The Zemoga Posts app has all the requirementes and extra points of the assignment.
The architecture of the app follows the best practices and recommended architecture for modern app development from the android developer guide using Clean Architecture in the Domain Layer following a simplified version of what has been published by Robert C Martin. This combination is also known as MVVM with Clean Architecture.
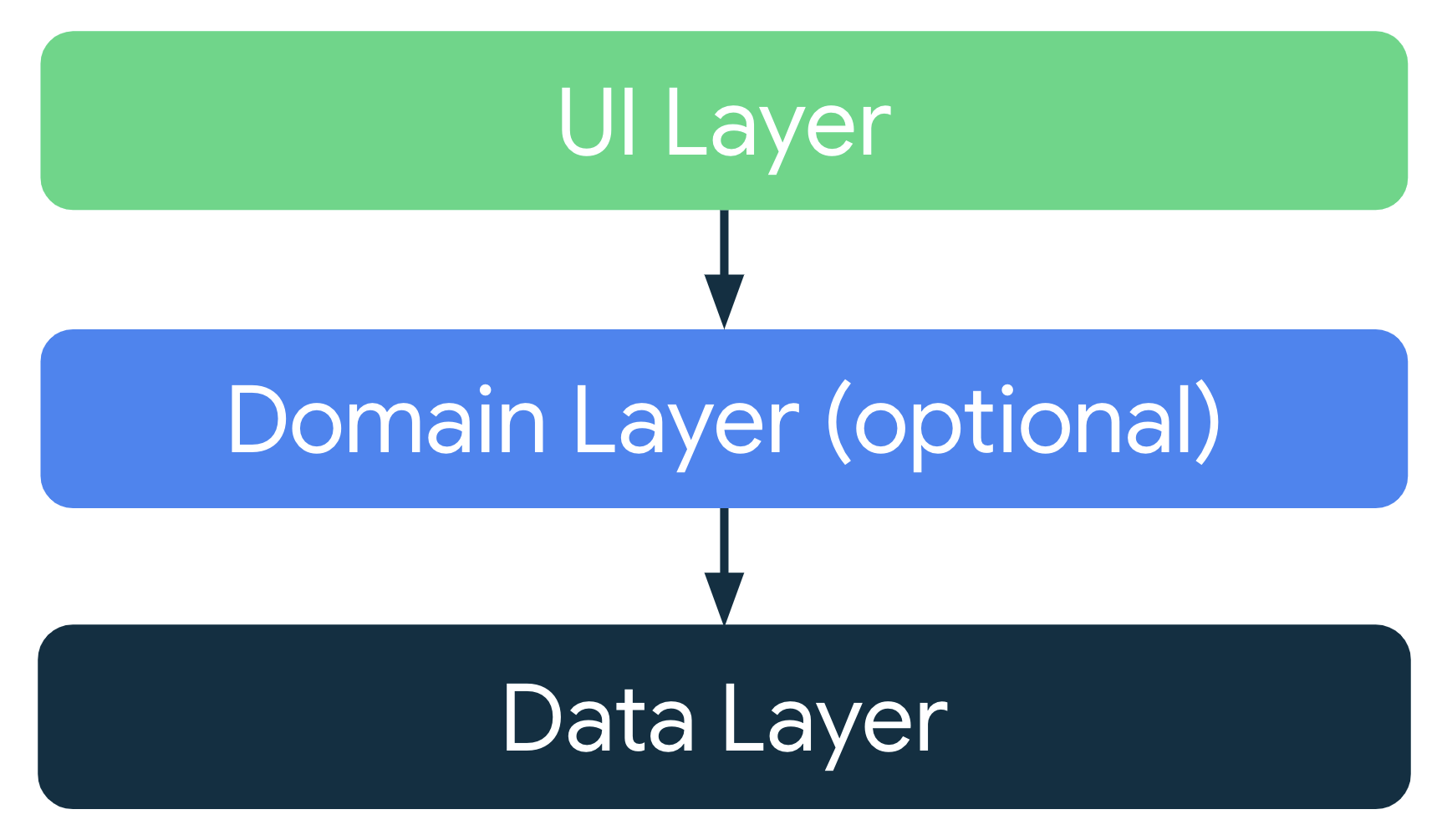
The overall architecture looks as shown on the image below:
The app has four main well-defined layers separated into packages
- Presentation:
- The Presentation layer, also known as UI layer, is responsible for displaying the application data on the screen and also serve as the primary entry point for user interaction.
- Inside the Presentation layer the app has the MainActivity which holds a NavHost that uses the Navigation library for adding Fragments and navigate through the app.
- In this layer the app has the
Activities,Fragmentsand itsViewModels.
- Data:
- The Data layer contains the application data itself and connects to the JSONPlaceholder API.
- Inside the Data layer the app has a Repository package that follows the
Repository Patternto fetch data. In this example data is fetched from the api which is accessed using the Retrofit library under the remote package. Finally there is a model package which is responsible for mapping the response we get from the API, here the app uses aDTOtype of class to convert between data models and domain models in order for the domain models to not have any dependency to the remote implementation selected.
- Domain:
- The Domain Layer sits between the Presentation and Data layers and it is responsible for encapsulating the business logic of the application.
- It is in this layer that the
UseCasesof the app will live. TheUseCasesare responsible for performing a business logic task - In here there is also a model package which contains the model classes of the app.
- Core:
- The core Layer contains some core classes that are used on the App.
- There is the
UseCaseabstract class definition and signature that should be extended by every UseCase. - A
CustomExceptionfor handling errors and aStateclass with three states (Loading, Success and Error).
Overall this architecture is very robust, follows the official android developer guideline and makes it easy to maintain and scale the application.
For unit testing the app currently only tests the UseCases which would have the business logic of the application.
For one of the tests it was necessary to mock the dependency of a repository in order to return mock data instead of actually fetching data from the server. The mock was done as a fake implementation that is provided as the dependency on the tests but it could also be done using any test mock library as well.
It would be nice to add tests for the ViewModel as well and also maybe setup some UI testing in the future.
This is a standard Android application, there are no special setup need. Just import the project into Android Studio and run the App.
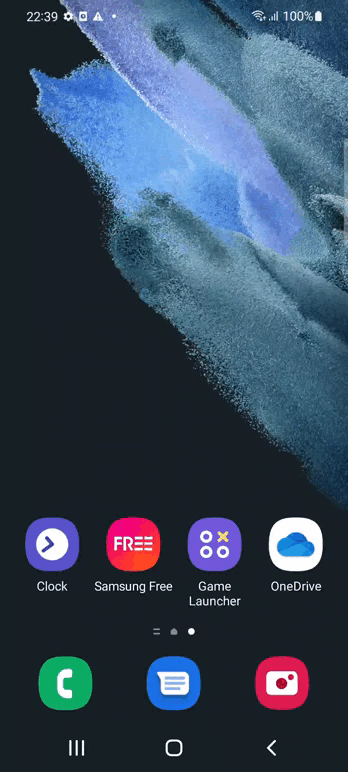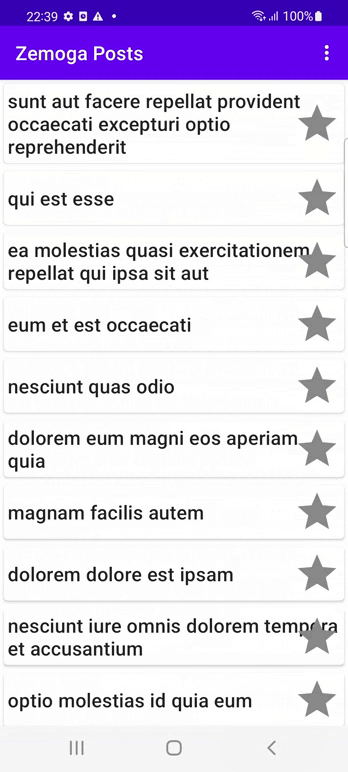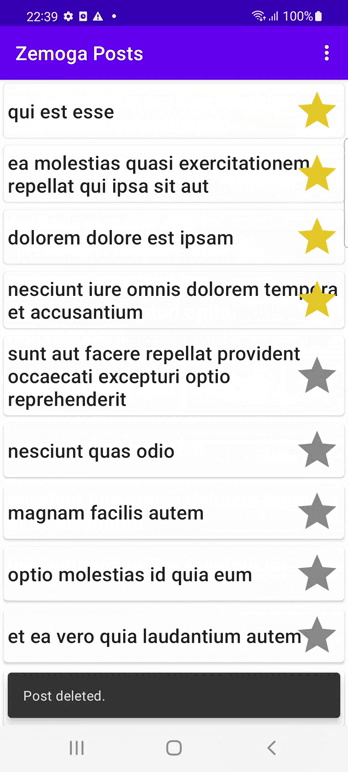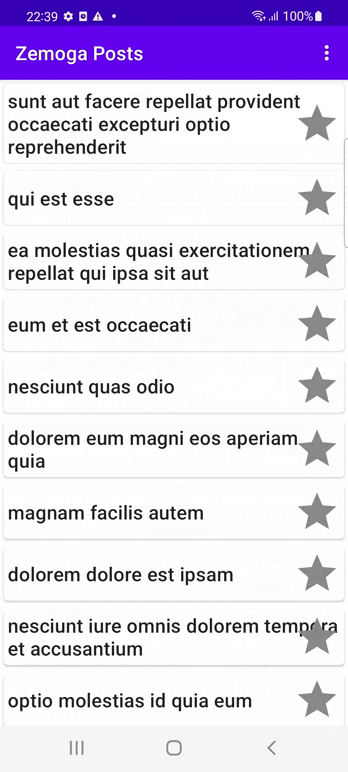
The following demo shows the app loading the posts from the JSON API and populating a RecyclerView with the title of the post and a favorite button. When a Post is tapped, the user is taken to to the Post Details Screen and it displays the Post details and its comments. When the user clcks on the favorite/unfavorite icon a post will be added to the favorites and will be shown at the top of the list with a yellow star indicator if it is not a favorite post the star icon will be grey. When a user swipes a post it gets deleted from the local storage and removed from the list. On the itens menu there are two optios: one for loading the posts from the API and update the cache and another one for removing all posts except the favorite ones.
The next demo shows that the app is an offline first app where the data retrieved from the API gets cached locally using Room and the user is able to see previously loaded posts if they don't have internet or can't access the API. All features from the previous demo work here as well.
The project was developed using some of the Android Jetpack Libraries and some third-party libraries as well.
- View/Data Binding: Feature that allows to write code that interacts with views, replacing the
findViewById. For more details see the official docs. - Navigation Component: Using the idea of a Single Activity and multiple Fragments, the Navigation Component is used to navigate between the views of the app. For more details see the official docs.
- Room: The Room persistence library provides an abstraction layer over SQLite to allow for more robust database access while harnessing the full power of SQLite. For more details see the official docs
- Kotlin coroutines: used to manage long-running tasks that might otherwise block the main thread. For more information see The Kotlin coroutines official doc for Android
- Koin: Library for dependency injection using a service locator in order to provide dependencies to the app. For more details see the official docs
- Retrofit + OkHttp: Http clients to simplify the communication with the JSONPlaceholder API. Official doc
- Moshi: Used to deserialize the JSON API response into a Kotlin Data Class; Official doc