Script collection for generating testssl.sh command lines that can be executed sequentially or in parallel with tools like GNU Parallel and importing the results into a structured document in ElasticSearch for further analysis.
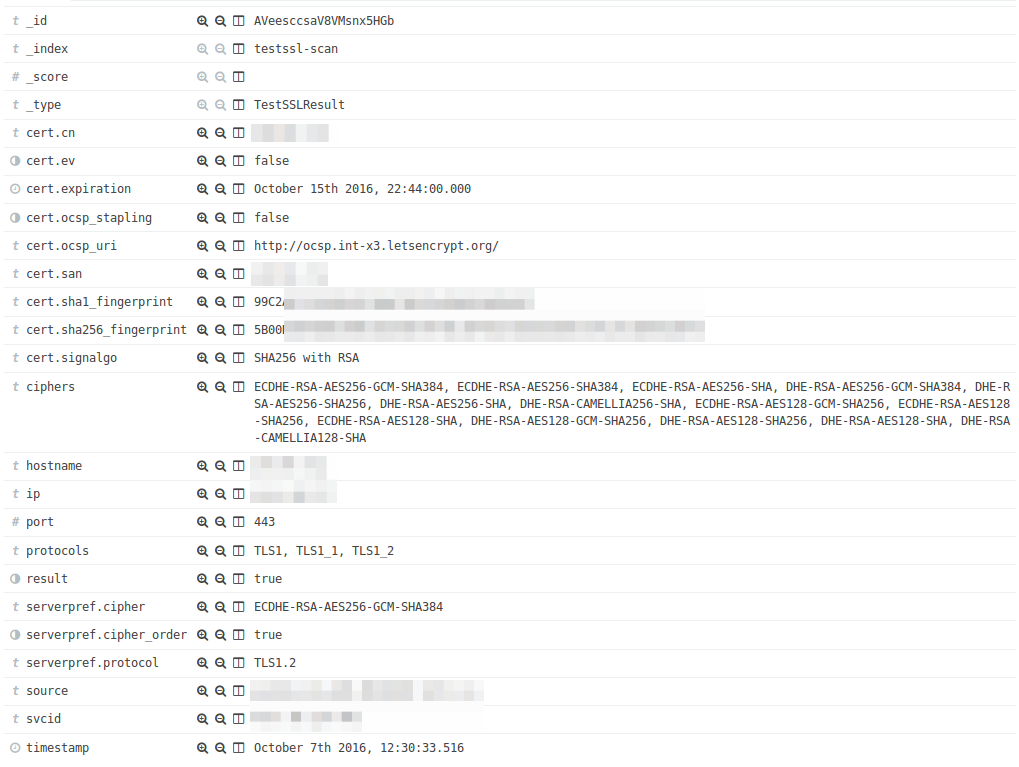
This is how the scan result of a service appears in Kibana:
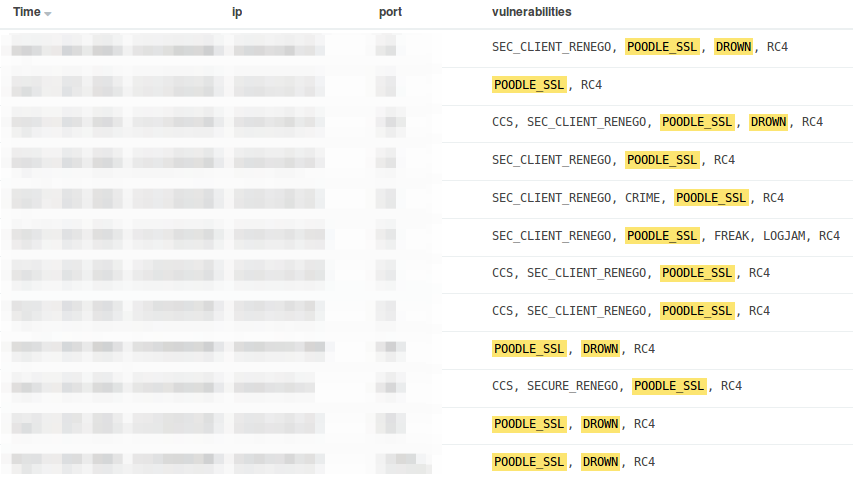
Create vulnerability lists:
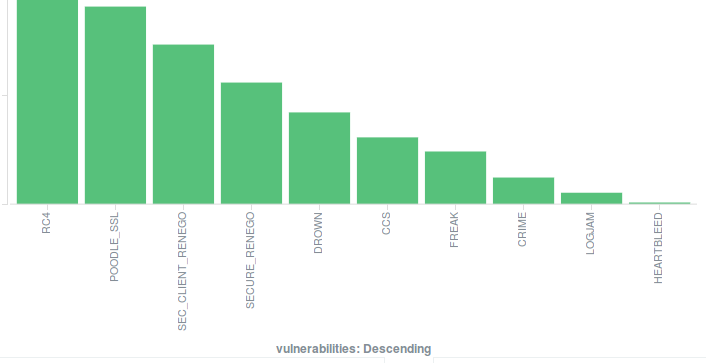
Visualize vulnerability distribution:
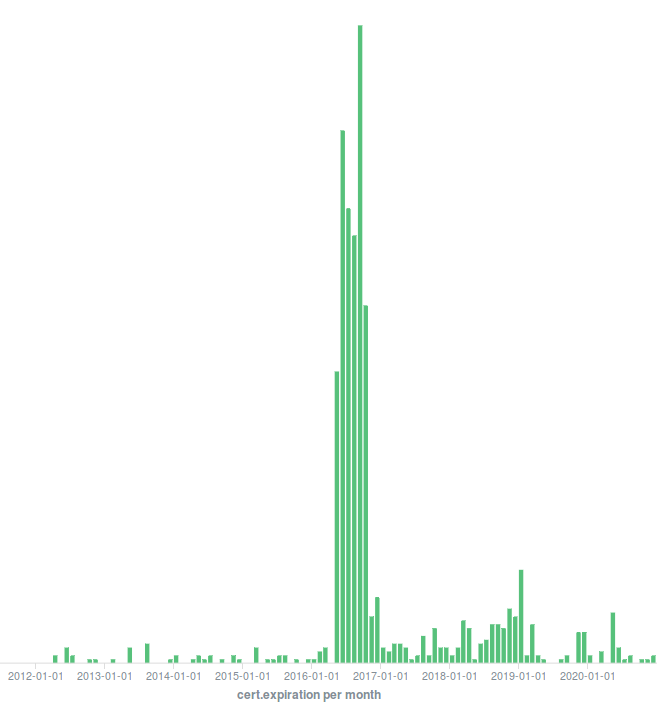
...or create vulnerability expiration graphs:
- testssl.sh 2.9dev branch or later version
- Python 3 with following modules:
- elasticsearch_dsl
- tzlocal
- Install dependencies (see above)
- Create input file with one
host:portpair per line. - Run
generate_scan_file.py inputfile > cmdfileto generate file with testssl.sh command lines. - Run
parallel < cmdfileto perform testssl.sh scans. - Run
import_testssl.sh_csv_to_ES.py *.csvto import scan results into ElasticSearch. - View/Analyze data with Kibana or the tool of your choice.
- Fix your TLS configurations :)
List all vulnerabilities in "host;port;vulnerabilities" CSV format:
curl -qsk 'localhost:9200/testssl-*/_search?q=_exists_:vulnerabilities&size=10000' | jq -r '.hits.hits[]._source | [ .ip, ( .port | tostring ), ( .vulnerabilities | join(", ") ) ] | join(";")'
...and add ciphertests field:
curl -qsk 'localhost:9200/testssl-*/_search?q=_exists_:(vulnerabilities+ciphertests)&size=10000' | jq -r '.hits.hits[]._source | [ .ip, ( .port | tostring ), ( .vulnerabilities | if . == null then "" else (. | join(", ") ) end ), ( .ciphertests | if . == null then "" else (. | join(", ") ) end ) ] | join(";")