nRF Logger Library
The library allows to easily create custom log entries from your application in the nRF Logger. It is being used by nRF Connect and nRF Toolbox, that are available on Google Play. The logger may be used for debugging purposes, as LogCat is not always available.
nRF Logger is available for Android 4.2.* and newer.
Usage
The nRF Logger API library is available on JCenter and Maven Central repositories. For Android Studio, add the following dependency to your component's gradle.build file:
implementation 'no.nordicsemi.android:log:2.3.0'For easy integration with Timber (4.7.1), use this instead:
implementation 'no.nordicsemi.android:log-timber:2.3.0'If your project is NOT migrated to AndroidX, use version 2.2.0.
If you use proguard, the following line will be automatically added to your proguard rules:
-keep class no.nordicsemi.android.log.** { *; }
Features
- Create log session from your application
- Append log entries to the session
- 6 log levels are available: DEBUG, VERBOSE, INFO, APPLICATION*, WARNING, ERROR
- Open the log in nRF Logger for viewing
APPLICATION level added in version 2.0 of the library.
Timber integration
After importing log-timber dependency, plant the nRFLoggerTree, as described on Timber website.
Important
- The log-timber library uses
@NonNulland@Nullablefrom androidx.annotation, instead of ones from org.jetbrains.annotations, like Timber does. - Log levels that Timber uses are incompatible with those in nRF Logger. In Timber, the APPLICATION level is missing, and DEBUG has higher priority then VERBOSE.
- Using Timber's (e.g.
Timber.i(...)) API it is not possible to log on APPLICATION level. - Logs logged with
Log.VERBOSEpriority will get VERBOSE log level, so will be upgraded. - Logs logged with
Log.DEBUGpriority will get DEBUG level, so will be downgraded. - Tags will be added before the message:
[TAG] message.
Example
The example project may be found in samples folder. It contains a simple application that shows how to create a log session:
logSession = Logger.newSession(context, key, name);and add entries:
Logger.log(logSession, Level.INFO, text);
Logger.e(logSession, R.string.error, someArg);If nRF Logger application is not installed on the device those methods do nothing.
Basic information
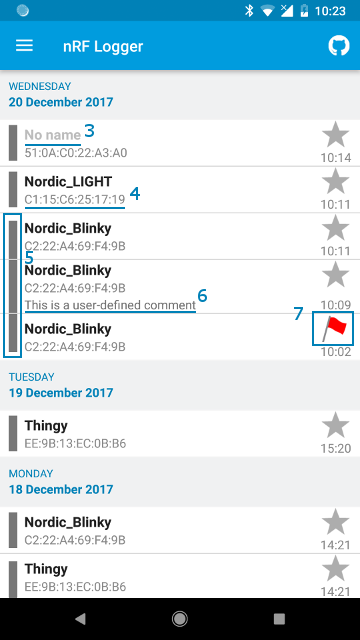
(1) When you create your first log session from your application its name will be added to nRF Logger drop-down menu.
logSession = Logger.newSession(context, key, name);(2) You may create multiple folders for different components of your application by creating a session with a profile name. It will be concatenated with the application name and visible as different entry in the drop-down menu.
logSession = Logger.newSession(context, "Profile Name", key, name);(3) The "name" parameter is shown as a title. If name is null, "No name" will be shown.
(4) The "key" parameter is used to group log sessions from the same day together. The "key" parameter may not be null.
(5) Log sessions from the same day with the same "key" value are grouped as shown on the picture.
(6) nRF Logger API allows you also to add a comment to a log session.
Logger.setSessionDescription(logSession, "This is a comment");(7) You may also mark a session with one of 6 symbols.
Logger.setSessionMark(logSession, Logger.MARK_FLAG_RED);Version 2.0
Local Log Content Provider
The version 2.0 introduced the LocalLogContentProvider class which may be used to keep logs even if the nRF Logger application is not installed. Local log database is a limited version of the one in nRF Logger. It does not support multiple applications as the new provider is designed to work only in one application. Also marking session with a flag/star or adding a description is not supported.
To use the LocalLogContentProvider you must extend extend this class in you project and add its definition to the AndroidManifest.xml file:
<provider
android:name="com.example.log.provider.MyLogContentProvider"
android:authorities="com.example.log"
android:exported="true" />If you want to use the local logger in threads that are owned by other applications, e.g. by Bluetooth scanner callbacks, you must set the exported attribute to true. Otherwise the Bluetooth application will not have the permission to add log events. You may also use Handler object to log in UI thread of your application.
ILogSession
In order to make the LocalLogSession work, a new interface has been created - ILogSession.
Both LogSession and LocalLogSession implement this interface. You will need to change the
type of your mLogSession object to ILogSession when migrating to version 2.0 of the library.