A set of a misc tools to work with files and processes.
Various oldish helper scripts/binaries I wrote to help myself with day-to-day tasks.
License for all scripts is WTFPL (public domain-ish), feel free to just copy and use these in whatever way you like.
Contents
- Scripts
- [-root-] Various CLI/system things
- [dev] Dev tools
- [backup] Backup helpers
- [desktop] Linux desktop stuff
- [vm] VM scripts
- [bpf] Linux eBPF filters
- [arch] ArchLinux(+ARM)
- [alpine] Alpine Linux
- [metrics] Charts and metrics
- [cron-checks] Things to run from crontab scripts for diffs/alerts
- [scraps]
- License (WTFPL)
Repository URLs:
File/link/dir and filesystem structure manipulation tools.
Non-interactive CLI tool to keep a list of files to symlink or copy into/from some "dotfiles" configuration dir or repository, and keep/check/update/restore metadata manifest for these files.
Keeps track of ACLs, POSIX capabilities and xattrs for metadata, runs file diffs for file copies and links, supports a bunch of neat symlinking options (like using relative symlinks, relative symlinks into symlinked repo-dir, etc).
Idea is to keep links and metadata manifest files in some configuration repo, and run the tool occasionally after system updates or manual changes to pull updated files into repo, update files on fs from the repo, fix links/permissions on fs, copy/add new ones, etc - all manifest/maintenance ops done via this script.
Format for links-list looks something like this:
.gitconfig -> .git/config /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Yekaterinburg -> /etc/localtime bpf -> /etc/bpf zshrc > /etc/zsh/zshrc kernel-config > /usr/src/linux/.config myapp/secret.conf -> /etc/myapp/secret.conf myapp/suid.bin -> /usr/local/bin/myapp myapp/caps.bin -> /usr/local/bin/myapp-helper
And metadata is also a simple plaintext file, with fancier stuff towards the end of lines, on paths where it's used/needed:
.gitconfig root:root:644 bpf root:wheel:750 zshrc root:root:644 kernel-config root:wheel:664 myapp/secret.conf root:root:600 myapp/suid.bin root:root:4711 myapp/caps.bin root:root:4700/EP:net_raw/u::rwx,u:netuser:--x,g::r-x,m::r-x,o::---
In addition to lists, there're separate links/meta exclude-files with regexps of paths to not warn about being missing in links-list or track metadata for.
Only needs python3 to run, has bundled implementation for parsing/encoding
modern linux ACLs/capabilities extended attributes.
Uses git diff --no-index for --diff-cmd by default, as it is very fast,
has nice colors and should be widely available.
Started as a cfgit project long time ago, evolved away into this more generic (and not necessarily git-related) tool.
Complex tool for high-level fs operations. Reference is built-in.
Copy files, setting mode and ownership for the destination:
fs -m600 -o root:wheel cp * /somepath
Temporarily (1hr) change attributes (i.e. to edit file from user's editor):
fs -t3600 -m600 -o someuser expose /path/to/file
Copy ownership/mode from one file to another:
fs cps /file1 /file2
fatrace-based script to read filesystem write events via linux fanotify system and match them against specific path and app name, sending matches to a FIFO pipe.
Use-case is to, for example, setup watcher for development project dir changes, sending instant "refresh" signals to something that renders the project or shows changes' results otherwise.
FIFO is there because fanotify requires root privileges, and running some potentially-rm-rf-/ ops as uid=0 is a damn bad idea. User's pid can read lines from the fifo and react to these safely instead.
Example - run "make" on any change to ~user/hatch/project files:
(root) ~# fatrace-pipe ~user/hatch/project (user) project% xargs -in1 </tmp/fatrace.fifo make
Convenience wrapper around fatrace like fatrace-pipe above, but intended to only filter by path prefix and run command on specified event(s).
For example, to e.g. reload nginx when anything under its config dir/subdirs changes:
# fatrace-run -p /etc/nginx -f 'WD<>' -- pkill -HUP -F /run/nginx.pid
(-p to also echo events to stdout, "-f W" will filter file writes, D - deletions, <> - renames)
Wrapper around GNU find to accept paths at the end of argv if none are passed before query.
Makes it somewhat more consistent with most other commands that accept options and a lists of paths (almost always after opts), but still warns when/if reordering takes place.
No matter how many years I'm using that tool, still sometimes type paths after query there, so decided to patch around that frustrating issue one day.
Python script to "shift" or "patch" uid/gid values with new container-id according to systemd-nspawn schema, i.e. set upper 16-bit to specified container-id value and keep lower 16 bits to uid/gid inside the container.
Similar operation to what systemd-nspawn's --private-users-chown option does (described in nspawn-patch-uid.c), but standalone, doesn't bother with ACLs or checks on filesystem boundaries.
Main purpose is to update uids when migrating systemd-nspawn containers or adding paths/filesystems to these without clobbering ownership info there.
Should be safe to use anywhere, as in most non-nspawn cases upper bits of uid/gid are always zero, hence any changes can be easily reverted by running this tool again with -c0.
bindfs wrapper script to setup id-mapping from uid of the mountpoint to uid/gid of the source directory.
I.e. after bindfs-idmap /var/lib/machines/home/src-user ~dst-user/tmp,
~dst-user/tmp will be accessible to dst-user as if they were src-user, with
all operations proxied to src-user's dir.
Anything created under ~dst-user/tmp will have uid/gid of the src dir.
Useful to allow temporary access to some uid's files in a local container to user acc in a main namespace.
For long-term access (e.g. for some daemon), there probably are better options than such bindfs hack - e.g. bind-mounts, shared uids/gids, ACLs, etc.
Simple bash script to symlink uppermost "merged" overlayfs layer of a running docker-compose setup container, to allow easy access to temporary files there.
Useful for testing stuff without the need to rebuild and restart whole container or a bunch of compose stuff after every one-liner tweak to some script that's supposed to be running in there, or to experiment-with and debug things.
These paths are very likely to change between container and docker-compose restarts for many reasons, so such symlinks are generally only valid during container runtime, and script needs a re-run to update these too.
Very simple "write 512B, skip N * 512B, repeat" binary for wiping some block device in a hurry.
Idea is not to erase every trace of data or to hide it, but just to make files probabilistically unusable due to such junk blocks all over the place.
With low-enough intervals it should also corrupt filesystem pretty badly, making metadata hard to access.
Fast loop of 512B writes to a device directly will likely hang that binary until it's done, as that's how such direct I/O seem to work on linux.
Writes only stop when write() or lseek() starts returning errors, so using this on some extendable file will result in it eating up all space available to it.
See head of the file for build and usage info.
Things that manipulate some kind of data formats or mangle generic file/pipe contents.
Ever needed to check if file has newlines or BOM in it, yet every editor is user-friendly by default and hides these from actual file contents?
One fix is hexdump or switching to binary mode, but these are usually terrible for looking at text, and tend to display all non-ASCII as "." instead of nicer \r \t \n ... escapes, not to mention unicode chars.
This trivial script prints each line in a file via python's repr(), which is usually very nice, has none of the above issues and doesn't dump byte codes on you for anything it can interpret as char/codepoint or some neat escape code.
Has opts for text/byte mode and stripping "universal newlines" (see newline= in built-in open() func).
Can also do encoding/newline conversion via -c option, as iconv can't do BOM or
newlines, and sometimes you just want "MS utf-8 mode" (repr -c utf-8-sig+r).
Using that with +i flag as e.g. repr -c utf-8-sig+ri file1 file2 ...
converts encoding+newlines+BOM for files in-place at no extra hassle.
Outputs terminal color sequences, making important output more distinctive.
Also can be used to interleave "tail -f" of several logfiles in the same terminal:
% t -f /var/log/app1.log | color red - & % t -f /var/log/app2.log | color green - & % t -f /var/log/app2.log | color blue - &
Or to get color-escape-magic for your bash script: color red bold p
Script (py3) to find all specified (either directly, or by regexp) hostnames and replace these with corresponding IP addresses, resolved through getaddrinfo(3).
Examples:
% cat cjdroute.conf
... "fraggod.net:21987": { ... },
"localhost:21987": { ... },
"fraggod.net:12345": { ... }, ...
% resolve-hostnames fraggod.net localhost < cjdroute.conf
... "192.168.0.11:21987": { ... },
"127.0.0.1:21987": { ... },
"192.168.0.11:12345": { ... }, ...
% resolve-hostnames -m '"(?P<name>[\w.]+):\d+"' < cjdroute.conf
% resolve-hostnames fraggod.net:12345 < cjdroute.conf
% resolve-hostnames -a inet6 fraggod.net localhost < cjdroute.conf
...
% cat nftables.conf
define set.gw.ipv4 = { !ipv4.name1.local, !ipv4.name2.local }
define set.gw.ipv6 = { !ipv6.name1.local, !ipv6.name2.local }
...
# Will crash nft-0.6 because it treats names in anonymous sets as AF_INET (ipv4 only)
% resolve-hostnames -rum '!(\S+\.local)\b' -f nftables.conf
define set.gw.ipv4 = { 10.12.34.1, 10.12.34.2 }
define set.gw.ipv6 = { fd04::1, fd04::2 }
...
Useful a as conf-file pre-processor for tools that cannot handle names properly (e.g. introduce ambiguity, can't deal with ipv4/ipv6, use weird resolvers, do it dynamically, etc) or should not be allowed to handle these, convert lists of names (in some arbitrary format) to IP addresses, and such.
Has all sorts of failure-handling and getaddrinfo-control cli options, can resolve port/protocol names as well.
Python/Jinja2 script to produce a text file from a template, focused specifically on templating configuration files, somewhat similar to "resolve-hostnames" above or templating provided by ansible/saltstack.
Jinja2 env for template has following filters and values:
dns(host [, af, proto, sock, default, force_unique=True])filter/global.getaddrinfo(3) wrapper to resolve
host(name or address) with optional parameters to a single address, raising exception if it's non-unique by default.af/proto/sock values can be either enum value names (without AF/SOL/SOCK prefix) or integers.
hosts- /etc/hosts as a mapping.For example, hosts-file line
1.2.3.4 sub.host.example.orgwill produce following mapping (represented as yaml):sub.host.example.org: 1.2.3.4 host.example.org: sub: 1.2.3.4 org: example: host: sub: 1.2.3.4Can be used as a reliable dns/network-independent names.--hosts-optscli option allows some tweaks wrt how that file is parsed.See also HostsNode object for various helper methods to lookup those.iface- current network interfaces and IPv4/IPv6 addresses assigned there (fetched from libc getifaddrs via ctypes).Example value structure (as yaml):
enp1s0: - 10.0.0.134 - fd00::134 - 2001:470:1f0b:11de::134 - fe80::c646:19ff:fe64:632f enp2s7: - 10.0.1.1 lo: - 127.0.0.1 - ::1 ip_vti0: []
Probably a good idea to use this stuff only when IPs are static and get assigned strictly before templating.
{% comment_out_if value[, comment-prefix] %}...{% comment_out_end %}Custom template block to prefix each non-empty line within it with specified string (defaults to "#") if value is not false-y.
Can be used when format doesn't have block comments, but it's still desirable to keep disabled things in dst file (e.g. for manual tinkering) instead of using if-blocks around these, or to make specific lines easier to uncomment manually.
it- itertools,_v/v_/_v_- global funcs for adding spaces before/after/around non-empty strings.Whatever is loaded from
--conf-file/--conf-dir(JSON/YAML files), if specified.
Use-case is a simple conf-file pre-processor for autonomous templating on
service startup with a minimal toolbox on top of jinja2, without huge dep-tree
or any other requirements and complexity, that is not scary to run from
ExecStartPre= line as root.
Tool to temporarily modify (patch) a file - until reboot or for a specified amount of time. Uses bind-mounts from tmpfs to make sure file will be reverted to the original state eventually.
Useful to e.g. patch /etc/hosts with (pre-defined) stuff from LAN on a
laptop (so this changes will be reverted on reboot), or a notification filter
file for a short "busy!" time period (with a time limit, so it'll auto-revert
after), or stuff like that.
Even though dst file is mounted with "-o ro" by default (there's "-w" option to disable that), linux doesn't seem to care about that option and mounts the thing as "rw" anyway, so "chmod a-w" gets run on temp file instead to prevent accidental modification (that can be lost).
There're also "-t" and "-m" flags to control timestamps during the whole process.
Python script with various terminal input/output piping helpers and tools.
Has multiple modes for different use-cases, collected in same script mostly because they're pretty simple and not worth remembering separate ones.
Disables terminal echo and outputs line-buffered stdin to stdout.
Example use-case can be grepping through huge multiline strings (e.g. webpage source) pasted into terminal, i.e.:
% term-pipe | g -o '\<http://[^"]\+' [pasting page here via e.g. Shift+Insert won't cause any echo] http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd http://www.bugzilla.org/docs/3.4/en/html/bug_page.html ...
There are better tools for that particular use-case, but this solution is universal wrt any possible input source.
Filter for screen/tmux/script output to send desktop notification (using sd-bus lib) when shell prompt is detected on stdin, to enable when some long job is running for example, so that you'd get notified immediately when it's done.
Shell prompt detection is done via simple regexp, highly specific to my prompt(s) and use-case(s), so might need tweaks in the code for different ones. -l/--log option can be useful when doing that - will print all input lines (with proper repr() wrapping), which can then be checked for desired patterns and tested against new detection regexps as necessary.
Example use in tmux.conf:
bind-key r pipe-pane 'exec term-pipe shell-notify' bind-key R pipe-pane
Should make "r" key (after prefix key) enable notifications and "shift+r" disable them. Use "pipe-pane -o" to toggle this via same key instead.
"exec ..." command there is passed to shell, so to debug errors after any significant changes, something like "2>/tmp/errors.log" can be added at the end.
Check options of this subcommand for rate-limiting and some other tweaks.
Converts yaml files to an indented json, which is a bit more readable and editable by hand than the usual compact one-liner serialization.
Due to yaml itself being json superset, can be used to convert json to pretty-json as well.
Converts yaml/json files to a flat "key: value" lines.
Nested keys are flattened to a dot-separated "level1.level2.level3" keys, replacing dots, spaces and colons there, to avoid confusing level separators with the keys themselves.
Values are also processed to always be one-liners, handling long values and empty lists/dicts and such in a readable manner too.
Output is intended for a human reader, to easily see value paths and such, and definitely can't be converted back to yaml or any kind of data safely.
Same thing as the common "head", but works with \x00 (aka null char/byte , NUL, ␀, \0, \z, \000, \u0000, %00, ^@) delimeters.
Can be done with putting "tr" in the pipeline before and after "head", but this one is maybe a bit less fugly.
Allows replacing input null-bytes with newlines in the output (--replace-with-newlines option) and vice-versa.
Common use-case is probably has something to do with filenames and xargs, e.g.:
% find -type f -print0 | shuf -z | hz -10 | xargs -0 some-cool-command % ls -1 | hz -z | xargs -0 some-other-command
I have "h" as an alias for "head" in shells, so "head -z" (if there were such option) would be aliased neatly to "hz", hence the script name.
Defaults to reading ALL lines, not just arbitrary number (like 10, which is default for regular "head")!
"Log Interleaver And Colorizer" python script.
Reads lines from multiple files, ordering them by the specified field in the output (default - first field, e.g. ISO8601 timestamp) and outputs each with (optional) unique-filename-part prefix and unique (ansi-terminal, per-file) color.
Most useful for figuring out sequence of events from multiple timestamped logs.
To have safely-rotated logs with nice timestamps from any arbitrary command's
output, something like stdbuf -oL <command-and-args> | svlogd -r _ -ttt
<log-dir> can be used.
Note "stdbuf" coreutils tool, used there to tweak output buffering, which
usually breaks such timestamps, and "svlogd" from runit suite (no deps, can be
built separately).
See blog post about liac tool for more info.
Script to create "fat" HTML files, embedding all linked images (as base64-encoded data-urls), stylesheets and js into them.
All src= and href= paths must be local (e.g. "js/script.js" or "/css/main.css"), and will simply be treated as path components (stripping slashes on the left) from html dir, nothing external (e.g. "//site.com/stuff.js") will be fetched.
Doesn't need anything but python, based on stdlib html.parser module.
Not optimized for huge amounts of embedded data, storing all the substitutions
in memory while it runs, and is unsafe to run on random html files, as it can
embed something sensitive (e.g. <img src="../.ssh/id_rsa">) - no extra
checks there.
Use-case is to easily produce single-file webapps or pages to pass around (or share somewhere), e.g. some d3-based interactive chart page or an html report with a few embedded images.
Simple and dirty regexp + backreferences something-ML (SGML/HTML/XML) parser to indent tags/values in a compact way without messing-up anything else in there.
I.e. non-closed tags are FINE, something like <@> doesn't cause parser to explode, etc.
Does not add any XML headers, does not mangle (or "canonize") tags/attrs/values in any way, except for stripping/adding those spaces.
Kinda like BeautifulSoup, except not limited to html and trivial enough so that it can be trusted not to do anything unnecessary like stuff mentioned above.
For cases when xmllint --format fail and/or break such kinda-ML-but-not-XML files.
Script to add base32-encoded content hash to filenames.
For example:
% hashnames -p *.jpg wallpaper001.jpg -> wallpaper001.kw30e7cqytmmw.jpg wallpaper893.jpg -> wallpaper893.vbf0t0qht4dd0.jpg wallpaper895.jpg -> wallpaper895.q5mp0j95bxbdr.jpg wallpaper898.jpg -> wallpaper898.c9g9yeb06pdbj.jpg
For collecting files with commonly-repeated names into some dir, like random "wallpaper.jpg" or "image.jpg" images above from the internets.
Use -h/--help for info on more useful options.
Produces lower-entropy "human hash" phrase consisting of aspell english dictionary words for input arg(s) or data on stdin.
It works by first calculating BLAKE2 hash of input string/data via libsodium, and then encoding it using consistent word-alphabet, exactly like something like base32 or base64 does.
Example:
% hhash -e AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIPh5/VmxDwgtJI0HiFBqZkbyV1I1YK+2DVjGjYydNp5o allan avenues regrade windups flours entropy-stats: word-count=5 dict-words=126643 word-bits=17.0 total-bits=84.8
Here -e is used to print entropy estimate for produced words.
Note that resulting entropy values can be fractional if word-alphabet ends up being padded to map exactly to N bits (e.g. 17 bits above), so that words in it can be repeated, hence not exactly 17 bits of distinct values.
Written in OCAML, linked against libsodium (for BLAKE2 hash function) via small C glue code, build with:
% ocamlopt -o hhash -O2 unix.cmxa str.cmxa \ -cclib -lsodium -ccopt -Wl,--no-as-needed hhash.ml hhash.ml.c % strip hhash
Caches dictionary into a ~/.cache/hhash.dict (-c option) on first run to produce consistent results on this machine. Updating that dictionary will change outputs!
Trivial file/stream encryption tool using PyNaCl's crypto_secretstream_xchacha20poly1305 authenticated encryption API.
Key can be either specified on the command line for simplicity or read from a file, and is always processed via scrypt, as it's likely some short string.
Usage examples:
% crypt -ek my-secret-key secret.tar secret.tar.enc % crypt -dk my-secret-key secret.tar.enc secret.tar.test % crypt -ek @~/.secret.key <secret.tar >secret.tar.enc
Intended for an ad-hoc temporary encryption when transferring stuff via a usb stick, making a temporary backup to a random untrusted disk or whatever.
Does not support any kind of appending/resuming or partial operation, which can be bad if there's a flipped bit anywhere in the encrypted data - decryption will stop and throw error at that point.
Simple stateless script to update sources in /usr/src/linux to some (specified) stable version.
Looks for "patch-X.Y.Z.xz" files (as provided on kernel.org) under /usr/src/distfiles (configurable at the top of the script), or downloads them there from kernel.org.
Does update (or rollback) by grabbing current patchset version from Makefile and
doing essentially patch -R < <patch-current> && patch < <patch-new> - i.e.
rolling-back the current patchset, then applying new patch.
Always does patch --dry-run first to make sure there will be no mess left
over by the tool and updates will be all-or-nothing.
In short, allows to run e.g. kernel-patch 3.14.22 to get 3.14.22 in
/usr/src/linux from any other clean 3.14.* version, or just
kernel-patch to have the latest 3.14 patchset.
Ad-hoc python script to check any random snippet with linux kernel
CONFIG_... values (e.g. "this is stuff you want to set" block on some wiki)
against kernel config file, current config in /proc/config.gz or such.
Reports what matches and what doesn't to stdout, trivial regexp matching.
Script to remove older kernel versions (as installed by /sbin/installkernel)
from /boot or similar dir.
Always keeps version linked as "vmlinuz", and prioritizes removal of older patchset versions from each major one, and only then latest per-major patchset, until free space goal (specified percentage, 20% by default) is met.
Also keeps specified number of last-to-remove versions, can prioritize cleanup
of ".old" verssion variants, keep config-* files... and other stuff (see --help).
Example:
# clean-boot --debug --dry-run -f 100 DEBUG:root:Preserved versions (linked version, its ".old" variant, --keep-min): 4 DEBUG:root: - 3.9.9.1 - System.map-3.9.9-fg.mf_master DEBUG:root: - 3.9.9.1 - config-3.9.9-fg.mf_master DEBUG:root: - 3.9.9.1 - vmlinuz-3.9.9-fg.mf_master DEBUG:root: - 3.10.27.1 - vmlinuz-3.10.27-fg.mf_master ... DEBUG:root: - 3.12.19.1 - System.map-3.12.19-fg.mf_master DEBUG:root: - 3.12.20.1 - config-3.12.20-fg.mf_master DEBUG:root: - 3.12.20.1 - System.map-3.12.20-fg.mf_master DEBUG:root: - 3.12.20.1 - vmlinuz-3.12.20-fg.mf_master DEBUG:root:Removing files for version (df: 58.9%): 3.2.0.1 DEBUG:root: - System.map-3.2.0-fg.mf_master DEBUG:root: - config-3.2.0-fg.mf_master DEBUG:root: - vmlinuz-3.2.0-fg.mf_master DEBUG:root:Removing files for version (df: 58.9%): 3.2.1.0 ... (removal of older patchsets for each major version, 3.2 - 3.12) DEBUG:root:Removing files for version (df: 58.9%): 3.12.18.1 ... (this was the last non-latest patchset-per-major) DEBUG:root:Removing files for version (df: 58.9%): 3.2.16.1 ... (removing latest patchset for each major version, starting from oldest - 3.2 here) DEBUG:root:Removing files for version (df: 58.9%): 3.7.9.1 ... DEBUG:root:Removing files for version (df: 58.9%): 3.8.11.1 ... DEBUG:root:Finished (df: 58.9%, versions left: 4, versions removed: 66).
("df" doesn't rise here because of --dry-run, -f 100 =
"remove all non-preserved" - as df can't really get to 100%)
Note how 3.2.0.1 (non-.old 3.2.0) gets removed first, then 3.2.1, 3.2.2, and so on, but 3.2.16 (latest of 3.2.X) gets removed towards the very end, among other "latest patchset for major" versions, except those that are preserved unconditionally (listed at the top).
Tools to manage ZNC IRC bouncer logs - archive, view, search, etc.
Tool to process znc chat logs, produced by "log" module (global, per-user or per-network - looks everywhere) and store them using following schema:
<net>/chat/<channel>__<yy>-<mm>.log.xz <net>/priv/<nick>__<yy>-<mm>.log.xz
Where "priv" differs from "chat" in latter being prefixed by "#" or "&". Values there are parsed according to any one of these (whichever matches first):
users/<net>/moddata/log/<chan>_<date>.logmoddata/log/<net>_default_<chan>_<date>.log(no "_" in<net>allowed)moddata/log/<user>_<net>_<chan>_<date>.log(no "_" in<user>or<net>allowed)
Each line gets processed by regexp to do [HH:MM:SS] <nick> some msg ->
[yy-mm-dd HH:MM:SS] <nick> some msg.
Latest (current day) logs are skipped. New logs for each run are concatenated to the monthly .xz file.
Should be safe to stop at any time without any data loss - all the resulting .xz's get written to temporary files and renamed at the very end (followed only by unlinking of the source files).
All temp files are produced in the destination dir and should be cleaned-up on any abort/exit/finish.
Idea is to have more convenient hierarchy and less files for easier shell navigation/grepping (xzless/xzgrep), plus don't worry about the excessive space usage in the long run.
Same as znc-log-aggregator above, but seeks/reads specific tail ("last n lines") or time range (with additional filtering by channel/nick and network) from all the current and aggregated logs.
Python script to list all currently active and non-transient systemd units, so that these can be tracked as a "system state", and e.g. any deviations there detected/reported (simple diff can do it).
Gets unit info by parsing Dump() snapshot fetched via sd-bus API of libsystemd (using ctypes to wrap it), which is same as e.g. "systemd-analyze dump" gets.
Has -m/--machines option to query state from all registered machines as well, which requires root (for sd_bus_open_system_machine) due to current systemd limitations.
See Dashboard-for-... blog post for extended rationale, though it's probably obsolete otherwise since this thing was rewritten.
Trivial script to ping systemd watchdog and do some trivial actions in-between to make sure os still works.
Wrote it after yet another silent non-crash, where linux kernel refuses to create new pids (with some backtraces) and seem to hang on some fs ops, blocking syslog/journal, but leaving most simple daemons running ok-ish for a while.
So this trivial script, tied into systemd-controlled watchdog timers, tries to create pids every once in a while, with either hang or crash bubbling-up to systemd (pid-1), which should reliably reboot/crash the system via hardware wdt.
Example watchdog.service:
[Service] Type=notify ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/systemd-watchdog -i30 -n \ -f /var/log/wdt-fail.log \ -x 'ip link' -x 'ip addr' -x 'ip ro' -x 'journalctl -an30' WatchdogSec=60 TimeoutStartSec=15 Restart=on-failure RestartSec=20 StartLimitInterval=10min StartLimitBurst=5 StartLimitAction=reboot-force [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
(be sure to tweak timeouts and test without "reboot-force" first though, e.g. pick RestartSec= for transient failures to not trigger StartLimitAction)
Can optionally get IP of (non-local) gateway to 1.1.1.1 (or any specified IPv4) via libmnl (also used by iproute2, so always available) and check whether it responds to fping probes, crashing if it does not - see -n/--check-net-gw option.
That's mainly for remote systems which can become unreachable if kernel network stack, local firewall, dhcp, ethernet or whatever other link fails (usually due to some kind of local tinkering), ignoring more mundane internet failures.
To avoid reboot loops (in abscence of any networking), it might be a good idea to only start script with this option manually (e.g. right before messing up with the network, or on first successful access).
-f/--fail-log option is to log date/time of any failures for latest boot and run -x/--fail-log-cmd command(s) on any python exceptions (note: kernel hangs probably won't cause these), logging their stdout/stderr there - e.g. to dump network configuration info as in example above.
Useless without systemd and requires systemd python module, plus fping tool if -n/--check-net-gw option is used.
Wrapper for systemd.resource control stuff to run commands in transient scopes within pre-defined slices, as well as wait for these and list pids within them easily.
Replacement for things like libcgroup, cgmanager and my earlier cgroup-tools
project, compatible with unified cgroup-v2 hierarchy and working on top of
systemd (use systemd.unified_cgroup_hierarchy on cmdline, if non-default).
Resource limits for cgrc scopes should be defined via hierarchical slices like these:
# apps.slice [Slice] CPUWeight=30 IOWeight=30 MemoryHigh=5G MemoryMax=8G MemorySwapMax=1G # apps-browser.slice [Slice] CPUWeight=30 IOWeight=30 MemoryHigh=3G
And then script can be used to start things there:
% cgrc apps-browser -- chromium % cgrc -u ff apps-browser -- firefox --profile myprofile
Where e.g. last command would end up running something like this:
% systemd-run -q --user --scope --unit ff \ --slice apps-browser -- firefox --profile myprofile
Note that .scope cgroups are always transient (vanish after run), and only .slice ones can be pre-defined with limits. Both get started/stopped by systemd on as-needed basis.
Tool also allows to check or list pids within scopes/slices with -c/-l options (to e.g. check if named scope already started or something running in a slice), as well as waiting on these (-q option, can be used to queue/run commands in sequence) and manipulating associated cgroup limits easily (-v option).
Run without any args/opts or with -h/--help to get more detailed usage info.
See also "backup" subsection.
ssh-keyscan, but outputting each key in every possible format.
Imagine you have an incoming IM message "hey, someone haxxors me, it says 'ECDSA key fingerprint is f5:e5:f9:b6:a4:6b:fd:b3:07:15:f6:d9:0c:f5:47:54', what do?", this tool allows to dump any such fingerprint for a remote host, with:
% ssh-fingerprint congo.fg.nym ... congo.fg.nym ecdsa-sha2-nistp256 AAAAE2VjZHNhLXNo...zoU04g= 256 MD5:f5:e5:f9:b6:a4:6b:fd:b3:07:15:f6:d9:0c:f5:47:54 /tmp/.ssh_keyscan.key.kc3ur3C (ECDSA) 256 SHA256:lFLzFQR...2ZBmIgQi/w /tmp/.ssh_keyscan.key.kc3ur3C (ECDSA) ---- BEGIN SSH2 PUBLIC KEY ---- ...
Only way I know how to get that
"f5:e5:f9:b6:a4:6b:fd:b3:07:15:f6:d9:0c:f5:47:54" secret-sauce is to either do
your own md5 + hexdigest on ssh-keyscan output (and not mess-up due to some
extra space or newline), or store one of the keys from there with first field
cut off into a file and run ssh-keygen -l -E md5 -f key.pub.
Note how "intuitive" it is to confirm something that ssh prints (and it prints only that md5-fp thing!) for every new host you connect to with just openssh.
With this command, just running it on the remote host - presumably from diff location, or even localhost - should give (hopefully) any possible gibberish permutation that openssh (or something else) may decide to throw at you.
Python script to extract raw private key string from ed25519 ssh keys.
Main purpose is easy backup of ssh private keys and derivation of new secrets from these for other purposes.
For example:
% ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -f test-key ... % cat test-key -----BEGIN OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY----- b3BlbnNzaC1rZXktdjEAAAAABG5vbmUAAAAEbm9uZQAAAAAAAAABAAAAMwAAAAtzc2gtZW QyNTUxOQAAACDaKUyc/3dnDL+FS4/32JFsF88oQoYb2lU0QYtLgOx+yAAAAJi1Bt0atQbd GgAAAAtzc2gtZWQyNTUxOQAAACDaKUyc/3dnDL+FS4/32JFsF88oQoYb2lU0QYtLgOx+yA AAAEAc5IRaYYm2Ss4E65MYY4VewwiwyqWdBNYAZxEhZe9GpNopTJz/d2cMv4VLj/fYkWwX zyhChhvaVTRBi0uA7H7IAAAAE2ZyYWdnb2RAbWFsZWRpY3Rpb24BAg== -----END OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY----- % ssh-keyparse test-key HOSEWmGJtkrOBOuTGGOFXsMIsMqlnQTWAGcRIWXvRqQ=
That one line at the end contains 32-byte ed25519 seed (with urlsafe-base64 encoding) - "secret key" - all the necessary info to restore the blob above, without extra openssh wrapping (as per PROTOCOL.key).
Original OpenSSH format (as produced by ssh-keygen) stores "magic string", ciphername ("none"), kdfname ("none"), kdfoptions (empty string), public key and index for that, two "checkint" numbers, seed + public key string, comment and a bunch of extra padding at the end. All string values there are length-prefixed, so take extra 4 bytes, even when empty.
Gist is that it's a ton of stuff that's not the actual key, which ssh-keyparse extracts.
To restore key from seed, use -d/--patch-key option on any existing ed25519 key,
e.g. ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -N '' -f test-key && ssh-keyparse -d <seed> test-key
If key is encrypted with passphrase, ssh-keygen -p will be run on a
temporary copy of it to decrypt, with a big warning in case it's not desirable.
There's also an option (--pbkdf2) to run the thing through PBKDF2 (tunable via --pbkdf2-opts) and various output encodings available:
% ssh-keyparse test-key # default is urlsafe-base64 encoding HOSEWmGJtkrOBOuTGGOFXsMIsMqlnQTWAGcRIWXvRqQ= % ssh-keyparse test-key --hex 1ce4845a6189b64ace04eb931863855ec308b0caa59d04d60067112165ef46a4 % ssh-keyparse test-key --base32 3KJ8-8PK1-H6V4-NKG4-XE9H-GRW5-BV1G-HC6A-MPEG-9NG0-CW8J-2SFF-8TJ0-e % ssh-keyparse test-key --base32-nodashes 3KJ88PK1H6V4NKG4XE9HGRW5BV1GHC6AMPEG9NG0CW8J2SFF8TJ0e % ssh-keyparse test-key --raw >test-key.bin
With encoding like --base32 (Douglas Crockford's human-oriented Base32, last digit/lowercase-letter there is a checksum), it's easy to even read the thing over some voice channel, if necessary.
Bash script to generate (init) ssh key (via ssh-keygen) without asking about various legacy and uninteresting options and safe against replacing existing keys.
I.e. don't ever want RSA, ECDSA or such nonsense (Ed25519 is the norm), don't need passwords for 99.999% of the keys, don't care about any of the ssh-keygen output, don't need any interactivity, but do care about silently overwriting existing key and want the thing to create parent dirs properly (which -f fails to do).
Has -m option to init key for an nspawn container under /var/lib/machines
(e.g. ssh-key-init -m mymachine) and -r option to replace any existing keys.
Sets uid/gid of the parent path for all new ones and -m700.
I.e. to run ssh-tunnel -ti 60 2223:nexthop:22 user@host -p2222 instead of
some manual loop (re-)connecting every 60s in the background using something like:
ssh \ -oControlPath=none -oControlMaster=no \ -oConnectTimeout=5 -oServerAliveInterval=3 -oServerAliveCountMax=5 \ -oPasswordAuthentication=no -oNumberOfPasswordPrompts=0 \ -oBatchMode=yes -oExitOnForwardFailure=yes -TnNqy \ -p2222 -L 2223:nexthop:22 user@host
Which are all pretty much required for proper background tunnel operation.
Python/asyncio scripts to establish multiple ssh reverse-port-forwarding ("ssh -R") connections to the same tunnel-server from mutliple hosts using same exact configuration on each.
Normally, first client host will bind the "ssh -R" listening port and all others will fail, but these two scripts negotiate unique port within specified range to each host, so there are no clashes and all tunnels work fine.
Tunnel server also stores allocated ports in a db file, so that each client gets more-or-less persistent listening port.
Each client negotiates port before exec'ing "ssh -R" command, identifying itself via --ident-* string (derived from /etc/machine-id by default), and both client/server need to use same -s/--auth-secret to create/validate MACs in each packet.
Note that all --auth-secret is used for is literally handing-out sequential numbers, and isn't expected to be strong protection against anything, unlike ssh auth that should come after that.
Same thing as ssh-reverse-mux-* scripts above, but for negotiating WireGuard tunnels, with persistent host tunnel IPs tracked via --ident-* strings with simple auth via MACs on UDP packets derived from symmetric -s/--auth-secret.
Client identity, wg port, public key and tunnel IPs are sent in the clear with relatively weak authentication (hmac of -s/--auth-secret string), but wg server is also authenticated by pre-shared public key (and --wg-psk, if specified).
Such setup is roughly equivalent to a password-protected (--auth-secret) public network.
Runs "wg set" commands to update configuration, which need privileges, but can be wrapped in sudo or suid/caps via --wg-cmd to avoid root in the rest of the script.
Does not touch or handle WireGuard private keys in any way by itself, and probably should not have direct access to these (though note that unrestricted access to "wg" command can reveal them anyway).
Example systemd unit for server:
# wg.service + auth.secret psk.secret key.secret # useradd -s /usr/bin/nologin wg && mkdir -m700 ~wg && chown wg: ~wg # cd ~wg && cp /usr/bin/wg . && chown root:wg wg && chmod 4110 wg [Unit] Wants=network.target After=network.target [Service] Type=exec User=wg WorkingDirectory=~ Restart=always RestartSec=60 StandardInput=file:/home/wg/auth.secret StandardOutput=journal ExecStartPre=+sh -c 'ip link add wg type wireguard 2>/dev/null; \ ip addr add 10.123.0.1/24 dev wg 2>/dev/null; ip link set wg up' ExecStartPre=+wg set wg listen-port 1500 private-key key.secret ExecStart=wg-mux-server --mux-port=1501 --wg-port=1500 \ --wg-net=10.123.0.0/24 --wg-cmd=./wg --wg-psk=psk.secret [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Client:
# wg.service + auth.secret psk.secret
# useradd -s /usr/bin/nologin wg && mkdir -m700 ~wg && chown wg: ~wg
# cd ~wg && cp /usr/bin/wg . && chown root:wg wg && chmod 4110 wg
# cd ~wg && cp /usr/bin/ip . && chown root:wg ip && chmod 4110 ip
[Unit]
Wants=network.target
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=exec
User=wg
WorkingDirectory=~
Restart=always
RestartSec=10
StandardInput=file:/home/wg/auth.secret
StandardOutput=journal
ExecStartPre=+sh -c '[ -e key.secret ] || { umask 077; wg genkey >key.secret; }
ExecStartPre=+sh -c '[ -e key.public ] || wg pubkey <key.secret >key.public
ExecStartPre=+sh -c 'ip link add wg type wireguard 2>/dev/null; ip link set wg up'
ExecStartPre=+wg set wg private-key key.secret
ExecStart=wg-mux-client \
20.88.203.92:1501 BcOn/q9D5zcqK0hrWmXGQHtaEKGGf6g5nTxZUZ0P4HY= key.public \
--ident-rpi --wg-net=10.123.0.0/24 --wg-cmd=./wg --ip-cmd=./ip --wg-psk=psk.secret \
--ping-cmd='ping -q -w15 -c3 -i3 10.123.0.1' --ping-silent
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
When enabled, these should be enough to setup reliable tunnel up on client boot, and then keep it alive from there indefinitely (via --ping-cmd + systemd restart).
Explicit iface/IP init in these units can be replaced by systemd-networkd .netdev + .network stuff, as it supports wireguard configuration there.
Bash script to list or kill users' sshd pids, created for "ssh -R" tunnels, that don't have a listening socket associated with them or don't show ssh protocol greeting (e.g. "SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_7.4") there.
These seem to occur when ssh client suddenly dies and reconnects to create new tunnel - old pid can still hog listening socket (even though there's nothing on the other end), but new pid won't exit and hang around uselessly.
Solution is to a) check for sshd pids that don't have listenings socket, and b) connect to sshd pids' sockets and see if anything responds there, killing both non-listening and unresponsive pids.
Only picks sshd pids for users with specific prefix, e.g. "tun-" by default, to be sure not to kill anything useful (i.e. anything that's not for "ssh -R").
Uses ps, ss, gawk and ncat (comes with nmap), only prints pids by default (without -k/--kill option).
Also has -s/--cleanup-sessions option to remove all "abandoned" login sessions (think loginctl) for user with specified prefix, i.e. any leftover stuff after killing those useless ssh pids.
See also: autossh and such.
Python wrapper for mosh-server binary to do UDP hole punching through local NAT setup before starting it.
Comes with mosh-nat-bind.c source for LD_PRELOAD=./mnb.so lib to force mosh-client on the other side to use specific local port that was used in "mosh-nat".
Example usage (server at 84.217.173.225, client at 74.59.38.152):
server% ./mosh-nat 74.59.38.152
mosh-client command:
MNB_PORT=34730 LD_PRELOAD=./mnb.so
MOSH_KEY=rYt2QFJapgKN5GUqKJH2NQ mosh-client <server-addr> 34730
client% MNB_PORT=34730 LD_PRELOAD=./mnb.so \
MOSH_KEY=rYt2QFJapgKN5GUqKJH2NQ mosh-client 84.217.173.225 34730
Notes:
- mnb.so is mosh-nat-bind.c lib. Check its header for command to build it.
- Both mnb.so and mosh-nat only work with IPv4, IPv6 shouldn't use NAT anyway.
- Should only work like that when NAT on either side doesn't rewrite src ports.
- 34730 is default for -c/--client-port and -s/--server-port opts.
- Started mosh-server waits for 60s (default) for mosh-client to connect.
- Continous operation relies on mosh keepalive packets without interruption.
- No roaming of any kind is possible here.
- New MOSH_KEY is generated by mosh-server on every run.
Useful for direct and fast connection when there's some other means of access available already, e.g. ssh through some slow/indirect tunnel or port forwarding setup.
Python (asyncio) tool to try connecting to specified TCP port until connection can be established, then just exit, i.e. to wait until some remote port is accessible.
Can be used to wait for host to reboot before trying to ssh into it, e.g.:
% tping myhost && ssh root@myhost
(default -p/--port is 22 - ssh, see also -s/--ssh option)
Tries establishing new connection (forcing new SYN, IPv4/IPv6 should both work) every -r/--retry-delay seconds (default: 1), only discarding (closing) "in progress" connections after -t/--timeout seconds (default: 3), essentially keeping rotating pool of establishing connections until one of them succeeds.
This means that with e.g. -r1 -t5 there will be 5 establishing connections
(to account for slow-to-respond remote hosts) rotating every second, so ratio of
these delays shouldn't be too high to avoid spawning too many connections.
Host/port names specified on the command line are resolved synchronously on script startup (same as with e.g. "ping" tool), so it can't be used to wait until hostname resolves, only for connection itself.
Above example can also be shortened via -s/--ssh option, e.g.:
% tping -s myhost 1234 % tping -s root@myhost:1234 # same thing as above % tping -s -p1234 myhost # same thing as above
Will exec ssh -p1234 root@myhost immediately after successful tcp connection.
Uses python stdlib stuff, namely asyncio, to juggle multiple connections in an efficient manner.
Picks first wireless dev from iw dev and runs hostapd + udhcpd (from
busybox) on it.
Use-case is plugging wifi usb dongle and creating temporary AP on it - kinda like "tethering" functionality in Android and such.
Configuration for both is generated using reasonable defaults - distinctive
(picked from ssid_list at the top of the script) AP name and random password
(using passgen from this repo or falling back to tr -cd '[:alnum:]'
</dev/urandom | head -c10).
Dev, ssid, password, ip range and such can also be specified on the command line (see --help).
If inet access thru local machine is needed, don't forget to also do something like this (with default ip range of 10.67.35.0/24 and "wlp0s18f2u2" interface name):
# sysctl -w net.ipv4.conf.all.forwarding=1 # iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.67.35.0/24 -j MASQUERADE # iptables -A FORWARD -s 10.67.35.0/24 -i wlp0s18f2u2 -j ACCEPT # iptables -A FORWARD -d 10.67.35.0/24 -o wlp0s18f2u2 -j ACCEPT
These rules are also echoed in the script, with IP and interface name that was used.
For consistent naming of network interfaces from usb devices (to e.g. have constant set of firewall rules for these), following udev rule can be used (all usb-wlan interfaces will be named according to NAME there):
SUBSYSTEM=="net", ACTION=="add", ENV{DEVTYPE}=="wlan",\
DEVPATH=="*/usb[0-9]/*", NAME="wlan_usb"
Systemd wrapper for wpa_supplicant or hostapd, enabling either to work with Type=notify, support WatchdogSec=, different exit codes and all that goodness.
Starts the daemon as a subprocess, connecting to its management interface and watching state/wpa_state changes, only indicating "started" state for systemd when daemon actually starts scanning/connecting (for wpa_supplicant) or sets state=enabled for hostapd.
WatchdogSec= issues PING commands to underlying daemon, proxying responses back, as long as daemon state is somehting valid, and not INTERFACE-DISABLED, locally-generated disconnect or such, usually indicating hw failure, kernel module issue or whatever else.
Such thing is needed to have systemd unit state follow AP/STA state, failing when e.g. wifi dongle gets pulled out from USB port, as that doesn't actually cause these things to fail/exit otherwise, which might be desirable if that wifi link is critical to other services or as a reboot-workaround for driver bugs.
Example systemd unit (AP mode):
[Service] ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/wpa-systemd-wrapper \ --exit-check '/run/wpa.wlan0.first-run:config' \ --ap-mode wlan0 /etc/hostapd.wlan0.conf Type=notify WatchdogSec=90 Restart=on-failure RestartPreventExitStatus=78 RestartSec=3 # StartLimitInterval=8min # StartLimitBurst=10 # StartLimitAction=reboot
This will run hostapd (due to -a/--ap-mode), and exit with special 78/CONFIG code if "first-run" file exists and hostapd never gets into ENABLED state on the first attempt - i.e. something likely wrong with the config and there's no point restarting it ad nauseum.
Python/asyncio, requires python-systemd installed, use -h/--help and -d/--debug opts for more info.
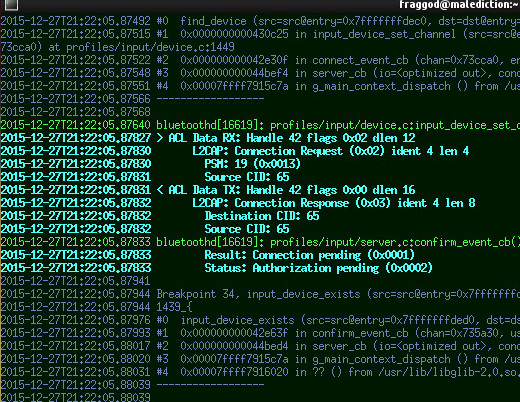
Note: you might want to look at "bneptest" tool that comes with bluez - might be a good replacement for this script, which I haven't seen at the moment of its writing (maybe wasn't there, maybe just missed it).
Bluetooth Personal Area Network (PAN) client/server setup script.
BlueZ does all the work here, script just sends it commands to enable/register appropriate services.
Can probably be done with one of the shipped tools, but I haven't found it, and there's just too many of them to remember anyway.
machine-1 # ./bt-pan --debug server bnep machine-2 # ./bt-pan --debug client <machine-1-bdaddr>
First line above will probably complain that "bnep" bridge is missing and list commands to bring it up (brctl, ip).
Default mode for both "server" and "client" is NAP (AP mode, like with WiFi).
Both commands make bluetoothd (that should be running) create "bnepX" network interfaces, connected to server/clients, and "server" also automatically (as clients are connecting) adds these to specified bridge.
Not sure how PANU and GN "ad-hoc" modes are supposed to work - both BlueZ "NetworkServer" and "Network" (client) interfaces support these, so I suppose one might need to run both or either of server/client commands (with e.g. "-u panu" option).
Couldn't get either one of ad-hoc modes to work myself, but didn't try particulary hard, and it might be hardware issue as well, I guess.
Misc one-off scripts that don't group well with anythin else.
Replacement for standard unix'ish "atd" daemon in the form of a bash script.
Usage: ./at [ -h | -v ] when < sh_script With -v flag ./at mails script output if it's not empty even if exit code is zero.
Simple script to grab a file using wget and then validate checksum of the result, e.g.:
$ wgets -c http://os.archlinuxarm.org/os/ArchLinuxARM-sun4i-latest.tar.gz cea5d785df19151806aa5ac3a917e41c
Using hash: md5
Using output filename: ArchLinuxARM-sun4i-latest.tar.gz
--2014-09-27 00:04:45-- http://os.archlinuxarm.org/os/ArchLinuxARM-sun4i-latest.tar.gz
Resolving os.archlinuxarm.org (os.archlinuxarm.org)... 142.4.223.96, 67.23.118.182, 54.203.244.41, ...
Connecting to os.archlinuxarm.org (os.archlinuxarm.org)|142.4.223.96|:80... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 416 Requested Range Not Satisfiable
The file is already fully retrieved; nothing to do.
Checksum matchedBasic invocation syntax is wgets [ wget_opts ] url checksum, checksum is
hex-decoded and hash func is auto-detected from its length (md5, sha-1, all
sha-2's are supported).
Idea is that - upon encountering an http link with either checksum on the page or in the file nearby - you can easily run the thing providing both link and checksum to fetch the file.
If checksum is available in e.g. *.sha1 file alongside the original one, it might be a good idea to fetch that checksum on a different host or a proxy, making spoofing of both checksum and the original file on the same connection a bit harder.
Simple bash wrapper for sendmail command, generating From/Date headers and stuff, just like mailx would do, but also allowing to pass custom headers (useful for filtering error reports by-source), which some implementations of "mail" fail to do.
Uses aspell english dictionaly to generate easy-to-remember passphrase - a Diceware-like method.
Use -e option to get a rough entropy estimate for the resulting passphrase, based on number of words in aspell dictionary dump that is being used.
Other options allow for picking number of words and sanity-checks like min/max length (to avoid making it too unwieldy or easy to bruteforce via other methods).
Simple script to parse long URL with lots of parameters, decode and print it out in an easily readable ordered YAML format or diff (that is, just using "diff" command on two outputs) with another URL.
No more squinting at some huge incomprehensible ecommerce URLs before scraping the hell out of them!
Some minor tools for network configuration from console/scripts, which iproute2 seem to be lacking, in a py3 script.
For instance, if network interface on a remote machine was (mis-)configured in initramfs or wherever to not have link-local IPv6 address, there seem to be no tool to restore it without whole "ip link down && ip link up" dance, which can be a bad idea.
ipv6-lladdr subcommand handles that particular case, generating ipv6-lladdr
from mac, as per RFC 4291 (as implemented in "netaddr" module) and can assign
resulting address to the interface, if missing:
# ip-ext --debug ipv6-lladdr -i enp0s9 -x
DEBUG:root:Got lladdr from interface (enp0s9): 00:e0:4c:c2:78:86
DEBUG:root:Assigned ipv6_lladdr (fe80::2e0:4cff:fec2:7886) to interface: enp0s9ipv6-dns tool generates *.ip.arpa and djbdns records for specified IPv6.
ipv6-name encodes or hashes name into IPv6 address suffix to produce an
easy-to-remember static ones.
iptables-flush removes all iptables/ip6tables rules from all tables,
including any custom chains, using iptables-save/restore command-line tools, and
sets policy for default chains to ACCEPT.
Script to blink gpio-connected leds via /sys/class/gpio interface.
Includes oneshot mode, countdown mode (with some interval scaling option), direct on-off phase delay control (see --pre, --post and --interval* options), cooperation between several instances using same gpio pin, "until" timestamp spec, and generally everything I can think of being useful (mostly for use from other scripts though).
Do openssl s_client -connect somesite </dev/null | openssl
x509 -fingerprint -noout -sha1 in a nicer way - openssl cli tool doesn't seem
to have that.
Also can be passed socks proxy IP:PORT to use socat and pipe openssl connection
through it - for example, to get fingerprint over Tor (with SocksAddress
localhost:1080) link:
% openssl-fingerprint google.com localhost:1080 SHA1 Fingerprint=A8:7A:93:13:23:2E:97:4A:08:83:DD:09:C4:5F:37:D5:B7:4E:E2:D4
Bash script to "nsenter" into specified machine's (as can be seen in ps -eo
machine or nsh when run without args) container namespaces and run login
shell there.
Machine in question must run systemd as pid-1 (e.g. systemd-nspawn container), as it gets picked as --target pid for nsenter.
Very similar to machinectl login <machine>, but does not asks for
user/password and does not start new "systemd --user" session, just runs
su - to get root login shell.
Essentially same as machinectl shell <machine>, but doesn't require
systemd-225 and machine being registered with systemd at all.
If running tty there says not a tty and e.g. screen bails out with
Must be connected to a terminal., just run extra getty tty there - will
ask to login (be mindful of /etc/securetty if login fails), and everything
tty-related should work fine afterwards.
If run without argument or with -l/--list option, will list running machines.
See also: lsns(1), nsenter(1), unshare(1)
Wrapper that opens specified PAM session (as per one of the configs in
/etc/pam.d, e.g. "system-login"), switches to specified uid/gid and runs
some command there.
My use-case is to emulate proper "login" session for systemd-logind, which
neither "su" nor "sudo" can do (nor should do!) in default pam configurations
for them, as they don't load pam_systemd.so (as opposed to something like
machinectl shell myuser@ -- ...).
This script can load any pam stack however, so e.g. running it as:
# pam-run -s system-login -u myuser -t :1 \
-- bash -c 'systemctl --user import-environment \
&& systemctl --user start xorg.target && sleep infinity'
Should initiate proper systemd-logind session (and close it afterwards) and start "xorg.target" in "myuser"-specific "systemd --user" instance (started by logind with the session).
Can be used as a GDM-less way to start/keep such sessions (with proper display/tty and class/type from env) without much hassle or other weirdness like "agetty --autologin" or "login" in some pty (see also mk-fg/de-setup repo), or for whatever other pam wrapping or testing (e.g. try logins with passwords from file), as it has nothing specific (or even related) to desktops.
Self-contained python script, using libpam via ctypes.
Warning: this script is no replacement for su/sudo wrt uid/gid-switching, and doesn't implement all the checks and sanitization these tools do, so only intended to be run from static, clean or trusted environment (e.g. started by systemd or manually).
Python script to print prime numbers in specified range.
For small ranges only, as it does brute-force [2, sqrt(n)] division checks, and intended to generate primes for non-overlapping "tick % n" workload spacing, not any kind of crypto operations.
Py script to run on early boot, checking specific directory for update-files and unpack/run these, recording names to skip applied ones on subsequent boots.
Idea for it is to be very simple, straightforward, single-file drop-in script to put on distributed .img files to avoid re-making these on every one-liner change, sending tiny .update files instead.
Update-file format:
- Either zip or bash script with .update suffix.
- Script/zip detected by python's zipfile.is_zipfile() (zip file magic).
- If zip, should contain "_install" (update-install) script inside.
- Update-install script shebang is optional, defaults to "#!/bin/bash".
Update-install script env:
BP_UPDATE_ID: name of the update (without .update suffix, e.g. "001.test").
BP_UPDATE_DIR: unpacked update zip dir in tmpfs.
Will only have "_install" file in it for standalone scripts (non-zip).
BP_UPDATE_STATE: /var/lib/boot-patcher/<update-id>
Persistent dir created for this update, can be used to backup various updated/removed files, just in case.
If left empty, removed after update-install script is done.
BP_UPDATE_STATE_ROOT: /var/lib/boot-patcher
BP_UPDATE_REBOOT: reboot-after flag-file (on tmpfs) to touch.
If reboot is required after this update, create (touch) file at that path.Reboot will be done immediately after this particular update, not after all of them.BP_UPDATE_REAPPLY: flag-file (on tmpfs) to re-run this update on next boot.
Can be used to retry failed updates by e.g. creating it at the start of the script and removing on success.
Example update-file contents:
2017-10-27.001.install-stuff.zip.update
_install:cd "$BP_UPDATE_DIR" exec pacman --noconfirm -U *.pkg.tar.xz
*.pkg.tar.xz- any packages to install, zipped alongside that ^^^2017-10-28.001.disable-console-logging.update (single update-install file):
patch -l /boot/boot.ini <<'EOF' --- /boot/boot.ini.old 2017-10-28 04:11:15.836588509 +0000 +++ /boot/boot.ini 2017-10-28 04:11:38.000000000 +0000 @@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ hdmitx edid setenv condev "console=ttyAML0,115200n8 console=tty0" -setenv bootargs "root=/dev/mmcblk1p2 ... video=HDMI-A-1:1920x1080@60e" +setenv bootargs "root=/dev/mmcblk1p2 ... video=HDMI-A-1:1920x1080@60e loglevel=1" setenv loadaddr "0x1080000" setenv dtb_loadaddr "0x1000000" EOF touch "$BP_UPDATE_REBOOT"
2017-10-28.002.apply-patches-from-git.zip.update
_install:set -e -o pipefail cd /srv/app for p in "$BP_UPDATE_DIR"/*.patch ; do patch -p1 -i "$p"; done
*.patch- patches for "app" from the repo, made by e.g.git format-patch -3.
Misc notes:
- Update-install exit code is not checked.
- After update-install is finished, and if BP_UPDATE_REAPPLY was not created, "<update-id>.done" file is created in BP_UPDATE_STATE_ROOT and update is skipped on all subsequent runs.
- Update ordering is simple alphasort, dependenciess can be checked by update scripts via .done files (also mentioned in prev item).
- No auth (e.g. signature checks) for update-files, so be sure to send these over secure channels.
- Run as
boot-patcher --print-systemd-unitfor the only bit of setup it needs.
Simple py3 script to decode audit messages from "journalctl -af -o json" output, i.e. stuff like this:
Jul 24 17:14:01 malediction audit: PROCTITLE proctitle=7368002D630067726570202D652044... (loooong hex-encoded string) Jul 24 17:14:01 malediction audit: SOCKADDR saddr=020000517F0000010000000000000000
Into this:
PROCTITLE proctitle='sh -c grep -e Dirty: -e Writeback: /proc/meminfo' SOCKADDR saddr=127.0.0.1:81
Filters for audit messages only, strips long audit-id/time prefixes, unless -a/--all specified, puts separators between multi-line audit reports, relative and/or differential timestamps (-r/--reltime and -d/--difftime opts).
Audit subsystem can be very useful to understand which process modifies some path, what's the command-line of some /bin/bash being run from somewhere occasionally, or what process/command-line connects to some specific IP and what scripts it opens beforehand - all without need for gdb/strace, or where they're inapplicable.
Some useful incantations (cheatsheet):
# auditctl -e 1 # auditctl -a exit,always -S execve -F path=/bin/bash # auditctl -a exit,always -F auid=1001 -S open -S openat # auditctl -w /some/important/path/ -p rwxa # auditctl -a exit,always -F arch=b64 -S connect # audit-follow -ro='--since=-30min SYSLOG_IDENTIFIER=audit' | grep --line-buffered -B1000 -F some-interesting-stuff | tee -a audit.log # auditctl -e 0 # auditctl -D
Simple ncurses-based interactive (TUI) decimal/hex/binary py3 converter script for the terminal.
Main purpose it to easily experiment with flipping bits and digits in values, seeing nicely aligned/formatted/highlighted immediate changes in other outputs and an easy converter tool as well.
Controls are: cursor keys, home/end, backspace, insert (insert/replace mode), 0/1 + digits + a-f, q to quit.
There's a picture of it on the blog page here.
Python script to iterate over all messages in all folders of a maildir and print (decoded) headers and plain + html body of each (decoded) message, with every line prefixed by its filename.
Intended use is to produce a text dump of a maildir for searching or processing it via any simple tools like grep or awk.
So using e.g. maildir-cat | grep 'important-word' will produce same output
as grep -r 'important-word' email-texts/ would if emails+headers were dumped
as simple text files there.
Small py3/asyncio UDP listener that receives ~100B pk || box(name:addr)
libnacl-encrypted packets, decrypts (name, addr) tuples from there,
checking that:
- Public key of the sender is in -a/--auth-key list.
- Name doesn't resolve to same IP already, among any others (-c/--check option).
- Name has one of the allowed domain suffixes (-d/--update option).
If all these pass, specified BIND-format zone-file (for e.g. nsd) is updated, or DNS service API used to same effect, with several retries on any fails (-r/--retry option) and rate-limiting, as well as --debug logging.
Useful wrapper for auto-updating names in delegated nsd-managed zone, or doing same via DNS APIs that only provide all-or-nothing access, while you want to setup convenience names from some shared-access VM, without giving away creds for the whole account on these services, with all other names and subdomains there.
Example snippet for sending update packets:
import socket, time, libnacl.public, base64, pathlib as pl
b64_decode = lambda s: ( base64.urlsafe_b64decode
if '-' in s or '_' in s else base64.standard_b64decode )(s)
class Conf:
proxy_addr = 'dns-proxy.host.net'
proxy_pk = 'wnQvfuzUNyjDgFhPa23y0z5iXJl8TuZ+rdL0G3vefxQ='
sk_file = 'local_key.secret' # use e.g. "wg genkey" or libnacl
key = libnacl.public.SecretKey(b64_decode(pl.Path(sk_file).read_text()))
box = libnacl.public.Box(key, b64_decode(proxy_pk))
encrypt = lambda s, msg: s.key.pk + s.box.encrypt(msg)
proxy_conf = Conf()
def update_dns(conf, name, addr):
msg = conf.encrypt(f'{name}:{addr}'.encode())
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM) as s:
for delay in [0.1, 0.5, 1, 3, 0]:
try: s.sendto(msg, conf.proxy_addr)
except (socket.gaierror, socket.error): pass
if delay: time.sleep(delay)
update_dns(proxy_conf, 'my.ddns.host.net', '1.2.3.4')
Python + async_dns authoritative DNS resolver daemon to return hashed-name results for testing DNS resolver operation.
For example:
% ./dns-test-daemon -k hash-key -b 127.0.0.1:5533 & % dig -p5533 @127.0.0.1 aaaa test.com ... test.com. 300 IN AAAA eb5:7823:f2d2:2ed2:ba27:dd79:a33e:f762 ...
Here, for AAAA "test.com" query, script returned first 16 bytes of "blake2s(test.com, key=hash-key, person=dnstd.1)" hash digest as a reponse (converted to address via inet_ntop).
Its purpose is to be run as an authoritative resolver for some stub zone forwarded to it, e.g. "*.test.mydomain.com", and then be able to make sure that any local DNS resolver works by querying e.g. "12345.test.mydomain.com" and checking that resulting address hash matches expected value (dependent only on queried name, hash key and that hardcoded person= string).
To run script in tester-client mode, simply pass it a name to test, along with same -k/--hash-key parameter as for daemon on the other end, e.g.:
% ./dns-test-daemon -k hash-key random-stuff.test.mydomain.com % ./dns-test-daemon -k hash-key --debug @.test.mydomain.com
It will exit with non-zero code if result is missing or doesn't match expected value in any way.
Does not import/use or require asyncio and async_dns modules in client mode.
Its -c/--continuous mode can be used together with systemd to kick/restart unreliable resolver daemon (e.g. unbound) when it hangs or fails in other ways:
[Service] Type=exec User=dnstd ExecStart=dns-test-daemon -c 150:6:100 -p 1.1.1.1 @.test.mydomain.com ExecStopPost=+bash -c '[[ "$$SERVICE_RESULT" = success ]] || systemctl try-restart unbound' # Using RestartForceExitStatus=53 should prevent unbound restarts on script bugs RestartForceExitStatus=53 RestartSec=5min [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.service
Note -p 1.1.1.1 ping-option there to avoid restarting the daemon if whole
network is down, which runs "fping" to check that on detected DNS failures.
Python/ctypes script to be used alongside nginx-stat-check module, reliably tailing any kind of access.log-like file(s) where first (space-separated) field is IP address and creating files with name corresponding to these in specified db_dir.
nginx-stat-check module then allows to use stat_check /some/db_dir/$remote_addr;
in nginx.conf to return 403 for all addresses processed in this way.
Created files are automatically renamed and cleaned-up after specified unblock/forget-timeouts and block-timeout either get extended or multiplied by specified k value (2x default) on repeated blocks after expiry.
Intended use it to block stupid bots and whatever spammers that don't care about robots.txt when these access some honeypot-file on nginx level (with proper 403 on specific URL paths), which normally should never be requested.
I.e. bots that are stupidly re-indexing giant file dumps or whatever dynamic content every N minutes.
Example nginx.conf snippet:
load_module /usr/lib/nginx/modules/ngx_http_stat_check.so;
log_format stat-block '$remote_addr :: $time_iso8601 "$http_referer" "$http_user_agent"';
...
location = /distro/package/mirror/open-and-get-banned.txt {
alias /srv/pkg-mirror/open-and-get-banned.txt;
access_log /var/log/nginx/bots.log stat-block;
}
location /distro/package/mirror {
alias /srv/pkg-mirror;
autoindex on;
stat_check /tmp/stat-block/$remote_addr;
}
And run script to populate /tmp/stat-block/ path from bots.log:
% ./nginx-access-log-stat-block --debug /tmp/stat-block/ /var/log/nginx/bots.log
Check -h/--help output for default block-timeout and such values.
Uses inotify to tail files via ctypes, detects log rotation but NOT truncation (use with append/remove-only logs), can tail multiple wildcard-matching files in a directory, closes opened/tailed logs after timeout.
Always opens files at the end, so can loose a line or two due to that, which is fine for intended purpose (bots spam requests anyway).
Bash script to check and wait for various system conditions, processes or thresholds like load average or PSI values.
Random examples:
% sys-wait -l 3 && run-less-heavy-task % sys-wait --load15 5 && run-next-heavy-task % sys-wait --pgrep '-x rsync' && run-other-rsync
Helps to avoid writing those annoyingly-common while :; do some-check ||
break; sleep 60; done; run-other-stuff when something heavy/long is already
running and you just don't have the heart to break and reschedule it properly.
Python + feedparser RSS-to-email notification script for YouTube RSS feeds.
Can process OPML of current YT subscriptions (from https://www.youtube.com/subscription_manager?action_takeout=1 ) or work with one-per-line list of channel/video RSS feed links.
Remembers last feed state(s) via auto-rotating log, uses EWMA to calculate delay between checks based on feed update interval.
Useful to keep track of YT channel updates via read/unread status in some dedicated mailbox folder, and click-open video links from there in mpv, like one could before Aug 2020 when google decided to stop sending all update notification emails on that platform.
Tool to filter, sort and compress list of colors - aka color palette - into base64, to then use as a compact blob in visualization scripts easily.
Input: a list of hex-encoded colors, separated by any spaces/newlines.
Filtering:
Removes colors too close to specified background color (using specified Delta E CIE 2000 color-diff threshold).
Compares colors all-to-all, and removes ones that are too close to each other, with a similar configurable threshold.
Ordering:
Picks next color based on min(deltas-with-others) value, to get the most distinct color on every step.
This is further configured by using higher weights of min(deltas-with-n-last) colors, so that next pick ends up being as distinct as possible from N ones that are right before it first, and then the rest of them.
Current default for
-k/--sort-delta-keys"weight:count" list is "0.3:5 0.2:10 0.1:20", with leftover 0.4 weight used for min(deltas-with-all-picked) value.Output:
Urlsafe-base64 of concatenated 3-byte color values in RGB order, instead of more bulky "lines of hex-encoded colors" or other color-spec types, to hardcode without taking too much space.
Intended use it to have output color list of 50+ values, and then pick them in order (for chart lines, tree branches, table row/cell backgrounds, etc), which should return most distinctive colors first, without resorting to repetition as quickly as with e.g. D3.js fixed 10/20-color palettes.
There are many great tools like "i want hue" that can be used to generate input color list for this script, with features like accounting for color blindness types, but it can be just a sequence of points from any nice gradient too - input ordering or similarity should not matter.
It's a small python script, which uses colormath module for Delta E CIE 2000 color-diff calculations. Can take some time to run with long lists due to how all*all combinatorics work, but using pypy instead of cpython can speed that up a lot.
Minor things I tend to use when writing code and stuff.
Very simple script to replace tabs with spaces and back, doing minor sanity checks and printing files with replacements to stdout.
Goal is to avoid all inconvenience with handling unfamiliar indent types in editor, and just have it setup for strictly one of those, doing translation before/after commits manually.
Script to indent lines in a file based on opening/closing braces and nothing else.
Works for files with any custom syntax instead of just code, like whatever configs, game save files, serializations, etc.
Has configurable braces and their output format strings to allow producing different indent styles, e.g. opening/closing brace on either same or new lines, their indents and such.
Doesn't re-encode input, so should work with any file encodings that can't include same byte as braces in other characters (like utf-8).
Running on large (multi-MiB) files via pypy3 works much faster than cpython.
Same idea as in "tabs_filter", but on a larger scale - basically does to Go what coffee-script does to the syntax of javascript - drops all the unnecessary brace-cancer, with the ability to restore original perfectly ("diff -u reverse original" is checked upon transformation to make sure of that), as long as code intentation is correct.
.git/config:
[filter "golang"] clean = golang_filter git-clean %f smudge = golang_filter git-smudge %f
.git/info/attributes or .gitattributes:
*.go filter=golang
Again, ideally no one should even notice that I actually don't have that crap in the editor, while repo and compiler will see the proper (bloated) code.
Tool to auto-update python package metadata in setup.py and README files.
Uses python ast module to parse setup.py to find "version" keyword there and update it (via simple regex replacement, not sure if ast can be converted back to code properly), based on date and current git revision number, producing something like "12.04.58" (year.month.revision-since-month-start).
Also generates (and checks with docutils afterwards) README.txt (ReST) from README.md (Markdown) with pandoc, if both are present and there's no README or README.rst.
Designed to be used from pre-commit hook, like ln -s /path/to/distribute_regen
.git/hooks/pre-commit, to update version number before every commit.
Ad-hoc tool to dissect and convert darcs bundles into a sequence of unified diff hunks. Handles file creations and all sorts of updates, but probably not moves and removals, which were outside my use-case at the moment.
Was written for just one occasion (re-working old bundles attached to tahoe-lafs tickets, which crashed darcs on "darcs apply"), so might be incomplete and a bit out-of-date, but I imagine it shouldn't take much effort to make it work with any other bundles.
Script to read NYM env var and run git using that ssh id instead of whatever
ssh-agent or e.g. ~/.ssh/id_rsa provides.
NYM var is checked for either full path to the key, basename in ~/.ssh, name
like ~/.ssh/id_{rsa,ecdsa,ed25519}__${NYM} or unique (i.e. two matches will
cause error, not random pick) match for one of ~/.ssh/id_* name part.
Can be used as NYM=project-x git-nym clone git@dev.project-x:component-y to
e.g. clone the specified repo using ~/.ssh/id_rsa__project-x key or as
NYM=project-x git nym clone ....
Also to just test new keys with git, disregarding ssh-agent and lingering control sockets with NYM_CLEAN flag set.
Git-command replacement for git-diff to run meld instead of regular (git-provided) textual diff, but aggregating all the files into one invocation.
For instance, if diffs are in server.py and client.py files, running
git meld will run something like:
meld \ --diff /tmp/.git-meld/server.py.hash1 /tmp/.git-meld/server.py.hash2 \ --diff /tmp/.git-meld/client.py.hash1 /tmp/.git-meld/client.py.hash2
Point is to have all these diffs in meld tabs (with one window per git meld)
instead of running separate meld window/tab on each pair of files as setting
GIT_EXTERNAL_DIFF would do.
Should be installed as git-meld somewhere in PATH and symlinked as
meld-git (git-meld runs GIT_EXTERNAL_DIFF=meld-git git diff "$@") to
work.
Similar to "cat" (specifically coreutils' cat -n file), but shows specific
line in a file with a few "context" lines around it:
% catn js/main.js 188
185: projectionTween = function(projection0, projection1) {
186: return function(d) {
187: var project, projection, t;
>> 188: project = function(λ, φ) {
189: var p0, p1, _ref1;
190: λ *= 180 / Math.PI;
191: φ *= 180 / Math.PI;
Above command is synonymous to catn js/main.js 188 3, catn
js/main.js:188 and catn js/main.js:188:3, where "3" means "3 lines of
context" (can be omitted as 3 is the default value there).
catn -q ... outputs line + context verbatim, so it'd be more useful for
piping to another file/command or terminal copy-paste.
Script to permanently delete files/folders from repository and its history - including "dangling" objects where these might still exist.
Should be used from repo root with a list of paths to delete, e.g.
git_terminate path1 path2.
WARNING: will do things like git reflog expire and git gc with agressive
parameters on the whole repository, so any other possible history not stashed or
linked to existing branches/remotes (e.g. stuff in git reflog) will be
purged.
Checks if passed tree-ish (hash, trimmed hash, branch name, etc - see "SPECIFYING REVISIONS" in git-rev-parse(1)) object(s) exist (e.g. merged) in a specified git repo/tree-ish.
Essentially does git rev-list <tree-ish2> | grep $(git rev-parse
<tree-ish1>).
% git_contains -C /var/src/linux-git ee0073a1e7b0ec172 [exit status=0, hash was found] % git_contains -C /var/src/linux-git ee0073a1e7b0ec172 HEAD notarealthing Missing: notarealthing [status=2 right when rev-parse fails before even starting rev-list] % git_contains -C /var/src/linux-git -H v3.5 --quiet ee0073a1e7b0ec172 [status=2, this commit is in HEAD, but not in v3.5 (tag), --quiet doesn't produce stdout] % git_contains -C /var/src/linux-git --any ee0073a1e7b0ec172 notarealthing [status=0, ee0073a1e7b0ec172 was found, and it's enough with --any] % git_contains -C /var/src/linux-git --strict notarealthing fatal: ambiguous argument 'notarealting': unknown revision or path not in the working tree. Use '--' to separate paths from revisions, like this: 'git <command> [<revision>...] -- [<file>...]' git rev-parse failed for tree-ish 'notarealting' (command: ['git', 'rev-parse', 'notarealting'])
Lines in square brackets above are comments, not actual output.
Renders gtk3 window with a slider widget and writes value (float or int) picked there either to stdout or to a specified file, with some rate-limiting delay.
Useful to mock/control values on a dev machine.
E.g. instead of hardware sensors (which might be hard to get/connect/use), just setup app to read value(s) that should be there from file(s), specify proper value range to the thing and play around with values all you want to see what happens.
Very simple script to bump version numbers for file(s) in a git repo before commit, implemented via git content filters and gitattributes(5).
Should be defined in .git/config of the repo:
[filter "version-bump"] clean = git-version-bump-filter %f
And then applied to specific files via repo .gitattributes like this:
/app.py filter=version-bump
(can be safely applied to files without versions in them as well)
It bumps last number in lines that contain comment-tags
that look like # git-version: py-tuple:
version = 1, 0 # git-version: py-tuple
Version before which will be auto-replaced by something like "1, 23" in the repo, with last number being number counting changes to that specific file.
Can run "git diff" right after adding that comment to see how line will look in the repo after content filtering was applied, i.e. whether/how it works.
Available replacement types, with examples where 0 will be auto-replaced:
some_version = 2, 3, 0 # git-version: py-tupleself.server_ver = '5.6.0' # git-version: py-str
Script also has -d/--date-ver option to generate full three-component
versions in a <YY>.<mm>.<commits-since-month-start> format, e.g. 22.05.3
(with tuple of 3 ints for py-tuple), which should generally be more meaningful
than just a monotonic number.
Beauty of this approach is that local file(s) remain unchanged unless checked back out from the repo, not triggering any kind of concurrent modification alerts from editors, and doesn't make commit process any more complicated either.
Can be run without arguments in a git repo to checkout all content-filtered files back out, making sure that they have no uncommitted changes first (to avoid loosing these).
Runs a single git-log and sed command under the hood, nothing fancy.
Common hook that I use for all git repos to append useful comment-lines to generated commit-msg, including which relative dir you're currently in, repository dir and a list of previous commit-msgs for reference.
These lines don't make it into the actual commit, but allow to, at a glance:
Make sure you're the right repository, and not e.g. clone or submodule somewhere else on the fs or sshfs, where you were testing things or something.
Provide good template for component you were editing there - subdir within the repo where you just ran "git commit" command.
Unless there's other convention in place, I often use such subdirs as a commit-msg prefix, esp. in monorepos that track separate things, like this one.
Give examples of commit msgs to maintain consistent style between these.
Check that you're on the right history, don't make duplicate or redundant commits, don't have anything unexpected left or merged in there.
Example of generated commit-msg comment with this hook:
# Please enter the commit message for your changes. Lines starting # with '#' will be ignored, and an empty message aborts the commit. # # Author: Mike Kazantsev <some-email@host.something> # # On branch master # Changes to be committed: # modified: README.rst # new file: dev/git-prepare-commit-msg-hook # # Untracked files: # bpf/bpf.cgroup-skb.nonet.o # desktop/exclip # desktop/xdpms # # # Commit dir: # Repo dir: /home/fraggod/hatch/fgtk # # desktop.media.ytdl-chan: youtube-dl -> yt-dlp # vm.linux: +NO_AT_BRIDGE=1 # vm: cleanup old redundant/unused scripts # desktop.hamster-tally: fix symlink updates with no logs ...
Everything that hook adds is at the end, and it detects merges, rebases, cherry-picks and such ops to not mess with non-interactive commit msgs.
Should be copied to .git/hooks/prepare-commit-msg in any repo where it should be used, or can potentially be used globally via core.hooksPath git-config setting, but that requires some work to also place proxies for all other hooks there, as it'd prevent running repo-local hooks by default otherwise.
After using it for couple years now (as of 2022), don't think I found a repo where I don't want to have this hook yet, but might be just me, of course.
Various dedicated backup tools and snippets.
"ssh -Rsync" - SSH shell and client to negotiate/run rsync pulls over ssh reverse tunnels ("ssh -R") without any extra client-side setup.
Just running ssh-r-sync user@backup-host somedir should ssh into
user@backup-host, with auto-selected reverse-tunnel (-R) spec depending on
local machine name, pass backup parameters and run rsync --daemon locally,
allowing remote backup-host to initiate a pull from this daemon over established
secure/authenticated ssh tunnel, picking appropriate destination path and most
rsync parameters, rotating/removing stuff on the backup-fs (via hooks) as necessary.
This is done to avoid following problematic things:
- Pushing stuff to backup-host, which can be exploited to delete stuff.
- Using insecure network channels and/or rsync auth - ssh only.
- Having any kind of insecure auth or port open on backup-host (e.g. rsyncd) - ssh only.
- Requiring backed-up machine to be accessible on the net for backup-pulls - can be behind any amount of NAT layers, and only needs one outgoing ssh connection.
- Specifying/handling backup parameters (beyond --filter lists), rotation and cleanup on the backed-up machine - backup-host will handle all that in a known-good and uniform manner.
- Running rsyncd or such with unrestricted fs access "for backups" - only runs it on localhost port with one-time auth for ssh connection lifetime, restricted to specified read-only path, with local filter rules on top.
- Needing anything beyond basic ssh/rsync/python on either side.
Idea is to have backup process be as simple as ssh'ing into backup-host, only specifying path and filter specs for what it should grab.
rsync is supposed to start by some regular uid on either end, so if full fs access is needed, -r/--rsync option can be used to point to rsync binary that has cap_dac_read_search (read) / cap_dac_override (write) posix capabilities or whatever wrapper script doing similar thing, e.g.:
# cp /usr/bin/rsync ~backup/ # setcap cap_dac_override,cap_chown,cap_fowner=ep ~backup/rsync
-r ~/rsync to ssh-r-sync-recv ForceCommand to use that binary.To use any special rsync options or pre/post-sync actions on the backup-host side
(such as backup file manifest, backup rotation and free space management,
rsync output/errors checking, etc), hook scripts can be used there,
see ssh-r-sync-recv --hook-list for more info.
ssh-r-sync-recv -h for sshd_config setup notes.Bash wrapper around ssh to run it in non-interactive command mode, storing output to specified path with date-suffix and optional compression/rotation.
Implements very basic operation of grabbing either some command output or file contents from remote host for backup purposes.
Passes bunch of common options to use ssh batch mode, disable non-key auth and enable keepalive in case of long-running remote commands.
Script to ssh into mikrotik routers with really old DSA-only firmware via specified ("--auth-file" option) user/password and get the /export backup, optionally compressing it.
Should not be needd for modern firmwares, where just using e.g. ssh
admin@router /export with RSA keys works perfectly well.
"ssh-dump" script above can be used to pass all necessary non-interactive
mode options and compress/rotate resulting file with these.
Simple py script to create ZFS snapshot and keep a number of older snapshots according to a retention policy, similar to how btrbk tool does it (specified via -p/--ret-policy option):
[<n>] [<hourly>h] [<daily>d] [<weekly>w] [<monthly>m] [<yearly>y]
Such policy defines max number of most recent -ly snapshots to preserve. I.e. "3 weekly" means to make sure one snapshot from this week, one from last week, and one from the week before that will be preserved.
Script only matches exact snapshots that it created (renaming these will make it ignore them), and removes all oldest ones that fall outside of retention policy string.
See built-in -h/--help output for more info and all the options.
Similar to sanoid, but much simplier and in python instead of perl.
Same as zfs-snapper script above, but for making and managing read-only snapshots of btrfs subvolumes in a specific directory for those, according to same retention policy string.
Similar to btrbk, but much simplier and more reliable/predictable, without a ton of extra features that's been piled-on there over time.
Similar to zfs-snapper and btrfs-snapper scripts above, except it simply rotates directories instead of running any fs-specific snapshotting commands.
Useful for generic "backup to a dir" scripts, where deduplication on fs level is handled somewhere else or unnecessary.
Helpers for more interactive (client) machine, DE and apps there.
Scripts to delegate downloads from browser to more sensible download managers, like passing magnet: links to transmission, or processing .torrent files.
Scripts - mostly wrappers around ffmpeg and pulseaudio - to work with (or process) various media files and streams.
Creates null-sink in pulseaudio and redirects browser flash plugin audio output stream to it, also starting "parec" and oggenc to record/encode whatever happens there.
Can be useful to convert video to podcast if downloading flv is tricky for whatever reason.
Queries pa sinks for specific pid (which it can start) and writes "media.name" (usually track name) history, which can be used to record played track names from e.g. online radio stream in player-independent fashion.
Simple script to toggle mute for all pluseaudio streams from a specified pid.
Script to toggle - load or unload - pulseaudio module.
For example, to enable/disable forwarding sound over network (e.g. to be played in vlc as rtp://224.0.0.56:9875):
% pa_modtoggle module-rtp-send \ source=alsa-speakers.monitor destination=224.0.0.56 port=9875 Loaded: [31] module-rtp-send source=alsa-speakers.monitor destination=224.0.0.56 port=9875
Same exact command will unload the module (matching it by module name only), if necessary.
Optional -s/--status flag can be used to print whether module is currently loaded.
Uses/requires pulsectl module, python.
Same as pa_track_history above, but gets tracks when mpv dumps icy-* tags (passed in shoutcast streams) to stdout, which should be at the start of every next track.
More efficient and reliable than pa_track_history, but obviously mpv-specific.
Simple script to dump "online radio" kind of streams to a bunch of separate files, split when stream title (as passed in icy StreamTitle metadata) changes.
By default, filenames will include timestamp of recording start, sequence number, timestamp of a track start and a stream title (in a filename-friendly form).
Sample usage: icy_record --debug -x http://pub5.di.fm/di_vocaltrance
Note that by default dumped streams will be in some raw adts format (as streamed over the net), so maybe should be converted (with e.g. ffmpeg) afterwards.
This doesn't seem to be an issue for at least mp3 streams though, which work fine as "MPEG ADTS, layer III, v1" even in dumb hardware players.
Wrapper around mpv_icy_track_history to pick and play hard-coded radio streams with appropriate settings, generally simplified ui, logging and echoing what's being played, with a mute button (on SIGQUIT button from terminal).
Any-media-to-ogg convertor, using ffmpeg and - optionally (with -l/--loudnorm) - its loudnorm filter (EBU R128 loudness normalization) in double-pass mode.
Main purpose is to turn anything that has audio track in it into podcast for an audio player.
Can process several source files or URLs (whatever youtube-dl accepts) in
parallel, split large files into chunks (processed concurrently), displays
progress (from ffmpeg -progress pipe), python/asyncio.
loudnorm filter is fairly recent addition to ffmpeg (added in 3.1 release of 2016-06-27, has libebur128 built-in in 3.2+), and might not be available in distros by default.
Needs youtube-dl installed if URLs are specified instead of regular files.
Wrapper around img2xterm tool to display images in a color-capable terminal (e.g. xterm, not necessarily terminology).
Useful to query "which image is it" right from tty. Quality of the resulting images is kinda amazing, given tty limitations.
Simple bash script to split media files into chunks of specified length (in
minutes), e.g. split some-long-audiobook.mp3 sla 20 will produce
20-min-long sla-001.mp3, sla-002.mp3, sla-003.mp3, etc.
split prefix -- *.mp3Uses ffprobe (ffmpeg) to get duration and ffmpeg with "-acodec copy -vn" (default, changed by passing these after duration arg) to grab only audio chunks from the source file.
Splits m4b audiobook files on chapters (list of which are encoded into m4b as metadata) with ffprobe/ffmpeg.
Chapter offsets and titles are detected via ffprobe -v 0 -show_chapters, and
then each gets extracted with ffmpeg -i ... -acodec copy -ss ... -to ...,
producing aac files with names corresponding to metadata titles (by default, can
be controlled with --name-format, default is {n:03d}__{title}.aac).
Doesn't do any transcoding, which can easily be performed later to e.g. convert resulting aac files to mp3 or ogg, if necessary.
A simple tool to randomly pick and copy files (intended usage is music tracks) from source to destination.
Difference from "cp" is that it will stop when destination will be filled (to a configurable --df-min threshold) or auto-cleanup files from -r/--clean-path as more space is needed for specified ones.
--debug can be used to keep track of what's being done, and calculates how much time is left based on df-goal and median rate.
Use-case is to copy files to simple mp3 player devices:
% mount /mnt/sd_card % pick-tracks -s 200 /mnt/music/OverClocked_Remix /mnt/sd_card/ocr INFO :: Finished: 1673.1M, rate: 1.29 MiB/s, df-after: 199.2M
And later on:
% pick-tracks -r /mnt/sd_card/ocr new-podcasts /mnt/sd_card/podcasts
Without needing to manage space there manually as much.
Source files are filtered by extensiona and are picked in random order to pick different stuff from same large dirs if used repeatedly.
As with "cp", pick-tracks /path1 /path2 /dst usage is perfectly valid.
Uses "rsync --inplace" and "find" to do the actual file listing/filtering and copy ops.
Optionally also uses unidecode and mutagen modules, by default if available, to generate more descriptive and compatible destination filenames, based on media tags, instead of reusing source filenames, unless disabled.
Script to download any time slice of a twitch.tv VoD (video-on-demand).
This is the latest version that's been tested and confirmed to work on Windows, see mk-fg's repository for the absolute latest version (which has been tested on a Unix-like OS and may or may not work on Windows).
youtube-dl - the usual tool for the job - doesn't support neither seeking to time nor length limits, but does a good job of getting a VoD m3u8 playlist with chunks of the video (--get-url option).
Also, some chunks getting stuck here at ~10-20 KiB/s download rates, making "sequentially download each one" approach of mpv/youtube-dl/ffmpeg/etc highly inpractical, and there are occasional errors too.
So this wrapper grabs that playlist, skips chunks according to EXTINF tags (specifying exact time length of each) to satisfy --start-pos / --length, and then passes all these URLs to aria2 for parallel downloading with stuff like --max-concurrent-downloads=5, --max-connection-per-server=5, --lowest-speed-limit=100K, etc (see TVFConfig at the start of the script), also scheduling retries for any failed chunks a few times with delays.
In the end, chunks get concatenated (literally, think "cat") together into one resulting mp4 file.
Process is designed to tolerate Ctrl+C (or SIGKILL) and resume from any point, keeping some temporary files around for that until file is fully downloaded.
Includes "--scatter" ("-x") mode to download every-X-out-of-Y timespans instead
of full video, and has source timestamps on seeking in concatenated result
(e.g. for -x 2:00/15:00, minute 3 in the video should display as "16:00",
making it easier to pick timespan to download properly).
Video chunks get concatenated into partial file as they get downloaded, allowing to start playback before whole process ends.
General usage examples (wrapped):
% twitch_vod_fetch \ http://www.twitch.tv/starcraft/v/15655862 sc2_wcs_ro8 \ http://www.twitch.tv/starcraft/v/15831152 sc2_wcs_ro4 \ http://www.twitch.tv/starcraft/v/15842540 sc2_wcs_finals \ http://www.twitch.tv/starcraft/v/15867047 sc2_wcs_lotv % twitch_vod_fetch -x 120/15:00 \ http://www.twitch.tv/redbullesports/v/13263504 sc2_rb_p01_preview % twitch_vod_fetch -s 4:22:00 -l 2:00:00 \ http://www.twitch.tv/redbullesports/v/13263504 sc2_rb_p01_picked_2h_chunk % twitch_vod_fetch -p \ http://www.twitch.tv/starcraft/v/24523048 sc2_blizzcon_finals \ &>sc2_blizzcon_finals.log & % mpv sc2_blizzcon_finals.mp4 # starts playback before download ends
Bash wrapper script around youtube-dl tool to download numbered range of videos (from n_first to n_last) for youtube channel in reverse order to how they're listed in the metadata cache file (usually latest-to-oldest, hence reverse order).
Basically a thing to binge-watch everything from some channel, in order, without instantly running out of disk space.
Usage is simply ytdl-chan 1 10 to e.g. download 10 (1st to 10th) oldest
videos (numbers are inclusive, 1-indexed) on the channel to the current dir,
numbering them accordingly (001__sometitle.mp4, 002__..., etc).
Run in an empty dir with any numbers to get more info on how to get metadata cache file (list of yt json manifests, one per line).
Be sure to use ~/.config/youtube-dl/config for any ytdl opts, as necessary,
or override these via env / within a script.
Requires youtube-dl and jq (to parse URLs from json).
Bash wrapper for streamlink to make dumping stream to a file more reliable, auto-restarting the process with new filename after any "stream ended" events or streamlink app exits.
Example use:
% streamdump --retry-streams 60 --retry-open 99999 \ --twitch-disable-hosting --twitch-disable-ads --twitch-disable-reruns \ twitch.tv/user 720p -fo dump
Will create "dump.000.mp4", "dump.001.mp4" and so on for each stream restart.
Intended use is for unreliable streams which go down and back up again in a minute or few, or working around streamlink quirks and fatal errors.
Wrapper for ImageMagick's convert and jpegoptim tools to process large images from multi-Mpx source like a phone camera and make it reasonably-sized instead of a giant multi-MiB file.
Can be used as image-compact image.jpg for default "fit into 1600x square"
mode, or with optional size argument to scale it differently, but always preserving
the aspect ratio.
A bunch of tools to issue various desktop notifications.
Wrapper to run specified command and notify (via desktop-notifications only atm) if it fails (including "no such binary" errors) or produces any stderr.
Optionally produces notification in any case.
Useful mainly for wrapping hooks in desktop apps like browsers, to know if click on some "magnet:..." link was successfully processed or discarded with some error.
% notify.exec -h --
usage: notify.exec [ options... -- ] command [ arguments... ]
Wrapper for command execution results notification.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-e, --exit-code-only Issue notification only if exit code not equals zero,
despite stderr.
-v, --notify-on-success
Issue notification upon successful execution as well.
-d, --dump Include stdou/stderr for all notifications.
...
Script to spam desktop-notifications when charger gets plugged/unplugged via udev rules on an old laptop with somewhat flaky power connector.
Useful to save a few battery/power cycles due to random electrical contact loss in charger or just plain negligence, if nothing else in DE has good indication for that already.
Script to watch log files (as many as necessary) for changes with inotify and report any new lines appearing there via desktop notifications, handling file rotation (via truncation or rename/unlink) and such.
Can remember last position in file either by recording it in file's xattrs or in a shelve db (specified via -x/--xattr-db option). Doesn't do much with it by default though, starting to read files from the end, but that can be fixed by passing --keep-pos.
Has --tb-rate-filter option to rate-limit occasional log-spam (reporting only "skipped N msgs" as soon as filter allows) via simple token-bucket filter, see -h/--help output for more info.
Somewhat advanced usage example:
% logtail \ --keep-pos --tb-rate-filter 1:5 \ --icon ~/media/appz/icons/biohazard_48x.png \ --xattr-db "$XDG_RUNTIME_DIR"/logtail.db \ /var/log/messages /var/log/important/*
Python, needs python-gobject ("gi" module, for notifications), uses inotify via ctypes.
Daemon script to monitor dovecot delivery logs (either generic ones, or produced via "mail_log" plugin), efficiently find delivered messages in maildir by their message-ids from the log, and issue desktop notification to a remote host with parsed message details (path it was filed under, decoded "from" and "subject" headers).
Things like rsyslog make it fairly easy to create a separate log with such notifications for just one user, e.g.:
if ( $programname == 'dovecot' and $syslogfacility-text == 'mail' and $syslogseverity-text == 'info' and re_match($msg, '^lda\\(someuser\\): sieve: msgid=[^:]+: stored mail into mailbox .*') ) then action( type="omfile" FileCreateMode="0660" FileOwner="root" FileGroup="someuser" File="/var/log/processing/mail.deliver.someuser.log" )
Remote notifications are delivered to desktop machines via robust zeromq pub/sub sockets as implemented in notification-thing daemon (one that I'm using), but script can easily be tweaked to use some other mechanism.
This hack doesn't require running a mail client, but it's possible that these might also support realtime notifications like these via IDLE and NOTIFY IMAP protocol commands, but claws-mail doesn't seem to support those yet, and that's the one I have here.
Script to display specified xdg icon or image in a transparent popup window, with specified size (proportional scaling) and offset.
Supposed to be used with compositing WMs to display an icon (e.g. png with transparency) on top of everything else as a very crude and "in your face" means of notification.
For example, icon -o=-10%:-10% -s=300 ~/battery-critical.png
will display specified png scaled proportionately to 300x300 px box
with 10% (of screen width/height) offset from bottom-right screen corner.
icon call-start will dislay "call-start" icon from the theme
(with -s/--size specifying icon size to pick, e.g. 32, 64, 128).
If file/icon cannot be found, Error: {icon-name} replacement text
will be displayed in a semi-transparent box instead.
Stuff gets displayed until process is terminated. Uses gtk3/pygobject.
Python script to list/shuffle/order and do some other things to LFN entries inside vfat filesystem directory without mounting the thing.
Implemented to work around limitations of crappy cheap mp3 players that don't have shuffle (or any ordering) functionality and cycle tracks in the same order as their dentries appear on fs.
Easy way to "shuffle" stuff for these in a quick and efficient manner is to swap dentries' places, which (unfortunately) requires re-implementing a bit of vfat driver code, which (fortunately) isn't that complicated.
Tool takes path to device and directory to operate on as arguments (see --help)
and has -l/--list (simply list files, default), -s/--shuffle (shuffle
operation), ---o/order, --rename plus some other action-opts (all support
-r/--recursive operation), and --debug --dry-run can be useful to check what
script does without making any fs changes (opens device read-only).
See -h/--help output for more info and usage examples.
One limitation is that it only works with FAT32 "vfat" fs type, which can be created via "mkfs.vfat" tool, not the stuff that "mkdosfs" tool creates, not FAT16, FAT12, exFAT or whatever other variations are out there (they're slightly different and I didn't need any of them, so not implemented).
Might be useful base to hack some fat32-related tool, as it has everything necessary for full r/w implementation - e.g. a tool to hardlink files on fat32, create infinite dir loops, undelete tool, etc.
Due to bunch of heavy parsing done inside, can take a few seconds to process whole fs structure, and works ~5x faster with pypy (e.g. 1.5s instead of 9s).
Uses python/pypy 3.x and construct module.
Somewhat similar project (which I didn't find at the time of implementing this back in 2013) - maxpat78/FATtools.
Script to control speed of dying laptop fan on Acer S3 using direct reads/writes
from/to /dev/ports to not run it too fast (causing loud screech and
vibrating plastic) yet trying to keep cpu cool enough.
Or, failing that, use cpupower tool to drop frequency (making it run cooler in general) and issue dire warnings to desktop.
Script to query beets music database (possibly on a remote host) with specified parameters and add found tracks to EMMS playlist (via emacsclient).
Also allows to just dump resulting paths or enqueue a list of them from stdin.
Old python2 script to backup firefox tab list and settings in a diff/scm-friendly manner - i.e. decoded from horrible one-liner json into pyaml, so that they can be tracked in git.
Written out of frustration about how YouTube Center seem to loose its shit and resets config sometimes.
Can/should be extended to all sorts of other ff/ext settings in the future - and probably is already, see its ff_backup.yaml output example for details.
Command-line tools to interact with firefox-like browsers and their profile settings/data, like list currently open tabs/URLs or (de-)compress .mozlz4 files.
Currently has following tools/commands implemented:
- tabs - list currently open tabs, as stored in
sessionstore-backups/recovery.jsonlz4file. - bookmarks - list and/or open bookmarks from latest "bookmarksbackup" file, optionally filtered/shuffled/cycled/limited via options, mostly to open N random bookmarks of some "time-waster feed" variety.
- mozlz4 - compress/decompress firefox lz4 files, which have slightly different format from what the usual "lz4" cli tool supports, has same interface as gzip, xz, zstd, lz4, and such compression tools.
To be extended with more stuff over time.
BlueZ bluetooth authorization agent script/daemon.
Usually included into DE-specific bluetooth applet or can be used from
"bluetoothctl" client (agent on), but I don't have former (plus just don't
want to rely on any DE much) and latter isn't suitable to run daemonized.
When run interactively (-i/--interactive option), will ask permission (y/n)
to authorize new pairings and enter PINs for these.
With -a/--authorize-services [whitelist-file] option (and optional list of
bdaddrs), will allow any paired device to (re-)connect without asking, allowing
to run it in the background to only authorize trusted (and/or whitelisted)
devices.
Does device power-on by default, has -p/--pairable [seconds],
-d/--discoverable [seconds] and -t/--set-trusted options to cover usual
initialization routines.
Python, needs dbus-python module with glib loop support.
Script to issue notification(s) after some specified period of time.
Mostly to simplify combining "sleep" with "date" and whatever notification means in the shell.
Parses timestamps as relative short times (e.g. "30s", "10min", "1h 20m", etc), iso8601-ish times/dates or falls back to just using "date" binary (which parses a lot of stuff).
Checks that specified time was parsed as a timestamp in the future and outputs how it was interpreted (by default).
Examples:
% alarm -q now
% alarm -c timedatectl now
Parsed time_spec 'now' as 2015-04-26 14:23:54.658134 (delta: just now)% alarm -t 3600 -i my-alarm-icon -s my-alarm-sound -f 'tomorrow 9am' \
'hey, wake up!!!' "It's time to do some stuff... here's the schedule:" \
-c 'curl -s http://my-site.com/schedule/today'
Parsed time_spec 'tomorrow 9am' as 2015-04-27 09:00:00 (delta: 18h 25m)Currently only uses desktop notifications, libcanberra sounds (optional), mail/wall (optional fallbacks) and/or runs whatever commands (use e.g. "zenity" to create modal windows or "wall" for terminal broadcasts).
Can keep track of pending alarms if -p/--pid-file option is used (see also -l/-list and -k/--kill opts), for persistent notifications (between reboots and such), there's an --at option to use at(1p) daemon.
Python, needs python-gobject ("gi" module) for desktop notifications.
Bash script to statelessly enable/disable (and not toggle) events in
/proc/acpi/wakeup (wakeup events from various system sleep states).
E.g. acpi-wakeup-config -LID0 to disable "opening lid wakes up laptop"
regardless of its current setting.
Usual echo LID0 > /proc/acpi/wakeup toggles the knob, which is inconvenient
when one wants to set it to a specific value.
Also has special +all and -all switches to enable/disable all events and
prints the whole wakeup-table if ran without arguments.
"one-letter-at-a-time" script to display (via gtk3/gi) a semi-transparent overlay with lines from stdin, which one can navigate up/down and left/right wrt highlighted characters.
Useful to do any kind of letter-by-letter checks and stuff manually.
Can also be an example code / stub for composited screen overlays with input grab.
Python/Gtk3 script to draw an empty colored/transparent window with custom hints (default: undecorated) and size/position just to cover some screen area.
Useful as a hack to cover windows that grab input or do something stupid on mouseover, but still be able to see their contents, or maybe just cover something on the screen entirely.
For example, to cover left half (960px-wide) of screen with greenish-tinted
half-transparent pane: blinds --pos=960xS+0 --color=0227107f
With custom wm hints/opacity:
blinds -o 0.2 -x 'stick keep_above skip_taskbar skip_pager -accept_focus -resizable'
(see -h/--help output for a full list of these)
Simple tool to bind events (and specific values passed with these) from arbitrary evdev device(s) to keyboard button presses (through uinput).
"evdev -> keyboard" mappings are specified in a YAML file, as well as some other minor parameters (e.g. how long to press keys for, intervals, delays, etc).
For example, to bind rightmost-ish joystick position to press "right" key,
yaml mapping can have this line: ABS_X >30_000: right (absolute right is
~32768, so anything >30k is "close enough", "30_000" is valid YAML integer spec).
Or, to type stuff on gamepad button press: BTN_SOUTH 1: [t,e,s,t,enter]
Requires python, python-evdev, standard "uinput" kernel module enabled/loaded, read access to specified evdev(s) and rw to /dev/uinput.
Small standalone C binary based on xclip code to copy primary X11 selection text (utf-8) from terminal (or whatever else) to clipboard as a single line, stripping any stray tabs/newlines that might get in there (due to terminal quirks, e.g. with screen/tmux/ncurses) and spaces at the start/end, unless -x/--verbatim is specified.
Basically what something like "xclip -out | <process> | xclip -in" would do, except as a tiny fast-to-run binary (to bind to a key), and with multiplexing (to clipboard and back to primary).
Build with: gcc -O2 -lX11 -lXmu exclip.c -o exclip && strip exclip
Safe wrt NUL-bytes, but should not be used without -x/--verbatim on multi-byte non-utf-8 encodings (where \n byte can mean something else), and won't strip any weird non-ascii utf-8 spaces.
Has -d/--slashes-to-dots and -t/--tabs-to-spaces options to process output in various ways - see -h/--help output for more info.
Tiny 50-line C tool, kinda like xprintidle, but instead of idle time, prints how
many seconds are left until dpms will turn off display(s) (dpms as in xset q),
or "0" if it already happened.
Purpose is to check whether some "display is disabled" action should be taken, or otherwise get the countdown until the next check.
Build with: gcc -O2 -lX11 -lXss -lXext xdpms.c -o xdpms && strip xdpms
Should work on Xorg systems, but under wayland same thing should probably be queried from compositor somehow, or ideally it might even emit on/off events somewhere, instead of needing this kind of polling.
Python/feedparser script to download items attached to RSS feeds fast using aria2 tool, or just printing the info/URLs.
Example use can be grabbing some range of podcast mp3s from a feed URL.
aria2 allows for parallel multi-chunk downloads of throttled items, and wrapper script has option to pass it destination filenames according to item date/time instead of the usual nonsensical, incoherent and inconsistent names authors seem to inevitably assign to files on a regular-content feeds.
Bash wrapper around qrencode and zbar tools to assemble/display or decode QR-encoded strings.
Encode-display mode provides an easy way to pass some data like WiFi AP creds to
a smartphone via fullscreen feh window in one command:
qr -s myssid -p some-passphrase
Has bunch of other options for different common use-cases.
CLI tool to calculate color values and print/convert them in various ways.
Initially made to convert any kind of GTK3 CSS color specs to an actual color value, e.g. "mix(#eee, shade(olive, 0.8), 0.9)" -> #6b6b21.
And for now that's the main use of it, as that CSS spec allows to mix and shade already, plan is to extend it later with any extra math as needed.
Prints resulting color back in all possible formats, including HSL and CIE L*a*b*, requires python/gtk3 to run.
Command-line python script to scan files for tagging based on paths or filename extensions (e.g. tag *.py with "py"), script shebangs or magic bytes (binary header).
Simplier and easiler-to-use replacement for tools like codetag and tmsu.
Allows for fast "sum of products" DNF queries, i.e. fairly arbitrary tag combinations, just convert them to DNF from whatever algebraic notation (e.g. via dcode.fr calculator).
List of tags and tagging criteria are hardcoded, currently mostly code-oriented, but should be trivial to expand with additional regexps for pretty much anything.
My main use-case is to quickly lookup and grep all python files on the machine, to find where I already implemented something familiar just couple days ago and forgot already :)
A tool to query activity logs from Project Hamster time-tracker lib/daemon/tools on a daily basis, aggregate it into weekly log files, and auto-commit/push it all into git repo.
Basically an advanced export functionality from hamster db into weekly-rotated append-only text files in a git repo, with the goal to tally and track project hours easily, using hamster tools to start/stop the timer and annotate timespans.
git is a nice tool to use in such tracking, as pushing to remotes with it can provide effectively immutable distributed history, yet one where edits are still allowed through follow-up commits.
Scripts to start and manage qemu/kvm based VMs I use for various dev purposes.
These include starting simple vde-based networking, syncing kernels and initramfs images out of vms (where needed), doing suspend/resume for running vms easily, etc.
Don't really need abstractions libvirt (and stuff using it) provide on top of qemu/kvm, as latter already have decent enough interfaces to work with.
eBPF at this point is kinda like generic "extension language" in linux, and supported at an ever-growing number of points, from tracing and accounting or network filtering to limiting sysctl in containers.
See head of specific .c files for compilation/loading/usage instructions.
(also, as of 2019, Cilium project has best docs on it)
Tools for automating various Arch Linux tasks.
Shows shared-lib dependencies for specified binary/so even if it's for different
arch (objdump-deps option), packages they might belong to (objdump-pkgs)
and deps-of-deps recursively (ldd-deep / ldd-deep-pkgs).
For instance, when one wants to figure out which .so files ELF32 binary might want to use:
% elf-deps objdump-deps ~player/gog/SRHK/game/SRHK /usr/lib/libGL.so.1 /usr/lib/libGL.so.1.2.0 /usr/lib/libGLU.so.1 ...
If one then wants to grab all these from some 32-bit packages (on a vm or maybe
some chroot, see also tar-strap tool), objdump-pkgs might help:
% elf-deps objdump-pkgs ~player/gog/SRHK/game/SRHK gcc-libs glibc ...
And to list all deps of a binary or a lib and their deps recursively, there's
ldd-deep and ldd-deep-pkgs:
% elf-deps ldd-deep /usr/lib/libGL.so /usr/lib/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 /usr/lib/libX11-xcb.so.1 ... % elf-deps ldd-deep-pkgs /usr/lib/libGL.so expat glibc libdrm ...
Can be useful for providing necessary stuff to run proprietary 32-bit binaries (like games or crapware) on amd64.
Creates text manifests for Arch setup in /var/lib/pacman/:
- db.explict - explicitly installed packages, names only.
- db.leaf - packages without anything depending on them, names only.
- db.extras - packages not in any pacman repos, names only.
- db.all - all installed packages, names and versions.
- db.diffs - list of
\.pac(new|orig|save)$files on the system (found via mlocate). - db.local - list of stuff in
/usr/local.
Taken together, these represent some kind of "current os state".
Useful to pull them all into some git to keep track what gets installed or updated in the system over time, including makepkg'ed things and ad-hoc stuff in /usr/local.
Lists files that don't belong to any of the packages in either in default
/etc /opt /usr dirs or whichever ones are specified.
My version of utility to merge .pacnew files with originals, using convenient
and familiar (at least to me) git add -p interface and git diffs in general.
Can build list of files to process from last update in pacman.log (-a/--auto option), locate (e.g. mlocate, -l/--locate opt) or these can be specified manually as args.
Copies all original and associated pacnew files to tmp dir, and runs git add
-p to apply/rebase original files on top of pacnew ones, showing resulting
git diff original merged and prompting for whether to apply all the changes
there.
Has misc options to skip parts of that process (-y/--yes, -o/--old, -n/--new), should be relatively safe against whatever accidents, breaks and typos - only changes stuff at the very end, if all commands worked, all checks pass and confirmation received.
Bash script, requires git and perl (as "git-add--interactive" is a perl script). Shorter and simplier than most scripts for same purpose, as git does most of the work in this case, less wheels re-invented, less interfaces to learn/remember.
Python script to validate checksums of fs files against ones recoded in mtree files stored by pacman on each package install under /var/lib/pacman/local/<pkg>.
Can be used with arbitrary root and pacman-db dirs, or with any non-pacman mtree files, like manifests made manually via bsdtar. Has options to skip various types of errors or path prefixes (to avoid checking /etc files for example).
Does not need pacman itself, only its mtree files (decompressing them via bsdcat), uses posix_fadvise to avoid needlessly trashing fs cache during operation.
Wrapper to quickly download and setup archlinux chroot (for e.g. systemd-nspawn container) using bootstrap tarball from https://mirrors.kernel.org/archlinux/iso/latest/
Checks gpg sig on the tarball with pacman-key, copies basic stuff like locale.gen, resolv.conf, mirrorlist, pacman gnupg setup, etc from the current root into the new one and runs arch-chroot into that.
Should be way faster than pacstrap, but kinda similar otherwise.
Either URL or path to source tarball should be specified on the command line.
Wrapper to bootstrap ready-to-use Arch container ("can") in /var/lib/machines, which (at the moment of writing) boils down to these steps:
mkdir && pacstrap
Copy layout files: localtime, profile, locale.conf, locale.gen.
Copy basic tools' configuration files, such as: zsh, screenrc, nanorc, gitconfig, etc.
But only copy each if it exists on the host machine (hence likely to be useful in a container as well).
systemd-nspawn into container and run locale-gen and do chsh to zsh, if it's set as $SHELL on the host.
pacstrap installs not just any specified packages, but intentionally prefixes each with "can-" - these are meta-packages that I use to pull in package groups suitable for containers.
They all should be in my archlinux-pkgbuilds repo, see e.g. can-base PKGBUILD for example of such metapackage.
Running can-strap -c pacman.i686.conf buildbot-32 tools -- -i
(intentionally complicated example) will produce "buildbot-32" container,
suitable to boot and log into with e.g. systemd-nspawn -bn -M buildbot-32.
XferCommand script to use in pacman.conf for trying package downloads from cache-servers (partial mirrors) first, using passed mirror URL as a fallback.
Example usage in pacman.conf:
XferCommand = curl-cache %o %u https://cache-mirror.local/archlinux/x86_64
Can include any number of cache URL prefixes as the trailing args.
Before pacman-6.0, this was easy to use by simply putting all these cache-mirrors at the top of the mirrorlist file, but since 6.0 pacman auto-disables these after hardcoded 3 errors (incl. 404), so that no longer works.
See related FS#71084 and FS#23407 tickets for upstream status on this, and -h/--help output from script for more options.
Various helper tools for automating Alpine Linux OS-level tasks.
Similar to pacman-manifest script above, but for alpine - creates text
manifest files for current Alpine setup in /etc/apk/:
- world.all - all currently installed packages with their versions,
cleaned-up and sorted version of
apk list -I. - world.extras - "orphaned" packages -
apk list -O. - world.custom - names of all installed custom-built packages.
- site.rc - all OpenRC init scripts and runlevel they're enabled at.
- site.conf-diffs - all
.apk-newfiles on the system (via mlocate). - site.local - contents of
/usr/local.
Same idea as with pacman-manifest - run this after updates or via cron, keep in some git to easily diff stuff for rollbacks, see what changes in the system and such routine operational tasks and visibility.
I.e. for when new service got added that you forgot to enable,
unmerged new config, custom packages replaced by upstream,
new/unnecessary/forgotten /usr/local stuff, etc.
Tools for working with various time-series databases and metrics-monitoring systems - collection, aggregation, configuration, graphs, etc.
Daemon script to grab data from whatever sensors and log it all via rrdtool.
Self-contained, configurable, handles clock jumps and weirdness (for e.g. arm boards that lack battery-backed RTC), integrates with systemd (Type=notify, watchdog), has commands to easily produce graphs from this data (and can serve these via http), print last values.
Auto-generates rrd schema from config (and filename from that), inits db, checks for time jumps and aborts if necessary (rrdtool can't handle these, and they are common on arm boards), cleans up after itself.
Same things can be done by using rrdtool directly, but it requires a ton of typing for graph options and such, while this script generates it all for you, and is designed to be "hands-off" kind of easy.
Using it to keep track of SoC sensor readings on boards like RPi (to see if maybe it's time to cram a heatsink on top of one or something), for more serious systems something like collectd + graphite might be a better option.
Command-line usage:
% rrd-sensors-logger daemon --http-listen --http-opts-allow & % rrd-sensors-logger print-conf-example ### rrd-sensors-logger configuration file (format: YAML) ### Place this file into ~/.rrd-sensors-logger.yaml or specify explicitly with --conf option. ... % rrd-sensors-logger print-last cpu.t: 30.22513627594576 gpu.t: 39.44316309653439 mb_1.t: 41.77566666851852 mb_2.t: 41.27842380952381 % curl -o graph.png http://localhost:8123/ % curl -o graph.png http://localhost:8123/t % curl -o graph.png 'http://localhost:8123/t/width:+1900,height:+800' % curl -o graph.png 'http://localhost:8123//start:+-2d,logarithmic:+true,title:+my+graph' % feh $(rrd-sensors-logger graph t -o 'start: -3h')
See top of the script for yaml config (also available via "print-conf-example") and systemd unit file example ("print-systemd-unit" command).
Uses yaml and rrdtool (python bindings that come with the binary), plus whatever sensor-related bindings - lm_sensors, Adafruit_DHT (also has internal driver for DHT22), sht_sensor, etc.
Didn't test sensor bindings after py2 -> py3 conversion, might need some small fixups to read stuff or use newer modules there.
Tool to load/dump stored graphite graphs through formats easily editable by hand.
For example, creating even one dashboard there is a lot of clicky-clicks, and 10
slightly different dashboards is mission impossible, but do
graphite-scratchpad dash:top (loaded straight from graphite db) and you
get:
name: top
defaultGraphParams:
from: -24hours
height: 250
until: -20minutes
width: 400
...
graphs:
- target:
- *.memory.allocation.reclaimable
- target:
- *.disk.load.sdb.utilization
- *.disk.load.sda.utilization
yMax: 100
yMin: 0
- target:
- *.cpu.all.idle
yMax: 100
yMin: 0
...
That's all graph-building data in an easily readable, editable and parseable format (yaml, nicely-spaced with pyaml module).
Edit that and do graphite-scratchpad yaml dash:top < dash.yaml to replace
the thing in graphite db with an updated thing. Much easier than doing anything
with GUI.
Rolling plot of "free" output via gnuplot.
Mostly a reminder of how to use the thing and what one can do with it.
There's more info on it in gnuplot-for-live-last-30-seconds blog post.
Boilerplate d3.js page for basic line chart to plot arbitrary JS function outputs or data array with axii, grid, mouseover datapoint tooltips and such.
Useful when for a quick chart to figure out some data or function output, or make it into a useful non-static link to someone, and don't want to deal with d3-v3/coding-style/JS diffs from bl.ocks.org.
Direct gh-pages link: d3-line-chart-boilerplate.html
Similar d3 boilerplate-chart as d3-line-chart-boilerplate,
but for plotting some kind of value distribution with vertical bars.
E.g. to quickly load find -type f -printf '%s\n' output of file sizes to see
which filesystem/parameters to pick depending on that at a glance.
Direct gh-pages link: d3-histogram-boilerplate.html
d3.js-based ES6 graphing app for time-series data from rather common temperature (t) and relative humidity (rh) sensors (DHT22, sht1x, etc) in tsv (tab-separated-values) files with [iso8601-ts, t, rh] fields.
Can be used directly via gh-pages: d3-temp-rh-sensor-tsv-series-chart.html
Bunch of real-world sample tsv files for it can be found alongside the html in d3-temp-rh-sensor-tsv-series-chart.zip.
Assembled (from simple html, d3.v4.js and main js) via html-embed script from this repo, doesn't have any external links, can be easily used as a local file.
More info can be found in the d3-chart-for-common-temperaturerh-time-series-data blog post.
d3.js-based xdiskusage implementation - app to parse du -b output and
display directory hierarchy as d3 "partition" layout, with node size
proportional to directory size from du output.
Can be used directly via gh-pages (d3-du-disk-space-usage-layout.html) or as a local file, doesn't have any external links.
Allows uploading multiple files to display in the same hierarchy, if paths in them are absolute (otherwise each one will be prefixed by "root-X" pseudo-node).
Script to poll 64-bit IF-MIB SNMPv3 counters for specified interface, checking for resets on these via NETSERVER-MIB::hrSystemUptime (uptime reset = fresh counter) and export these to prometheus.
It runs SNMP queries with specified -t/--snmp-poll-interval to check uptime, polls interface name table to find counter indexes, and then hr-counters for actual values.
Exports iface_traffic_bytes metric (with "iface" and "dir" labels for interface/direction),
as well as snmp_query_* metrics for info on general router responsiveness.
Use -m/--metric-prefix option to add some namespace-prefix to these.
Usage example:
% prometheus-snmp-iface-counters-exporter \ -i lte router:161 snmp-auth.secret counters.json
(run with -h/--help to get info on various options)
Uses prometheus_client and pysnmp modules for exporting and querying.
Aggregator to query prometheus server for specified metrics/labels, aggregate them by-day/week/month/year to sqlite db tables and export these via uWSGI for Grafana Simple JSON Datasource.
For building nice "traffic by day" (and week, month, year) bar-charts in Grafana.
Has two modes of operation:
Cron/timer mode to update aggregated values.
Example for counters from "prometheus-snmp-iface-counters-exporter" script above:
% prometheus-grafana-simplejson-aggregator \ --agg-labels 'dir iface' \ -p http://localhost:9090/p -d aggregate.sqlite \ -a 'iface_traffic_bytes:iface_traffic_bytes_{span}'All combinations of existing labels will be queried and aggregated. See also -h/--help output for more options/tweaks.
Will update aggregation timespans from last one stored in db (for each specified metric/label combos) to the current one.
uWSGI application for serving values for Grafana SimpleJson plugin.
To run from terminal:
% uwsgi --http :9091 --wsgi-file prometheus-grafana-simplejson-aggregator
Proper ini file and e.g. systemd socket activation can be used in the real setup.
Settings can be controlled via environment vars (--env uwsgi directive):
PMA_DEBUG=t- enable verbose logging, printing all headers, requests, etc.PMA_DB_PATH=/path/to/db.sqlite- aggregation database to use.
Use "table" queries in grafna in the following format:
metric ["[" label "=" val "]"] [":" span] ["@" name]
Example -
iface_traffic_bytes_day[dir=in]:m@traffic-in- where:- "iface_traffic_bytes_day" - metric name.
- "dir=in" - specific combination of label values, in alpha-sorted order.
- "m" - monthly aggregation (default - daily, see --agg-spans option).
- "traffic-in" - export values with "traffic-in" name/label for graph legend.
These should always be combined to update db on some interval and serve values from there on as-needed basis (uWSGI provides a lot of options for interfaces and to optimize efficiency).
Script to log JSON-lines with available cpu/mem/io cgroup stats for matched unit file(s), as well as their start/stop events.
Uses systemctl list-units -ao json to find/fnmatch initial set of units
(unless --new option is used) to monitor and systemd.journal from there to
add/remove units from set and log start/stop events.
Scrapes contents of cpu.stat, memory.stat and io.stat cgroup nodes on configurable -i/--poll-interval, translating their contents to cpu/mem/io-prefixed json keys, and device names for io stats. Runs until stopped or there's nothing more to monitor with --stop option. Uses configurable RotatingFileHandler for output json-lines log.
Intended use is collecting temporary data for some testing/debugging cgroup(s), docker containers and such (use e.g. prometheus for anything more long-term instead):
# systemd-cglog -ns /dev/stdout 'docker-*.scope'
{"ts": 1657877464.7816184, "ev": "start", "u": "docker-ef7c216d.scope"}
{"ts": 1657877464.7819324, "ev": "stat", "u": "docker-ef7c216d.scope",
"cpu.usage_usec": 240007, "cpu.user_usec": 205953, "cpu.system_usec": 34054, ...
"mem.anon": 74563584, "mem.file": 24576, "mem.kernel": 745472, ...
"io.vda.rbytes": 1416105984, "io.vda.wbytes": 372867072, "io.vda.rios": 68490, ... }
...
{"ts": 1657877504.207708, "ev": "stop", "u": "docker-ef7c216d.scope"}
Metrics collected this way can then be filtered/disaggregated by jq or a trivial script and visualized separately as needed. Idea here is just to gather all useful numbers over time.
Typically templates for simple host-specific scripts that run from cron daemon to check something and produce stderr output and non-0 exit code upon detecting any anomalies.
Standard template for a trivial bash + coreutils "df" checker to put into crontab on any random linux box, to warn when any of the mountpoints are about to run out of space/inodes.
Bash script to monitor for diffs in extended attributes on dirs/mountpoints like /usr /var /etc /opt, which are typically under package manager's control, and send diffs if there are any changes.
Also just strips xattrs from binaries in a separate list.
Idea is to detect when new suid files/dirs or ones with special ACLs/capabilities get installed, and either note new potential insecurity or strip them of these.
General observation is that almost all dangerous suid binaries (that get routinely exploited - see xorg, policykit, net tools, etc) are not actually used for anything but providing glaring security issues, but still get bundled as a dependencies with other stuff.
So an easy thing to do is to track any new ones and put them on a "strip xattrs" list, unless installed deliberately, or it's clear that xattrs are needed there.
All configuration stuff is at the top of the script. Should be smart enough to navigate btrfs subvols, but not data mountpoints.
Self-contained python script (no deps) to build a manifest of full linux permissions for all files under git control in specified repository(-ies), to stdout.
Included permissions are: uname, gname, path-type, mode, acls, capabilities, xattrs -
with default -o/--output flags and uid/gid options.
Intended to be used with repos of config files on mutable hosts, which are directly used there by apps, so permissions on them and their paths matter.
Output should look roughly like this:
/path/to/repo user:group:d0755 .git user:group:d0755 README.rst user:group:f0644 secret.conf root:root:f0600 suid.bin root:root:f4711 caps.bin root:root:f4700/EP:net_raw/u::rwx,u:netuser:--x,g::r-x,m::r-x,o::--- logs user:group:d0755 logs/test.log user:group:f0644///user.tail-pos:line=287 /some/other/repo user:group:d0755 ...
Stable for diffs, with all data needed to restore permissions/xattrs in there.
These can be diff'ed in crontab to alert on changes, or checked into git, to be tracked there alongside files themselves.
-f/--git-ls-file option allows to run potentially-unsafe "git ls-files"
command separately, or use file lists from some other non-git source.
There're also some output and uid/gid mangling options (names, dec/hex ints, offset/mask).
Can be combined with tools like b2tag to make a manifest with checksums in xattrs:
script.sh ///user.shatag.blake2b512=3fc5c347...,user.shatag.ts=1669540773.658921171
Symlink to a systemd-dashboard script - it kinda belongs here too.
Misc prefabs and really ad-hoc scripts, mostly stored here as templates to make something out of later.
Script to sync paths, based on berkley db and rsync.
Keeps b-tree of paths (files and dirs) and corresponding mtimes in berkdb,
comparing state when ran and building a simple merge-filter for rsync (+
/path line for each changed file/dir, including their path components, ending
with - *). Then it runs a single rsync with this filter to efficiently sync
the paths.
Note that the only difference from "rsync -a src dst" here is that "dst" tree doesn't have to exist on fs, otherwise scanning "dst" should be pretty much the same (and probably more efficient, depending on fs implementation) b-tree traversal as with berkdb.
Wrote it before realizing that it's quite pointless for my mirroring use-case - do have full source and destination trees, so rsync can be used to compare (if diff file-list is needed) or sync them.
Processor for tshark's xml (pdml) output, for cases when wireshark's filtering/ui is not enough or it should be automated.
Python script (or a template of one) designed to be run periodically to process latest entries in some log via regexp, match some timestamped lines from those.
Handles log rotation/truncation and multiple-changing-logs cases.
Only reads lines appended to the file(s) since last check, storing last position and hash of "N bytes after that" (incl. N itself) in files' "user." xattrs, to reliably detect if file was rotated/truncated on the next run (offset doesn't exist or there's diff data there).
Also stores state of the line-processing in xattrs, which is a simple "check occurence of regexp 'name' group within last hour, print msg if there isn't" in the script, with example input-log for this template-script looking like this:
2022-10-15T12:33:44+05:00 name1 2022-10-15T12:35:44+05:00 name2 2022-10-15T12:36:44+05:00 name1 ...
To test with: ./scraps/log-tail-check -n name1 -n name2 -n name3 test.log
Script to resize RPi's boot FAT32 partition and filesystem to conver as much of the SD card as possible, from RPi itself, while booted from the same card.
Needs python-2.7, modern util-linux tools (lsblk and sfdisk with -J option for json output), sleuthkit (to query size of FAT fs), and parted.
More info on this script can be found in the resizing-first-fat32-partition-... blog post.
Py script to parse output of asciitree.LeftAligned tree, as produced by asciitree module (see module docs for format examples).
Can be embedded into python code as a parser for easily-readable trees of strings, without need to abuse YAML or something less-readable for those.
Script (python) to copy trusted.* xattrs to user.* and/or wipe out either one of these.
Useful when running patched glusterd in a container, as described in running-glusterfs-in-a-user-namespace blog post here, and probably not much else.
Python script to blink bit-pattern from a passed argument using linux led subsystem (i.e. one of the leds in /sys/class/leds).
Useful to make e.g. RPi boards booted from identical OS img distinguishable by blinking last bits of their IP address, MAC, serial number or stuff like that.
Python script to blink any arbitrary on/off sequence or numbers (using bits) on an LED, using sysfs interface (/sys/class/leds or /sys/class/gpio).
Sequence is expressed using simple embedded language, for example:
+1s r:5 [ -100 +100 ] -1.5s 237 -5s <
Where:
{ '+' | '-' }{ ms:int | s:float 's' }(e.g. "+100", "+1s", "-1.5s") is a simple on/off state for specified number of seconds or ms.r[epeat]:{N}(e.g. "r:5") instructs to repeat next command N times.[ ... ]is used to group commands for repeating.- Simple number (or more complex
n[/bits][-dec]form) will be blinked in big-endian bit order with 150ms for 0, 1.3s for 1 and 700ms in-between these (see BlinkConfig, also adjustable viabit-repr:{bit1_ms),{bit0_ms),{interval_ms)command). <repeats whole thing from the start forever.
Somewhat easier than writing one-off "set(0), sleep(100), set(1), ..." scripts with mostly boilerplate or extra deps for this simple purpose.
Bash script to setup/destroy GRE tunnel with Generic UDP Encapsulation (GUE).
One command instead of bunch of them, with some built-in templating to make it easier to use on identical remote hosts.
Basic script to automate wpa_supplicant matching AP in a python script (e.g. by ssid regexp or any other parameters), pick best/working BSSID and connect to it.
For cases when wpa_supplicant.conf is not powerful enough.
Python, uses dbus-python module and its glib eventloop.
Unfinished simple python script to search/replace memory of a process via process_vm_readv / process_vm_writev calls while it's running.
Useful for hacks to update stuff in running binary apps without having to restart or disrupt them in any way, but found that this approach was too tedious in my specific case due to how stuff is stored there, so didn't bother with process_vm_writev part.
Python script to capture and print mouse events from GPM (as in libgpm) in specified tty.
Main event receiver is gpm-track.c (build with gcc -O2 gpm-track.c -o
gpm-track -lgpm -lrt) proxy-binary though, which writes latest mouse position
to mmap'ed shared memory file (under /dev/shm) and sends SIGRT* signals to main
process on mouse clicks.
Python wrapper runs that binary and reads position at its own pace, reacting to clicks immediately via signals.
Such separation can be useful to have python only receive click events while C binary tracks position and draws cursor itself in whatever fashion (e.g. on a top-level layer via RPi's OpenVG API), without needing to do all that separate low-latency work in python.
Note that GPM tracks x/y in row/column format, not pixels, which isn't very useful for GUIs, alas.
Wrappers to test tools that tend to spam /dev/log regardless of their settings.
rsyslogs.c is a SUID wrapper binary that uses mount --bind + unshare to replace /dev/log with /dev/null within namespace where it'd run rsyslog, and is made to silence rsyslogd in particular.
Example use (see also top of rsyslogs.c itself):
% gcc -O2 -o rsyslogs scraps/rsyslogs.c && strip rsyslogs % sudo chown root:user rsyslogs && sudo chmod 4110 rsyslogs % cp scraps/rsyslogs.conf rsyslog.conf % ./rsyslogs
rsyslogs.ldpreload.c is an LD_PRELOAD wrapper suitable for simplier single-process tools (e.g. "logger") where it's enough to override connect/sendto/sendmsg and such:
% gcc -nostartfiles -fpic -shared -ldl -D_GNU_SOURCE rsyslogs.ldpreload.c -o sd.so % LD_PRELOAD=./sd.so logger test
Use something like these occasionally when setting up logging on a dev machine, where such uncommon spam to syslog gets delivered via desktop notifications (see desktop/notifications/logtail tool in this repo) and annoys me.
Small .c binary around librelp to build and send syslog message over RELP protocol to daemons like rsyslog with specified timeout.
It's basically sample_client.c from librelp repository which also adds current ISO8601 timestamp and puts syslog message fields in the right order.
Usage:
% gcc -O2 -lrelp -o relp-test relp-test.c && strip relp-test % ./relp-test 10.0.0.1 514 60 34 myhost myapp 'some message'
Run binary without args to get more usage info and/or see .c file header for that.
Script to download Chaos Communication Congress (ccc/c3) videos as simple .mp4 files from a given fahrplan or media.ccc.de link (at least rc3 2020 ones).
Kinda surprised how needlessly complicated it is otherwise, as there are separate URLs for re-live streams, hd/sd videos, etc, none of which are easy to find.
Frontend URLs there just tend to show useless crappy player and not allow to download anything, and you have to either grab the URL from browser request debugger or navigate http file listings of their archives and find/match the talk in one of these.
This script simplifies it to one command, querying their JSON APIs under the hood, using all proper IDs and such, which is still like 3-4 complicated json-parsing requests, hence the need for a proper script to do it.
5-liner C binary to execvp() whatever was passed to it as arguments.
Can be used to act as an unique wrapper for AppArmor profiles bound to executable path, or whatever trivial suid-root hacks.
DO WHAT THE FUCK YOU WANT TO PUBLIC LICENSE
Version 2, December 2004
Copyright (C) 2010-2038 Mike Kazantsev
Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim or modified
copies of this license document, and changing it is allowed as long
as the name is changed.
DO WHAT THE FUCK YOU WANT TO PUBLIC LICENSE
TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR COPYING, DISTRIBUTION AND MODIFICATION
0. You just DO WHAT THE FUCK YOU WANT TO.