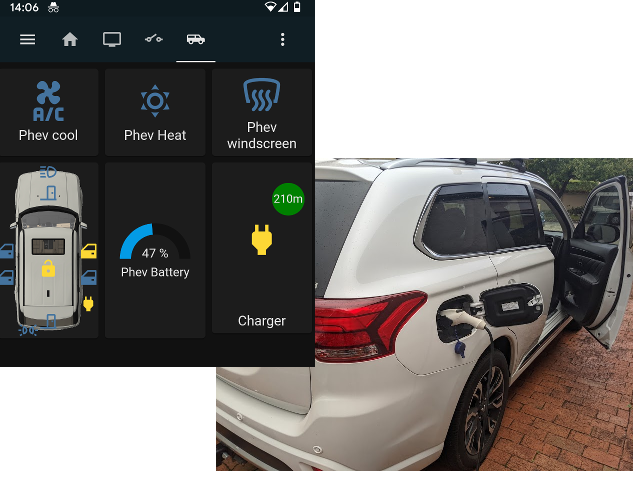
Utility to interact with a Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV via the Wifi remote control protocol.
Inspired by https://github.com/phev-remote/ but written entirely in Go.
For further hacking, read the protocol documentation.
Tested against a MY18 vehicle.
- MQTT proxy to Phev
- Home Assistant discovery
- Register client to car
- Fetch battery, charge, door, light status
- Set lights and charge enable
- Near-instant response to commands
- Only tested on a MY18 Phev
Also includes some debugging utilities.
- Go compiler
Licenced under the GPLv2.
Copyright 2021 Ben Buxton bbuxton@gmail.com
Contributions and PRs are welcome.
- Download and install the latest Go compiler
- Your distro packager may have a version thats too old
- For raspbian choose the ARMv6 release
- Ensure you have install the libpcap-dev package
- Download the phev2mqtt archive
- Extract it
- Go into its the top level directory and run go build
- Verify it runs with ./phev2mqtt -h
On your computer running the phev2mqtt tools, configure a new Wifi connection to the car's SSID,
Follow the Mitsubishi instructions to find the Wifi credentials provided with the car.
Verify that your Wifi connection to the car is established - your local IP address should be 192.168.8.47.
Follow the Mitsubishi instructions and put the car into registration mode ("Setup Your Vehicle"). You may need to re-establish the Wifi connection.
Register by running phev2mqtt client register and you should shortly see a message
indicating successful registration.
Once connected to the car, you can sniff for messages by running phev2mqtt client watch. The phone client needs to be disconnected for this to work. You'll see a bunch of data go by - some of those will be decoded into readable messages such as charge and AC status.
The primary feature of this code is to run as a proxy between the car and MQTT. Registers with car status are sent to MQTT, both as raw register values and decoded functional values. Commands sent on MQTT topics can be used to control certain aspects of the vehicle.
Start the MQTT gateway with:
./phev2mqtt client mqtt --mqtt_server tcp://<your_mqtt_address:1883/ [--mqtt_username <mqtt_username>] [--mqtt_password <mqtt_password>]
The following topics are published:
| Topic/prefix | Description |
|---|---|
| phev/register/[register] | Raw values of each register, as hex strings |
| phev/available | Wifi connection status to car. online or offline |
| phev/battery/level | Current drive battery level as a percent |
| phev/climate/status | Whether the car AC is on |
| phev/climate/mode | Mode of the AC, if on. cool, heat, windscreen |
| phev/climate/[mode] | Alternative of above. Modes are cool, heat, windscreen which can be off or on |
| phev/charge/charging | Whether the battery is charging. on or off |
| phev/charge/plug | If the charging plug is unplugged or connected. |
| phev/charge/remaining | Minutes left, if charging. |
| phev/door/locked | Whether the car is locked. on or off |
| State of doors. closed or open | |
| State of doors. closed or open | |
| phev/door/front_passenger | State of doors. closed or open |
| phev/door/driver | State of doors. closed or open |
| phev/door/rear_left | State of doors. closed or open |
| phev/door/rear_right | State of doors. closed or open |
| phev/door/bonnet | State of doors. closed or open |
| phev/door/boot | State of doors. closed or open |
| phev/lights/parking | Parking lights. on or off |
| phev/lights/head | Head lights. on or off |
| phev/vin | Discovered VIN of the car |
| phev/registrations | Number of wifi clients registered to the car |
The following topics are subscribed to and can be used to change state on the car:
| Topic/prefix | Description |
|---|---|
| phev/set/register/[register] | Set register 0x[register] to value 0x[payload] |
| phev/set/parkinglights | Set parking lights on or off |
| phev/set/headlights | Set head lights on or off |
| phev/set/cancelchargetimer | Cancel charge timer (any payload) |
| phev/set/climate/[mode] | Set ac/climate state (cool/heat/windscreen/off) for [payload] (10[on]/20/30) |
| phev/connection | Change car connection state to (on/off/restart) |
The client supports Home Assistant MQTT Discovery by default.
After initial discovery, re-run the binary for the entities to appear. You can search for "phev" in your entity list. Your car should also appear as a device in the Devices tab.
You can disable this with --ha_discovery=false or change the discovery prefix, the default is --ha_discovery_prefix=homeassistant.
It's useful to have the tool auto-start when running on e.g a Raspberry Pi. The following describes how to set this up.
- Edit or add to
/etc/systemd/network/00-default.linkwith the following:
[Match]
# This should be the 'real' (default) mac address of the Pi's wireless interface.
MACAddress=b8:27:eb:50:c0:52
[Link]
# This should be the MAC address to use to connect to the car, per above.
MACAddress=ee:4d:ec:de:7a:91
NamePolicy=kernel database onboard slot path
- Add the car's Wifi info to
/etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf:
ctrl_interface=DIR=/var/run/wpa_supplicant GROUP=netdev
update_config=1
country=AU
network={
ssid="REMOTE45bhds"
scan_ssid=1
psk="blahblahbla12314"
}
- Add the following to
/etc/systemd/system/phev2mqtt.service, updating the MQTT address to suit your setup:
[Unit]
Description=phev2mqtt service script
StartLimitIntervalSec=5
After=syslog.target network.target
[Service]
Type=exec
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/phev2mqtt --config=/dev/null client mqtt --mqtt_server tcp://192.168.0.88:1883 -v=debug
# Restart script if stopped
Restart=always
# Wait 30s before restart
RestartSec=30s
# Tag things in the log
# View with: sudo journalctl -f -u phev2mqtt -o cat
SyslogIdentifier=phev2mqtt
StandardOutput=syslog
StandardError=syslog
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
-
Copy the
phev2mqttbinary to /usr/local/bin and make sure it's executable. -
Start the service with
sudo systemctl start phev2mqtt.service -
Enable the service to run at boot, with
sudo systemctl enable phev2mqtt.service. -
Restart the Pi and verify that it can connect to the car. Also run
ifconfigand check that thewlan0interface has the correct mac address. You should also see this interface have the IP address192.168.8.47. -
Verify that the phev2mqtt service is communicating with the car, by checking the logs:
sudo journalctl -f -u phev2mqtt -o cat
Further development of this library can be done with a packet dump of the official Mistubishi app.
A number of sniffer apps for phones are available for this. Two that the author have used are Packet Capture and PCAP Remote. These do not require root access, yet can successfully sniff the traffic into PCAP files for further analysis.
Packet Capture can save the PCAP files to your local phone storage which you can then extract off the phone.
PCAP Remote is a little more involved, but allows for live sniffing of the traffic.
Once you have downloaded the PCAP file(s) from the phone, you can analyse them with the command phev2mqtt decode pcap . Adjust the verbosity level (-v) between 'info', 'debug' and 'trace' for more details.
Additionally, the flag '--latency' will use the PCAP packet timestamps to decode the packets with original timings which can help pinpoint app events.