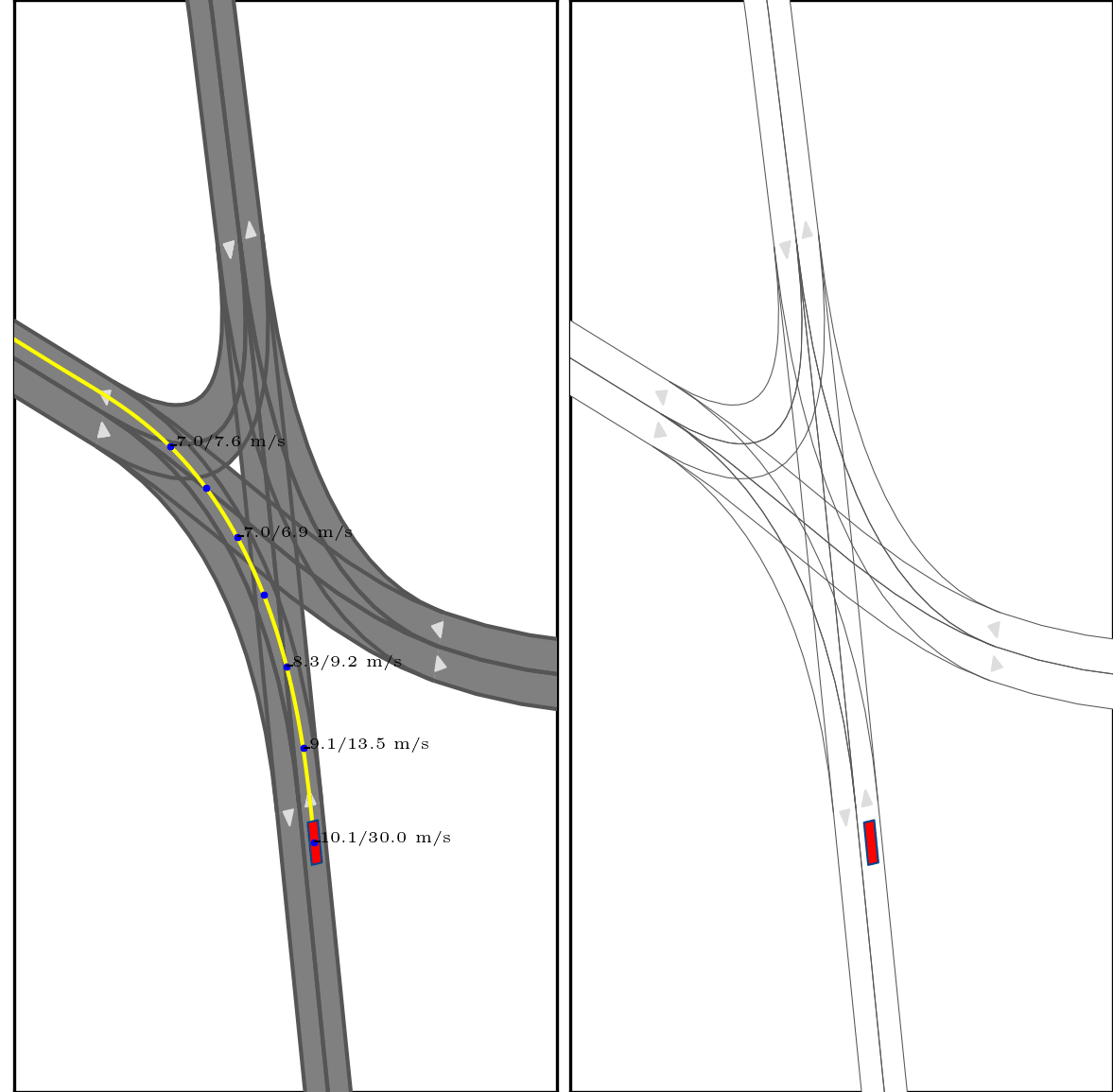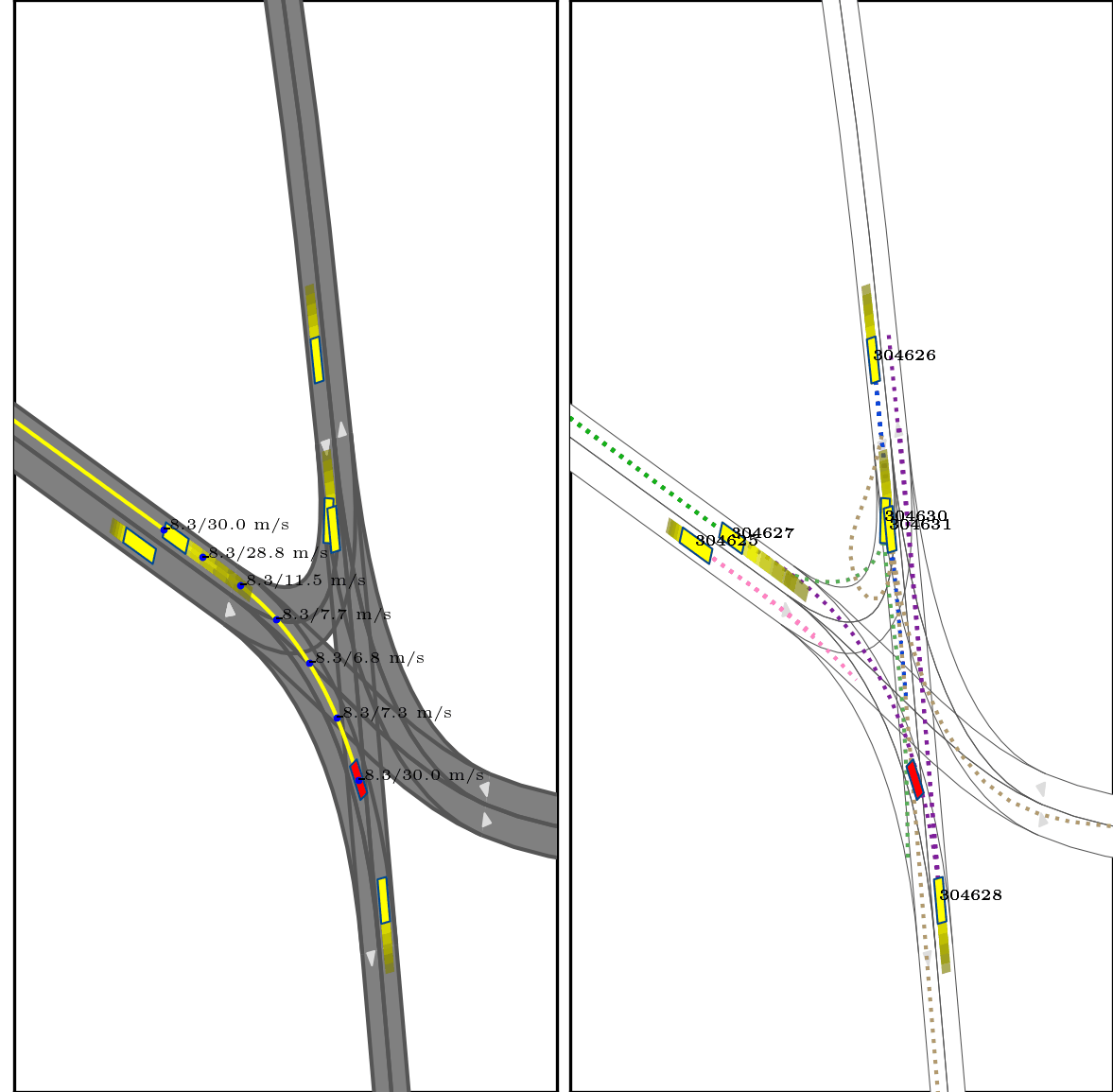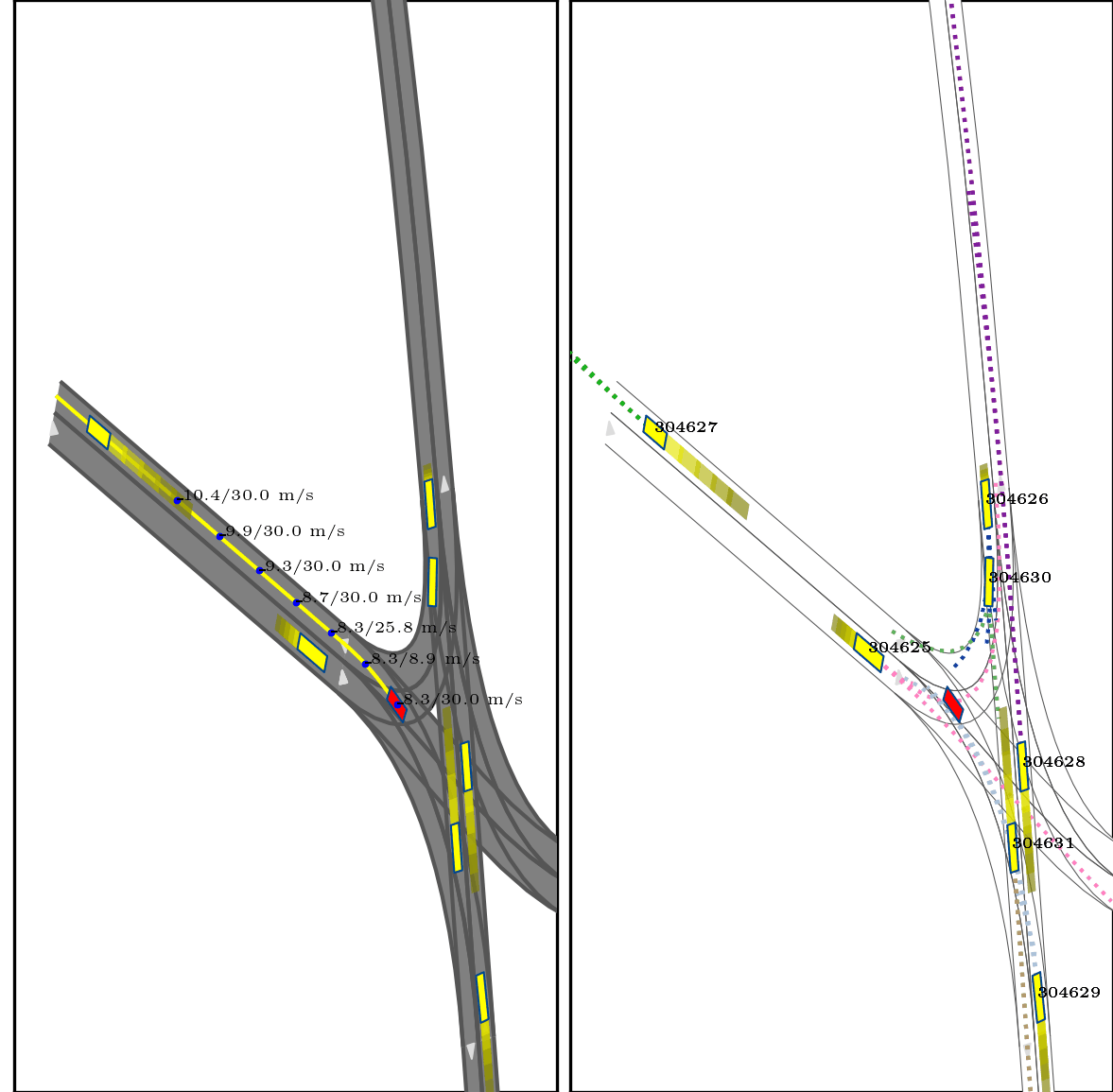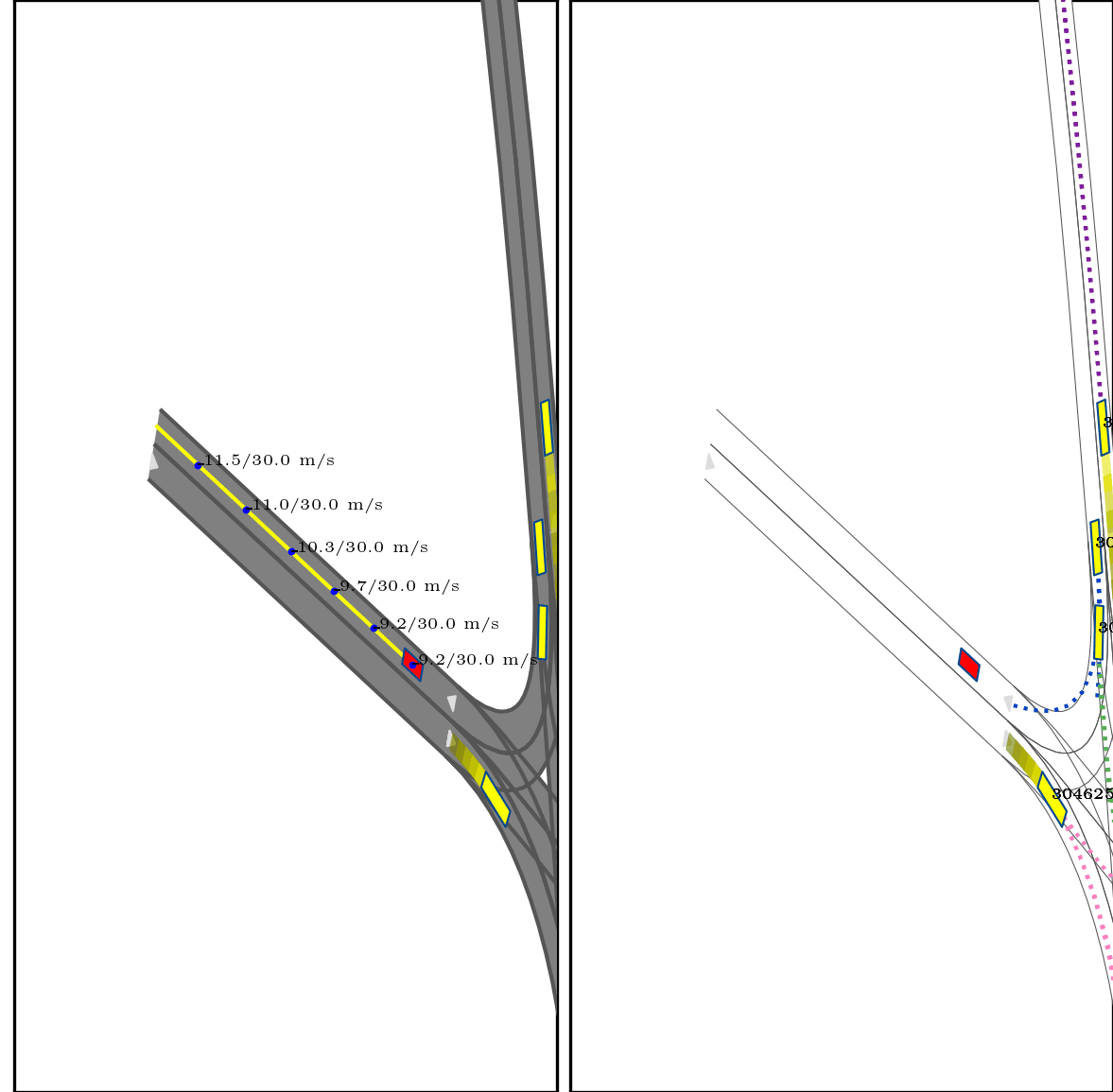
Our approach integrates interaction modeling into s-t planning by recording and updating interaction relationships for every planned state throughout the planning process. More specifically, the interaction relationships are modified through forward search, guided by the interaction formulations we put forth. These formulations clarify appropriate interaction dynamics, encompassing reactions (e.g., overtaking and yielding), and delineate strategies to influence the trajectories of other agents, providing guidance on the timing and execution of these actions.
Simulation Verification: The proposed planning method is validated under prediction results from pgp-network [1] in Commonroad [2] closed-loop simulation.
BibTex: If you find this repository useful, please consider giving us a star 🌟 and citing it by
@article{chen2024ir,
title={IR-STP: Enhancing Autonomous Driving With Interaction Reasoning in Spatio-Temporal Planning},
author={Chen, Yingbing and Cheng, Jie and Gan, Lu and Wang, Sheng and Liu, Hongji and Mei, Xiaodong and Liu, Ming},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems},
year={2024},
publisher={IEEE}
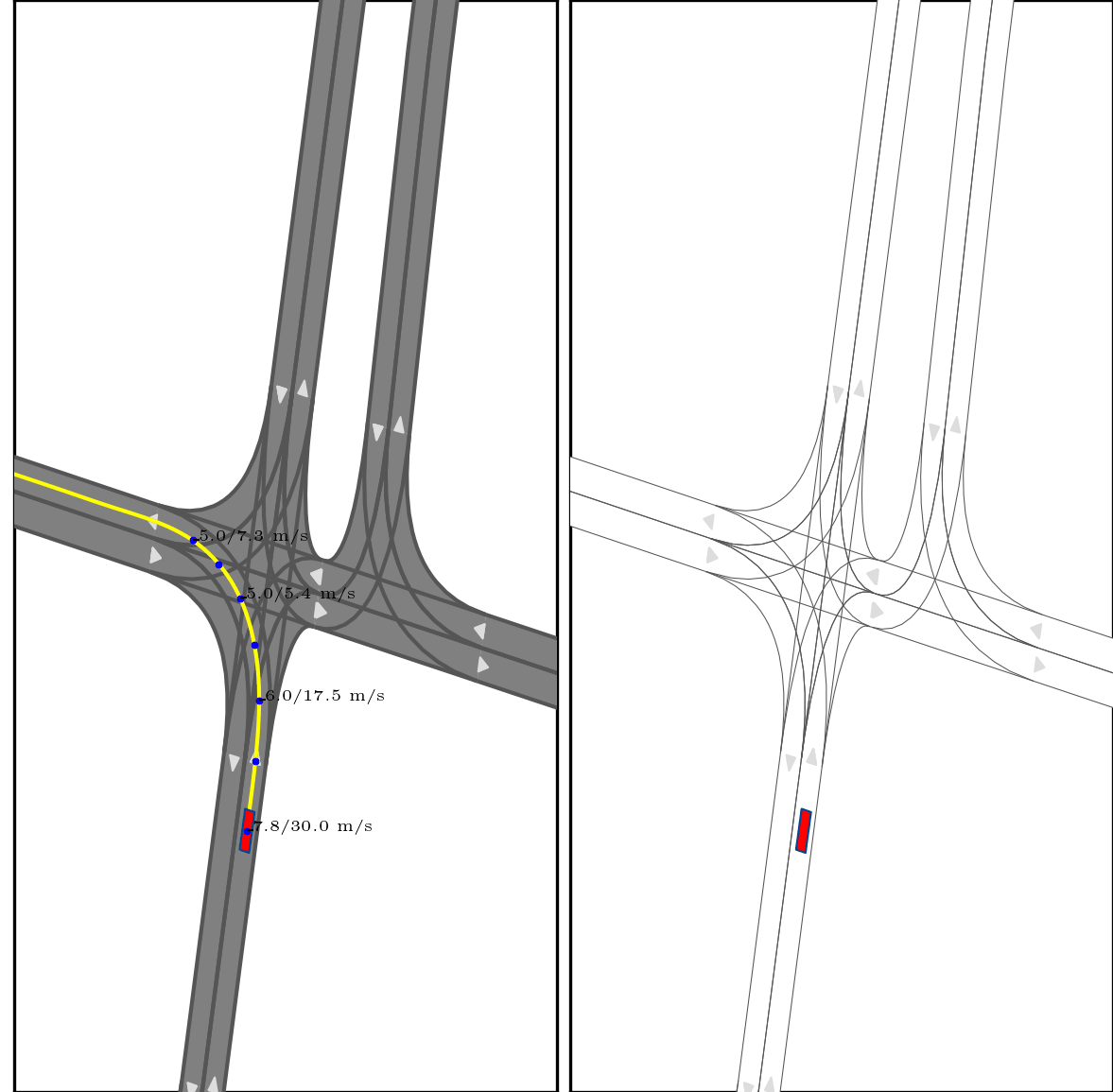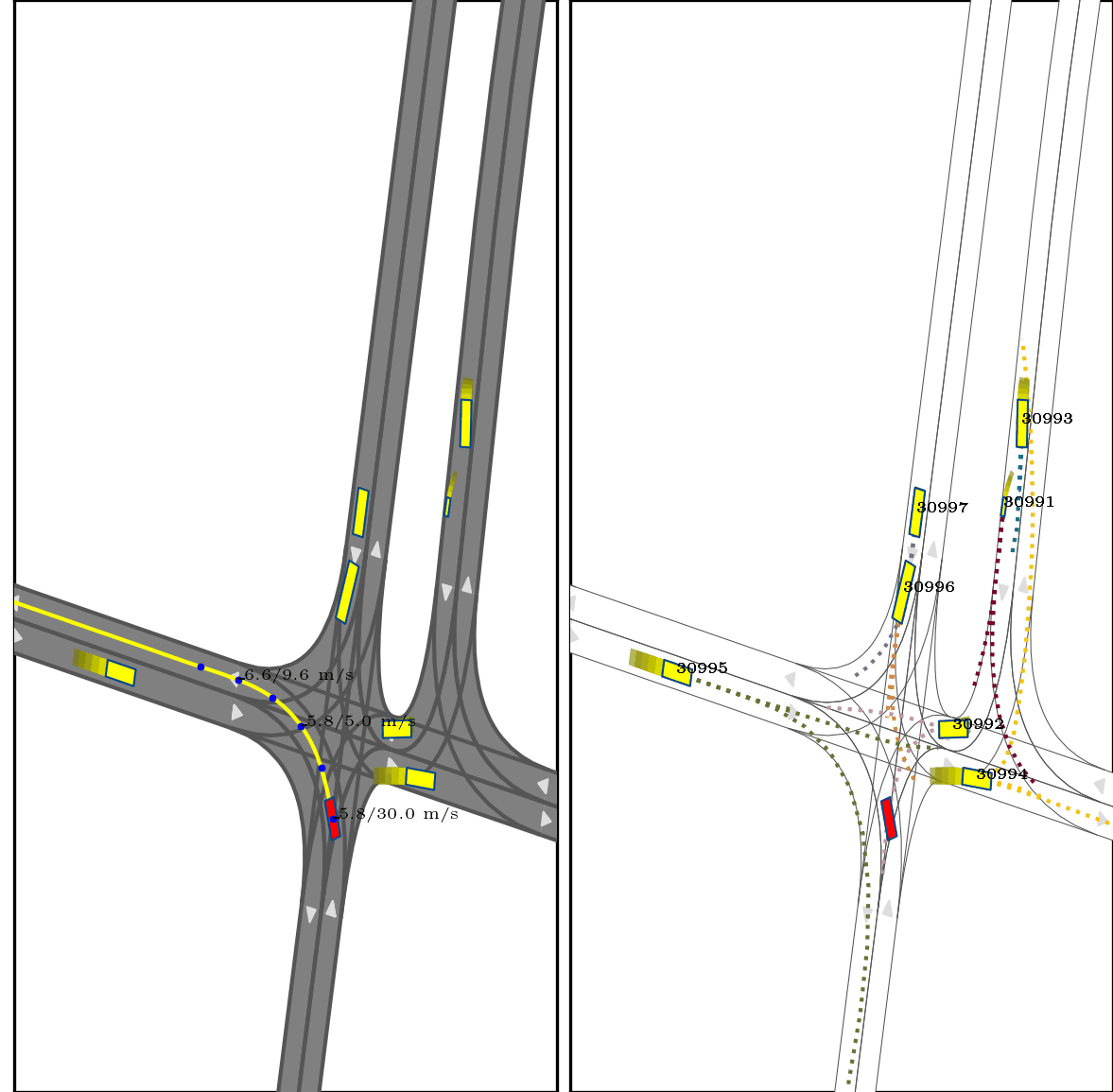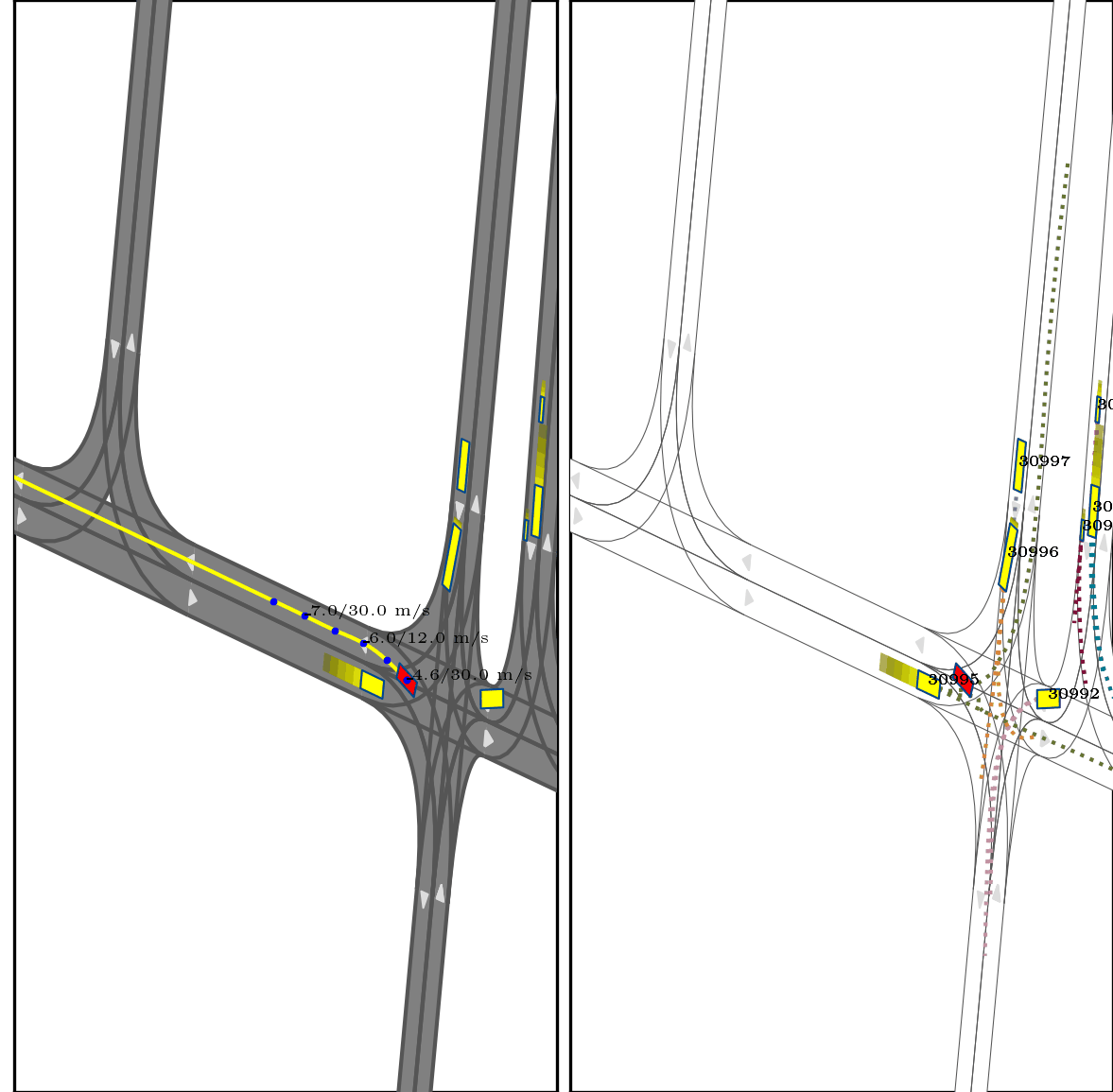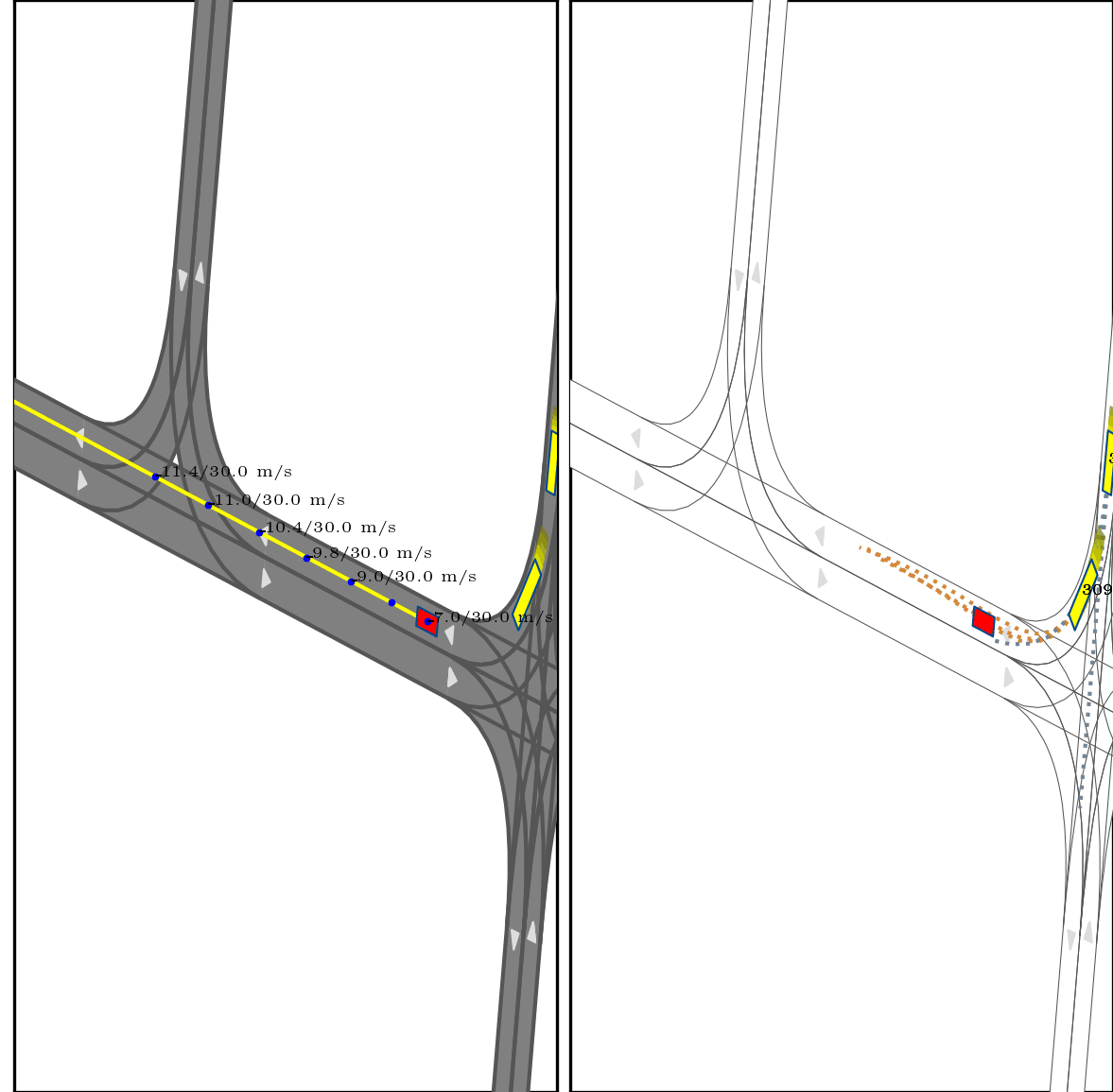
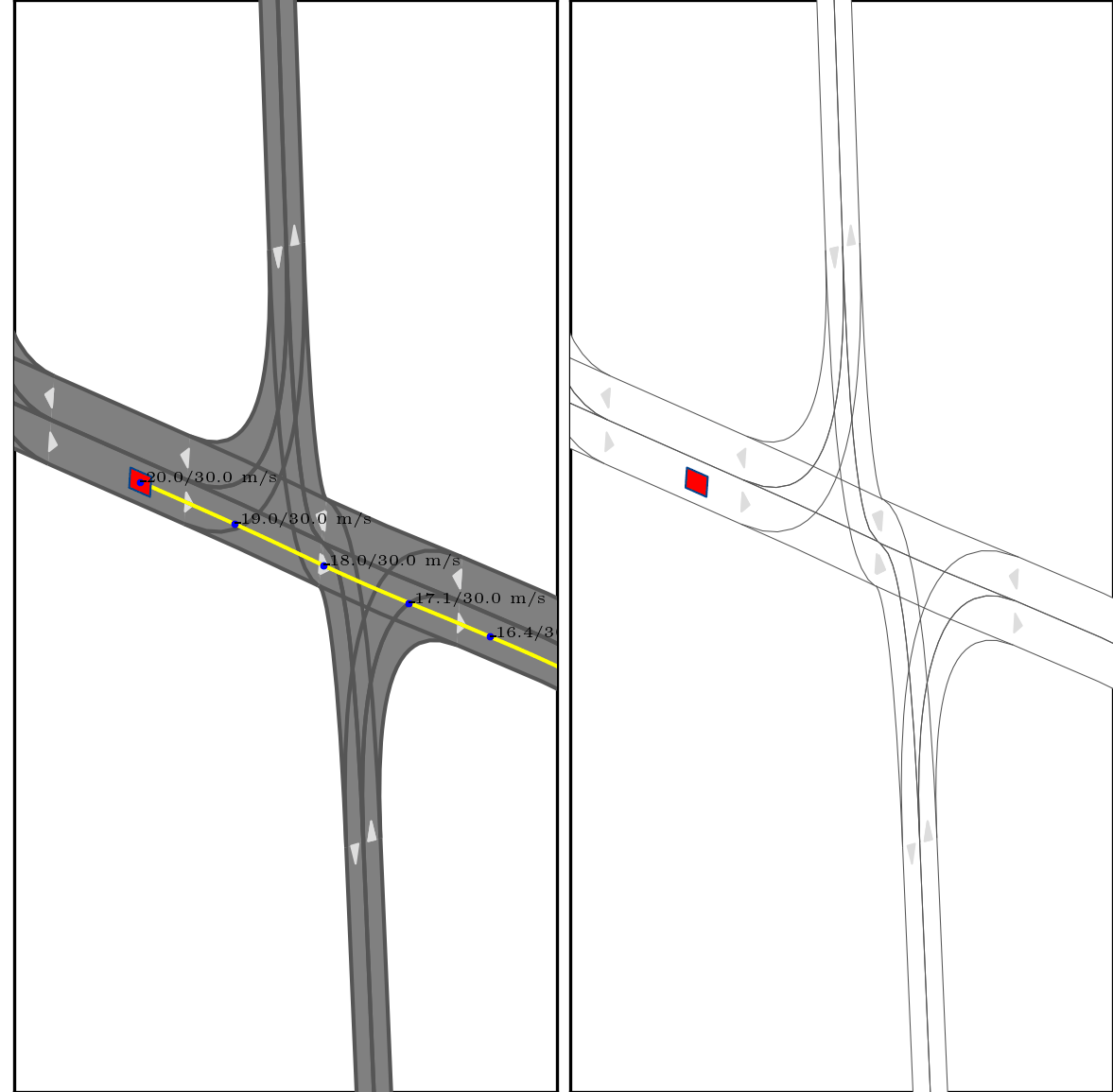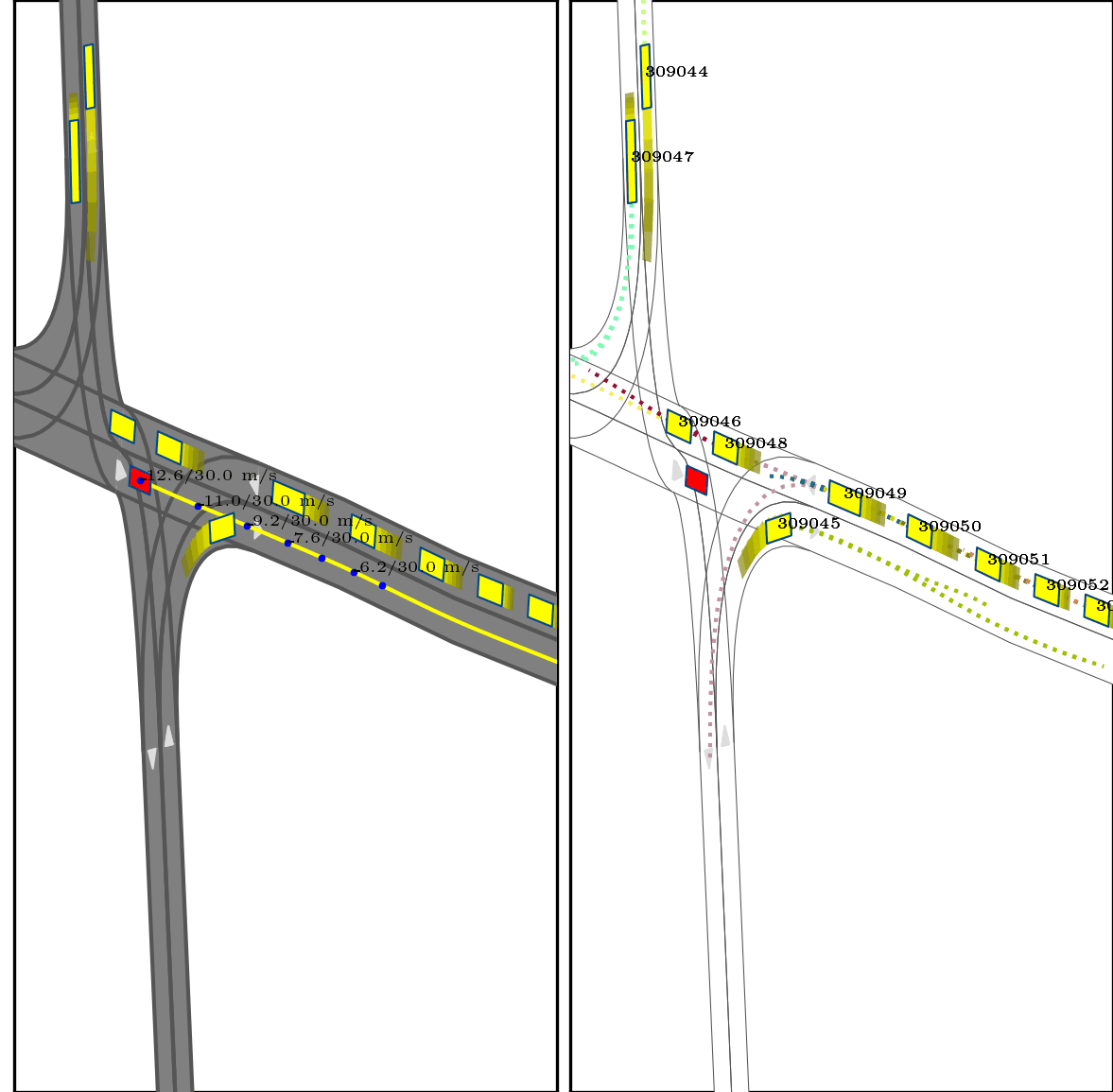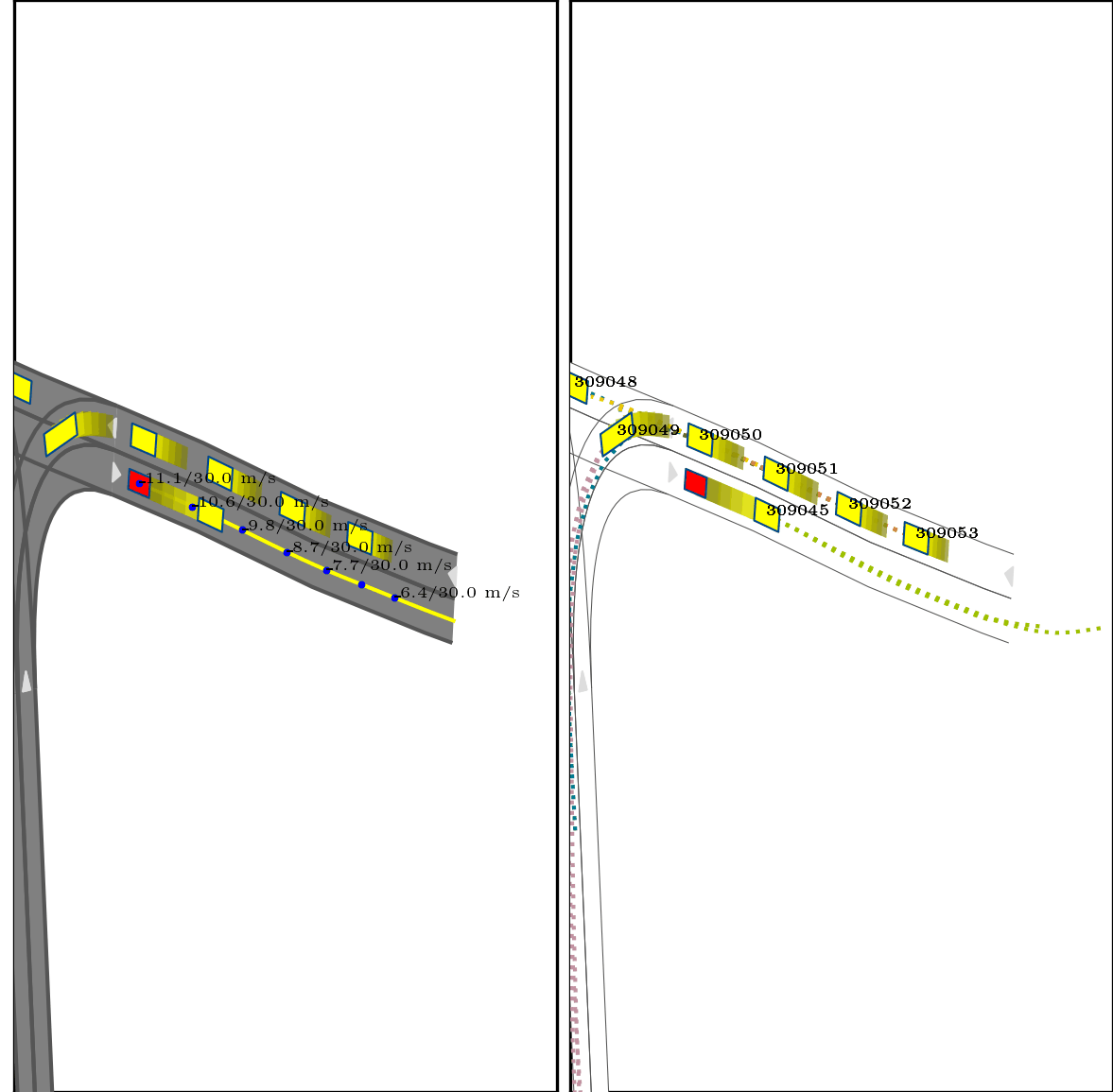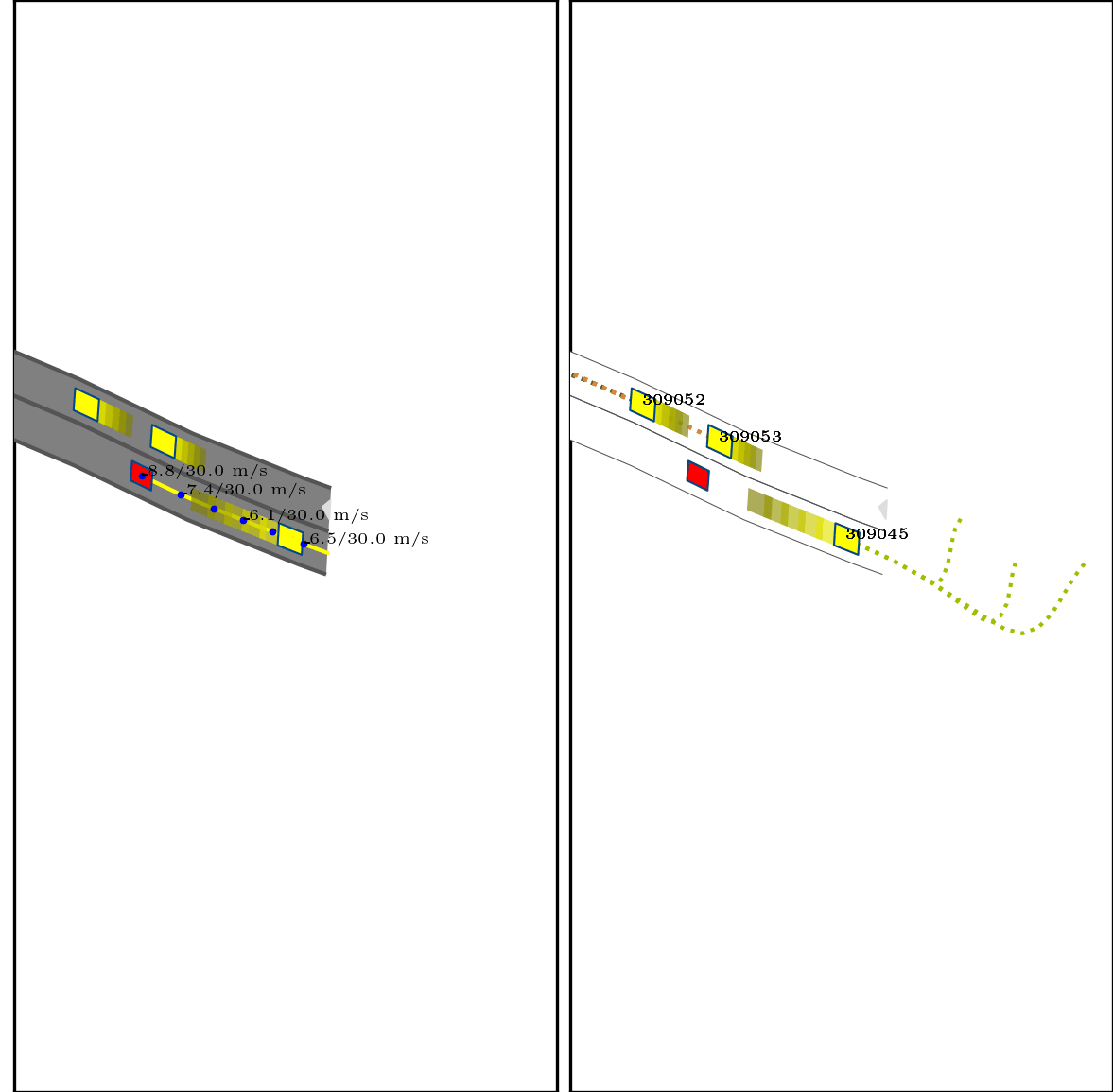
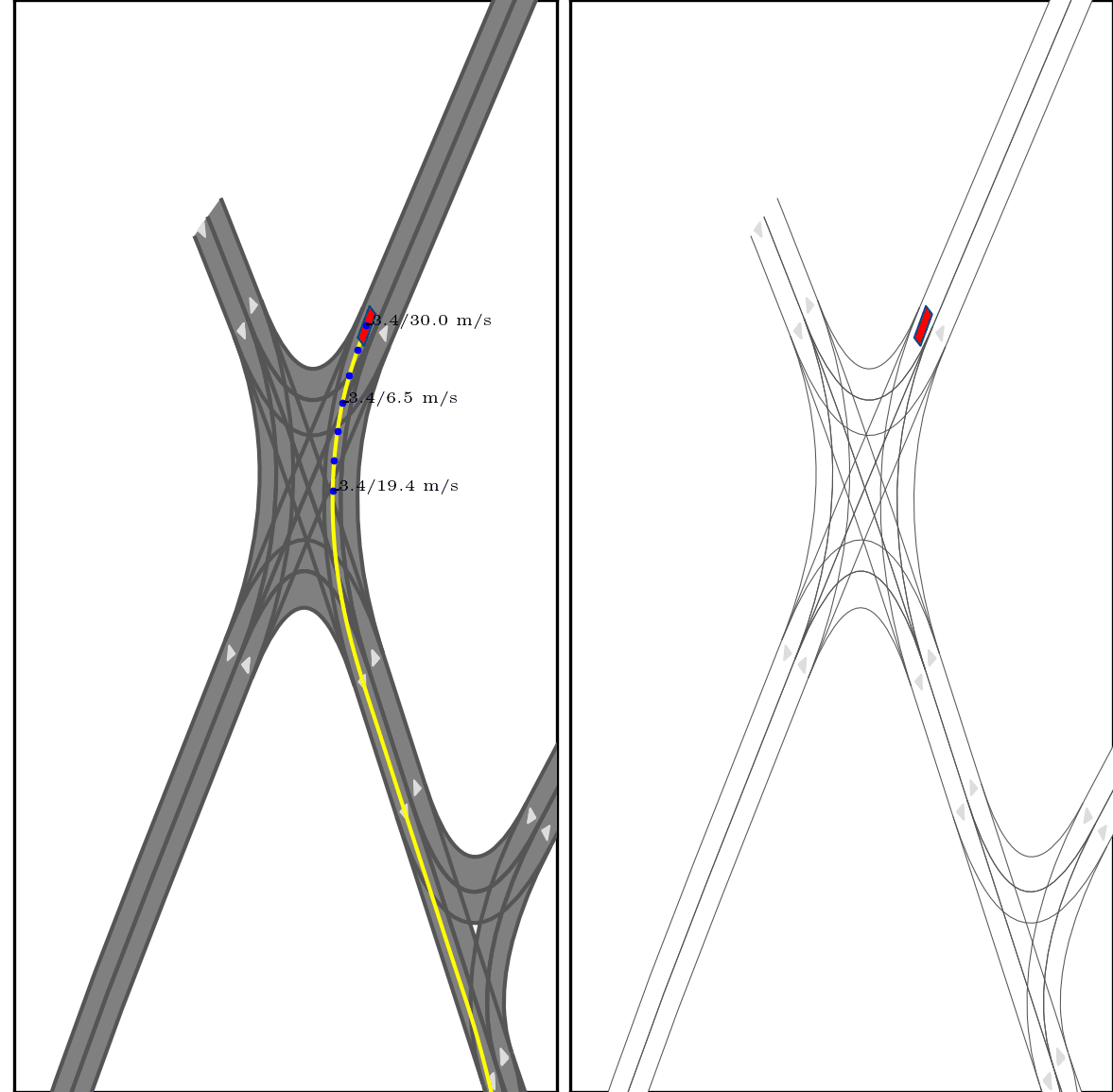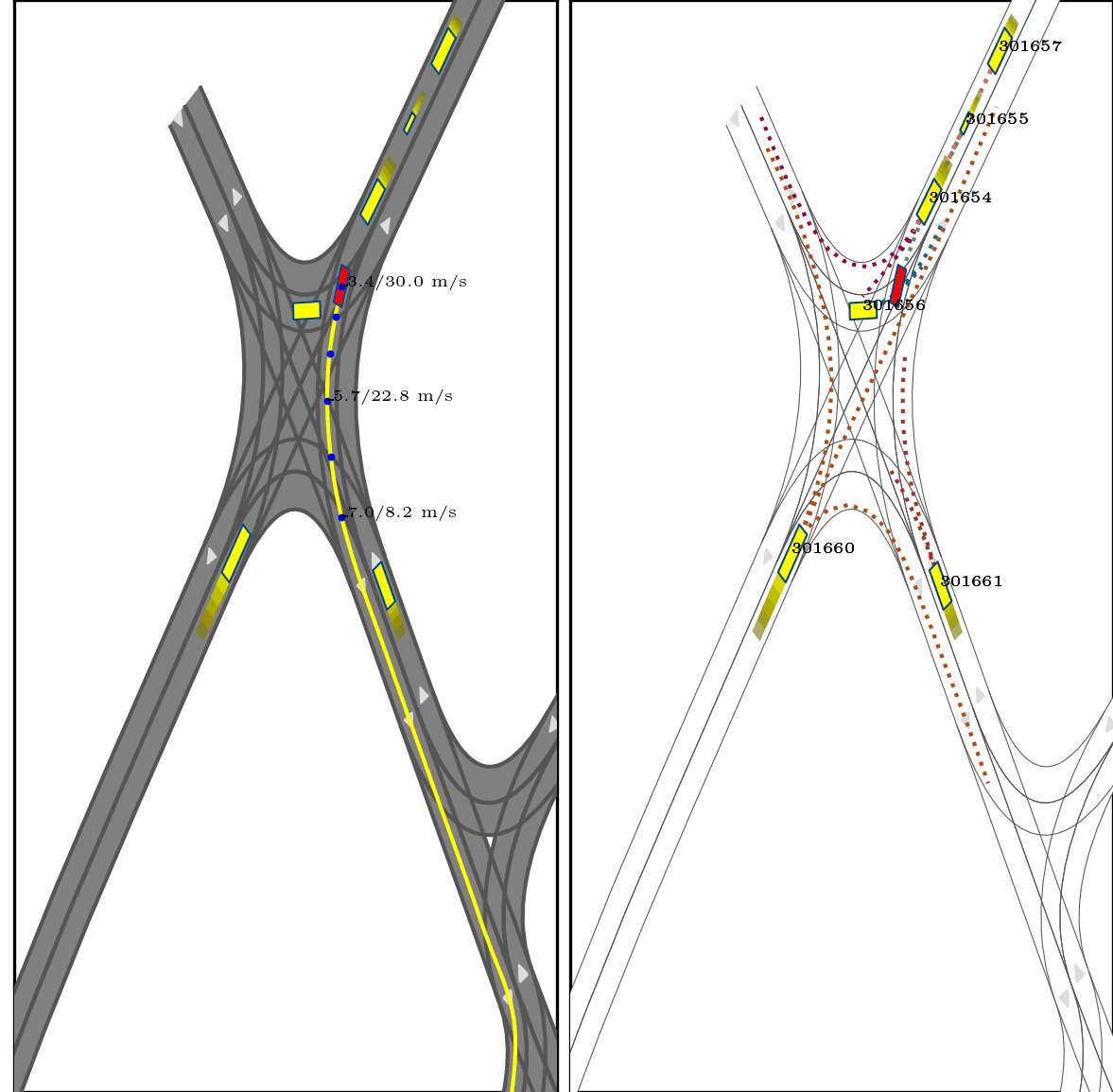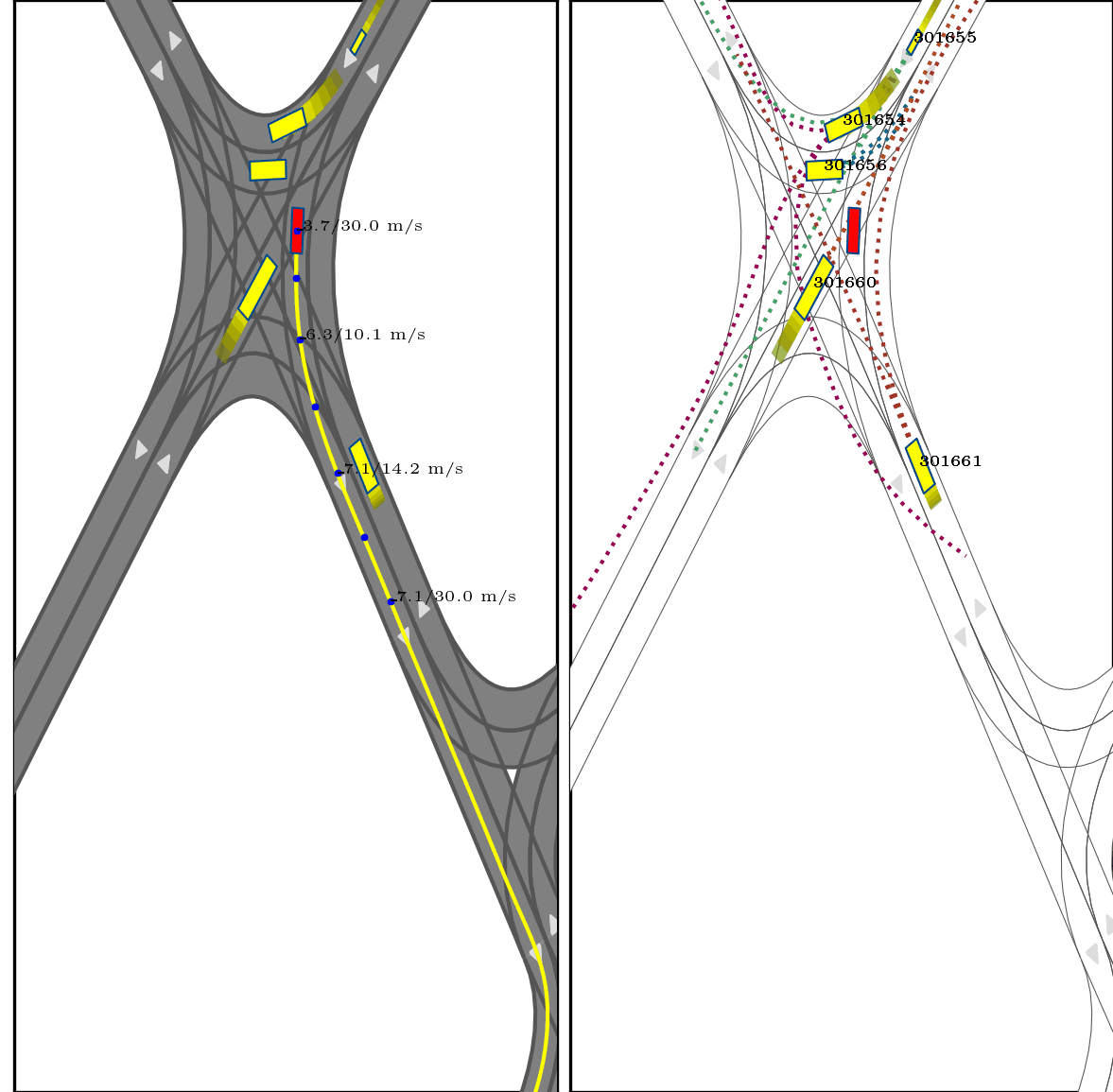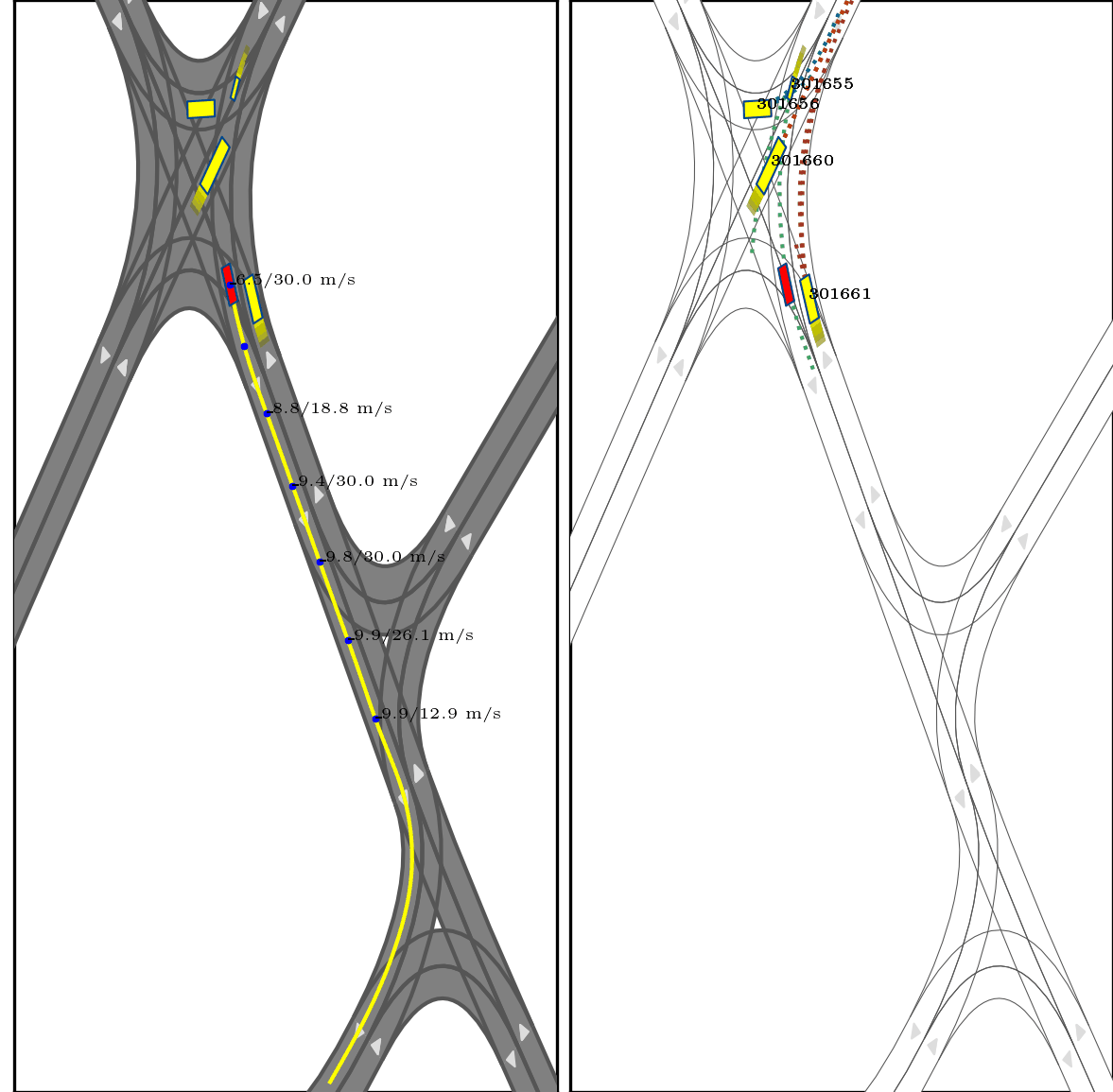
}Below show part of experimental results, for more details, pls see arxiv.
Red box: ego vehicle;
Yellow line (left): the reference route;
Blue points (left): the planned trajectory;
dotted lines (right): multi-modal prediction results;
- 15/01/2024 Accepted by IEEE T-ITS.
- 07/11/2023 Initialize paper link
- 15/08/2023 Submitted.
- 28/07/2023 Initialization.
The code and tutorial have been released, any questions or inquiries are welcomed.
Code includes
- Training/Evaluation codes of pgp prediction networks implemented in Commonroad Env.
- The proposed IR-STP planning method.
- Evaluation tools Commonroad Env., including solution caching as well as metric extraction.
Tutorials see documentation ./docs/tutorial.md.
References:
[1] Deo N, Wolff E, Beijbom O. Multimodal trajectory prediction conditioned on lane-graph traversals[C]//Conference on Robot Learning. PMLR, 2022: 203-212.
[2] Althoff M, Koschi M, Manzinger S. CommonRoad: Composable benchmarks for motion planning on roads[C]//2017 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV). IEEE, 2017: 719-726.
[7] Cui A, Casas S, Sadat A, et al. Lookout: Diverse multi-future prediction and planning for self-driving[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. 2021: 16107-16116.
[8] Pan Y, Lin Q, Shah H, et al. Safe planning for self-driving via adaptive constrained ILQR[C]//2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). IEEE, 2020: 2377-2383.