- Background and Motivation
- System Functions
- Schema Design
- Design Models
- Normalization strategy
- Operations can be Conducted on the Database System
- Screen shots of your GUI
- Future Works
- Conclusion & Database Grading Criteria
The provided code sets up the necessary database structure for a store management system. It creates the required tables and inserts sample data for testing purposes. The code can serve as a foundation for building a complete store management application.
Please note that additional code and user interface implementation may be required to utilize the database effectively in a real-world scenario.
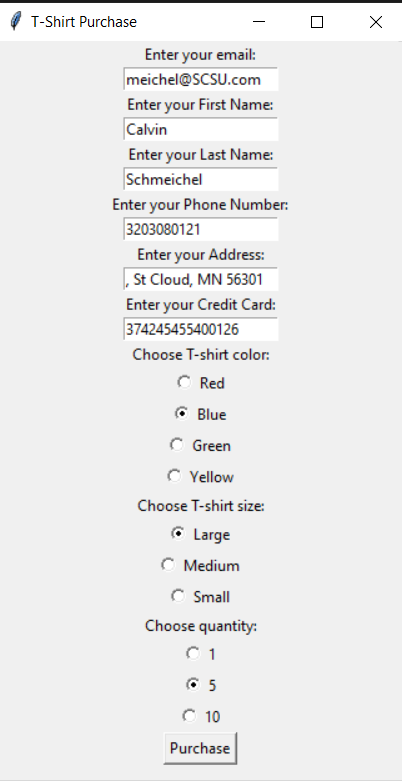
This code is written in Python and utilizes the tkinter library to create a graphical user interface (GUI) for handling T-shirt purchases. The code allows users to enter their personal information, select the desired T-shirt color, size, and quantity, and then generate a mock receipt.
Importing the required library:
- The
mysql.connectorlibrary is imported to establish a connection to the MySQL database. - Establishing a connection to the database: The mysql.connector.connect() method is used to establish a connection to the MySQL database. The host, port, username, password, and database name are provided as parameters.
- Creating a cursor object: A cursor object is created using the db.cursor() method to execute SQL queries.
- Defining the printsql() function: The printsql() function is defined to iterate through the query results and print them.
- Dropping the existing database (if exists): The mycursor.execute() method is used to execute the SQL query DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS myStore;. This query drops the existing database named "myStore" if it exists.
- Creating a new database: The mycursor.execute() method is used to execute the SQL query CREATE DATABASE myStore;. This query creates a new database named "myStore".
- Using the newly created database: The mycursor.execute() method is used to execute the SQL query USE myStore;. This query sets the newly created "myStore" database as the current database.
- Creating tables for the store management system:
- The mycursor.execute() method is used to execute a series of SQL queries to create the following tables:
- Customers table: Stores information about customers, including their ID, first name, last name, phone number, and email address.
- Products table: Stores details about products, such as the ID, color, size, and brand.
- Tracking table: Tracks the delivery status of orders, including the delivery date, delivery address, status, and a unique tracking ID.
- Orders table: Manages the orders placed by customers, including the order ID, customer ID, product ID, order date, status, and tracking ID.
- Stock table: Keeps track of the stock quantity for each product.
- Payment table: Handles payment information for orders, storing the order ID and credit card number.
- Cart table: Tracks the items added to the cart by customers, including the customer ID, product ID, and quantity.
- Inserting sample data into the Products table: The mycursor.execute() method is used to execute an SQL query to insert sample data into the Products table. The INSERT INTO statement is used to specify the columns (Color, Size, Brand) and the values for each row.
- Inserting sample data into the Customers table: The mycursor.execute() method is used to execute an SQL query to insert sample data into the Customers table. The INSERT INTO statement is used to specify the columns (Fname, Lname, Phone, Email) and the values for each row.
- Retrieving data from the Customers table: The mycursor.execute() method is used to execute an SQL query to select all data from the Customers table. The query is then passed to the printsql() function to print the query results.
- Retrieving data from the Products table: The mycursor.execute() method is used to execute an SQL query to select all data from the Products table. The query is then passed to the printsql() function to print the query results.
- The mycursor.execute() method is used to execute a series of SQL queries to create the following tables:
The code consists of the following key components:
handle_purchase() function: This function is called when the user clicks the "Purchase" button. It retrieves the user's email, T-shirt color, size, and quantity from the respective input fields. It then generates a mock receipt string using f-strings and prints it to the console. Finally, it clears the email input field for the next entry.
Main window creation: The main window is created using the tk.Tk() method. The title of the window is set to "T-Shirt Purchase" using the title() method.
User input fields: The code creates several input fields for the user to enter their personal information, including email, first name, last name, and phone number. Each input field is created using the tk.Entry() method, and a label is associated with each input field using the tk.Label() method.
T-shirt color selection: The user can choose the desired T-shirt color by selecting one of the available options (Red, Blue, Green, Yellow). Radio buttons are created for each color option using the tk.Radiobutton() method. The selected color is stored in the color_var variable, which is of type tk.StringVar().
T-shirt size selection: Similar to the color selection, the user can choose the T-shirt size by selecting one of the available options (Large, Medium, Small). Radio buttons are created for each size option using the tk.Radiobutton() method. The selected size is stored in the size_var variable, which is of type tk.StringVar().
Quantity selection: The user can choose the quantity of T-shirts they want to purchase by selecting one of the available options (1, 5, 10). Radio buttons are created for each quantity option using the tk.Radiobutton() method. The selected quantity is stored in the quantity_var variable, which is of type tk.StringVar().
Purchase button: The "Purchase" button is created using the tk.Button() method. When clicked, it calls the handle_purchase() function.
GUI event loop: The code enters the GUI event loop using the mainloop() method of the main window. This ensures that the GUI remains responsive and can handle user interactions.
erDiagram
CUSTOMER ||--o{ ORDERS : Uses_Customers_Primary_Key_ID
CUSTOMER {
int ID PK "Primary Key"
string Fname "First Name"
string Lname "Last Name"
string Phone
string Email
}
ORDERS ||--|{ PRODUCT : Uses_Orders_ProductID
ORDERS ||--o{ TRACKING : Uses_Orders_TrackingID
ORDERS {
int ID PK "Primary Key"
int CustomerID FK "Foreign Key"
int ProductID FK "Foreign Key"
date Date
string Status
int TrackingID FK "Foreign Key"
}
PRODUCT ||--o{ STOCK : Uses_Orders_Primary_Key_ID
PRODUCT {
int ID PK "Primary Key"
string Color
string Size
string Brand
}
Payment ||--o{ ORDERS : Uses_Orders_Primary_Key_ID
Payment {
int OrderID FK "Foreign Key"
string CreditCardNumber
}
TRACKING {
int ID PK "Primary Key"
date DeliveryDate
string DeliveryAddress
string Status
}
STOCK {
int ProductID FK "Foreign Key"
int Quantity
}
CART ||--o{ ORDERS : Uses_ORDERS_CustomerID
CART ||--o{ ORDERS : Uses_ORDERS_ProductID
CART {
int OrderID FK "Foreign Key"
int CustomerID FK "Foreign Key"
int ProductID FK "Foreign Key"
int Quantity
datetime DateTime
}
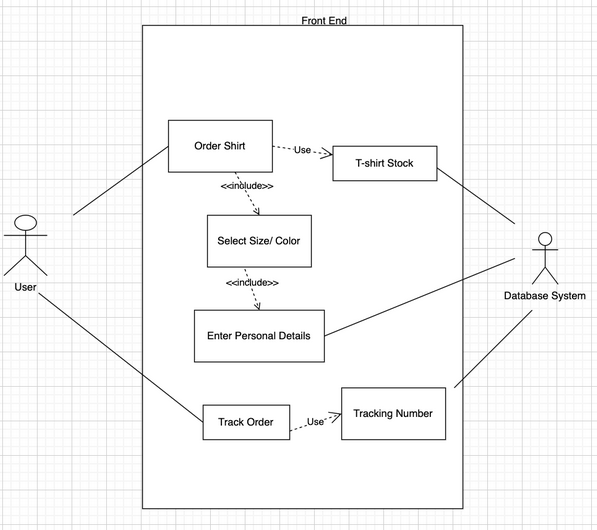
We chose to go with the Entity-Relationship (ER) model. We thought it made the most sense for our project since ER:
- Is primarily used for database design. It represents data in a database as entities and the relationships between these entities.
- In our schema, we have tables like Customers, Products, Orders, etc., which are typical entities. The relationships are indicated through foreign keys (EX: CustomerID in Orders references ID in Customers).
- The ER model is great for conceptualizing and designing a database at a high level, especially for relational databases like MySQL. As represented in our Database Schema
With out normalization strategy we wanted to make sure we:
- Reduce redundant data waste risk space
- Eliminate repeating groups in individual columns
- Use primary keys to show data is in relation with one another
- Create separate tables for each potential set of related data
Those were our core values throuout the project. If we had more time we would have liked to focus on and add:
- Supporting Future Scalability
- Minimizing Null Values
- Balancing Normalization with Performance
- Indexing Strategy
- Documenting the Database Schema
- Audit and Security
Multiple operations can and are used on our Database System. We used Python and a third party library called mysql.connector to interface with our database. Some of these operations are:
DROP DATABASE- We used this operator to wipe our database clean for demo purposes.
mycursor.execute("DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS myStore;")CREATE DATABASE- We used the operator to create our database.
mycursor.execute("CREATE DATABASE myStore;")USE- We used the operator to specify what database we are using for our demo.
mycursor.execute("USE myStore;")CREATE TABLE- We used the operator to generate our tables. (EX: Customers, Products, Tracking, Orders, Stock, Payment, Cart)
mycursor.execute("CREATE TABLE Customers(ID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,Fname VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL,Lname VARCHAR(40),Phone VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL,Email VARCHAR(40));")INSERT INTO- We used the operator to insert our products into the database and the users input from the GUI to create and store their order and receipt.
mycursor.execute("INSERT INTO Products (Color, Size, Brand)VALUES ('Red', 'Large', 'Calvin Klein'),('Red', 'Medium', 'Calvin Klein'),('Red', 'Small', 'Calvin Klein'),('Blue', 'Large', 'Calvin Klein'),('Blue', 'Medium', 'Calvin Klein'),('Blue', 'Small', 'Calvin Klein'),('Green', 'Large', 'Calvin Klein'),('Green', 'Medium', 'Calvin Klein'),('Green', 'Small', 'Calvin Klein'),('Yellow', 'Large', 'Calvin Klein'),('Yellow', 'Medium', 'Calvin Klein'),('Yellow', 'Small', 'Calvin Klein');")SELECT- We used the operator to search and locate the correct ID keys when inserting into our tables.
mycursor.execute(f"SELECT ID FROM Products WHERE Color = '{color_var.get()}' AND Size = '{size_var.get()}';")Example input:
CalvinSchmeichel@SCSU.com
Calvin
Schmeichel
3203080121
720 4th Ave S, St Cloud, MN 56301
374245455400126
Terminal Output:
Database Generated
Generate Customer Entry
(1, 'John', 'Doe', '123-456-7890', 'john.doee@example.com')
(2, 'John', 'Doe', '123-456-7890', 'john.doe@example.com')
(3, 'Calvin', 'Schmeichel', '3203080121', 'CalvinSchmeichel@SCSU.com\n')
Generate Tracking Entry
(1, datetime.date(2023, 12, 7), '720 4th Ave S, St Cloud, MN 56301\n', 'In Transit', 'SLMI98YFA3')
Generate Order Entry
4
(1, 3, 4, datetime.datetime(2023, 12, 7, 0, 0), 'Processing', 1)
Generate Cart Entry
(3, 4, 5, '2023-11-30')
Generate Payment Entry
(1, 374245455400126)
===========================================================================
Making Receipt
===========================================================================
Thank you for shopping with us! Here is your Receipt!
Calvin Schmeichel bought 5 Large Blue T-Shirt(s) today (2023-11-30)
This purchase was made with 374245455400126 and plans to arrive at 720 4th Ave S, St Cloud, MN 56301
on 2023-12-07
There are a few things we would like to add in the future.
- An expanded on GUI: For me (Calvin Schmeichel) is a Cybersecurity major I could only leverage knowledge known from my beginner Python class. But I think with more time we could leverage other tools such as a web GUI client to allow for more dynamic GUI that you would see like on Amazon.com.
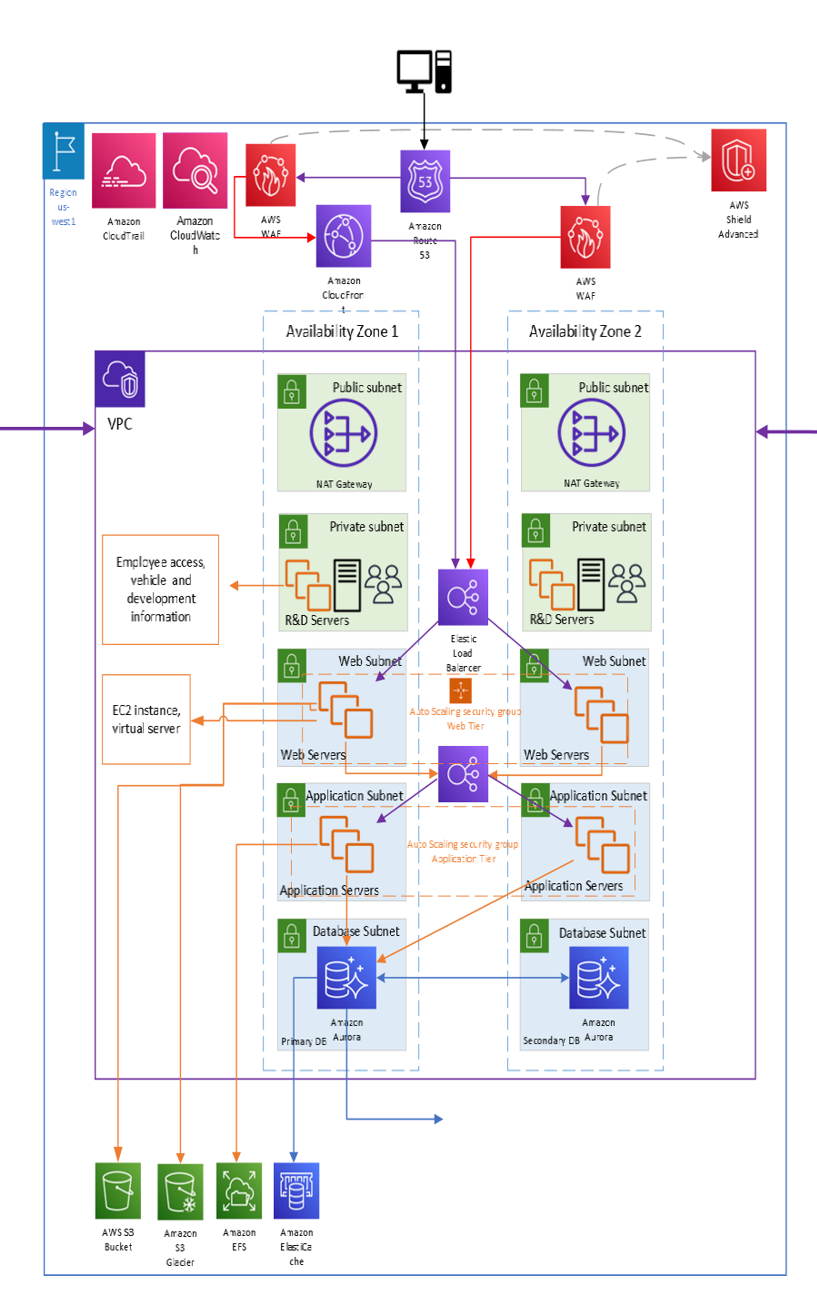
- Another idea we had was to run our MySQL instance on a Docker Container Using GitHub. I (Calvin Schmeichel) made and example guide on how to set one up which is linked in this repo. We could then use that Docker methodology to create a cusotom Docker image to host in an AWS Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR). Then attach them to auto-matic load ballencers to increase container volume with more traffic. Below I have linked in image of a mock AWS network diagram we could use. I helped make this diagram for my Cloud computing Course and is appropriately applicable in this situation.
The provided code demonstrates the use of tkinter library to create a GUI for handling T-shirt purchases. Users can enter their personal information, select the T-shirt color, size, and quantity, and generate a mock receipt. The code can serve as a basis for building a more comprehensive T-shirt purchasing system with additional features and database integration.
Please note that further improvements, such as error handling and data validation, can be implemented to enhance the user experience and ensure data integrity.
Overall this was a really fun project to work on and we learnd a lot more about MySQL and Python. These skills will be very valuable in the workplace after we graduate!
- We used this GitHub Repo README as our report writeup
- We also made a general PowerPoint on our project too