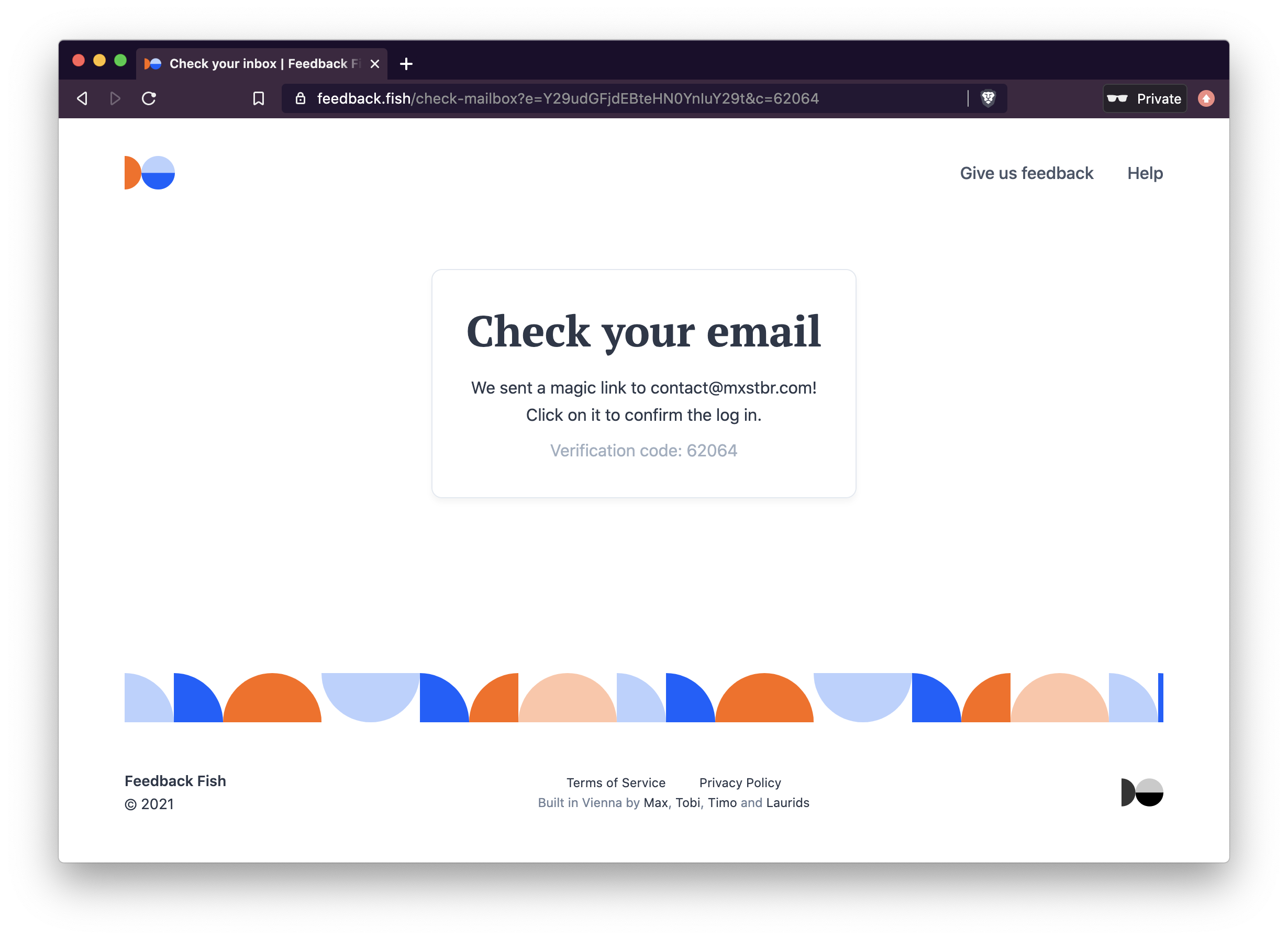
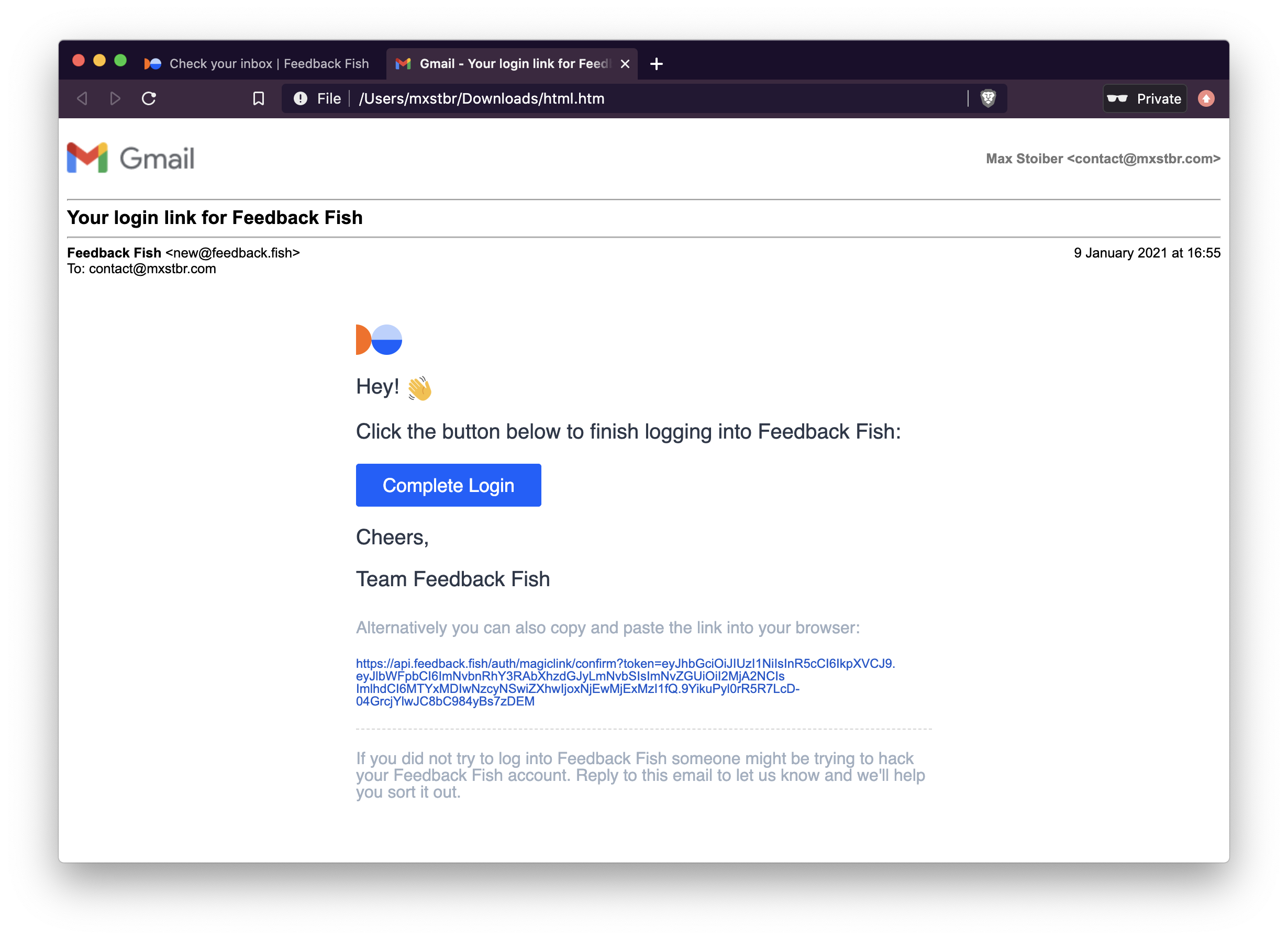
Forked from Passport Magic Login
Passwordless/Modern authentication with magic links for Passport.js 🔑
- User signup and login without passwords
- Supports magic links sent via email, SMS or any other method you prefer
- User interface agnostic: all you need is an input and a confirmation screen
- Handles secure token generation, expiration and confirmation
Originally implemented by Tobias Lins for Splitbee and eventually extracted for Feedback Fish:
To use magic link authentication, you have to:
- Setup the Passport strategy and Express routes on your server
- POST a request with the users email or phone number from the client once they have entered it into the login input
npm install passport-modern-magic-links
This is what the usage from the frontend looks like once you've set it all up. It only requires a single request:
// POST a request with the users email or phone number to the server
fetch(`/auth/magiclogin`, {
method: `POST`,
body: JSON.stringify({
// `destination` is required.
destination: email,
// However, you can POST anything in your payload and it will show up in your verify() method
name: name,
}),
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' }
})
.then(res => res.json())
.then(json => {
if (json.success) {
// The request successfully completed and the email to the user with the
// magic login link was sent!
// You can now prompt the user to click on the link in their email
// We recommend you display json.code in the UI (!) so the user can verify
// that they're clicking on the link for their _current_ login attempt
document.body.innerText = json.code
}
})To make this work so easily, you first need to setup passport-modern-magic-links:
import MagicLoginStrategy from "passport-modern-magic-links"
// IMPORTANT: ALL OPTIONS ARE REQUIRED!
const magicLogin = new MagicLoginStrategy({
// Used to encrypt the authentication token. Needs to be long, unique and (duh) secret.
secret: process.env.MAGIC_LINK_SECRET,
// The authentication callback URL
callbackUrl: "/auth/magiclogin/callback",
// Called with th e generated magic link so you can send it to the user
// "destination" is what you POST-ed from the client
// "href" is your confirmUrl with the confirmation token,
// for example "/auth/magiclogin/confirm?token=<longtoken>"
sendMagicLink: async (destination, href) => {
await sendEmail({
to: destination,
body: `Click this link to finish logging in: https://yourcompany.com${href}`
})
},
// Once the user clicks on the magic link and verifies their login attempt,
// you have to match their email to a user record in the database.
// If it doesn't exist yet they are trying to sign up so you have to create a new one.
// "payload" contains { "destination": "email" }
// In standard passport fashion, call callback with the error as the first argument (if there was one)
// and the user data as the second argument!
verify: (payload, callback) => {
// Get or create a user with the provided email from the database
getOrCreateUserWithEmail(payload.destination)
.then(user => {
callback(null, user)
})
.catch(err => {
callback(err)
})
}
})
// Add the passport-modern-magic-links strategy to Passport
passport.use(magicLogin)Once you've got that, you'll then need to add a couple of routes to your Express server:
// This is where we POST to from the frontend
app.post("/auth/magiclogin", magicLogin.send);
// The standard passport callback setup
app.get(magicLogin.callbackUrl, passport.authenticate("magiclogin"));That's it, you're ready to authenticate! 🎉
Licensed under the MIT license. See LICENSE for more information!