WSL 1 (not wsl 2) Docker Desktop integration.
WSL 2 is cool, but... wsl2 filesystem performance is much slower than wsl1 in /mnt.
If you work in WSL 2 in the mounted (/mnt/xxx) windows volumes, you will feel very slow filesystem performance, a much slower then in WSL 1.
Fortunately, you can configure Docker Desktop to work with WSL 1.
Tested on:
- Ubuntu 18.04 LTS - works fine.
- Debian 10 "Buster" - works fine.
- Ubuntu 20.04 LTS - error
sleep: cannot read realtime clock: Invalid argumentin the docker install script. But you can download script manually fromhttps://get.docker.comand just removesleepstring from there. It should work. Or just install docker manually.
Step 0.
At first, your docker settings should look something like this:
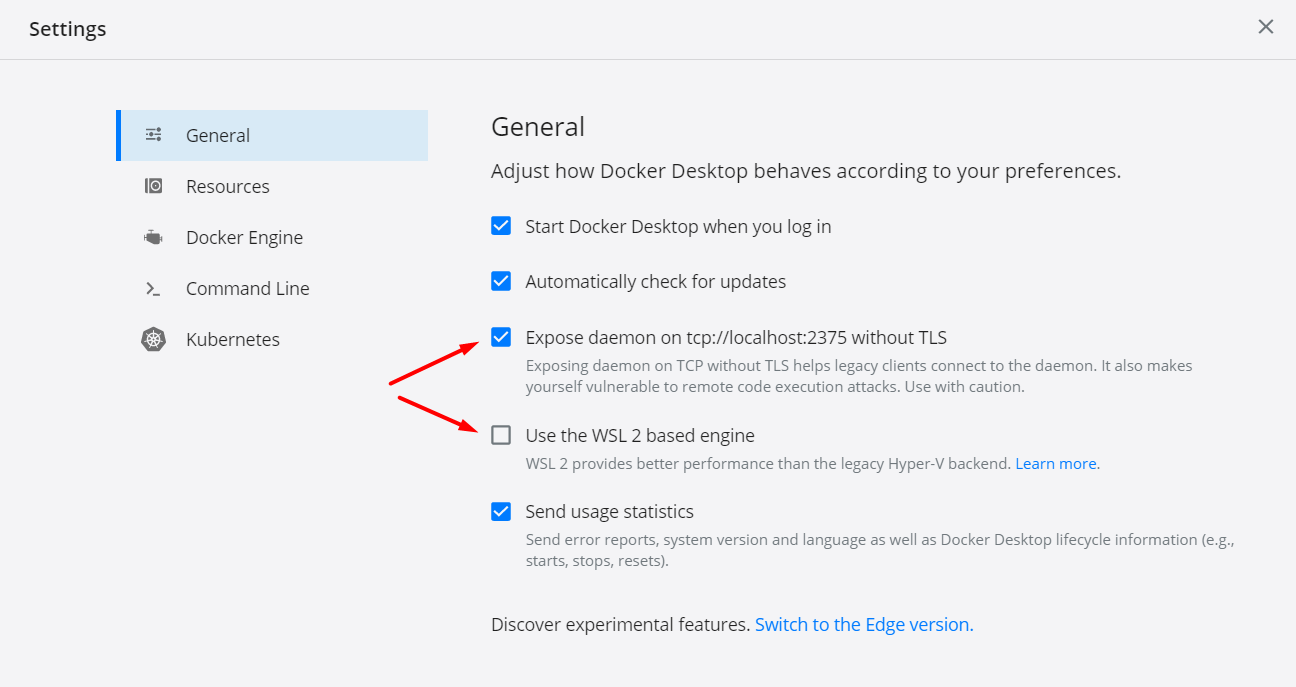
Don't forget to set the version of your wsl to 1:
wsl --set-version DISTRO_NAME 1Step 1.
You may have built-in placeholder docker and docker-compose commands (usually in Ubuntu):
> docker
> The command 'docker' could not be found in this WSL 1 distro.
> We recommend to convert this distro to WSL 2 and activate
> the WSL integration in Docker Desktop settings.
>
> See https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/wsl/ for details.
If your linux os image just doesn't have this commands, just go to the step 2.
But if you have this commands, your must to remove them at first.
To remove them add this at the end of your ~/.bashrc (nano ~/.bashrc):
# Remove docker placeholders from $PATH
rpath(){
for path in "$@";do
PATH="$(echo "$PATH" |sed -e "s#\(^\|:\)$(echo "$path" |sed -e 's/[^^]/[&]/g' -e 's/\^/\\^/g')\(:\|/\{0,1\}$\)#\1\2#" -e 's#:\+#:#g' -e 's#^:\|:$##g')"
done
echo "$PATH"
}
PATH="$(rpath '/mnt/c/Program Files/Docker/Docker/resources/bin' '/mnt/c/ProgramData/DockerDesktop/version-bin')"Step 2.
Reopen your shell and execute the command:
clear && sudo apt-get update && \
sudo curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com -o get-docker.sh && sudo sh get-docker.sh && sudo usermod -aG docker $USER && \
sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.26.2/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose && sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose && \
echo "export PATH=\"$PATH:$HOME/.local/bin\"" >> ~/.profile && source ~/.profile && \
echo "export DOCKER_HOST=tcp://localhost:2375" >> ~/.bashrc && source ~/.bashrc && \
printf '[automount]\nroot = /\noptions = metadata' | sudo tee -a /etc/wsl.confStep 3.
Then you must wait while WSL reloads the os image. Close all shells and wait around 10-20 seconds. Run this command in your PowerShell to verify that needed machine is stopped:
wsl -l -vIf it had stopped, you can run shell and use your docker now directly from WSL 1.
Windows disks now are mounted at the root / path, not in the /mnt (this is mandatory, Docker Desktop uses this paths format).