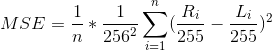An open source implementation of the deep learning platform for undersampled MRI reconstruction described by Hyun et. al. (https://arxiv.org/pdf/1709.02576.pdf). In cojunction with this reimplementation, there is a writeup including extension experiments beyond those described in Hyun et. al. (http://corey-zumar.github.io/submrine/).
Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a technique that uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate images of the body based on signals from protons. It is used to non-invasively provide physicians with visual information of a patient's anatomy. MRI is an expensive technique, it can be difficult to apply to children due to its sensitivity to movement, and its long scan duration can prove troublesome for some patients with claustrophobia. If a system could take undersampled MRI data and produce medically acceptable images, then the MRI scan time could be reduced, decreasing the procedure's cost and allowing more access for claustrophobic patients.
MRI techniques collect raw data, known as k-space data, and produce images through complex data processing and inverse Fourier transforms. The raw k-space data is known to be low-quality with many missing entries, motivating research surrounding image reconstruction. Current MRI techniques must use intrascan data to reconstruct medically acceptable images, with state of the art techniques beginning to leverage inter-scan data to improve MRI acquisition.
Producing medically acceptable images from highly undersampled (25-30% of the current standard) MR data was the main challenge faced by Hyun et. al. In their paper, they demonstrated that the use of subsampling in conjunction with deep learning methods can produce high-resolution MR images while reducing data collection and processing overhead. Here, we present a reimplementation of Hyun et. al.'s described method as a user-friendly python package. In addition to providing tools to replicate the results of Hyun et. al. using full-resolution training and test data, we include an evaluation procedure for reconstructing undersampled MR images for which full-resolution versions may not exist.
This implementation is packaged to be PyPI compatible. The package is called submrine. It can be installed by invoking the following from the repository's root directory:
$ pip install -e submrineThe installation process creates three console entry points: submrine-train, submrine-test, and submrine-eval that can be used to:
- Train reconstruction networks
- Test the full reconstruction process on test images and datasets, respectively
- Evaluate the reconstruction network (a component of the full process) on undersampled images
The following training and evaluation examples make use of the free OASIS dataset of saggital plane brain images.
-
Download and extract a disc of brain images from the OASIS data set.
-
Move the RAW images from the disc to a separate training disc
$ mv /path/to/disc/root/*/RAW /path/to/training/disc -
Train the Keras MR image reconstruction network on a subset of the training disc of size
SIZE:$ submrine-train -d /path/to/training/disc -s <SIZE> -c /path/to/checkpoints/directory -g <num_gpus> -b <batch_size> -s 4 -f .04
-
After each training iteration of SGD, network checkpoints will be saved to the checkpoints directory specified by the
-c/--checkpoints_dirflag.
These testing procedures allow users to benchmark the effectiveness of the implementation quantitatively or qualitatively by operating on a dataset of full-resolution MR images. These MR images are deliberately subsampled, reconstructed, and compared against their original contents to provide insight into the method's effectiveness. As in the training section, these examples make use of the OASIS dataset.
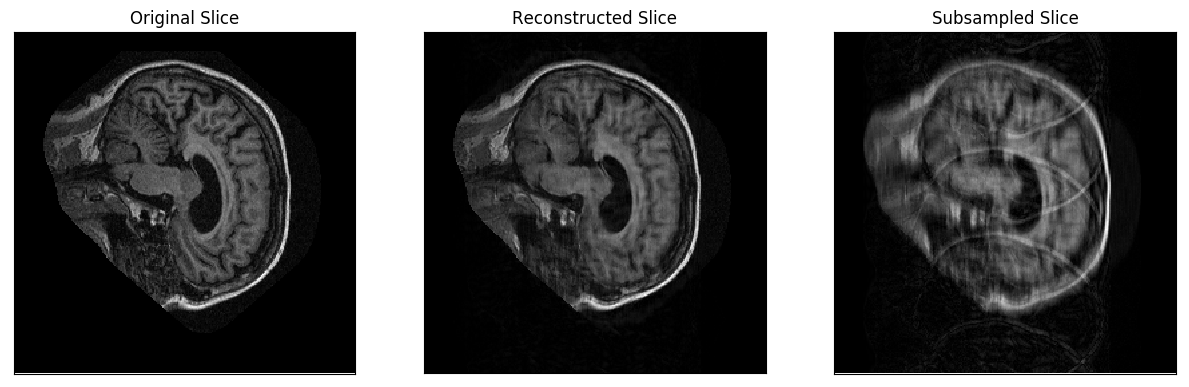
For testing purposes, this procedure will produce diff plots for each slice in a specified full-resolution MR image. The diff plots for every slice consists of the following grayscale images:
- The original slice
- A subsampled copy of the slice
- A reconstruction of the subsampled slice
The steps for obtaining these plots are as follows:
-
Select a saggital plane brain test image from the OASIS dataset.
-
Select one of the reconstruction neural networks that you have trained on the OASIS dataset. Alternatively, select one of the pretrained neural networks for the OASIS dataset.
-
Subsample, reconstruct, and obtain diff-plots for every slice in the OASIS test image by invoking the following command:
$ submrine-test -n /path/to/reconstruction/network -i /path/to/test/image -r /path/to/results/dir -s 4 -f .04
The diff plots for every slice will be saved in the directory specified by the
-r/--results_dirflag. Note that the values associated with the-s/--substepand-f/--lf_percentflags are consistent with the values used in the training section. The same values should be used for training and testing.
For testing purposes, this procedure will produce loss metrics over a test dataset of full-resolution MR images. These loss metrics consist of the following information:
- The MSE (or SSIM) between original MR image slices and their reconstructed versions after subsampling.
- The standard deviation associated with (1)
- The MSE (or SSIM) between original MR image slices and their subsampled (aliased) versions
- The standard deviation associated with (3)
-
MSE (mean normalized per-pixel squared error) is defined as:
such that
L_iis a slice of a full-resolution MR image andR_iis a subsampled and reconstructed version of the slice. For a detailed explanation of this definition, please refer to the Loss Calculation subsection on Page 4 of the writeup (http://corey-zumar.github.io/submrine/). -
Information regarding SSIM is available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Structural_similarity
The steps for obtaining these results on a sample test set are as follows:
-
Download and extract a different disc of brain images from the OASIS data set.
-
Move the RAW images from the disc to a separate test disc
$ mv /path/to/disc/root/*/RAW /path/to/test/disc -
Compute loss metrics over a subset of the test disc of size
SIZEas follows:$ submrine-test -n /path/to/reconstruction/network -d /path/to/test/disc -r /path/to/results/dir -t <SIZE> -s 4 -f .04
The stated loss metrics will be computed over a subset of the test disc consisting of
SIZEslices sampled contiguously (in directory order) from the MR images in the test disc. These metrics will be saved as a JSON-formatted file under the directory specified by-r/--results_dir. Again, note that the values associated with the-s/--substepand-f/--lf_percentflags are consistent with the values used in the training section. The same values should be used for training and testing.
Given an undersampled MR image, this evaluation procedure will produce a corrected image by evaluating the reconstruction network on its pixel representation. This corrected image will be plotted next to the original (undersampled) MR image.
These steps will describe the process of performing reconstruction and obtaining the associated plots for an undersampled saggital plane brain image.
-
We note that saggital plane brain images are well-encapsulated by the OASIS dataset. Therefore, it is reasonable to use the OASIS dataset to obtain a network for reconstructing our undersampled image. Select one of the reconstruction neural networks that you have trained on this dataset. Alternatively, select one of the pretrained neural networks for the OASIS dataset.
-
Reconstruct (using the deep neural network) and obtain diff-plots for every slice in the undersampled image by invoking the following command:
$ submrine-eval -n /path/to/reconstruction/network -i /path/to/undersampled/image -r /path/to/results/dir
The diff plots for every slice will be saved in the directory specified by the
-r/--results_dirflag
GitHub usernames are in parentheses.
- Corey Zumar (
Corey-Zumar) - Alex Kot (
Alex-Kot)