.gz -C ./smug && sudo mv smug/smug /usr/local/bin && rm -rf smugDon't forget to replace smug_0.1.0_Darwin_x86_64.tar.gz with the archive that you've downloaded.
The easiest way is to clone Smug from GitHub and install it using go-cli:
cd /tmp
git clone https://github.com/ivaaaan/smug.git
cd smug
go installOn macOS, you can install Smug using MacPorts or Homebrew.
brew install smugsudo port selfupdate
sudo port install smugThere's AUR with smug.
git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/smug.git
cd smug
makepkg -sismug <command> [<project>] [-f, --file <file>] [-w, --windows <window>]... [-a, --attach] [-d, --debug]
-f, --file A custom path to a config file
-w, --windows List of windows to start. If session exists, those windows will be attached to current session.
-a, --attach Force switch client for a session
-i, --inside-current-session Create all windows inside current session
-d, --debug Print all commands to ~/.config/smug/smug.log
--detach Detach session. The same as `-d` flag in the tmux
You can pass custom settings into your configuration file. Use ${variable_name} syntax in your config and then pass key-value args:
xyz@localhost:~$ smug start project variable_name=valueTo create a new project, or edit an existing one in the $EDITOR:
xyz@localhost:~$ smug new project
xyz@localhost:~$ smug edit projectTo start/stop a project and all windows, run:
xyz@localhost:~$ smug start project
xyz@localhost:~$ smug stop projectAlso, smug has aliases to the most of the commands:
xyz@localhost:~$ smug project # the same as "smug start project"
xyz@localhost:~$ smug st project # the same as "smug stop project"
xyz@localhost:~$ smug p ses # the same as "smug print ses"When you already have a running session, and you want only to create some windows from the configuration file, you can do something like this:
xyz@localhost:~$ smug start project:window1
xyz@localhost:~$ smug start project:window1,window2
xyz@localhost:~$ smug start project -w window1
xyz@localhost:~$ smug start project -w window1 -w window2
xyz@localhost:~$ smug stop project:window1
xyz@localhost:~$ smug stop project -w window1 -w window2Also, you are not obliged to put your files in the ~/.config/smug directory. You can use a custom path in the -f flag:
xyz@localhost:~$ smug start -f ./project.yml
xyz@localhost:~$ smug stop -f ./project.yml
xyz@localhost:~$ smug start -f ./project.yml -w window1 -w window2Configuration files can stored in the ~/.config/smug directory in the YAML format, e.g ~/.config/smug/your_project.yml.
You may also create a file named .smug.yml in the current working directory, which will be used by default.
session: blog
root: ~/Developer/blog
before_start:
- docker-compose -f my-microservices/docker-compose.yml up -d # my-microservices/docker-compose.yml is a relative to `root`
env:
FOO: BAR
stop:
- docker stop $(docker ps -q)
windows:
- name: code
root: blog # a relative path to root
manual: true # you can start this window only manually, using the -w arg
layout: main-vertical
commands:
- docker-compose start
panes:
- type: horizontal
root: .
commands:
- docker-compose exec php /bin/sh
- clear
- name: infrastructure
root: ~/Developer/blog/my-microservices
layout: tiled
panes:
- type: horizontal
root: .
commands:
- docker-compose up -d
- docker-compose exec php /bin/sh
- clearsession: blog
root: ~/Code/blog
before_start:
- docker-compose up -d
stop:
- docker-compose stop
windows:
- name: code
layout: main-horizontal
commands:
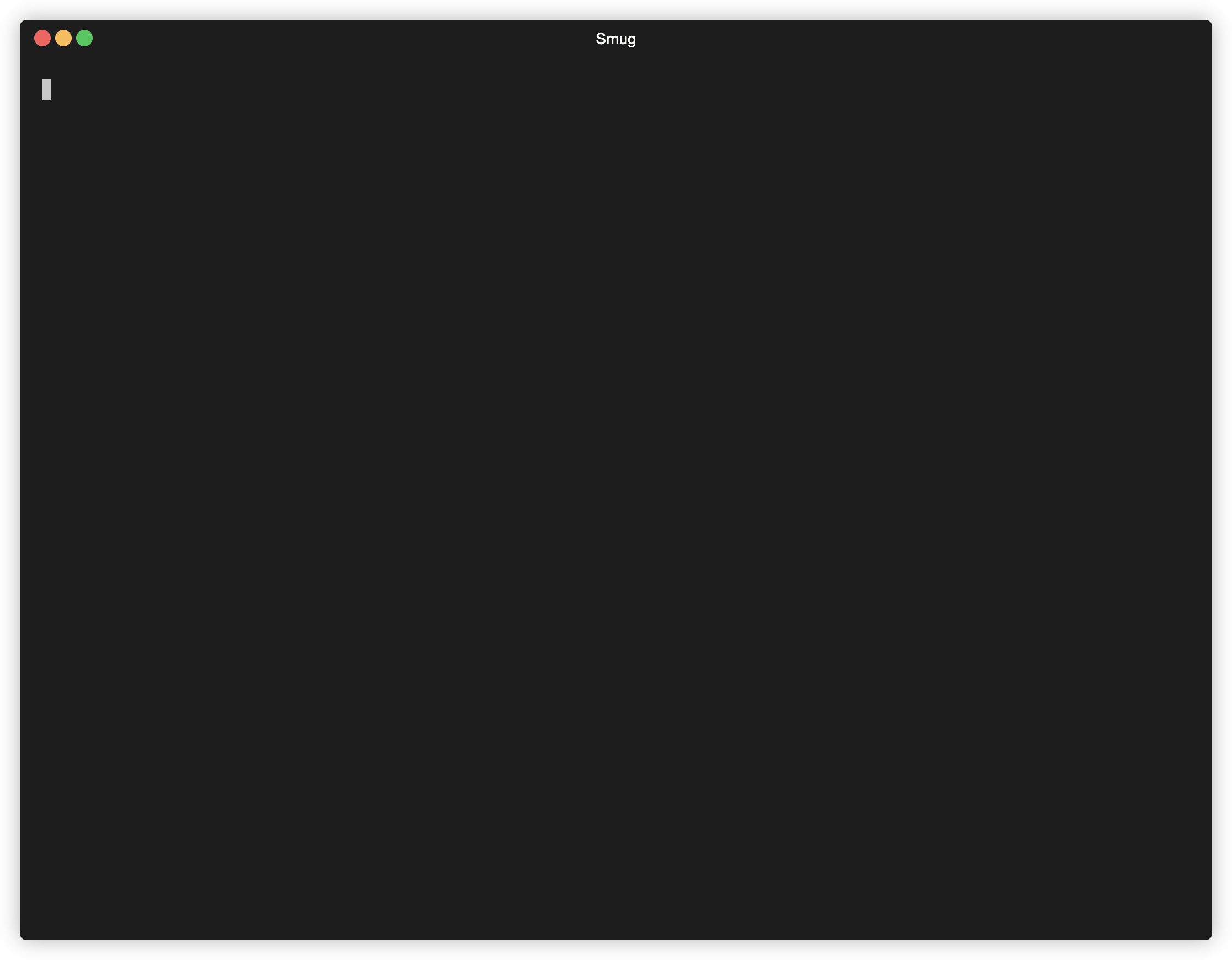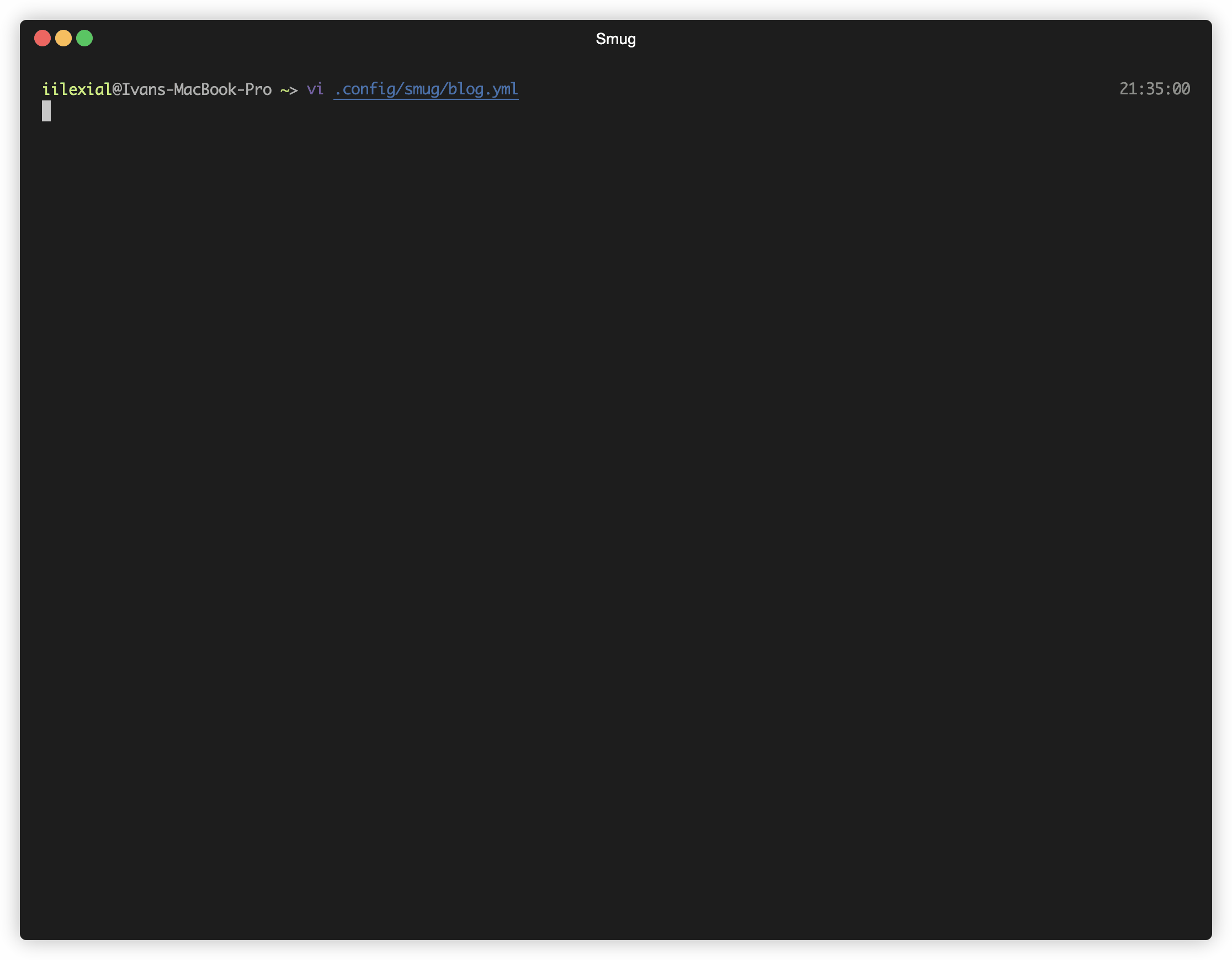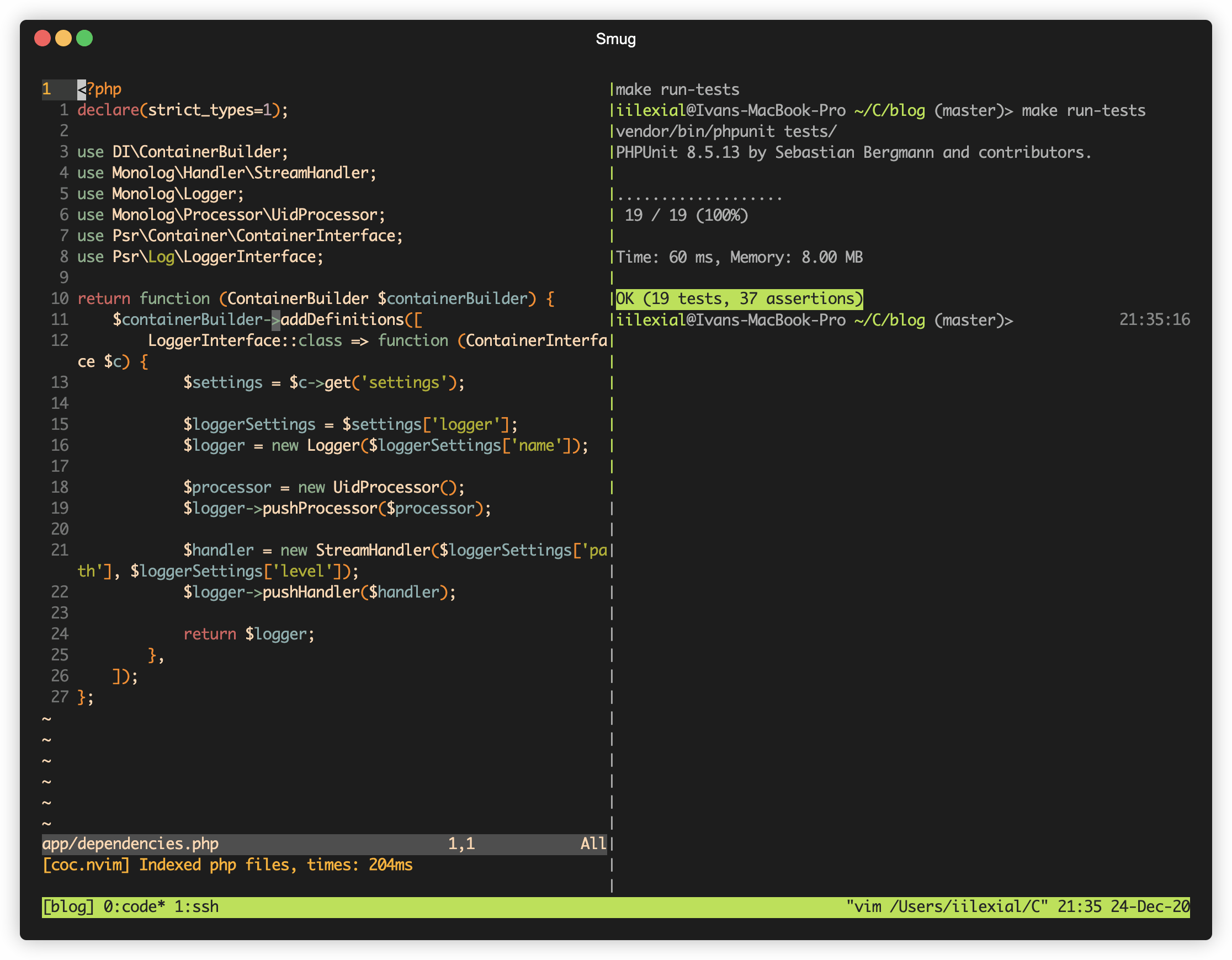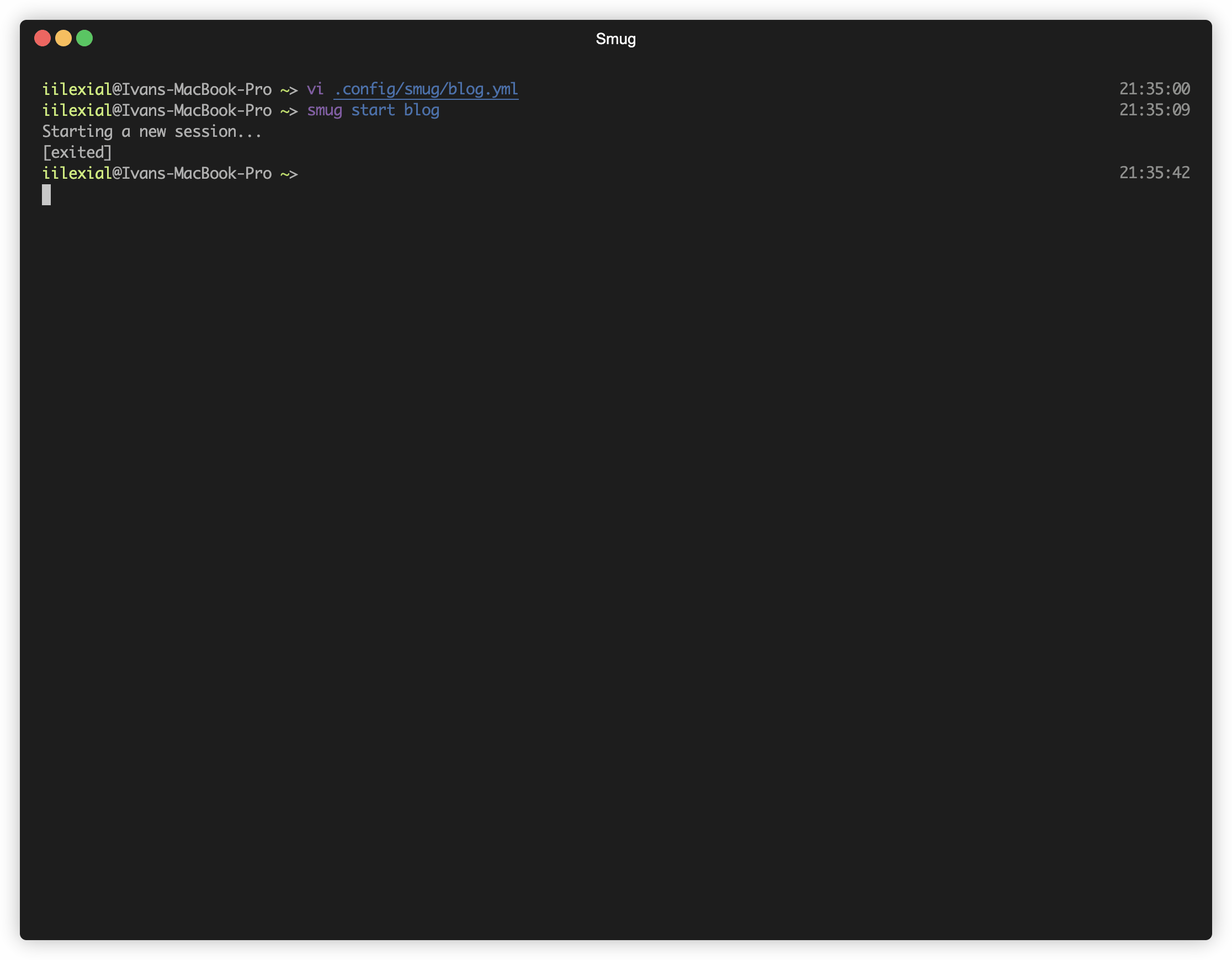
- $EDITOR app/dependencies.php
panes:
- type: horizontal
commands:
- make run-tests
- name: ssh
commands:
- ssh -i ~/keys/blog.pem ubuntu@127.0.0.1