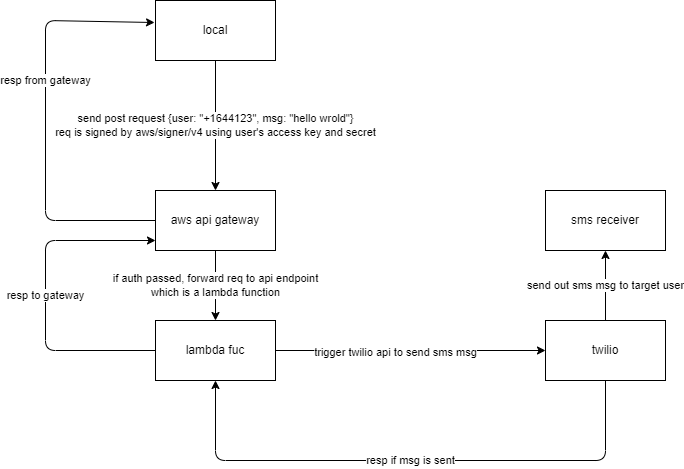
- setup lambda function to send request to twilio api
package main
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"os"
"github.com/aws/aws-lambda-go/lambda"
"github.com/twilio/twilio-go"
twilioApi "github.com/twilio/twilio-go/rest/api/v2010"
)
type Payload struct {
To string `json:"to"`
Msg string `json:"msg"`
}
func HandleRequest(ctx context.Context, event *Payload) (*string, error) {
fmt.Println(event)
if event == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("received nil event")
}
SendSMS(*event)
message := fmt.Sprintf("send message %s to %s!", event.Msg, event.To)
return &message, nil
}
func main() {
lambda.Start(HandleRequest)
}
func SendSMS(payload Payload) (resp []byte, err error) {
from := os.Getenv("from")
username := os.Getenv("username")
password := os.Getenv("password")
// from := os.Getenv("TWILIO_TO_PHONE_NUMBER")
client := twilio.NewRestClientWithParams(twilio.ClientParams{
Username: username,
Password: password,
})
params := &twilioApi.CreateMessageParams{}
params.SetTo(payload.To)
params.SetFrom(from)
params.SetBody(payload.Msg)
t, err := client.Api.CreateMessage(params)
if err != nil {
return
}
resp, err = json.Marshal(*t)
return
}p.s. remember to add environmental variable in lambda configuration tab.
- build your main.go into a zip file, then upload to lambda function
.PHONY: build
build:
GOOS=linux go build -tags lambda.norpc -o ./bootstrap main.go;\
zip bootstrap.zip bootstrapp.s. the output executable file name has to be bootstrap. remember to upload it to lambda console under code tab and change the handler name to main in Runtime settings. p.s.2. The aws-lambda-go library provides a build tag called lambda.norpc to remove all RPC logic from the built binary, reducing its size. Binary size contributes to Lambda cold-start time, so any reduction we make will help improve this metric.
-
build api create api -> REST API -> enter api name -> create
-
associate that lambda function as a endpoint create resource -> enter resource name: sms -> create resource
now you should have a /sms resource under root path. then you can
create method -> lambda function -> select request method (POST) -> select the lambda function you just created -> create method
now you should have a POST method under /sms resource
- add auth for the api-gateway This can be done several ways. I tried the following two approaches: attach policy to user group or attach policy to api-gateways
3.1.1 create a group which has access policy to the api gateway: create group -> enter group name -> seach AmazonAPIGatewayInvokeFullAccess policy -> create iser group
in case AmazonAPIGatewayInvokeFullAccess policy changed, the actual policy is like this:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"execute-api:Invoke",
"execute-api:ManageConnections"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:execute-api:*:*:*"
}
]
}IAM console->create new user -> enter user name -> add user to group -> select the group you just created -> create user
3.1.3 create access keys for user and copy that key in your host machines' .aws/config file, like this:
[profile user1]
region = us-west-1
service = execute-api
aws_access_key_id = xxxxxxx
aws_secret_access_key = xxxxxxxx
[profile user2]
region = us-west-1
service = execute-api
aws_access_key_id = xxxxx
aws_secret_access_key = xxxxx
this approach can be used to implement further detailed control the access to each endpoint of that gateway.
3.1.2 create a user in IAM and copy its ARN. 3.1.3 attach policy: API gateway console -> Resource policy -> add policy then paste the following policy:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": [
"arn:aws:iam::xxx:user/di2",
"arn:aws:iam::xxx:user/di",
"arn:aws:iam::xxx:root"
]
},
"Action": "execute-api:Invoke",
"Resource": "arn:aws:execute-api:us-west-1:xxx:xxx/beta/POST/lambdav2"
}
]
}which is modified based on AWS account allow list template.
Remember to deploy api again to take that policy into effect.
after api deployed, you can see a invoke url displayed in stage details panel. We need to call the url attached to the endpoint which bind with lambda function to invoke the lambda function. And in order to auth, we need to sign the request using aws-sdk-go-v2/aws/signer/v4.
package main
import (
"bytes"
"context"
"crypto/sha256"
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"time"
v4 "github.com/aws/aws-sdk-go-v2/aws/signer/v4"
"github.com/aws/aws-sdk-go-v2/config"
)
func main() {
/*
load shared credentials files from ~/.aws/config,
sample config file:
[profile admin]
region = us-west-1
service = execute-api
aws_access_key_id = xxxxxx
aws_secret_access_key = xxxxxxxxxx
visit https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sdkref/latest/guide/file-format.html for more details
*/
ctx := context.Background()
cfg, err := config.LoadDefaultConfig(ctx, config.WithSharedConfigProfile("di2"))
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("unable to load SDK config, %v", err)
}
// check if credential is valid
credentials, err := cfg.Credentials.Retrieve(ctx)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Credentials.Retrieve err, %v", err)
}
apiUrl := "your-invoke-url"
// apiUrl := "https://<endpoint-url>"
// Request body
// jsonStr := []byte(`{"To":"<target-phone-number>","Msg":"hello world"}`)
jsonStr := []byte(`{"To":"+1xxxxx","Msg":"asdfasd"}`)
req, err := http.NewRequest("POST", apiUrl, bytes.NewBuffer(jsonStr))
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("http.NewRequest err, %v", err)
}
reqBodyHashBytes := sha256.Sum256(jsonStr)
reqBodyHashHex := fmt.Sprintf("%x", reqBodyHashBytes)
signer := v4.NewSigner()
if err = signer.SignHTTP(ctx, credentials, req, reqBodyHashHex, "execute-api", cfg.Region, time.Now()); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error signing request.\n")
return
}
client := &http.Client{}
resp, err := client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error reading response body:", err)
return
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
fmt.Println("response Status:", resp.Status)
// Print the response body
buf := new(bytes.Buffer)
buf.ReadFrom(resp.Body)
fmt.Println("response Body:", buf.String())
}