- Compile the program
$ cd FIFO $ mkdir build $ cd build $ cmake .. $ make
- Run the program
make run
- Resulting image is saved as
./build/out.bmp
- Original image
- Filtered image
// gaussian mask
const double mask[MASK_N][MASK_X][MASK_Y] =
{{
{1.0/273, 4.0/273, 7.0/273, 4.0/273, 1.0/273},
{4.0/273, 16.0/273, 26.0/273, 16.0/273, 4.0/273},
{7.0/273, 26.0/273, 41.0/273, 26.0/273, 7.0/273},
{4.0/273, 16.0/273, 26.0/273, 16.0/273, 4.0/273},
{1.0/273, 4.0/273, 7.0/273, 4.0/273, 1.0/273}
}};
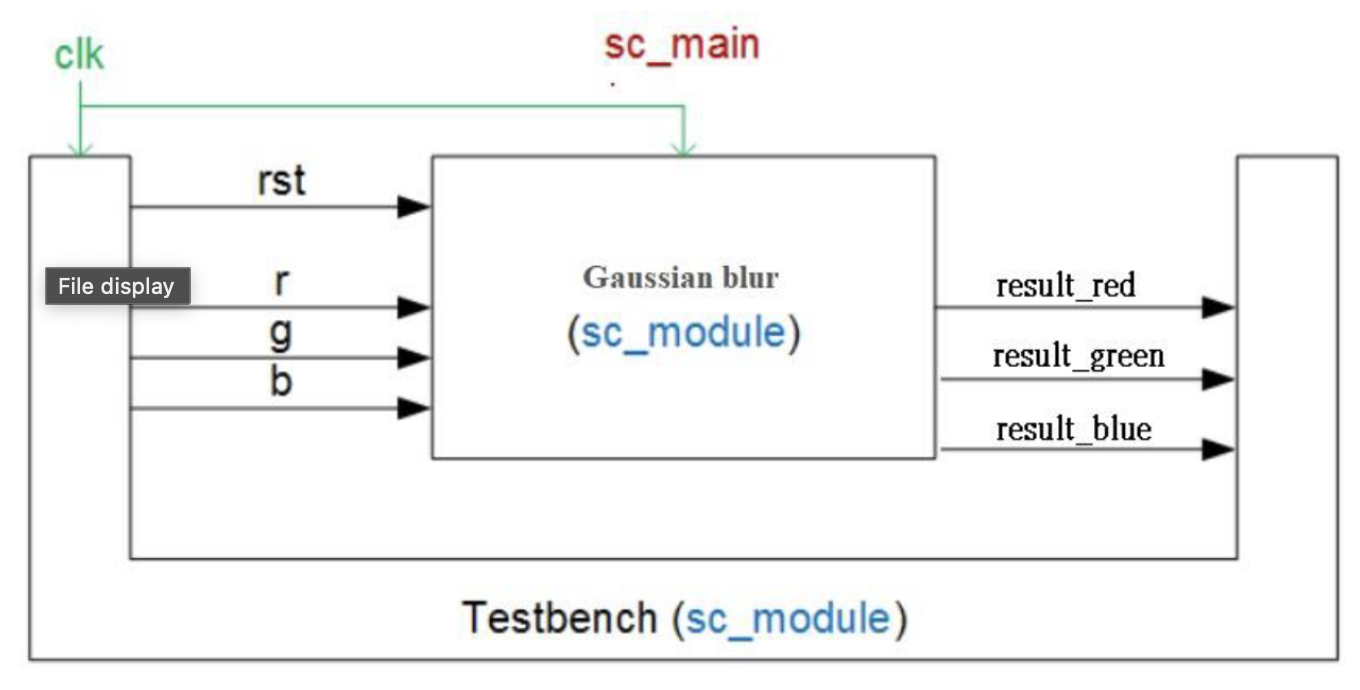
Implement a Gaussian blur filter with SystemC modules connected with SystemC FIFO channels between Testbench and GaussianFilter.
Testbench sends the input R, G, and B via 3 different sc_fifo channels to GaussianFilter. After the operation of convolution, GaussianFilter sends back the output result via another sc_fifo channels to Testbench. The declaration of the fifo channels are as follows.
In GaussianFilter.h :
sc_fifo_in<unsigned char> i_r;
sc_fifo_in<unsigned char> i_g;
sc_fifo_in<unsigned char> i_b;
sc_fifo_out<int> o_result;In Testbench.h :
sc_fifo_out<unsigned char> o_r;
sc_fifo_out<unsigned char> o_g;
sc_fifo_out<unsigned char> o_b;
sc_fifo_in<int> i_result;In Testbench.cpp :
Read the original RGB image.bmp, and write to r, g, b sc_fifo channels respectively.
void Testbench::do_gaussian() {
int x, y, v, u; // for loop counter
unsigned char R, G, B; // color of R, G, B
int adjustX, adjustY, xBound, yBound;
int total;
int total_pixels = 0;
o_rst.write(false);
o_rst.write(true);
for (y = 0; y != height; ++y) {
for (x = 0; x != width; ++x) {
adjustX = (MASK_X % 2) ? 1 : 0; // 1
adjustY = (MASK_Y % 2) ? 1 : 0; // 1
xBound = MASK_X / 2; // 1
yBound = MASK_Y / 2; // 1
for (v = -yBound; v != yBound + adjustY; ++v) { //-1, 0, 1
for (u = -xBound; u != xBound + adjustX; ++u) { //-1, 0, 1
if (x + u >= 0 && x + u < width && y + v >= 0 && y + v < height) {
R = *(source_bitmap +
bytes_per_pixel * (width * (y + v) + (x + u)) + 2);
G = *(source_bitmap +
bytes_per_pixel * (width * (y + v) + (x + u)) + 1);
B = *(source_bitmap +
bytes_per_pixel * (width * (y + v) + (x + u)) + 0);
} else {
R = 0;
G = 0;
B = 0;
}
o_r.write(R);
o_g.write(G);
o_b.write(B);
total_pixels = total_pixels + 1;
wait(1); //emulate channel delay
}
}
// ......
}
}
sc_stop();
}In GaussianFilter.cpp
Read data via r, g, b sc_fifo channels, do the convolution by 5 x 5 Gaussian bur filter, and finally write the data via o_result sc_fifo channel
void GaussianFilter::do_filter() {
while (true) {
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < MASK_N; ++i) {
val[i] = 0;
}
for (unsigned int v = 0; v < MASK_Y; ++v) {
for (unsigned int u = 0; u < MASK_X; ++u) {
//0.299 R + 0.587 G + 0.114 B
unsigned char gray = (0.299 * i_r.read() + 0.587 * i_g.read() + 0.114 * i_b.read());
for (unsigned int i = 0; i != MASK_N; ++i) {
val[i] += gray * mask[i][u][v];
}
}
}
double total = 0;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i != MASK_N; ++i) {
total += val[i] * val[i];
}
int result = (int)(std::sqrt(total));
o_result.write(result);
wait(10); //emulate module delay
}
}In Testbench.cpp :
Read the filtered results via i_result sc_fifo channel, and write in to *target_bitmap as output matrix of the filtered image.
for (y = 0; y != height; ++y) {
for (x = 0; x != width; ++x) {
// ......
if(i_result.num_available()==0) wait(i_result.data_written_event());
total = i_result.read();
//cout << "Now at " << sc_time_stamp() << endl; //print current sc_time
*(target_bitmap + bytes_per_pixel * (width * y + x) + 2) = total;
*(target_bitmap + bytes_per_pixel * (width * y + x) + 1) = total;
*(target_bitmap + bytes_per_pixel * (width * y + x) + 0) = total;
}
}
sc_stop();
}- Compile the program
$ cd FIFO_buffer $ mkdir build $ cd build $ cmake .. $ make
- Run the program
make run
- Resulting image is saved as
./build/out.bmp
- Original image
- Filtered image
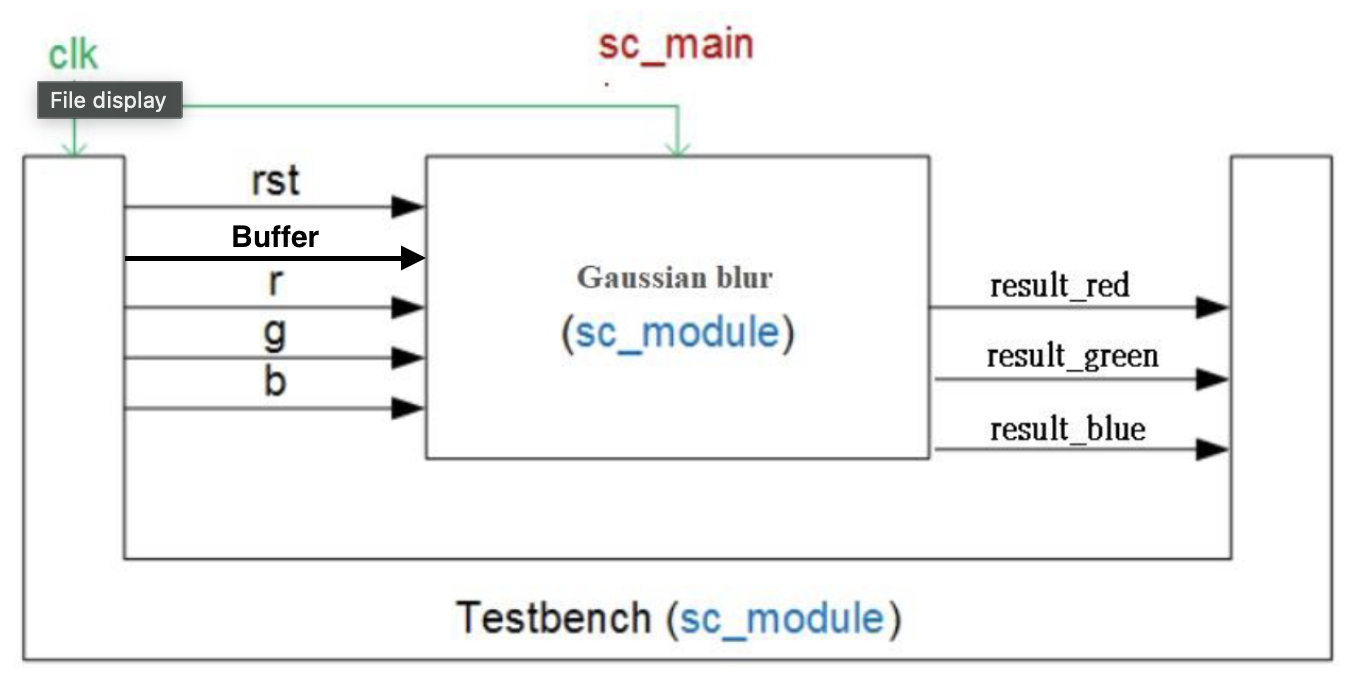
Continued from part1, and with additional input data buffer, which can reduce the data transfer between testbench and GaussianFilter module.
- utilize 2D 5 x 5 array as the bufer size, which can at most cache 25 pixels.
In GaussianFilter.h :
sc_fifo_in<unsigned char> i_r;
sc_fifo_in<unsigned char> i_g;
sc_fifo_in<unsigned char> i_b;
// input buffer control signal
sc_fifo_in<bool> i_buffer;
sc_fifo_out<int> o_result;In Testbench.h :
sc_fifo_out<unsigned char> o_r;
sc_fifo_out<unsigned char> o_g;
sc_fifo_out<unsigned char> o_b;
sc_fifo_out<bool> o_buffer;
sc_fifo_in<int> i_result;In GaussianFilter.cpp
Read data via r, g, b sc_fifo channels, do the convolution by 5 x 5 Gaussian bur filter, and finally write the data via o_result sc_fifo channel
void GaussianFilter::do_filter() {
// Initializes a 5x5 buffer to store pixel values.
unsigned char buffer[5][5] = {0};
while (true) {
// Initializes an array to store the filtered value (the sum of the products of the mask and the pixel values).
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < MASK_N; ++i) {
val[i] = 0;
}
// If there's new data in i_buffer
if(i_buffer.read()) {
// Populate the buffer with grayscale values calculated from input RGB values and apply filtering
for (unsigned int v = 0; v < MASK_Y; ++v) {
for (unsigned int u = 0; u < MASK_X; ++u) {
unsigned char gray = round((i_r.read() * 0.299 + i_g.read() * 0.587 + i_b.read() * 0.114));
buffer[v][u] = gray;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < MASK_N; ++i) {
val[i] += (double)gray * mask[i][v][u];
}
}
}
}
// Otherwise
else {
// shifts the buffer contents to emulate a shift register and reads a new pixel
for (unsigned int v = 0; v < MASK_Y; ++v) {
for (unsigned int u = 0; u < MASK_X; ++u) {
if(u != (MASK_X - 1)) {
buffer[v][u] = buffer[v][u + 1]; // emulate shift register (buffer shifing left)
// Apply Gaussian mask to the shifted buffer
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < MASK_N; ++i) {
val[i] += (double)buffer[v][u] * mask[i][v][u];
}
}
else {
unsigned char gray = round((i_r.read() * 0.299 + i_g.read() * 0.587 + i_b.read() * 0.114));
buffer[v][u] = gray;
// Apply Gaussian mask to the new pixel data
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < MASK_N; ++i) {
val[i] += (double)gray * mask[i][v][u];
}
}
}
}
}
double total = 0;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < MASK_N; ++i) {
total += val[i] * val[i];
}
//int result = (int)(std::sqrt(total));
int result = static_cast<int>(sqrt(total));
o_result.write(result);
wait(10); //emulate module delay
}
}Compare the number of pixel transfer of between the original implementation (part1) and the one with buffers(part2)
We can notice that w/o the input buffer, the pixel data transfer is 6553600 / 1308960 = 4.96 greater.
-
w/o buffer (part1):
6553600 pixelstransferred.Each pixels for calculation requires 5 x 5 data transfer. For 512 x 512 pixels input data, it requires
512 x 512 x (5 x 5) = 6553600data transfer.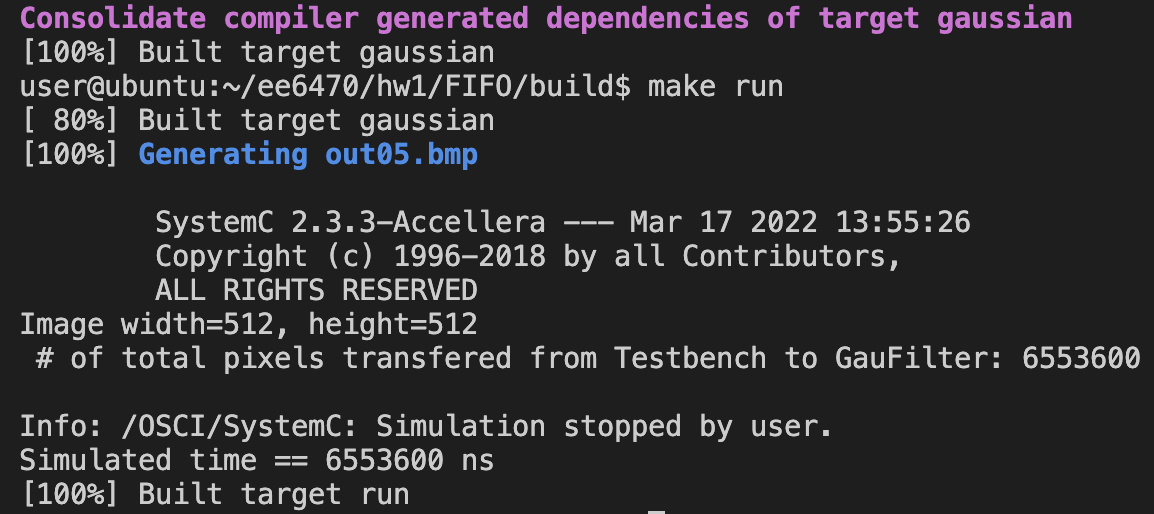
-
w/ buffer (part2):
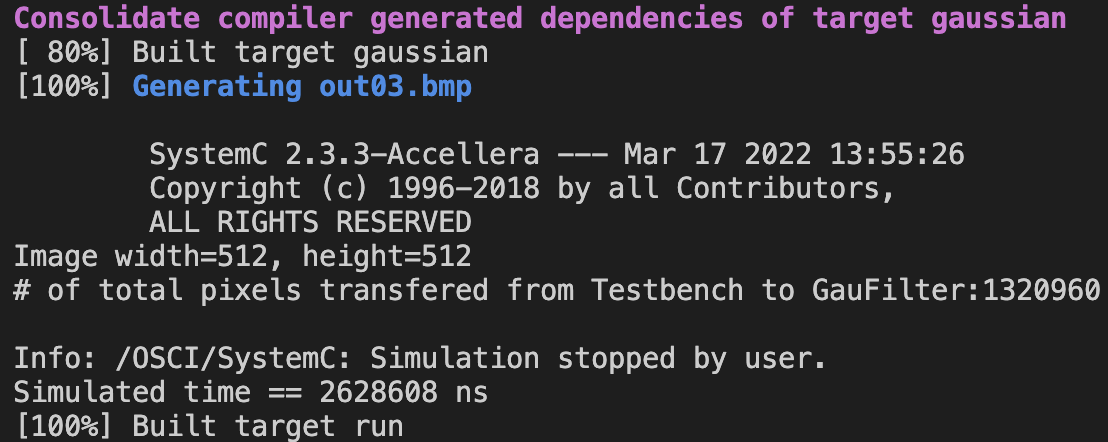
1320960 pixelstransferred.Calculation for first row requires 5 x 5 data transfer. AS for the remaining pixels, each pixel require 5 data transfer. For 512 x 512 pixels input data, it requires
512 cols x (5 x 5) = 12800for first row pixels, and512 cols x 511 rows x 5 = 1308160for the remaining pixels. Thus, the total data transfer =12800 + 1308160 = 1320960