Gregory Holste, Evangelos K. Oikonomou, Bobak J. Mortazavi, Andreas Coppi, Kamil F. Faridi, Edward J. Miller, John K. Forrest, Robert L. McNamara, Lucila Ohno-Machado, Neal Yuan, Aakriti Gupta, David Ouyang, Harlan M. Krumholz, Zhangyang Wang, Rohan Khera
European Heart Journal | 23 August 2023
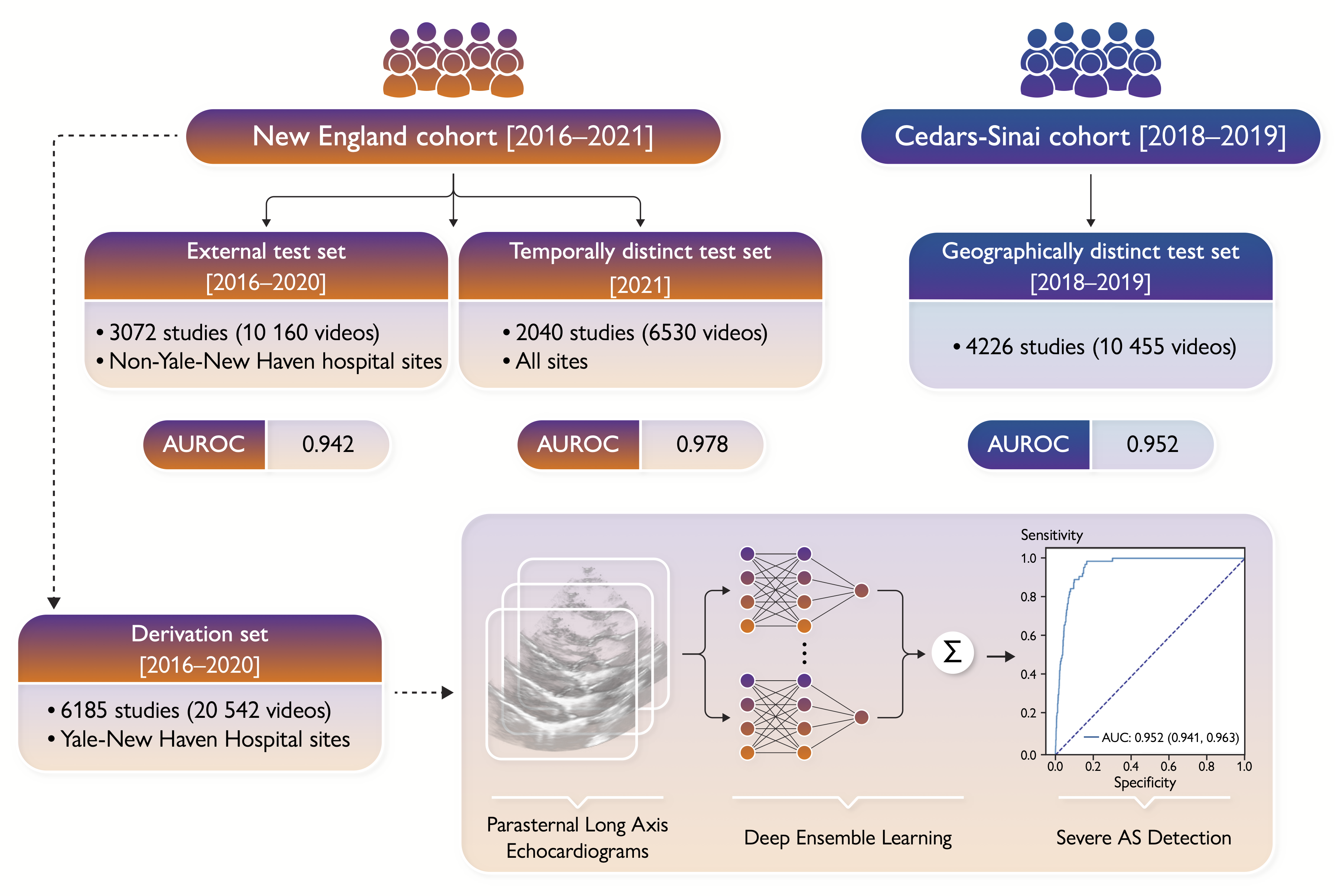
Early diagnosis of aortic stenosis (AS) is critical to prevent morbidity and mortality but requires skilled examination with Doppler imaging. This study reports the development and validation of a novel deep learning model that relies on two-dimensional (2D) parasternal long axis videos from transthoracic echocardiography without Doppler imaging to identify severe AS, suitable for point-of-care ultrasonography.
In a training set of 5257 studies (17 570 videos) from 2016 to 2020 [Yale-New Haven Hospital (YNHH), Connecticut], an ensemble of three-dimensional convolutional neural networks was developed to detect severe AS, leveraging self-supervised contrastive pretraining for label-efficient model development. This deep learning model was validated in a temporally distinct set of 2040 consecutive studies from 2021 from YNHH as well as two geographically distinct cohorts of 4226 and 3072 studies, from California and other hospitals in New England, respectively. The deep learning model achieved an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) of 0.978 (95% CI: 0.966, 0.988) for detecting severe AS in the temporally distinct test set, maintaining its diagnostic performance in geographically distinct cohorts [0.952 AUROC (95% CI: 0.941, 0.963) in California and 0.942 AUROC (95% CI: 0.909, 0.966) in New England]. The model was interpretable with saliency maps identifying the aortic valve, mitral annulus, and left atrium as the predictive regions. Among non-severe AS cases, predicted probabilities were associated with worse quantitative metrics of AS suggesting an association with various stages of AS severity.
This study developed and externally validated an automated approach for severe AS detection using single-view 2D echocardiography, with potential utility for point-of-care screening.
# Create conda environments
conda env create -f tf_gpu.yml
conda env create -f echo.yml
conda activate echo
## PREPROCESSING ##
# Load videos from DICOM format, deidentify frames, and save to AVI format
cd preprocessing/
python deidentify.py --data_dir <path_to_dicom_data> --output_dir <path_to_output_avis> --n_jobs <num_cpus>
# Run videos through view classifier to identify PLAX clips
conda deactivate
conda activate tf_gpu
python classify_view.py --data_dir <path_to_output_avis> --output_dir <path_to_output_plax_prob_csv> --csv_name <plax_prob_csv_name>
# More thoroughly mask peripheral pixels, downsample frames, and randomly split internal data into train/val/test
conda deactivate
conda activate echo
python preprocess.py --output_dir <path_to_preprocessed_data> --label_csv_path <path_to_label_csv> --plax_csv_path <path_to_plax_prob_csv>
## SELF-SUPERVISED LEARNING (SSL) ##
# Perform SSL pretraining on training set. Model trained for 300 epochs on two NVIDIA RTX 3090 GPUs.
cd ../ssl_pretraining/
python main.py --data_dir <path_to_preprocessed_data> --out_dir <path_to_results> --model_name <model_name>
## SUPERVISED FINETUNING ON AS DETECTION TASK ##
cd ../AS_detection/
# Finetune model from SSL initialization
python main.py \
--output_dir <path_to_ssl_model_results> \
--max_epochs 30 \
--patience 5 \
--batch_size 88 \
--label_smoothing 0.1 \
--use_class_weights \
--dropout_fc \
--augment \
--ssl <path_to_ssl_model_directory> \
--lr 0.1
# Finetune model from Kinetics-400 initialization
python main.py \
--output_dir <path_to_kinetics_model_results> \
--max_epochs 30 \
--patience 5 \
--batch_size 88 \
--label_smoothing 0.1 \
--use_class_weights \
--dropout_fc \
--augment
# Finetune model from random initialization
python main.py \
--output_dir <path_to_random_model_results> \
--max_epochs 30 \
--patience 5 \
--batch_size 88 \
--label_smoothing 0.1 \
--use_class_weights \
--dropout_fc \
--augment \
--rand_init
## ANALYSIS AND VISUALIZATION ##
# Run GradCAM on representative videos (5 true positives, 1 true negative, 1 false positive) and save output
python gradcam.py --data_dir <path_to_preprocessed_data> --out_dir <path_to_ssl_gradcam_output> --model_name ssl
python gradcam.py --data_dir <path_to_preprocessed_data> --out_dir <path_to_kinetics_gradcam_output> --model_name kinetics
python gradcam.py --data_dir <path_to_preprocessed_data> --out_dir <path_to_random_gradcam_output> --model_name random
# From GradCAM output, apply 2D max projection and overlay on frame from each video
python viz_gradcam.py --data_dir <path_to_preprocessed_data> --model_name ssl --gradcam_dir <path_to_ssl_gradcam_output>
python viz_gradcam.py --data_dir <path_to_preprocessed_data> --model_name kinetics --gradcam_dir <path_to_kinetics_gradcam_output>
python viz_gradcam.py --data_dir <path_to_preprocessed_data> --model_name random --gradcam_dir <path_to_random_gradcam_output>
# From GradCAM outputs for each model, generate frame-by-frame saliency maps. Save video showing overlaid saliency maps side by side by side.
python viz_gradcam_videos.py --data_dir <path_to_preprocessed_data> --gradcam_dirs <path_to_ssl_gradcam_output> <path_to_kinetics_gradcam_output> <path_to_random_gradcam_output>
# Get all results external test cohorts, output in .tsv format.
cd ../analysis/
bash get_results.sh
# Plot ROC and precision-recall (PR) curves
python plot_curves.py
# Plot graded relationship between model predictions and cardiologist-determined AS severity level
python AS_severity_violin_plots.py
# Perform analysis of performance on paradoxical low-flow, low-gradient (LFLG) AS cases
python lflg_analysis.py
MLA:
Holste, Gregory, et al. "Severe aortic stenosis detection by deep learning applied to echocardiography." European Heart Journal (2023): ehad456. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehad456.
BibTeX:
@article{holste2023,
author = {Holste, Gregory and Oikonomou, Evangelos K and Mortazavi, Bobak J and Coppi, Andreas and Faridi, Kamil F and Miller, Edward J and Forrest, John K and McNamara, Robert L and Ohno-Machado, Lucila and Yuan, Neal and Gupta, Aakriti and Ouyang, David and Krumholz, Harlan M and Wang, Zhangyang and Khera, Rohan},
title = "{Severe aortic stenosis detection by deep learning applied to echocardiography}",
journal = {European Heart Journal},
pages = {ehad456},
year = {2023},
month = {08},
issn = {0195-668X},
doi = {10.1093/eurheartj/ehad456},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehad456},
eprint = {https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/eurheartj/ehad456/51224730/ehad456.pdf},
}