This is the implementation code and instruction of the proposed work "Language-enhanced Object Reasoning Networks for Video Moment Retrieval with Text Query" (LEORN).
Our code runs based on the following dependencies:
- python3
- torch
- numpy
- tqdm
- h5py
- argparse
- tensorboard
- easydict
- torchtext
- terminaltables
The datasets we used for training and evaluation are listed as follow:
- TACoS: https://www.mpi-inf.mpg.de/departments/computer-vision-and-machine-learning/research/vision-and-language/tacos-multi-level-corpus
- Charades-STA: https://prior.allenai.org/projects/charades
Using the following command to train and evaluate our model.
TACoS
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=2 moment_localization/train_muti.py --gpus 0,1 --cfg experiments\tacos\LEORN-128x128-K5L8.yaml --verbose
Charades-STA
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=2 moment_localization/train_muti.py --gpus 0,1 --cfg experiments/charades/LEORN-64x64-K9L4.yaml --verbose
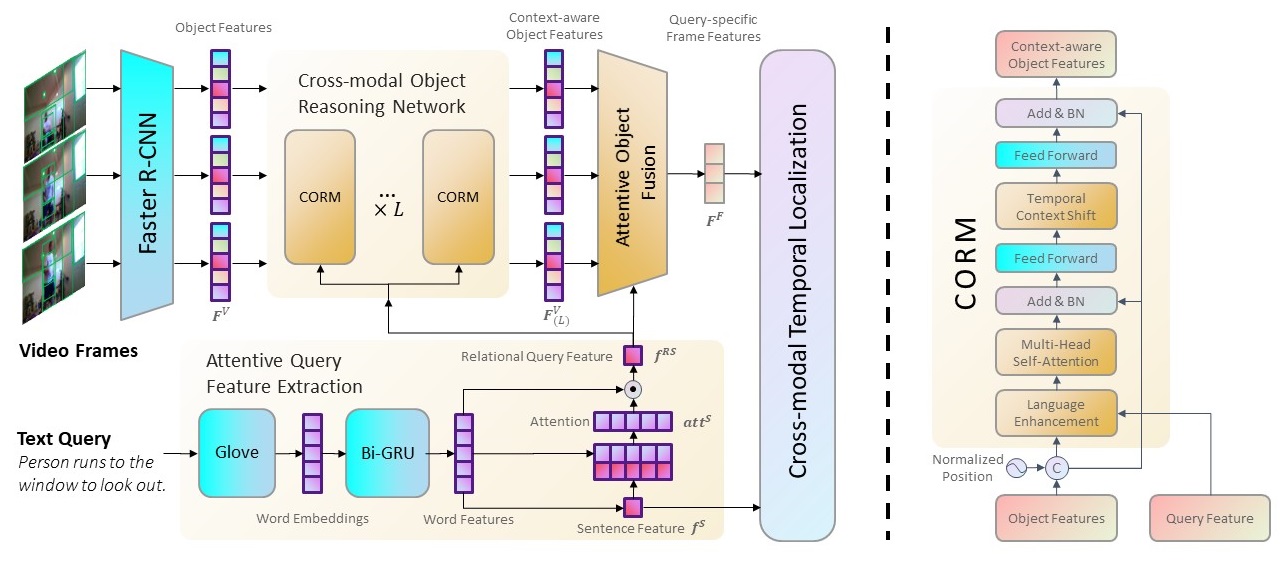
We propose a novel Language-enhanced Object Reasoning Networks (LEORN) for video moment retrieval with text query, as shown in the figure below.
- The proposed LEORN uses the object features extracted by the object detection network and incorporates the language features to model the relation between the objects within the frame.
- Besides, we design a temporal context shift mechanism to model the temporal relationship of objects while reducing the noise from irrelevant objects in the adjacent frames.
- Furthermore, as a general video understanding networks for object-level features, the proposed LEORN shows great potential on migrating to other cross-modal video understanding tasks.
- We propose a novel model termed Language-enhanced Object Reasoning Networks (LEORN) for video moment retrieval, which leverages object-level features for cross-modal object reasoning. The fully-reasoned features contain abundant implicit information with good compatibility so as to better understand the video content.
- We design an attentive feature query extraction mechanism to extract relational query feature which is more consistent with the object reasoning process.
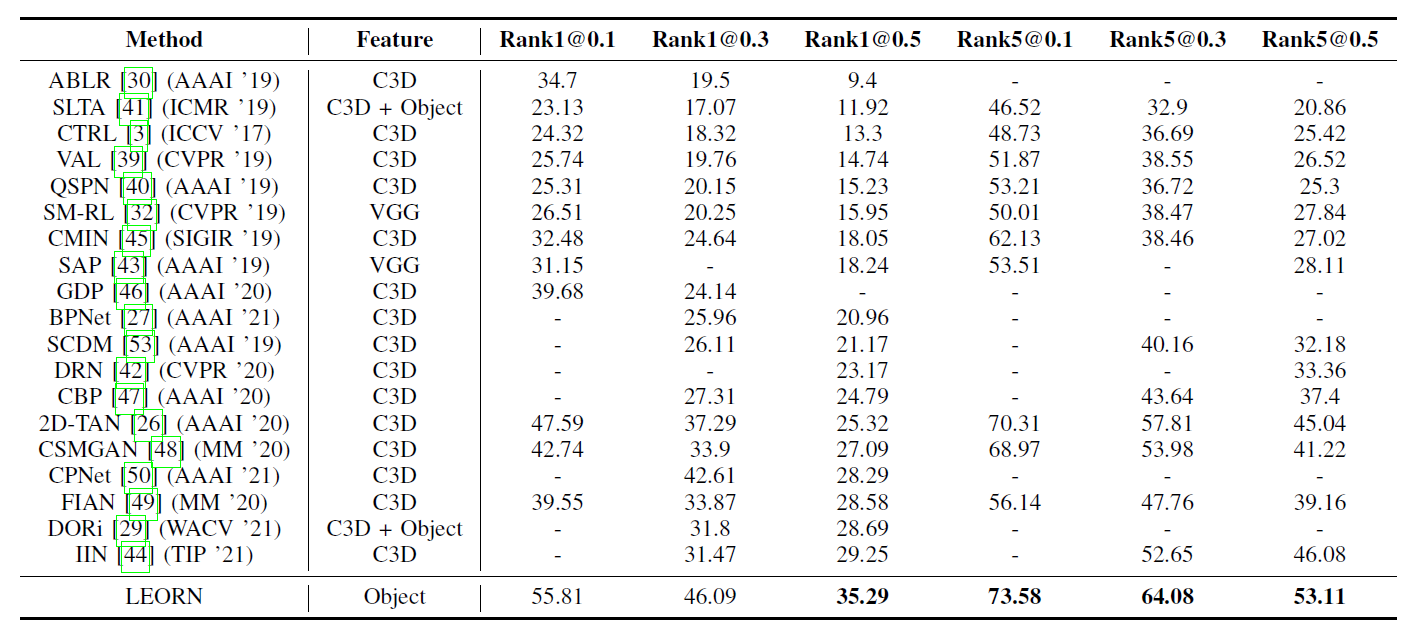
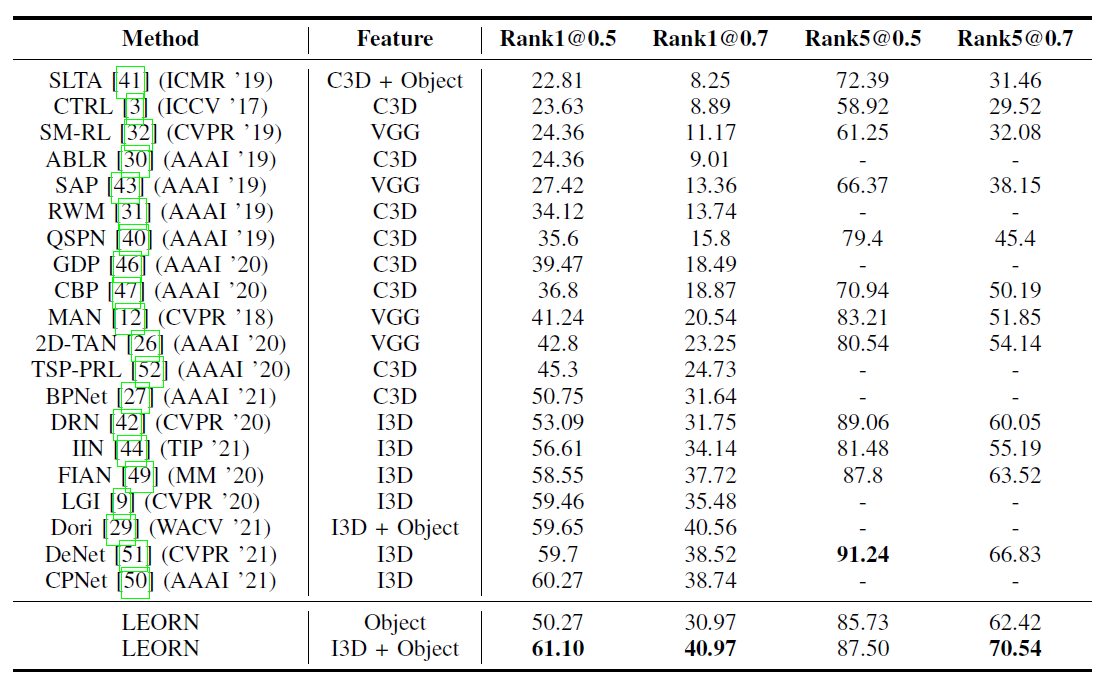
- We conduct extensive experiments on two public datasets: TACoS and Charades-STA. The experimental results show that our proposed method with object-level features can achieve competitive results and the model in a comparable experimental setting outperforms other state-of-the-art approaches that demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method with object features.
- Our proposed LEORN shows great potential on migrating to other cross-modal video understanding tasks.