Ray Tracing is an algorithm used to create realistic graphics.
Any Ray Tracing algorithm requires the representation of objects in a 3D space.
A vector is a line segment that extends from point A to point B in a 2D or 3D plane.
We need to be able to operate on vectors.
Normalizing a vector involves scaling its magnitude/size to 1 while retaining its direction. This can be useful for other operations such as distance calculation or clustering.
The formula for the cross product is given by:
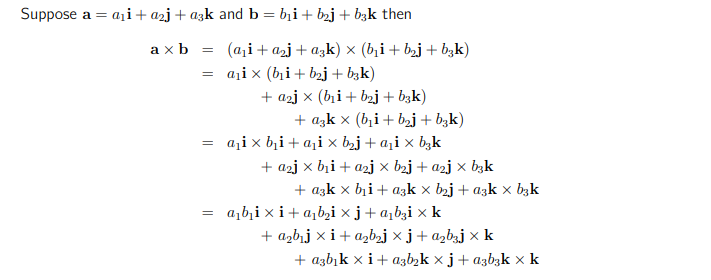
To implement the calculation, the following steps were taken:
- Create an empty list called
new_result - Iterate over the vector
result - In each iteration, add the previous value to the next one
- Store this result in
new_result - Display
new_result
To calculate the magnitude of a vector:
- Iterate over the vector elements
- Square each element
- Sum the squared values
- Take the square root of the resulting value
forloopmath.Pow(2, 10)append
- Iterate over the vector
v1[x] - Square each
v1[x] - Store the squared values in another vector
[x] - Sum the values in this new vector
[x]








