Content-Addressable Transformers (CATs) is a unified Data Service Collaboration framework for organizations. CATs connect collaborators between organizations on a Data Mesh with interoperable parallelized and distributed computing at horizontal & vertical scale. CATs' establish a scalable and self-serviced Data Platform as a Data Mesh network of scalable and interoperable distributed computing workloads with Data Provenance deployable on Kubernetes. These workloads [CAT(s)] enable for Big Data processing with Scientific Computing capabilities. CATs are integration points which enable scaled data processing portability between client-server cloud platforms and mesh (p2p) networks with minimal rework or modification.
CATs enables the continuous reification of Data Initiatives by cataloging discoverable, accessable, and re-executable workloads as Data Service Collaboration composable records between organizations. These records provide a reliable and efficient way to manage, share, and reference data processes via Content-Addressing Data Provenance records.
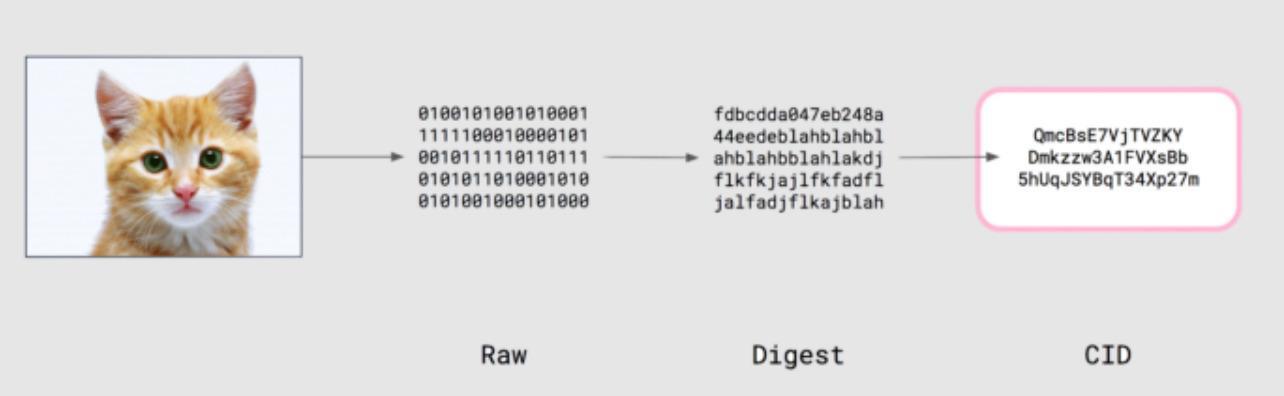
Content-Addressing is a method of uniquely identifying and retrieving data based on its content rather than its
location or address. CATs provides verifiable data processing and transport on a Mesh network of CATs interconnected by
Content-Addressing Data Provenance records with IPFS
CIDs (Content-Identifiers) as content addresses issued by IPFS
client to identify and retrieve inputs,
transformations, outputs, and infrastructure (as code [IaC]) for verifying transformation accuracy given CIDs.
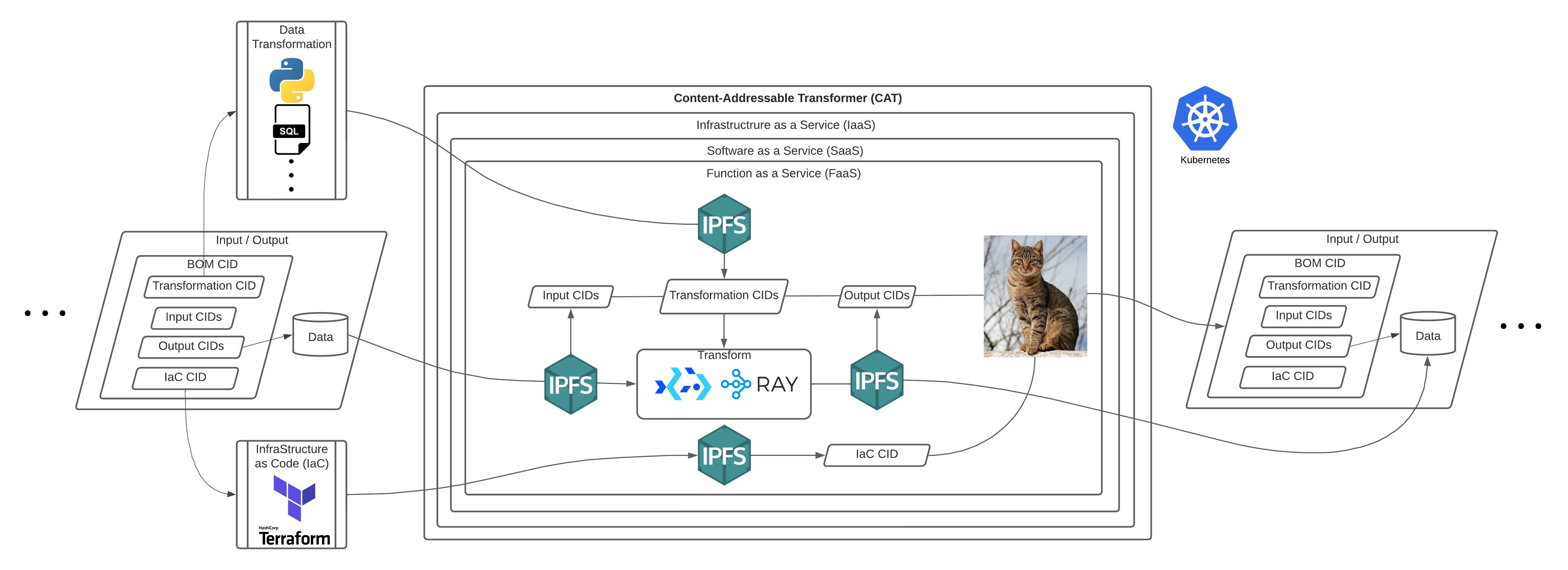
CATs' utilizes Ray for interoperable & parallelized distributed computing frameworks deployable on Kubernetes for Big Data processing with Scientific Computing. Ray is a unified compute framework that enables the development of parallel and distributed applications for scalable data transformation, Machine Learning, and AI. Ray provides CATs with interoperable computing frameworks with its ecosystem integrations such as Apache Spark, and PyTorch.
Ray is deployed as an execution middleware on top of Bacalhau’s Compute Over Data (CoD).
CoD enables IPFS to serve as CATs' Data Mesh's network layer to provide parallelized data ingress and egress for IPFS
data. This portability closes the gap between data analysis and business operations by connecting the network planes of
the cloud service model (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS) with IPFS. CATs connect these network planes by enabling the instantiation of
FaaS with cloud services in AWS, GCP, Azure, etc. on a Data Mesh network of CATs. CoD enables this connection as p2p
distributed-computing job submission in addition to the client-server job submission provided by Ray.
- Install Dependencies
- Install CATs:
git clone git@github.com:BlockScience/cats.git cd cats # Optional: Create Virtual Environment # python -m venv ./venv # source ./venv/bin/activate python -m pip install --upgrade pip pip install dist/*.whl
- Demo: Establish a CAT Mesh
- Test: CAT Mesh Verification
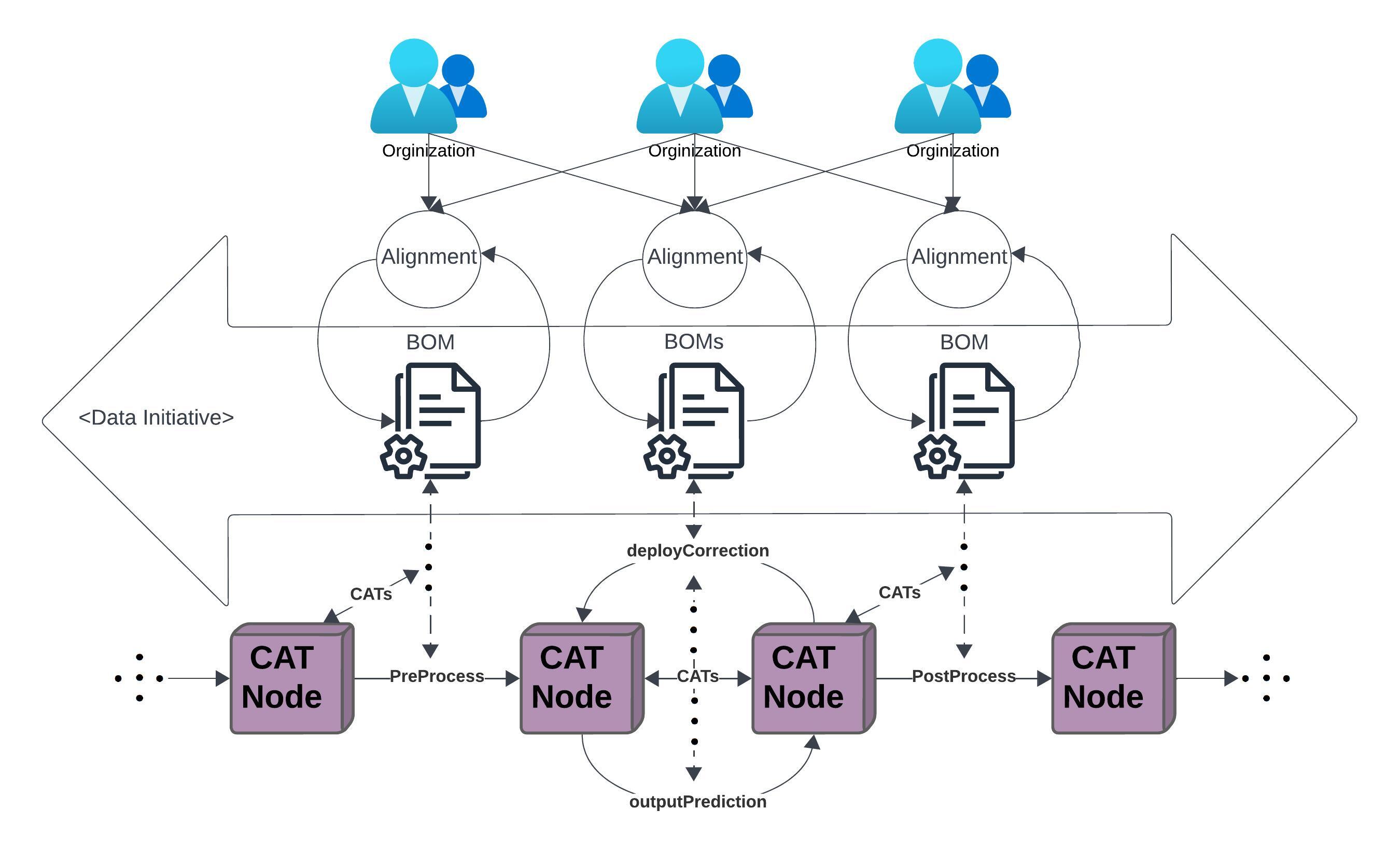
Organizations and collaborators participating will employ CATs for rapid ratification of service agreements within
collaborative feedback loops of Data Initiatives.
CATs' apply an Architectural Quantum Domain-Driven Design principle described in
Data Mesh of Data Products to reify Data Initiatives.
(* Design Description)
Data Initiatives will be naturally reified as a result of Data Service Collaboration on CATs. CATs will be
compiled and executed as interconnecting services on a Data Mesh that grows naturally when organizations communicate
CATs provenance records within feedback loops of Data Initiatives.
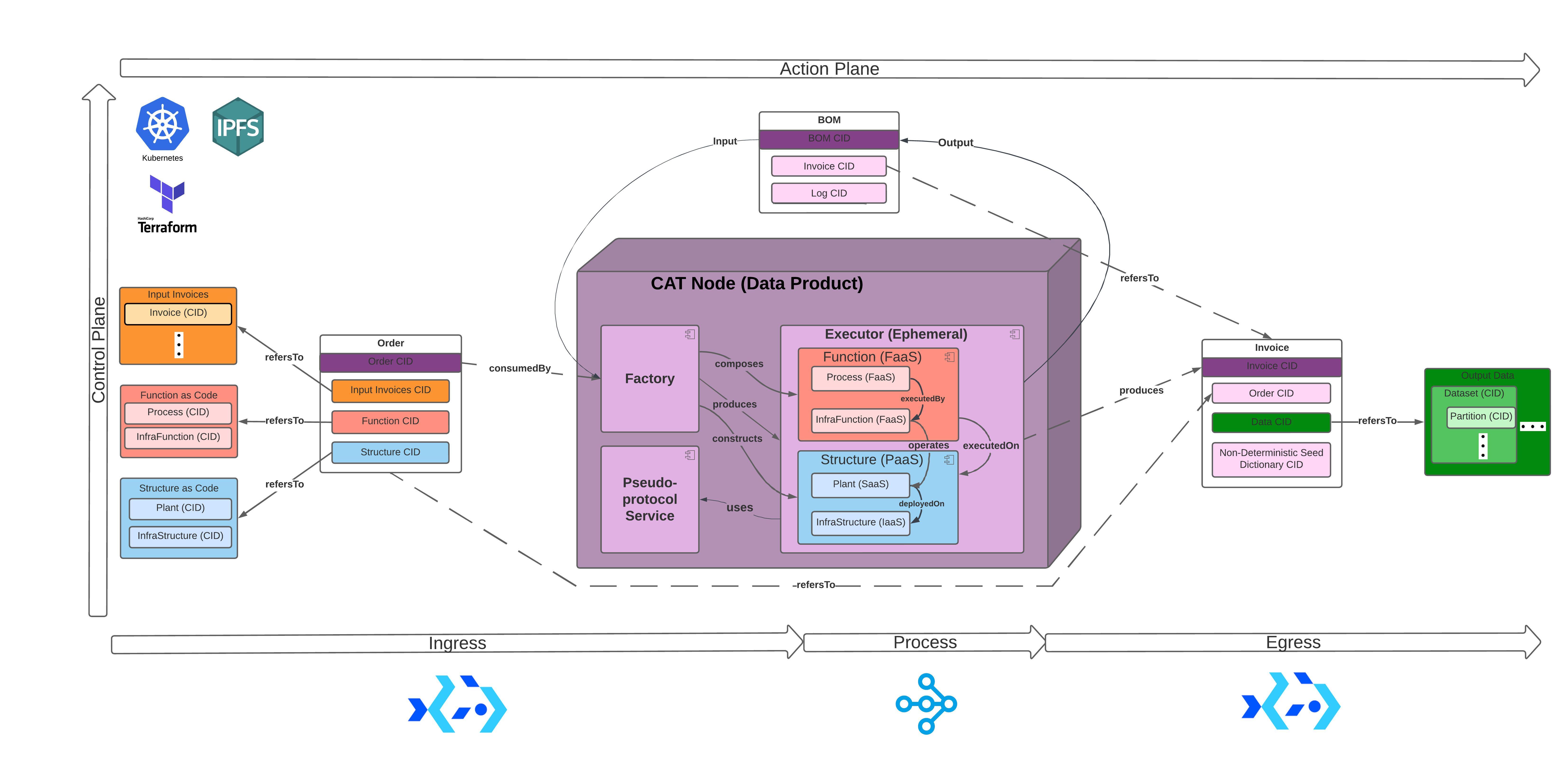
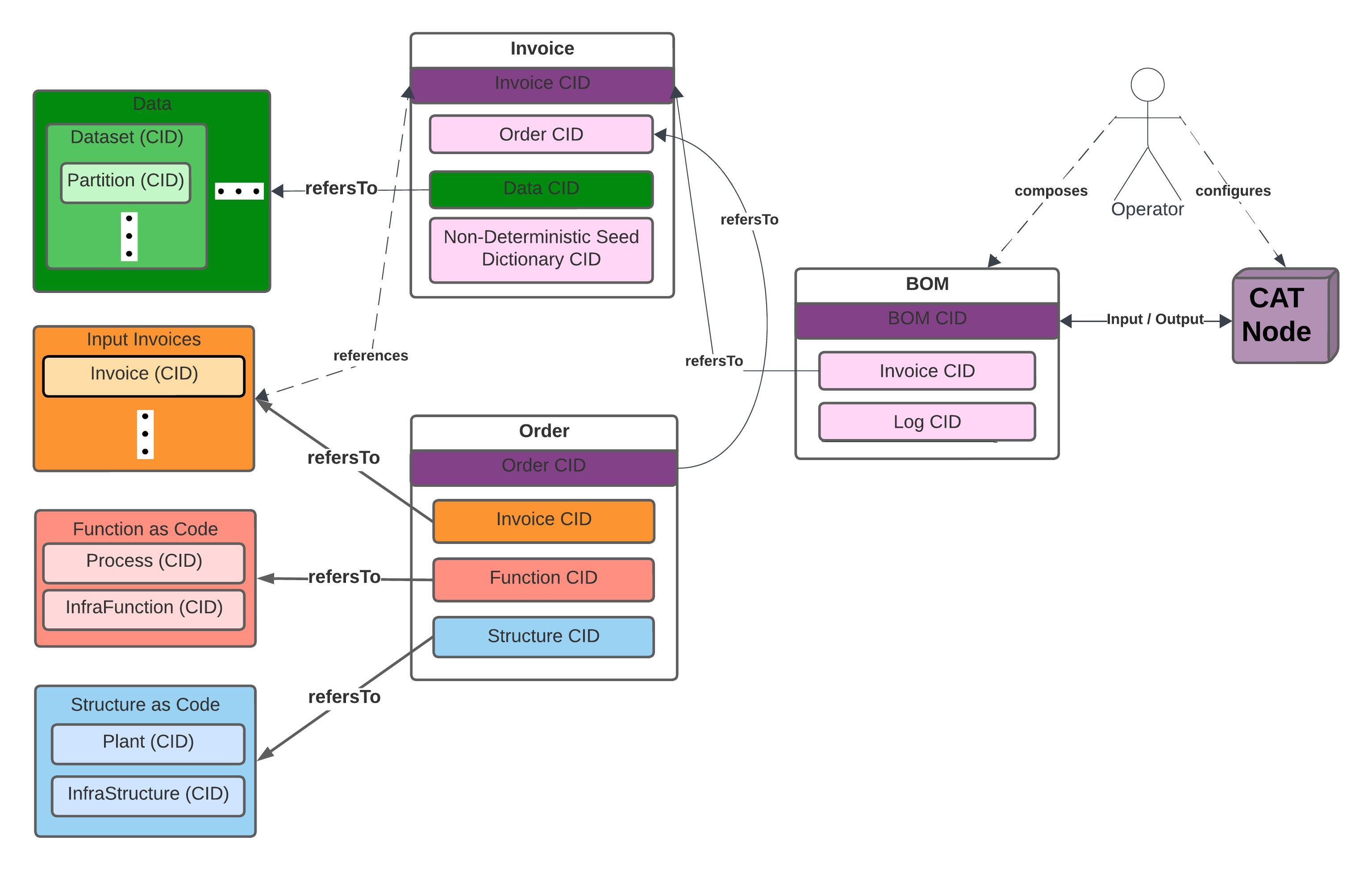
BOM (Bill of Materials) are CATs' Content-Addressed Data Provenance record for verifiable data processing and transport on a Mesh network of CATs. BOMs are used as CAT’ input & output that contain CATs’ means of data processing.
- BOMs employ CIDs for location-agnostic retrieval based on its content as well as processes and
Data Verification. BOM CIDs can be used to verify the means of processing
data (input, transformation / process, output, infrastructure-as-code (IaC)) they can also make CATs resilient by
enabling re-execution via retrieval. CATs certifies the accuracy of data processing on data products and pipelines by
enabling maintenance and reporting of
data and process lineage & provenance as chains of
evidence using CIDs.
- CAT Mesh is composed by CATs executing BOMs.
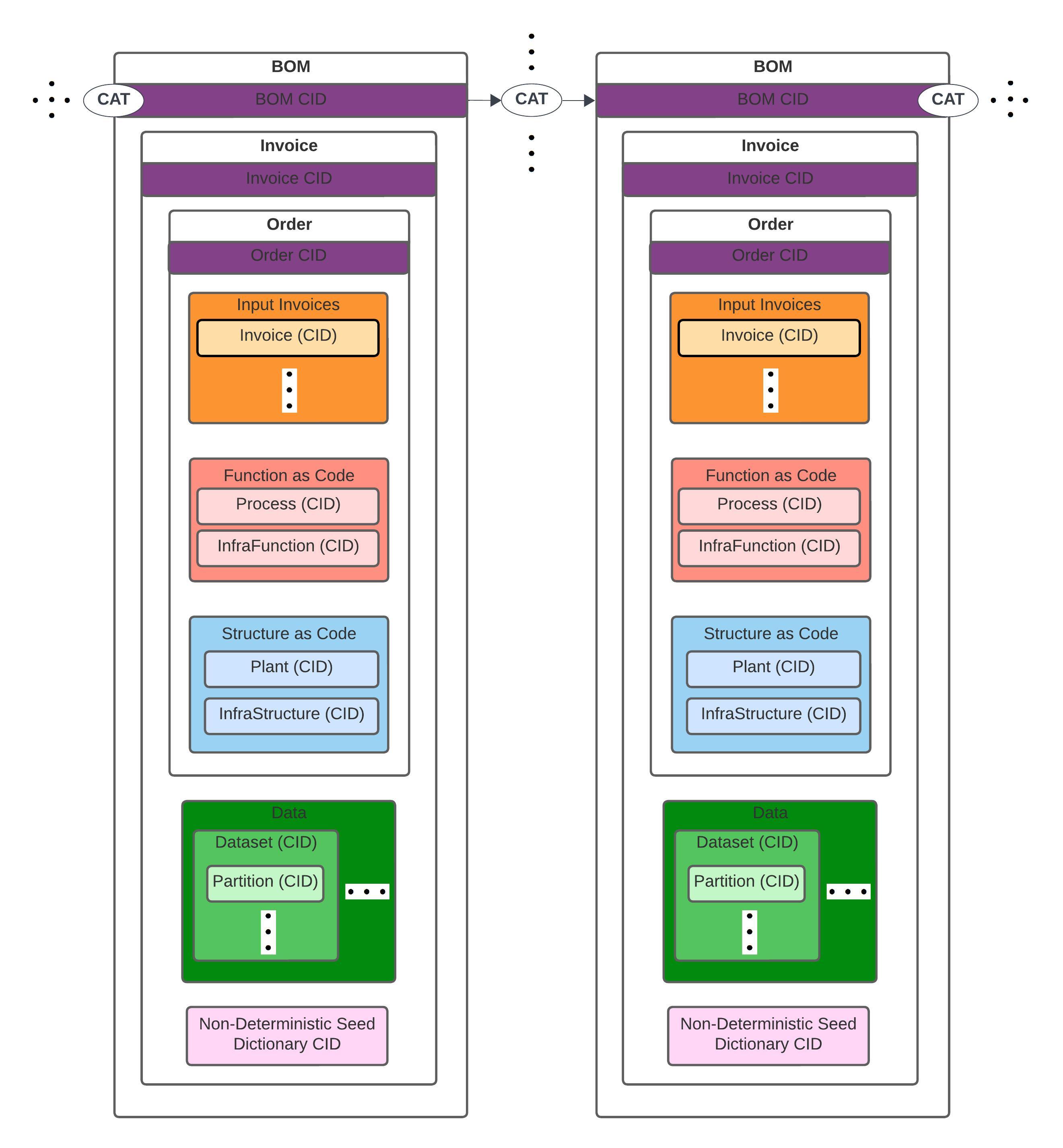
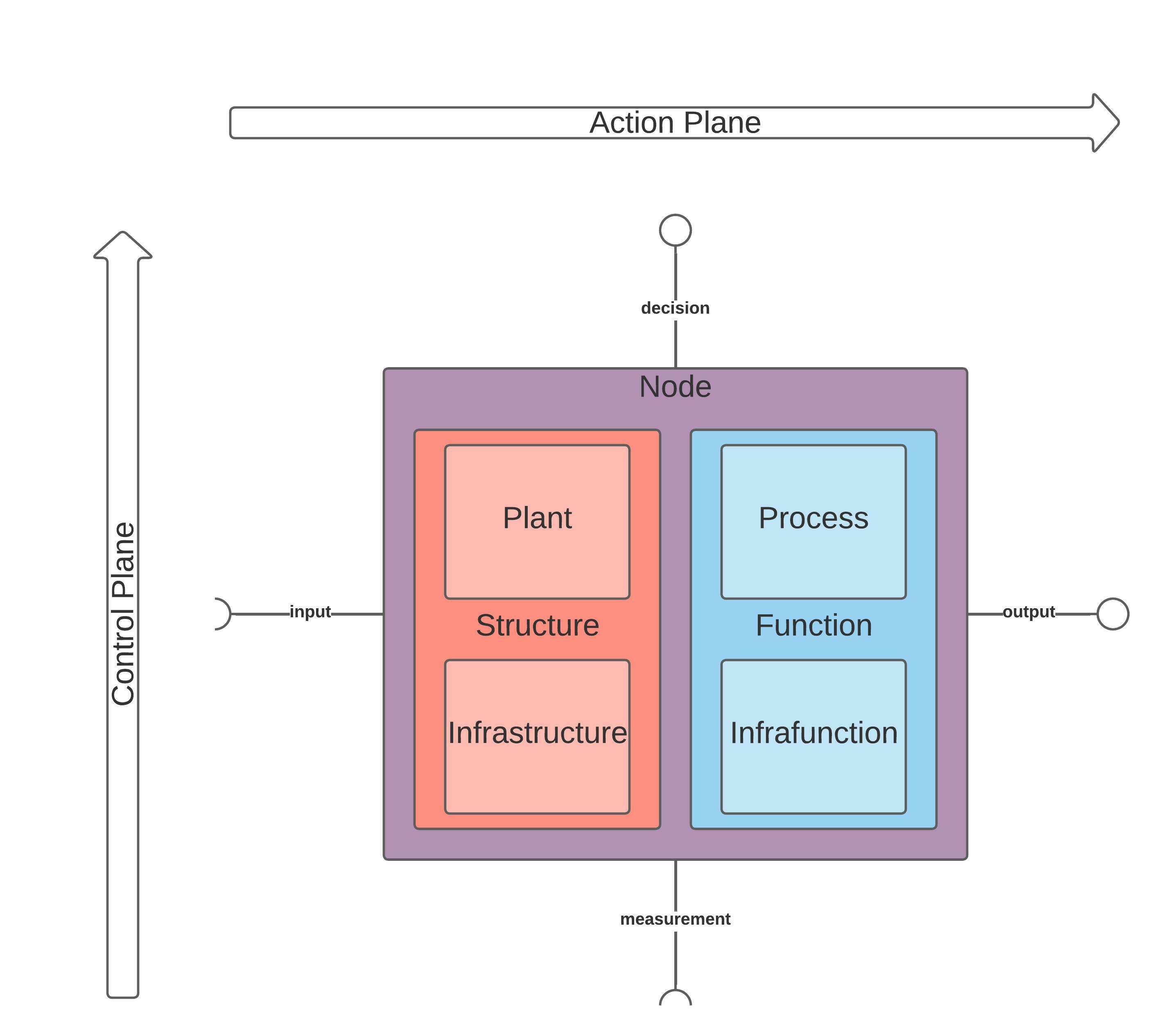
CAT Mesh is a self-serviced Data Mesh platform with Data Provenance. CAT Nodes are CAT Mesh peers that enable workloads to be portable between client-server cloud platforms and p2p mesh network with minimal rework or modification.
Multi-disciplinary and cross-functional teams can use CAT Nodes to verify and scale distributed computing workloads. Workloads (CATs) executed by CAT Nodes interface cloud service model (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS) offered by providers such as AWS, GCP, Azure, etc. on a Mesh Network interconnected by IPFS.
CAT Nodes are Data Products - peer-nodes on a mesh network that encapsulate components (*) to function as a service providing access to a domain's analytical data as a product; * code, data & metadata, and infrastructure.
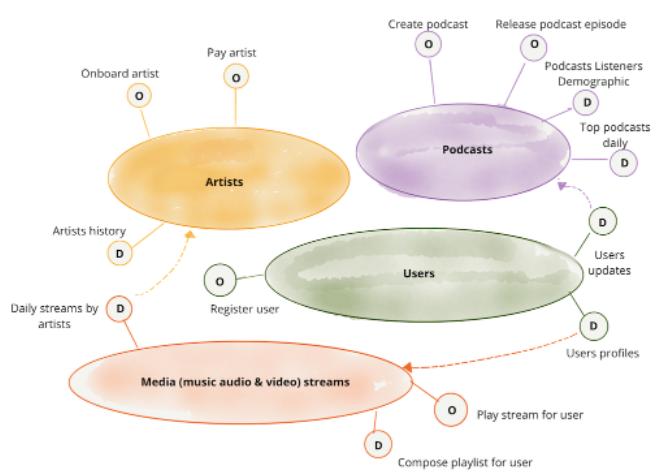
In the following image:
- Large ovals in the image above represent Data Products servicing each other with Data
- "O" ovals are Operational Data web service endpoints
- "D" ovals are Analytical Data web service endpoints
- Source: Data Mesh Principles and Logical Architecture - Zhamak
Dehghani, et al.
- Data Verification - a process for which data is checked for accuracy and inconsistencies before processed
- Data Provenance - a means of proving data lineage using historical records that provide the means of pipeline re-execution and data validation
- Data Lineage - reporting of data lifecyle from source to destination
- Distributed Computing - typically the concurrent and/or parallel execution of job tasks distributed to networked computers processing data
- Bill of Materials (BOM) - an extensive list of raw materials, components, and instructions required to construct, manufacture, or repair a product or service