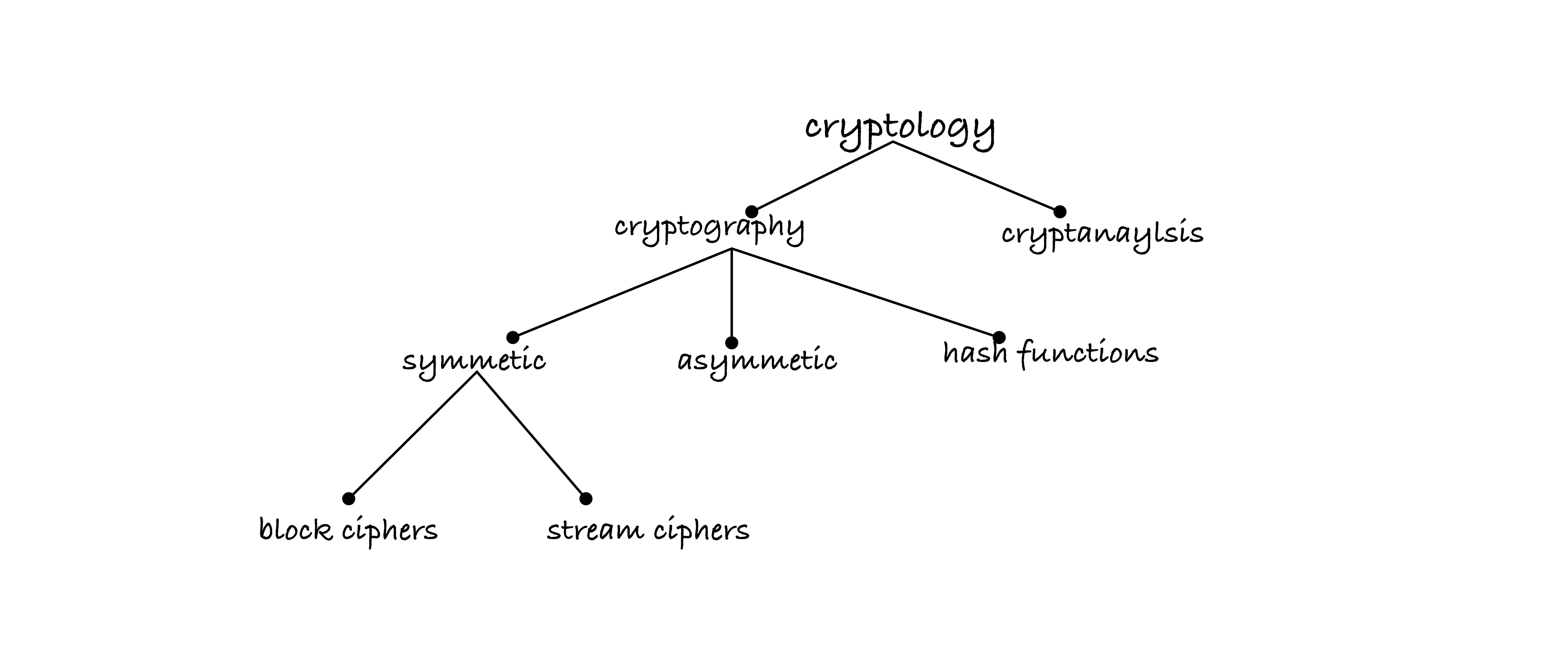
Cryptography broken down into:
TranspositionSubstitution
Codes: systems in which individual words, phrases, or even whole sentences are replaced with specific code words or symbols.
Ciphers: cryptographic techniques that involve the transformation of individual characters or blocks of characters in a systematic way.
Nomenclators: specific type of code used for secret communication.
- monoalphabetic
- Polyalphabetic
- Caesar’s Cipher
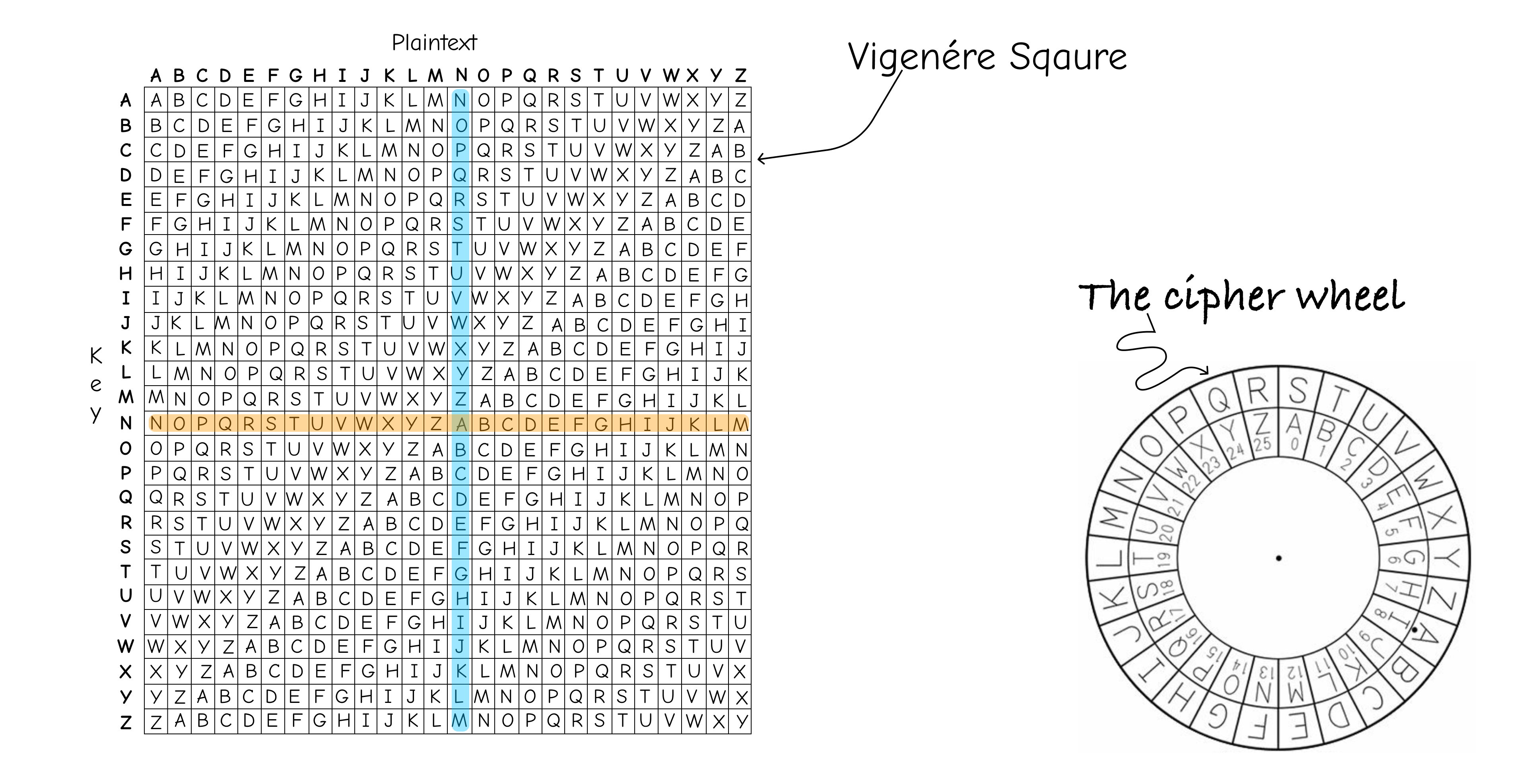
- Vigenere Cipher
- Enigma Cipher
- AES (Variant of Rijndael)
Good to Know: Keyspace is the entire range of values that can be used to construct an individual key
- Symmetric Encryption (Private encryption)
- DES, 3DES
- AES (Rijndael)
- Blowfish
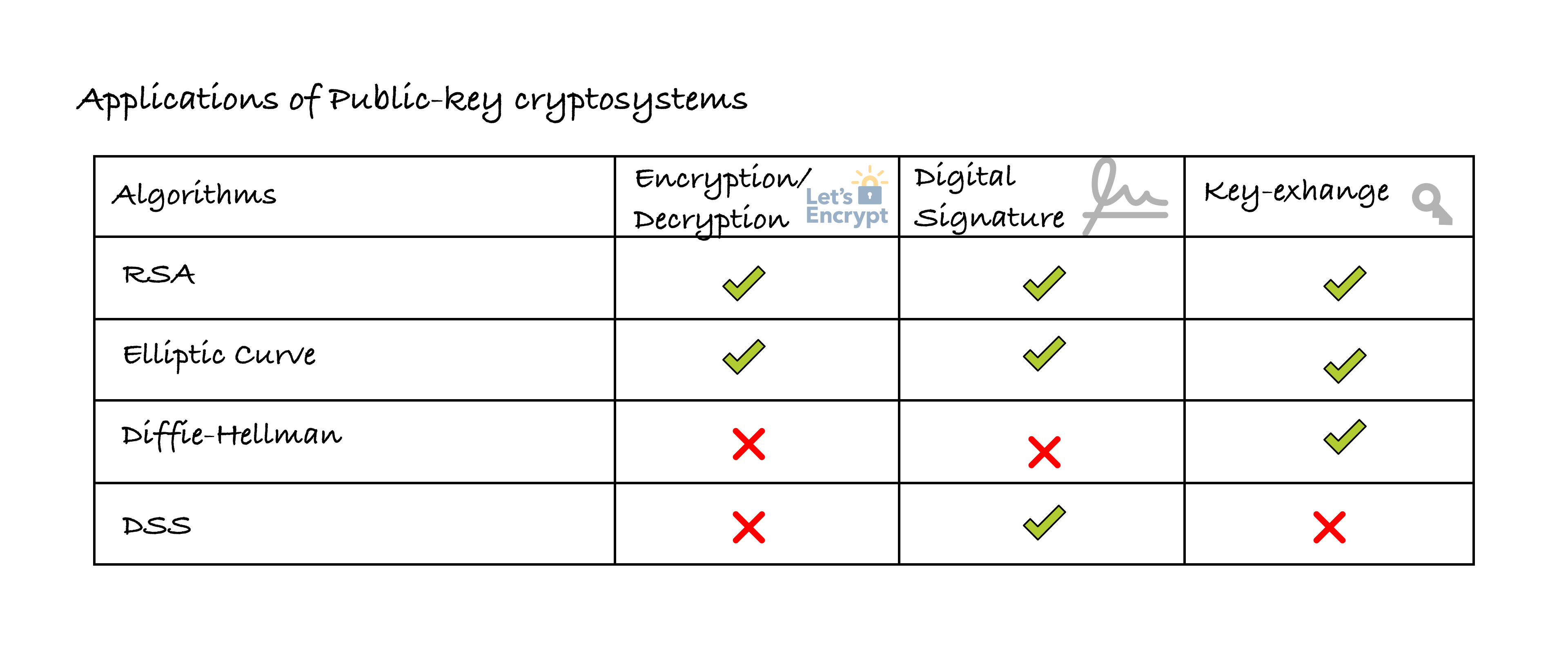
- Asymmetric Encryption (Public encryption)
- ECC (Elliptic Curve Crytography)
- RSA
- Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange
- The ElGamal public-key encryption scheme
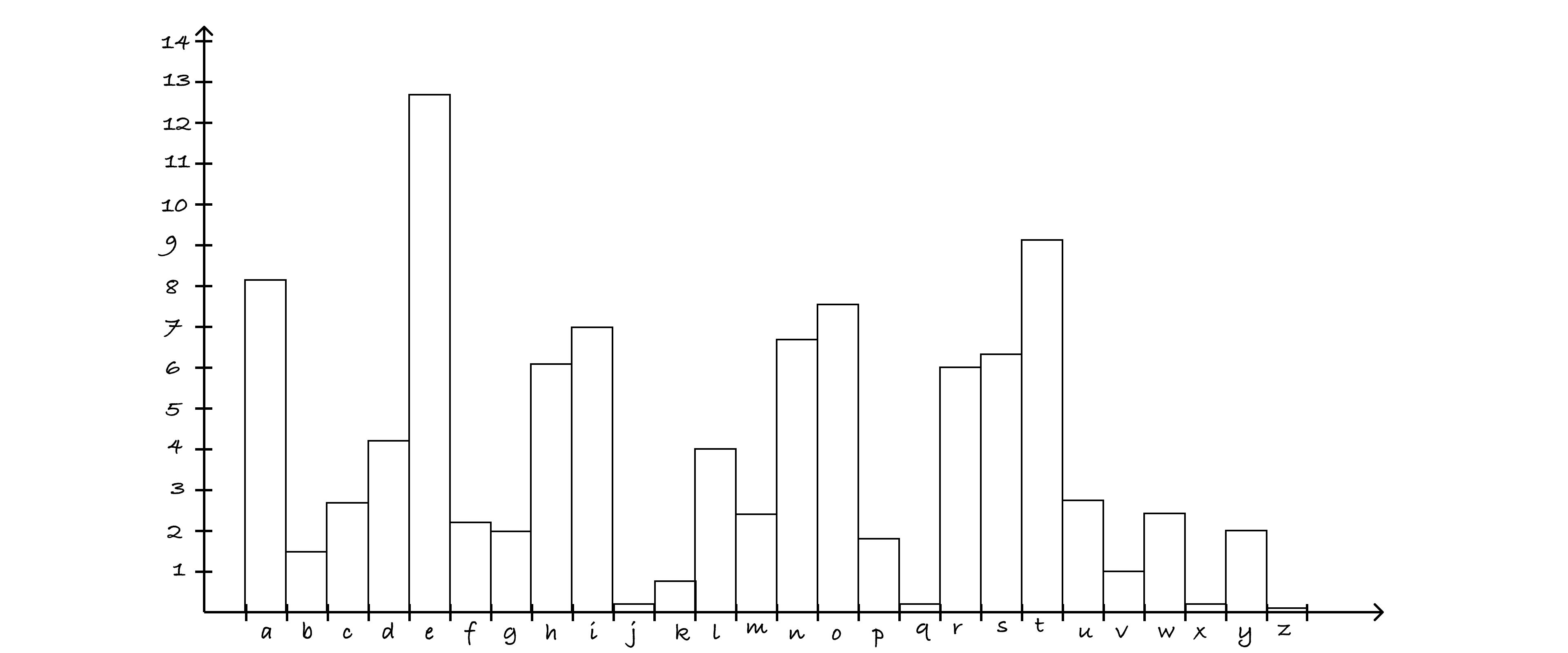
Letter frequency analysis is a fundamental technique in cryptography used to analyze and break substitution ciphers, particularly monoalphabetic ciphers. It's based on the observation that in most languages, certain letters and combinations of letters appear with different frequencies. forexample in the english language, e is the most common letter and the is the most common word. Alpha Frequency, related Google Web Trillion Word Corpus
Create a Python program that encrypts and decrypts given text using the Caesar cipher. A user should be prompted for input i.e. the text to encrypt/decrypt and the key (number of shifts to make).
def caesar_cipher(text, key, mode):
"""
Encrypts or decrypts a given text using the Caesar cipher.
:param text (str): The text to be encrypted or decrypted.
:param key (int): The key (number of shifts) to be used for encryption or decryption.
:param mode (str): The mode of operation, either 'encrypt' or 'decrypt'.
:return (str): The encrypted or decrypted text.
"""
result = ""
for char in text:
if char.isalpha():
shift = key % 26
if char.islower():
if mode == 'encrypt':
shifted_char = chr(((ord(char) - ord('a') + shift) % 26) + ord('a'))
elif mode == 'decrypt':
shifted_char = chr(((ord(char) - ord('a') - shift) % 26) + ord('a'))
elif char.isupper():
if mode == 'encrypt':
shifted_char = chr(((ord(char) - ord('A') + shift) % 26) + ord('A'))
elif mode == 'decrypt':
shifted_char = chr(((ord(char) - ord('A') - shift) % 26) + ord('A'))
else:
shifted_char = char
result += shifted_char
return result
def main():
while True:
print("Caesar Cipher")
print("1. Encrypt")
print("2. Decrypt")
print("3. Quit")
choice = input("Enter your choice (1/2/3): ")
if choice == '1':
text = input("Enter the text to encrypt: ")
key = int(input("Enter the key (number of shifts): "))
encrypted_text = caesar_cipher(text, key, 'encrypt')
print("Encrypted text:", encrypted_text)
elif choice == '2':
text = input("Enter the text to decrypt: ")
key = int(input("Enter the key (number of shifts): "))
decrypted_text = caesar_cipher(text, key, 'decrypt')
print("Decrypted text:", decrypted_text)
elif choice == '3':
print("Goodbye!")
break
else:
print("Invalid choice. Please enter 1, 2, or 3.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
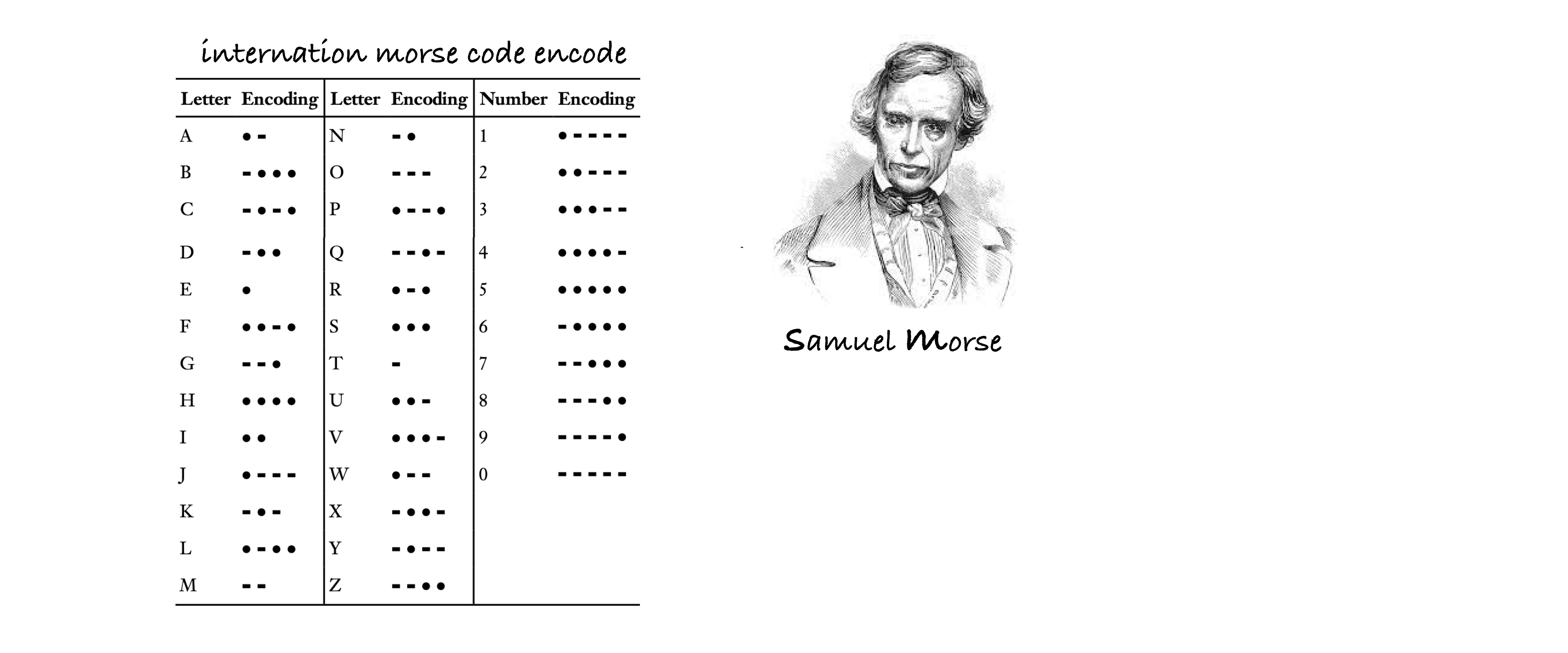
main()(Not directly related to cryptology)
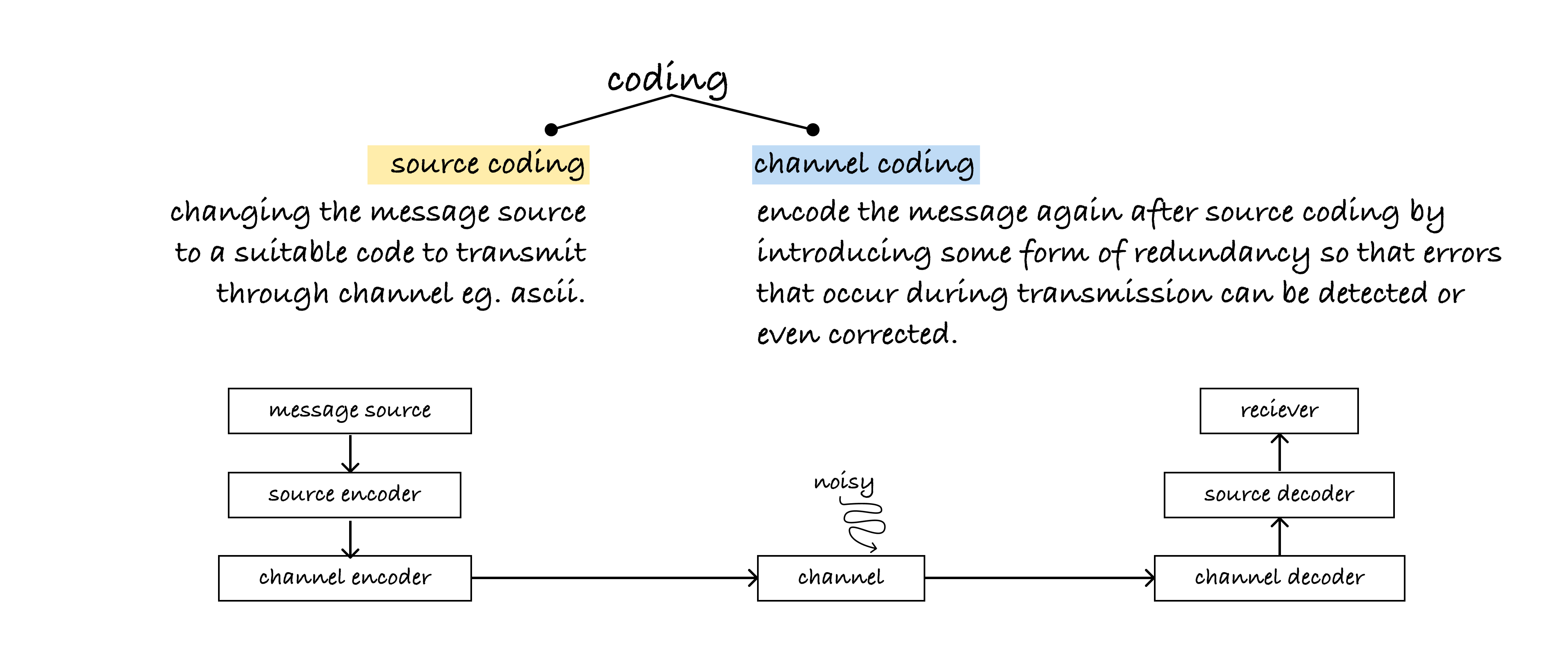
Coding Theory is a branch of mathematics concerned with transmitting data across noisy channels and recovering the messages.
- Detect errors
- or even Correct errors
Parity code in coding theory is a type of error-detecting code that is used to detect errors in data transmission or storage. It involves adding an extra bit (or more) to a block of data to ensure that the total number of bits in the block, including the extra bits, adheres to a specific parity rule. The parity bit only detects errors.
Channels: physical medium through which information is stored or transmitted
Noise: any unwanted or random interference or distortion that affects the transmission or storage of data e.g. rain, lighting.
- Backward Error Correction
- Receiver only detects the errors
- Forward Error Correction
- Receiver corrects a certain amount of errors.
- fast encoding messages
- Easy transmission of encoded messages
- Fast decoding of received messages
- Maximum transfer of information
- Beautiful Mind
- Imitation Game
- Mr. Robot