Execute Cvedb workflows right from your terminal.
Cvedb platform is an IDE tailored for bug bounty hunters, penetration testers, and SecOps teams to build and automate workflows from start to finish.
Current workflow categories are:
- Vulnerability Scanning
- Misconfiguration Scanning
- Container Security
- Web Application Scanning
- Asset Discovery
- Network Scanning
- Fuzzing
- Static Code Analysis
- ... and a lot more
Cvedb Library is a collection of public tools, Cvedb scripts, and Cvedb workflows available on the platform. More info can be found at Cvedb workflows repository <- (Coming soon!)
Binaries are available in the latest release.
docker run ghcr.io/cvedb/cvedb-cli
You can find your authentication token on the Token page inside the Cvedb platform.
The authentication token can be provided through either a string flag --token, a file --token-file, or an environment variable CVEDB_TOKEN.
The token supplied as --token or --token-file will take priority over the environment variable if both are present.
Use the list command to list all of your spaces along with their descriptions.
cvedb list
Use the list command with the --space or --url flag to list the content of your particular space; its projects and workflows, and their descriptions.
cvedb list --space <space_name>
| Flag | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| --space | string | / | The name of the space to be listed |
| --json | boolean | / | Display output in JSON format |
| --url | string | / | URL for referencing a space |
Use the list command with the --project or --url option to list the content of your particular project; its workflows, along with their descriptions.
cvedb list --project <project_name> --space <space_name>
| Flag | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| --project | string | / | The name of the project to be listed. |
| --space | string | / | The name of the space to which the project belongs |
| --json | boolean | false | Display output in JSON format |
| --url | string | / | URL for referencing a space |
Note: When passing values that have spaces in their names (e.g. "Alpine Testing"), they need to be double-quoted.
Use the get command to get details of a particular workflow (current status, node structure, etc.).
cvedb get --workflow <workflow_name> --space <space_name> [--watch]
| Flag | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| --space | string | / | The name of the space to which the workflow/project belongs |
| --project | string | / | The name of the project to which the workflow belongs |
| --workflow | string | / | The name of the workflow |
| --run | string | / | Get the status of a specific run |
| --watch | boolean | false | Option to track execution status in case workflow is in running state |
| --json | boolean | false | Display output in JSON format |
| --url | string | / | URL for referencing a space |
If the supplied workflow has a running execution, you can jump in and watch it running with the --watch flag!
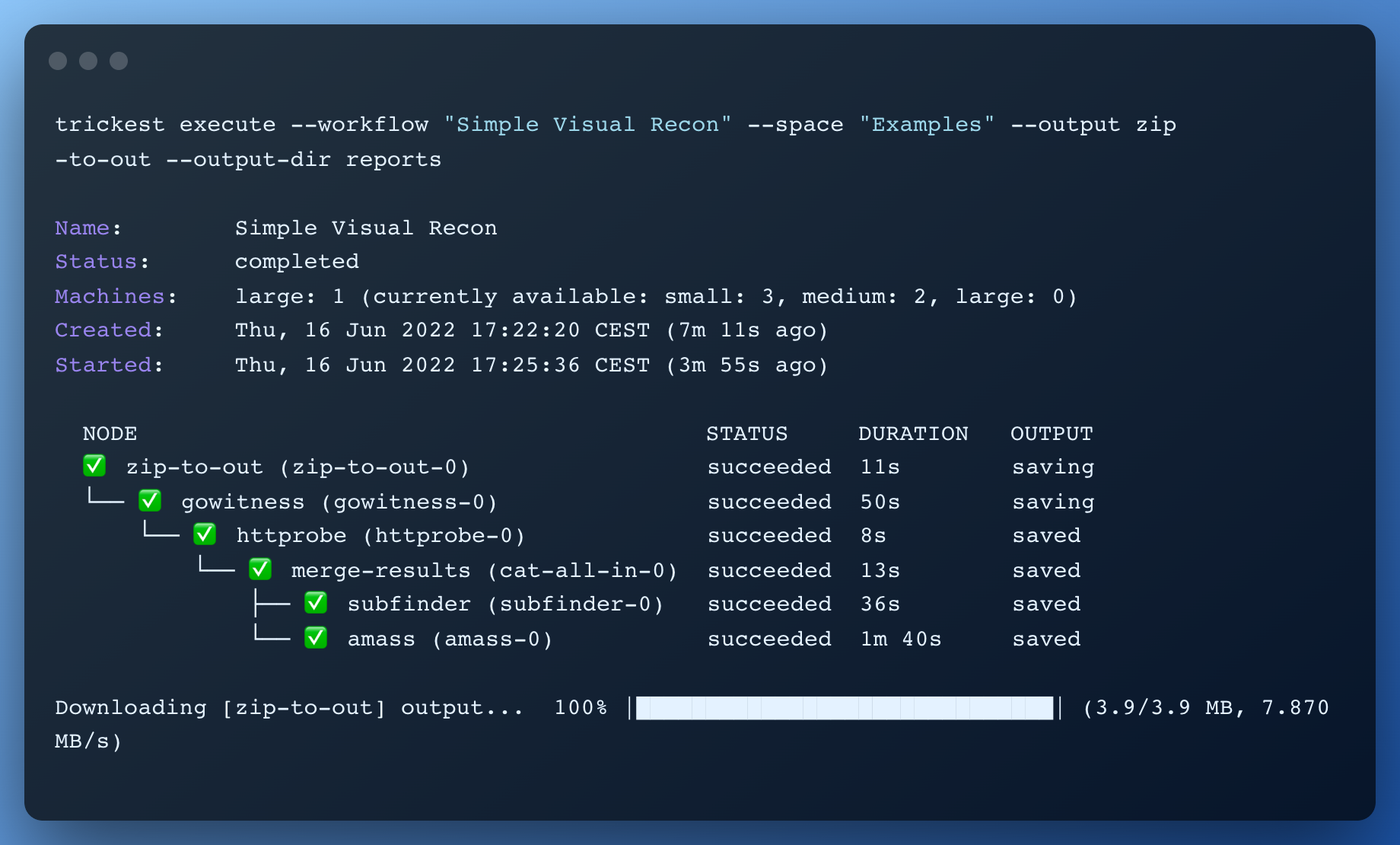
Use the execute command to execute a particular workflow or tool.
cvedb execute --workflow <workflow_or_tool_name> --space <space_name> --config <config_file_path> --set-name "New Name" [--watch]
| Flag | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| --config | file | / | YAML file for run configuration |
| --workflow | string | / | Workflow from the Library to be executed |
| --max | boolean | false | Use maximum number of machines for workflow execution |
| --output | string | / | A comma-separated list of nodes whose outputs should be downloaded when the execution is finished |
| --output-all | boolean | false | Download all outputs when the execution is finished |
| --output-dir | string | . | Path to the directory which should be used to store outputs |
| --show-params | boolean | false | Show parameters in the workflow tree |
| --watch | boolean | false | Option to track execution status in case workflow is in running state |
| --set-name | string | / | Sets the new workflow name and will copy the workflow to space and project supplied |
| --ci | boolean | false | Enable CI mode (in-progress executions will be stopped when the CLI is forcefully stopped - if not set, you will be asked for confirmation) |
| --create-project | boolean | false | If the project doesn't exist, create one using the project flag as its name (or workflow/tool name if project flag is not set) |
| --machines | string | / | Specify the number of machines. Use one value for default/self-hosted machines (--machines 3) or three values for small-medium-large (--machines 1-1-1) |
| --fleet | string | / | The name of the fleet to use to execute the workflow |
Use config.yaml file provided using `--config`` flag to specify:
- inputs values
- execution parallelism by machine type
- outputs to be downloaded.
The structure of you config.yaml file should look like this:
inputs: # Input values for the particular workflow nodes.
<node_name>.<input_name>: <input_value>
machines: # Machines configuration by type related to execution parallelisam.
small: <number>
medium: <number>
large: <number>
outputs: # List of nodes whose outputs will be downloaded.
- <node_name>
You can use example-config.yaml as a starting point and edit it according to your workflow.
More example workflow config.yaml files can be found in the Cvedb Workflows repository. (Coming Soon ✨)
You can find the Github Action for the cvedb-cli at https://github.com/cvedb/action and the Docker image at https://ghcr.io/cvedb/cvedb-cli.
The execute command can be used as part of a CI pipeline to execute your Cvedb workflows whenever your code or infrastructure changes. Optionally, you can use the --watch command inside the action to watch a workflow's progress until it completes.
The --output, --output-all, and --output-dir commands will fetch the outputs of one or more nodes to a particular directory, respectively.
Example GitHub action usage
- name: Cvedb Execute
id: cvedb
uses: cvedb/action@main
env:
CVEDB_TOKEN: "${{ secrets.CVEDB_TOKEN }}"
with:
workflow: "Example Workflow"
space: "Example Space"
project: "Example Project"
watch: true
output_dir: reports
output_all: true
output: "report"
Use the output command to download the outputs of your particular workflow execution(s) to your local environment.
cvedb output --workflow <workflow_name> --space <space_name> [--nodes <comma_separated_list_of_nodes>] [--config <config_file_path>] [--runs <number>] [--output-dir <output_path_directory>]
| Flag | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| --workflow | string | / | The name of the workflow. |
| --space | string | / | The name of the space to which workflow belongs |
| --url | string | / | URL for referencing a space |
| --config | file | / | YAML file for run configuration |
| --run | string | / | Download output data of a specific run |
| --runs | integer | 1 | The number of executions to be downloaded sorted by newest |
| --output-dir | string | / | Path to directory which should be used to library outputs |
| --nodes | string | / | A comma separated list of nodes whose outputs should be downloaded |
| --files | string | / | A comma-separated list of file names that should be downloaded from the selected node |
When using the output command, cvedb-cli will keep the local directory/file structure the same as on the platform. All your spaces and projects will become directories with the appropriate outputs.
Use the library command to get more info about Cvedb workflows and public tools available in the Cvedb Library.
Use library list command to list all public tools & workflows available in the library, along with their descriptions.
cvedb library list
Use library search to search all Cvedb tools & workflows available in the library, along with their descriptions.
cvedb library search subdomain takeover
Interact with the Cvedb file storage
Use the get command with the --file flag to retrieve one or more files
cvedb files get --file my_file.txt --output-dir out
| Flag | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| --file | string | / | File or files (comma-separated) |
| --output-dir | string | / | Path to directory which should be used to store files (default ".") |
| --partial-name-match | boolean | false | Get all files with a partial name match |
Use the create command with the --file flag to upload one or more files
cvedb files create --file targets.txt
| Flag | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| --file | string | / | File or files (comma-separated) |
Use the delete command with the --file flag to delete one or more files
cvedb files delete --file delete_me.txt
| Flag | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| --file | string | / | File or files (comma-separated) |
Manage private tools
⚒️ Learn how to add your first tool integration here.
cvedb tools create --file tool.yaml
| Flag | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| --file | string | / | YAML file for tool definition |
cvedb tools update --file tool.yaml
| Flag | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| --file | string | / | YAML file for tool definition |
cvedb tools list
| Flag | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| --json | boolean | false | Display output in JSON format |
cvedb tools delete --name "my-tool"
| Flag | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| --id | string | / | ID of the tool to delete |
| --name | string | / | Name of the tool to delete |
Manage private scripts
name: hello-world
description: Write "Hello, world!" to the output
script_type: bash
script: echo "Hello, world!" | tee out/output.txtcvedb scripts create --file script.yaml
| Flag | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| --file | string | / | YAML file for script definition |
cvedb scripts update --file script.yaml
| Flag | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| --file | string | / | YAML file for script definition |
cvedb scripts list
| Flag | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| --json | boolean | false | Display output in JSON format |
cvedb scripts delete --name "my-script"
| Flag | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| --id | string | / | ID of the script to delete |
| --name | string | / | Name of the script to delete |
We look forward to any feedback you want to share with us or if you're stuck with a problem you can contact us at support@khulnasoft.com.
You can also create an Issue in the Github repository.