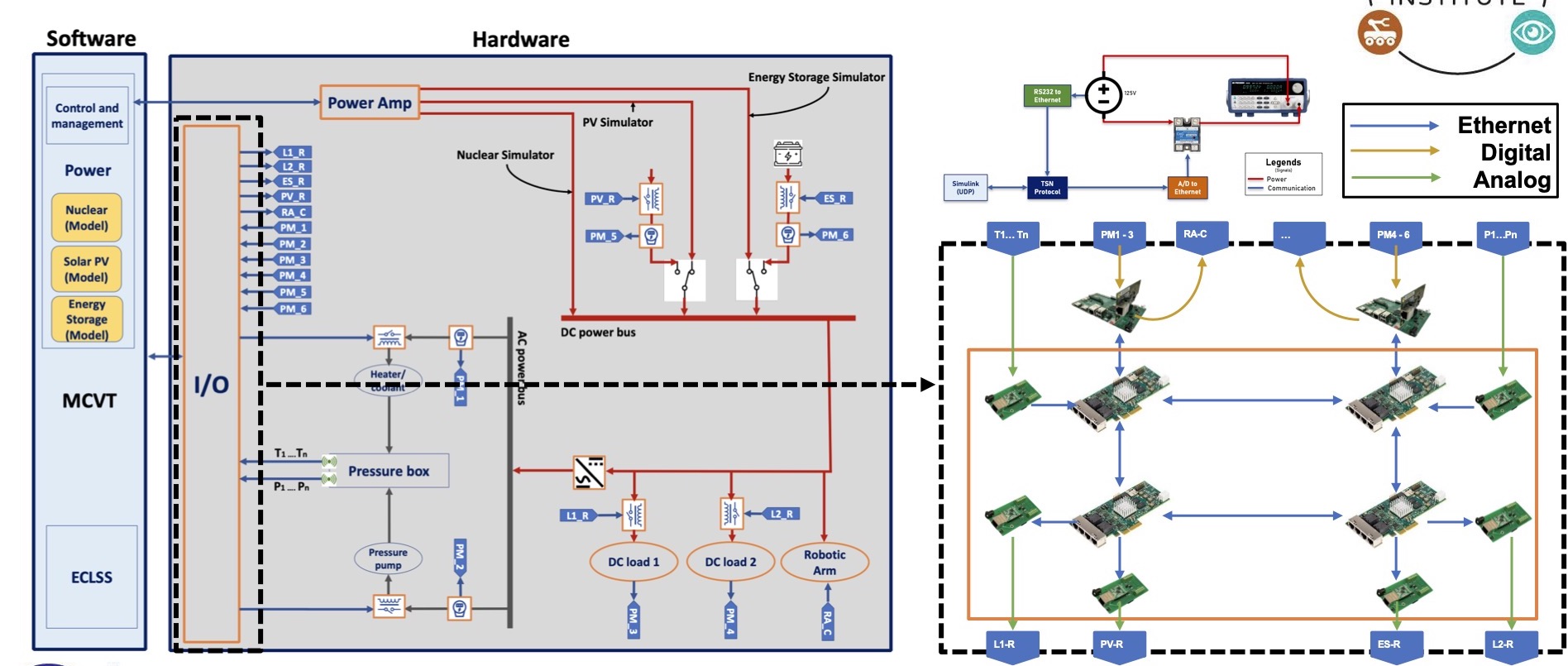
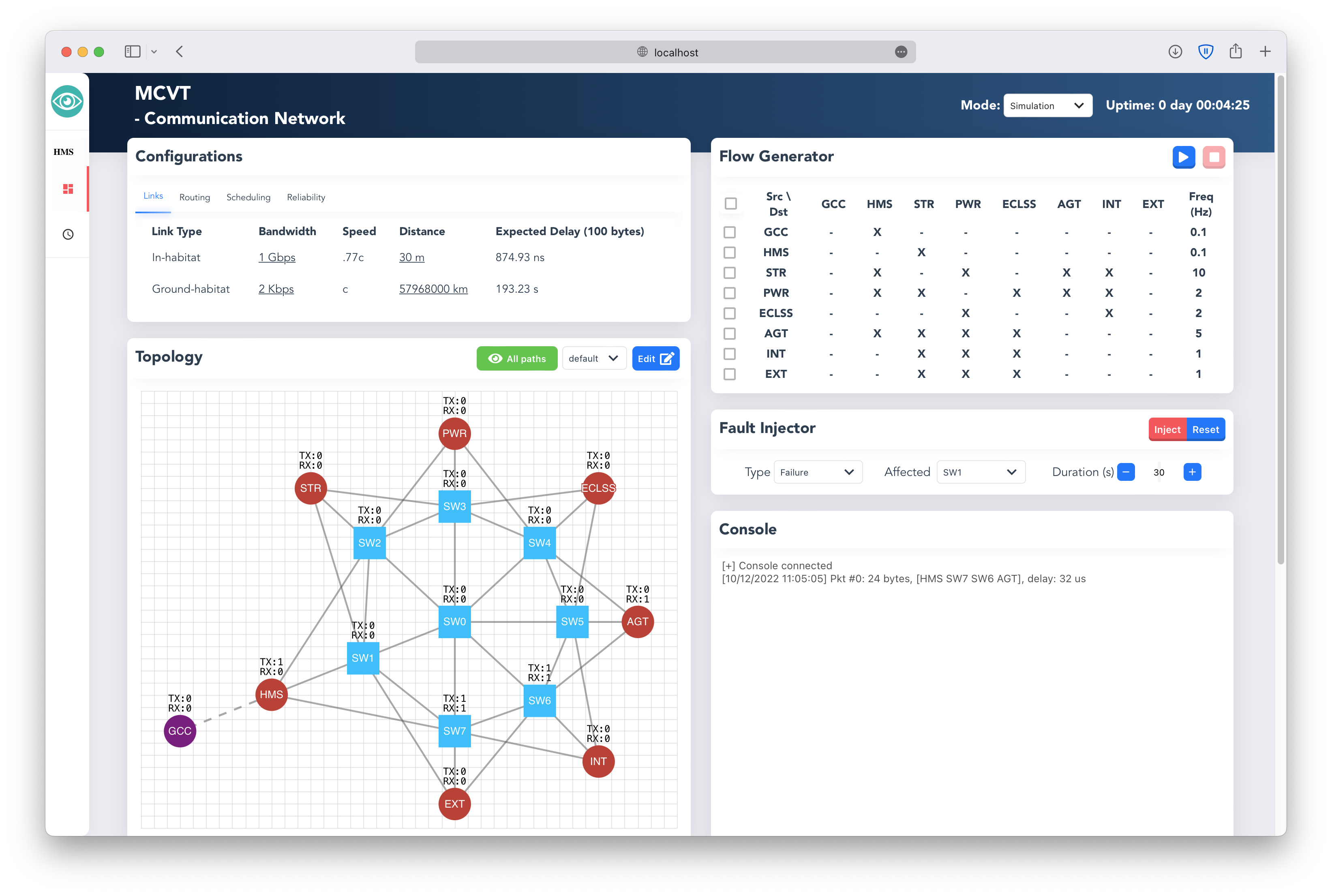
The DRDS System in MCVT manages the data exchange among individual subsystems and GCC. It provides a reliable and easy-to-use back-end for data transfer and data storage with proposed service APIs and protocols. With these data services, individual subsystems do not need to know the specific mechanisms for communication with other subsystems or databases, such as creating sockets and encoding/decoding data or retrieving data with specific query language. Instead, the DRDS handles all the details and presents a unified high-level interface for real-time data collection and distribution.
The core part of the DRDS is developed in the Go language and the data service APIs are developed in Go, Python, JavaScript, and Simulink to allow effective interaction with other subsystem developed using different languages. Furthermore, to achieve fast and consistent configuration and integration with other subsystems, we also dockerized the DRDS application with a docker-compose.yml file. A subsystem does not need to know the dependencies with other subsystems and can run the integration with a single docker-compose up command.
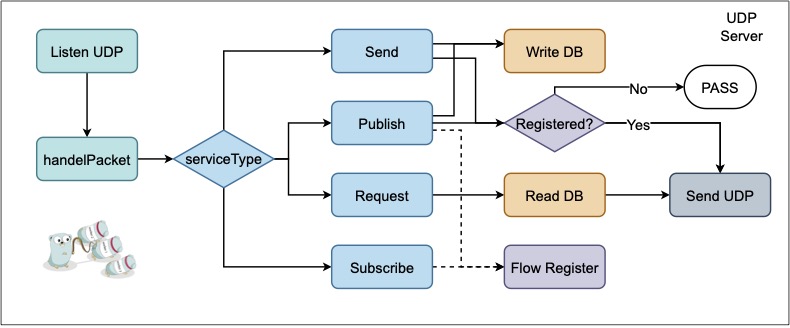
UDP Server:
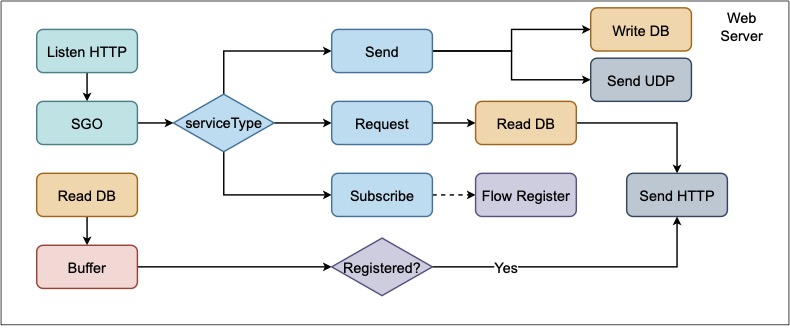
Web Server:
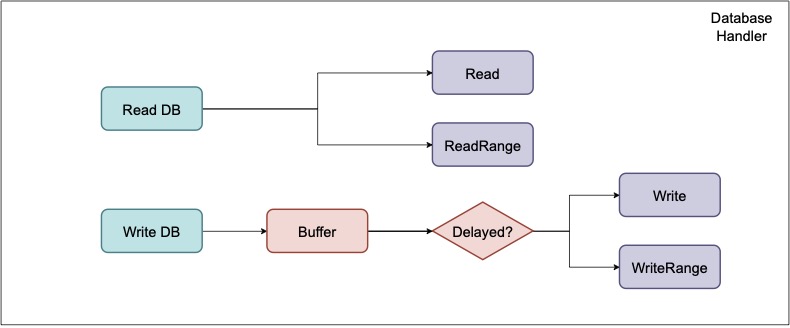
Database Handler:
- For Python, please refer to demo.py and api.py.
- For GoLang, please refer to main.go.
- For JavaScript, please refer to demo.html
- For Simulink, please refer to MCVT_v6_shell.slx
- For other Language, please implement by following standards:
Please following standard is only for developers to implement the API. MCVT modelers can use above already implemented API in different programming languages, more detail usages can be found in the user manual /doc/RETHi_Communication_Network_Guide.pdf
Data packet is the basic form to send data and also to implement service API:
Communication network packet
1 2 3
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| SRC | DST | TYPE | PRIO | VER | RES |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| PHYSICAL_TIMESTAMP |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| SIMULINK_TIMESTAMP |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| SEQUENCE | LEN |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| DATA…
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
Data Service packet
1 2 3
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| SRC | DST | TYPE | PRIO | VER | RES |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| PHYSICAL_TIMESTAMP |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| SIMULINK_TIMESTAMP |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| SEQUENCE | LEN |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| SERVICE | FLAG | OPTION1 | OPTION2 |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| SUBFRAME_NUM | DATA_ID |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| TIME_DIFF | ROW | COL |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| LENGTH | DATA...
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
Src and Dst
| Field | Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Src (Dst) | GCC | 0x00 | Ground Command and Control Subsystem |
| Src (Dst) | HMS | 0x01 | Health Management System |
| Src (Dst) | STR | 0x02 | Structural System |
| Src (Dst) | PWR | 0x03 | Power System |
| Src (Dst) | ECLSS | 0x05 | Environmental Control and Life Support System |
| Src (Dst) | AGT | 0x06 | Agent System |
| Src (Dst) | EXT | 0x07 | Exterior Environment |
| Src (Dst) | IE | 0x08 | Interior Environment |
| Src (Dst) | DTB | 0x09 | Disturbance |
| Src (Dst) | CN | 0x0A | Communication Network |
| Src (Dst) | SPL | 0x0B | Structural Protective Layer |
Message Type
| Field | Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| MessageType | PKT | 0x00 | Communication packet defined by communication network |
| MessageType | SPKT | 0x01 | Service packet defined by data service through network |
| MessageType | JPKT | 0x02 | Service JSON struct defined by data service |
Data Type
| Field | Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| DataType | Null | 0x00 | No data |
| DataType | FDD | 0x01 | Fault detection data |
| DataType | SD | 0x02 | Cyber sensor data |
| DataType | AD | 0x03 | Agent data |
| DataType | PSD | 0x04 | Physical sensor data |
| DataType | Other | 0x05 | Undefined data |
Priority
Priority(priority): Quality of Service (QoS) prioritizes network traffic and manages available bandwidth so that the most important traffic goes first.
| Field | Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Priority | Low priority | 0x00, 0x01 | Best effort data as back ground flow |
| Priority | Normal priority | 0x02, 0x03 | Audio vedio data to maximum throughput |
| Priority | Medium priority | 0x04, 0x05 | Sensor data to minimize latency |
| Priority | High Priority | 0x06, 0x07 | FDD or agent data as time critical message |
Service (Service selection)
| Field | Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Opt | Send | 0x00 | Send data record to data server |
| Opt | Request | 0x01 | Request data record from data server |
| Opt | Publish | 0x02 | Publish data stream to data server |
| Opt | Subscribe | 0x03 | Subscribe data stream from data server |
| Opt | Response | 0x0A | Response from data server |
Flag
| Field | Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flag | Complete | 0x00 | Completed signal or data in payload |
| Flag | Segment | 0x01 | Signal or data segment requires rearrange |
| Flag | Warning | 0x02 | Abnormal operation needs to be verified |
| Flag | Error | 0x03 | Invalidate operation may lead to system collapse |
Others
- SimulinkTime(simulink_time): Simulink time from 0 to 4294967295, which is the iteration of simulink when packet is genereated.
- PhysicalTime(physical_time): Physical Unix time from 0 to 4294967295, which is the clock on the host of simulink when packet is genereated.
- Row(raw): Length of data
- Col(col): Width of data
- Length(length): Flatten length of data (Row * Col)
- Option1(opt1): Depends on Service
- Option2(opt): Depends on Service
- Data(data): Data in bytes (only exists in Json message)
Before use the API, please make sure:
- Understand IP and Port of server
- Understand IP, Port and ID of client: ID should be unique from 0 to 255, ID 0 is saved for habitat db, ID 1 is saved for ground db.
- Client information must be registered in server configuration files.
To send asynchronous data, first set up headers:
| SRC | DST | TYPE | PRIORITY | VERSION | RESERVED | PHYTIME | SIMU_TIME |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Client ID | Server ID | 0x01 | - | 0x00 | 0x00 | - | - |
| SEQUENCE | LENGTH | SERVICE | FLAG | OPTION_1 | OPTION_2 | SUBFRAME | |
| - | - | 0x00 | 0x00 | 0x00 | 0x00 | - |
| DATA_ID | TIME_DIFF | ROW | COL | LENGTH | DATA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | - | - | - | - |
Finally send this packet by UDP channel to server.
To require asynchronous data, first set up headers:
| Src | Dst | Type | Priority | Version | Reserved | PhyTime | SiTime |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Client ID | Server ID | 0x01 | - | 0x00 | 0x00 | - | Request Start Time |
| Sequence | Length | Service | Flag | Opt1 | Opt2 | Subframe | |
| - | - | 0x01 | 0x00 | 0x00 | 0x00 | - |
| Data ID | Time Diff | Row | Col | Length | Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data ID | Request Duration | - | - | - | - |
Then send this packet by UDP channel to server.
If Time_diff == 0xffffffff, it returns the last record. If Simulink_Time < 0xffffffff and Time_diff == 0xffff, it returns the data from Simulink_Time to the last data
Next keep listening from server, a packet followd by send service API will send back. Please note the length of returned data should be decoded by its shape [Row * Col].
To publish data synchronously, set up headers and send to server for registering publish first:
| Src | Dst | Type | Priority | Version | Reserved | PhyTime | SiTime |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Client ID | Server ID | 0x01 | - | 0x00 | 0x00 | - | Start time of publish |
| Sequence | Length | Service | Flag | Opt1 | Opt2 | Subframe | |
| - | - | 0x02 | 0x00 | 0x00 | 0x00 | - |
| Data ID | Time Diff | Row | Col | Length | Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data ID | Data Rate | - | - | - | - |
Keep listening from server, a same packet will be send back which means the client is successully registered for publish.
Then start continuously pushing streaming to server by send api with required frequency.
To terminate publishing, send to server:
| Src | Dst | Type | Priority | Version | Reserved | PhyTime | SiTime |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Client ID | Server ID | 0x01 | - | 0x00 | 0x00 | - | End time of publish |
| Sequence | Length | Service | Flag | Opt1 | Opt2 | Subframe | |
| - | - | 0x02 | 0x00 | 0x00 | 0x00 | - |
| Data ID | Time Diff | Row | Col | Length | Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data ID | 0 | - | - | - | - |
To subscribe data synchronously, set up headers for registering subscribe first:
| Src | Dst | Type | Priority | Version | Reserved | PhyTime | SiTime |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Client ID | Server ID | 0x01 | - | 0x00 | 0x00 | - | Start time of Subscribe |
| Sequence | Length | Service | Flag | Opt1 | Opt2 | Subframe | |
| - | - | 0x03 | 0x00 | 0x00 | 0x00 | - |
| Data ID | Time Diff | Row | Col | Length | Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data ID | Data rate | - | - | - | - |
Note: Use SiTime = 0x0 to get all data, and SiTime = 0xffffffff subscribing to get only future data (ignore historical data)
Next keep listening from server, a continous packet flow followd by send service API will send back with required data rate. Please note the length of returned data should be decoded by its shape [Row * Col].
To terminate Subscribe function, send
| Src | Dst | Type | Priority | Version | Reserved | PhyTime | SiTime |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Client ID | Server ID | 0x01 | - | 0x00 | 0x00 | - | End time of Subscribe |
| Sequence | Length | Service | Flag | Opt1 | Opt2 | Subframe | |
| - | - | 0x03 | 0x00 | 0x00 | 0x00 | - |
| Data ID | Time Diff | Row | Col | Length | Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data ID | 0 | - | - | - | - |
Step1: Download Docker Desktop in latest version. For windows user, please install WSL following the guidence in Docker.
Step2: Copy docker-compose.yml and db_info_v6.json from this GitRepo to an empty folder in your local machine, and run docker-compose up in the same folder. This yml file can be found here. Following outputs from terminal implies the application is running successfully.
comm_1 | Start Communication Network
comm_1 | *SGo* -- Listen on :8000
data_service_1 | Database has been initialized
data_service_1 | Database has been initialized
data_service_1 | Database habitat has been connected!
data_service_1 | Habitat Server Started
Step3: Go website http://localhost:8000 , the dashboard of HMS: Communication Network Subsystem should be running. The source code and usage details can be found in https://github.com/AmyangXYZ/RETHi-Comm.
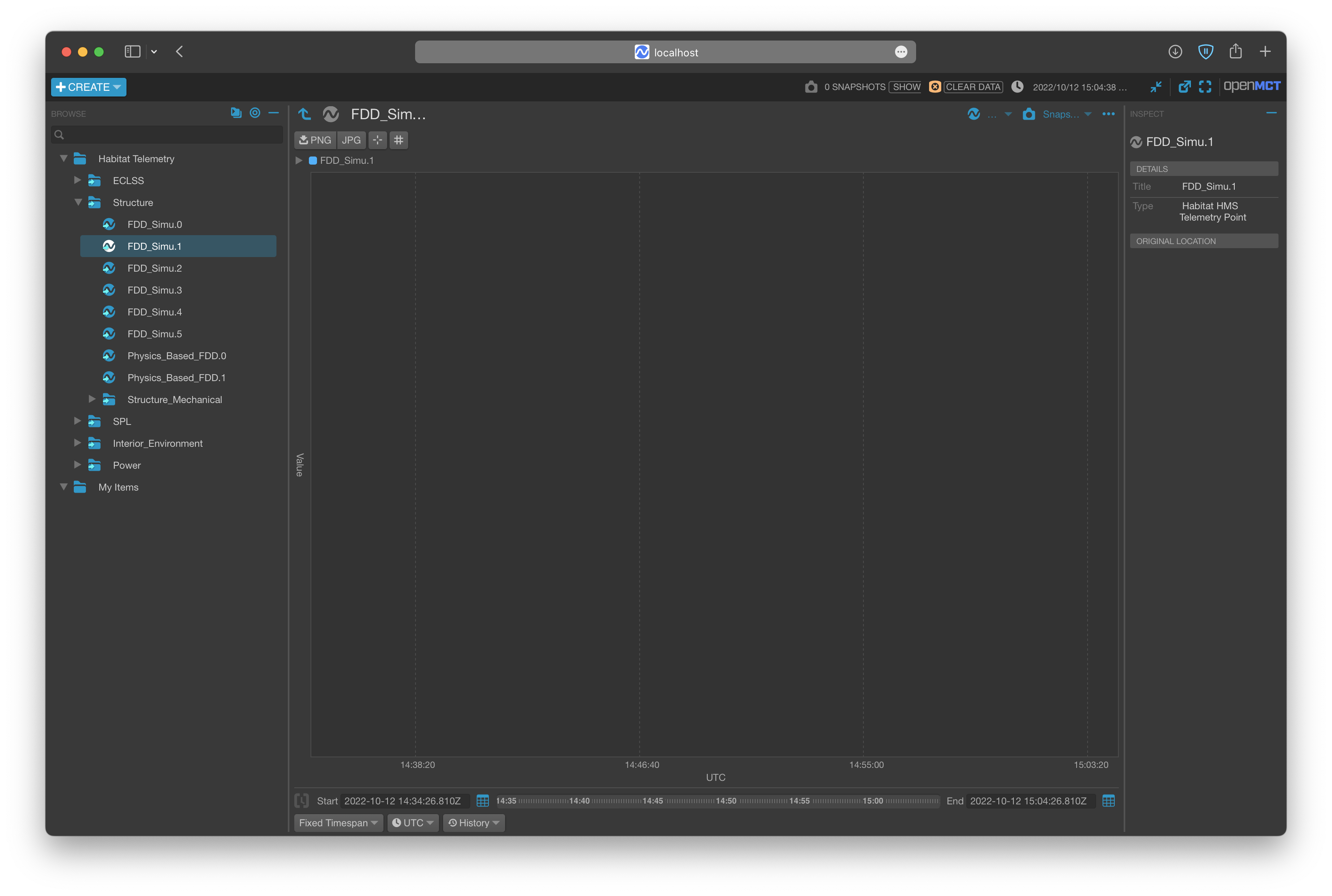
Step4: Go website http://localhost:8080, the dashboard of HMS: Data Visualization Subsystem should be running. The source code and usage details can be found in https://github.com/HFBZZ/RETHi_HMS_Vis.
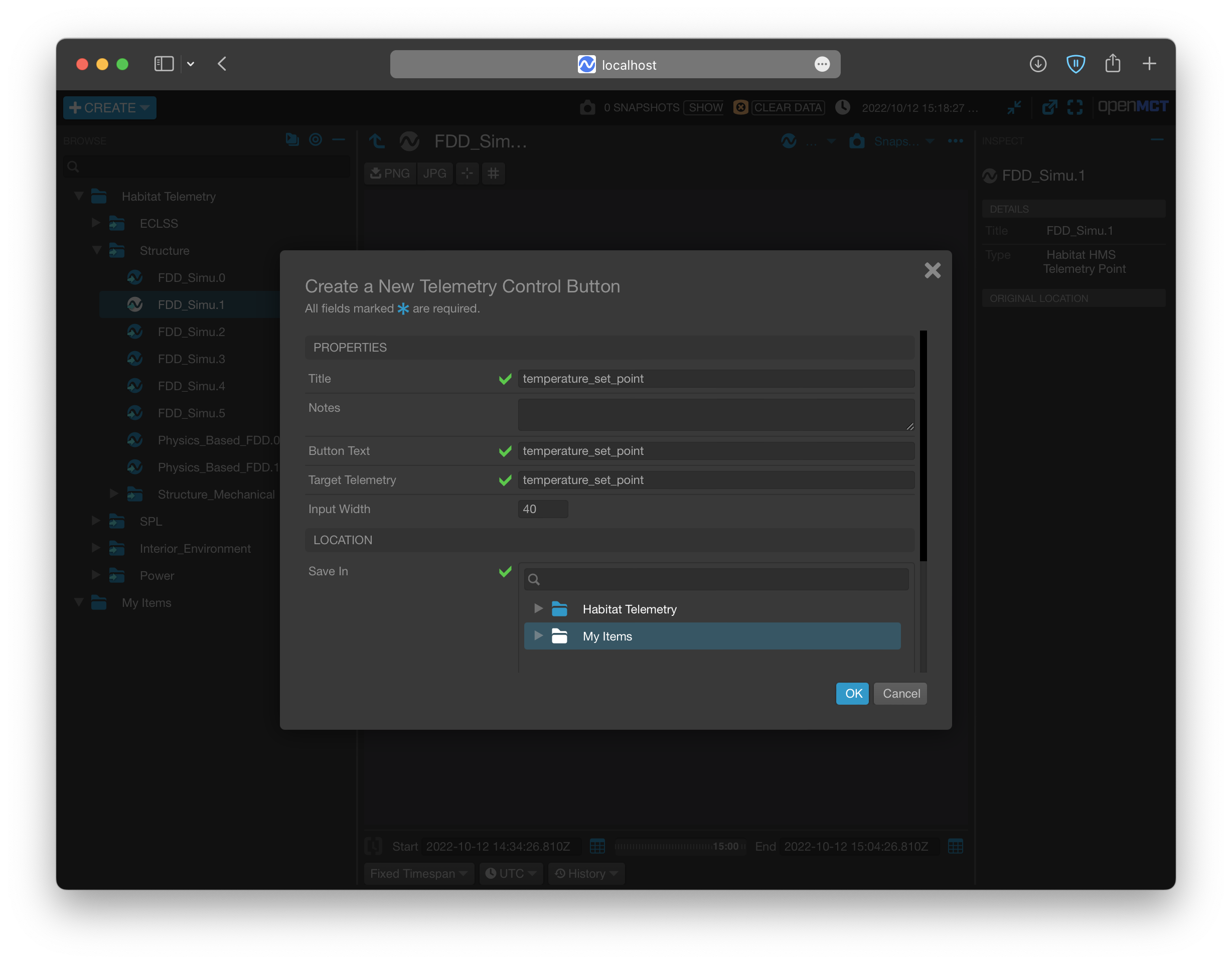
Set-point Control: By clicking the ➕CREATE button on the top-left corner, you can create Telemetry Control Button to change the set-point in corresponding subsystems.
Step5: Copy pkt_generator.py from this GitRepo to the folder with db_json_v6.json to generate fake data for testing. This python script can be found here. You should observe the data flow in communication network dashboard and data changes in human interface. All data are defined in this online datasheet in Communication-Data-Service tab.
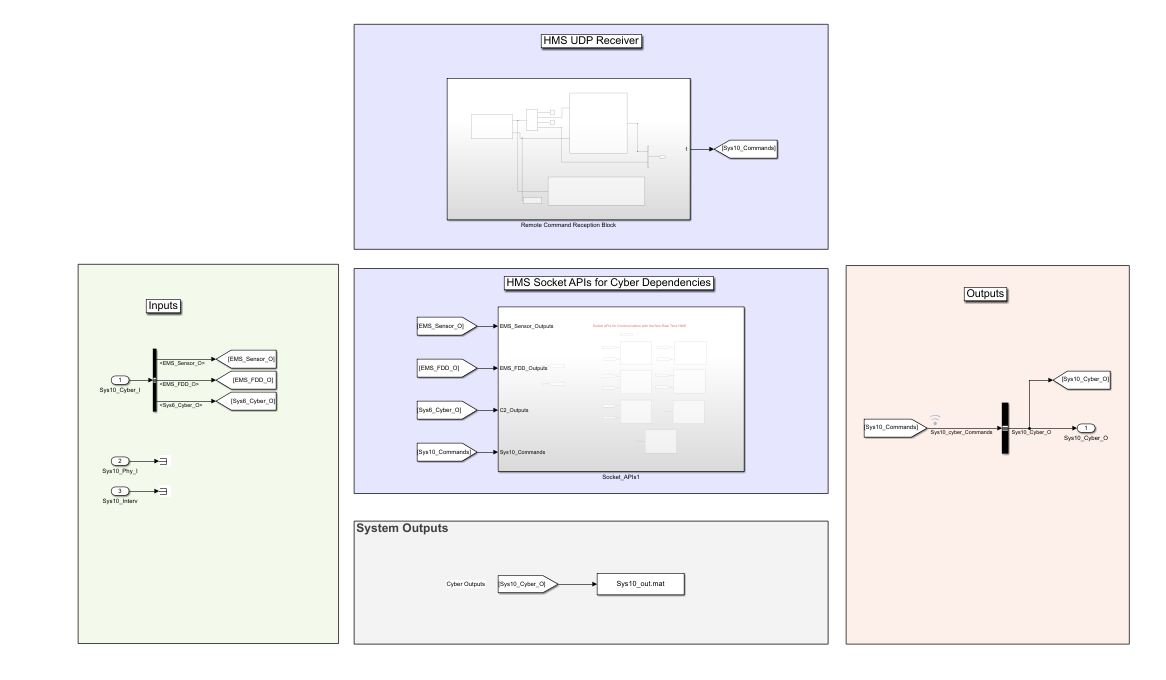
Or you can play with the real MCVT v6.2 to interact with HMS application. To make sure you are using the correct MCVT version, the components in Communication Network (Sys10) subsystem should contains Inputs, Outputs, System Outputs, HMS Socket APIs, and HMS UDP Receiver blocks.
Put api.py and utils.py in the same folder with your application first.
Using api.init function to set ip and port of local and remote server.
import api
## The local port and remote port address are hard-code for local testing.
## Make sure the `remote_ip` is consistent with the server IP address, and the `remote_port` is consistent with the port server is listening on.
api.init(
local_ip = "127.0.0.1",
local_port= 65533,
remote_ip = "127.0.0.1",
remote_port = 65531,
src_id = 1,
dst_id = 1
)
Using api.request(Data_ID, Simulink_Time, Priority) -> Data request history data.
## Request data(SPG DUST) whose ID == 3 at simulink time 1000
re = api.request(synt=1, id=3)
## Request data(SPG DUST) whose ID == 3 the lasted updated value
re = api.request(synt=0xffffffff, id=3)
## Request 5 records of data(SPG DUST) whose ID == 3 after simulink time 1
re = api.request(synt=(1, 5), id=3)
## Request data(SPG DUST) whose ID == 3 from simulink time 1 to the lasted update value (this method severely rely on the correct setting of data frequency)
re = api.request(synt=(1, 0xffff), id=3)
## The return value 're' is the Packet object defined in utils.py
## You can use re.subpackets[k].payload to access the data in double64 of the `k`-th subpacket.
## Also you can use `re.field` like `re.length` to reterive the header field.
Using api.send(Data_ID, Simulink_Time, Data, Priority, type) -> None send data to server (You can send to different subsystems by api.init function, but currently only AGENT and COMMUNICATION subsystems implemented with Simulink Receiving API).
## Send data (SPG DUST) whose ID == 3 at simulink time 1000
api.send(synt=1000, id=3, value = [0.1, 0.1, 0.1])
Using api.subscribe_reguster(Data_ID, Simulink_Time) -> None subscribe real-time data.
## This framework helps you subscribe multiple data concurrently:
def update_data(api: api.API, q: Queue):
'''
Receive data from data repository
'''
print("[1] Subprocess is working")
while True:
data = api.subscribe()
q.put(
{
'time':data.header.simulink_time,
'length':data.subpackets[0].header.length,
'payload':list(data.subpackets[0].payload),
}
)
## Tell DataService you want to subscribe data 5002
conn.subscribe_register(5002, 0)
print("[0] Subscribed")
## Queue is for communication between 2 process
q = Queue(QUEUE_SIZE)
## Create a process to collect data
p = Process(target=update_data, args=(
conn,
q,
))
## Start the process
p.start()
## Get data here without blocking
while True:
if not q.empty():
data = q.get()
print(data)
Python API also supports subscribing multiple data simultaneously with only ONE client by simply changing line 20 in above code as following:
## Tell DataService you want both data 5002 and 5003 from SIMULINK_TIME 0
conn.subscribe_register(5002, 0)
conn.subscribe_register(5003, 0)
 This project is supported by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration
This project is supported by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration