The code and related document is in this repo
Behavioral Cloning Project
The goals / steps of this project are the following:
- Use the simulator to collect data of good driving behavior
- Build, a convolution neural network in Keras that predicts steering angles from images
- Train and validate the model with a training and validation set
- Test that the model successfully drives around track one without leaving the road
- Summarize the results with a written report
My project includes the following files:
- model.py containing the script to create and train the model
- drive.py for driving the car in autonomous mode
- model.h5 containing a trained convolution neural network
- README.md summarizing the results
Using the Udacity provided simulator and my drive.py file, the car can be driven autonomously around the track by executing
python drive.py model.h5The model.py file contains the code for loading the images, training and saving the convolution neural network. the main function 'train_model()' finsish the acutual work.
The model is in the function 'model_navidia2b()'.(line 428-500) This model use Navidia End to End training model.
It consists of 7 conv layer and 4 fully connect layer.
The paper not mentioned about the activation and drop. I use RELU as activation fucntion and add 0.2 drop at conv layer and 0.5 drop at fully connect layer.
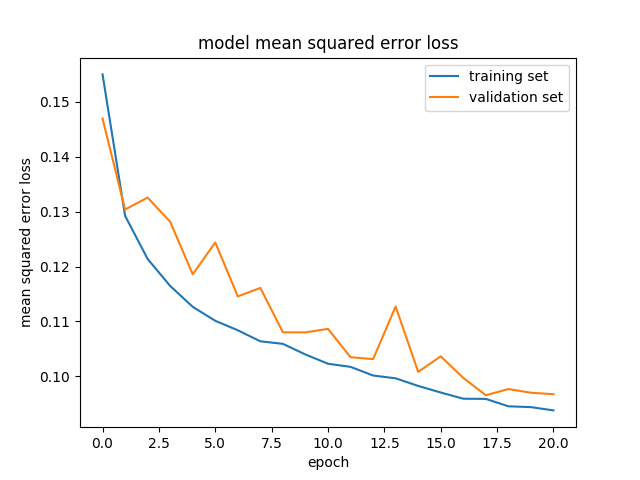
The model was trained and validated on different data sets to ensure that the model was not overfitting. It use track 1 data provide by Udacity and Track 2 data collect on local enviroment. In line 574, train_model function indicate the data source and data handleing and training parameters.
train_model(data_path=('./data/', './data_t2_2/', './data_t2_reverse/'), sample_rate=1, data_sub_read=False, data_sample_balance=0.01, sides_image=True, sides_image_offset=0.3, data_augmentation=3,
model='nvidia2b', input_color='YUV', learn_par=(0.001, 256, 30))The model used an adam optimizer, mse cost function and a callback fucntion for earlystopping. line(489, 495) Use the adam optimizer default setting. Change the batch_size from default 32 to 256. Epoch = 30, but has callback earlystopping to monitor.
The simulator could provide the center/left/right camera image @160X320 RGB. Three image used. Left/right image was adjust by offset compare with center image.
Training the model use the Udacity data. Load the center image and right/left image same time.
Serveral adjust points:
- the left/right image offset
- center image straight/curve data ration
- data augmentation
After try the left/right offset 0.06, 0.11, 0.22, 0.3, find 0.11-0.22 is suitable for the track 1. The Udacity provided data include 8036 samples. More than half of the samples, the steering value is <0.02. After several try, keep 20% of the 'zero' data is a reaonable ration could keep a balance of straight/curve data. To generate more data, randomly ratate and shift the image. (1x augmentation seems engough for track 1)
after handle the imput data, the model work well, try drive the car use the model in differet speed.
30MPH, the screen shot could find here.
Track 2 need more data. Collect the track 2 data two loop in clockwise and anticlockwise. Use the same stragety of track 1, adjust the left/right offset, center image straight/curve data ration and data augmentation.
The model could work at 10MPH, but fail at 20MPH.
10MPH, the screen shot could find here.
20MPH, failed.
The training of Track 2 use a EarlyStopping call back. 30 epochs, stop at 20 epochs.