Ktot (Keep track of time) try to make time tracking much more convinient. Ktot is (for the most part) operated by using hotkey combinations
-
Which simply means that Ktot will work even if it's not focused. You need not Alt-Tab to the specific window and then click (or even worse, type) to start/stop the tracking. Just simply press the assigned hotkey from any window to get going
-
You can define your own custom labels to track. You can add/remove as many labels as you want.
-
Name of existing labels can also be updated without losing their respective track log.
-
By default, timestamps of the beginning and ending of each individual session of every label is recorded.
-
Ktot has built in option to show simple statistics of every label. It can show basic information like number of sessions, total session time, etc.
-
The control hotkeys can be customized according to one's preference or to avoid conflict with existing hotkey combination.
git clone https://github.com/CodePleaseRun/ktot.git
cd ktot
python install.pyIf the installation failed using python install.py, you can also manually install the packages using pip install
Windows:
rich>=10.7.0click>=8.0.1keyboard>=0.13.5
Linux:
rich>=10.7.0click>=8.0.1pynput>=1.7.3
Simply run the following command within the ktot/ directory:
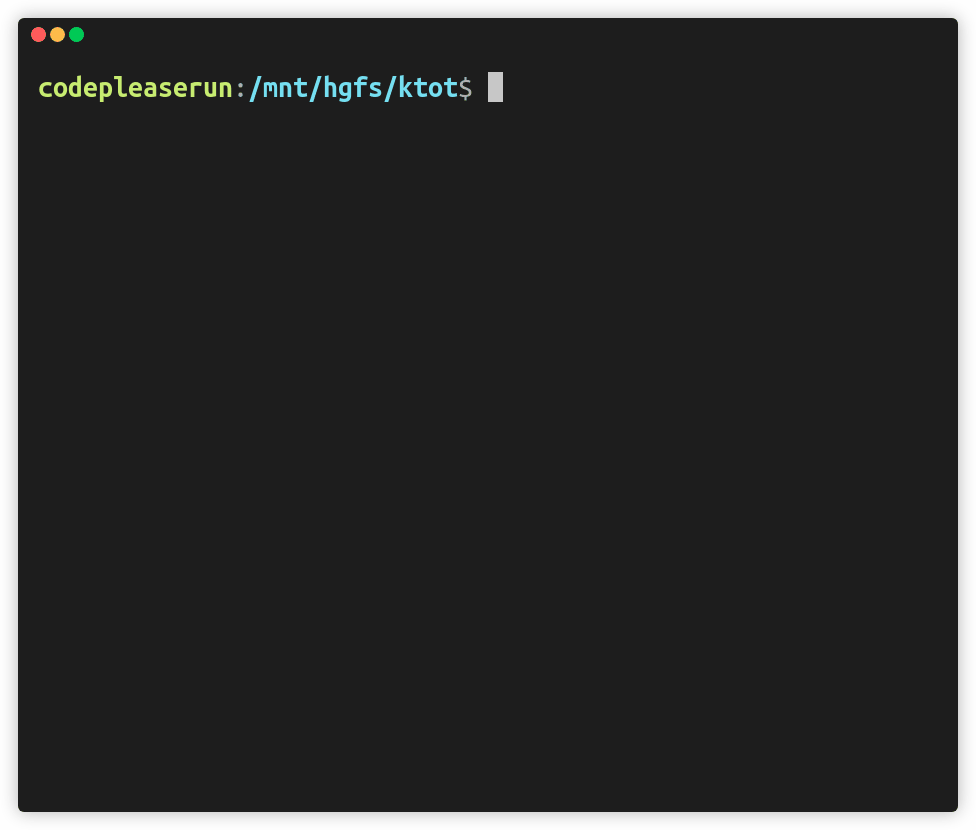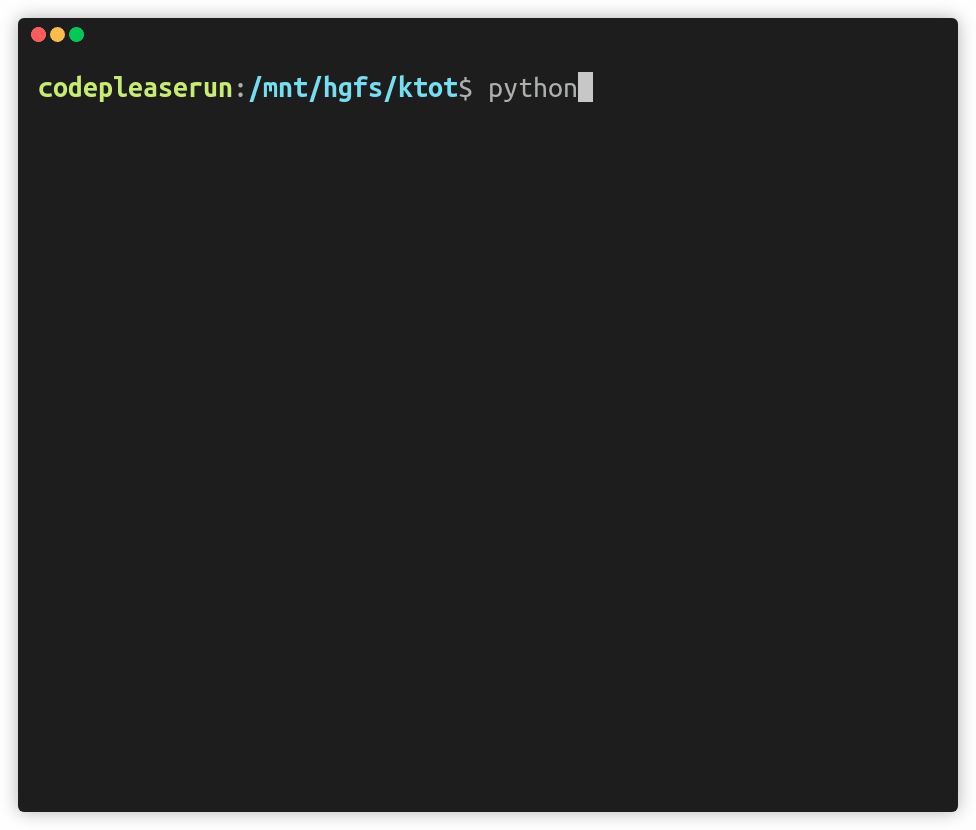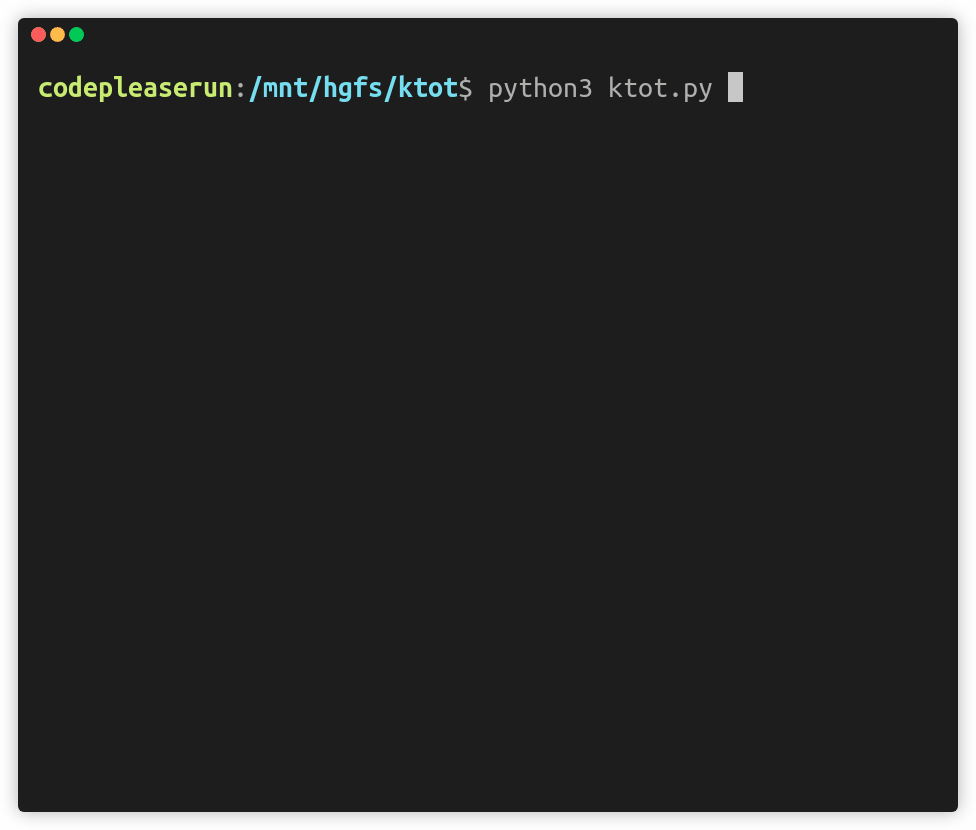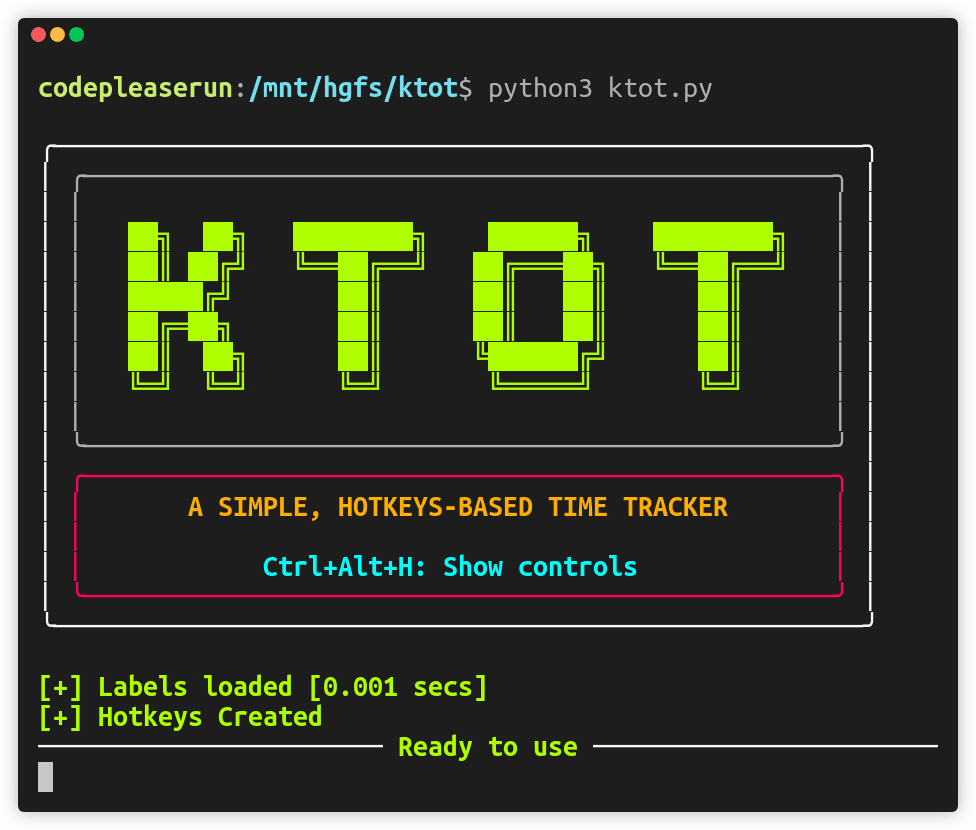
python3 ktot.pyIt will try to read existing session log from json/labels.json and load it.
If it's your first time running the program then labels.json wiil be created in json/ & a prompt will ask to add a label.
The porgram is then controlled using hotkeys from deafult control scheme.
All the sessions recorded are saved in labels.json as a single dictionary. Each label is saved as a key whose value is a single list. Each element of the list is another list of 3 elements (call it l1):
[beginning_timestamp, ending_timestamp, elapsed_time]
beginning_timestamp & ending_timestamp are saved as seconds since epoch. Each list (l1) represent a single session.
There are 2 options (or flags) which can be toggled. For more info run:
python ktot.py --help-
By deafult, both starting and ending timestamps are saved as
(begining_stamp, ending_stamp, elsapsed_time).--timestamp=Falsewould save onlyelapsed_timeand replaces bothbeginning_timestamp&ending_timestampwith-1as[-1, -1, elapsed_time].
keyboard package is used for Windows and pynput is used for Linux.
Both packages have different syntax for parsing the same hotkey combination. Thus, json/hotkeys.json contains a single combination written in 2 slightly different format, one for each package.
-
Windows:
keyboardparses both alphanumberic and special keys in same way. All keys are written in lowercase and separated by+.- Ctrl + Shift + Space is written as
ctrl+shift+space - Ctrl + Alt + X is written as
ctrl+alt+x
- Ctrl + Shift + Space is written as
-
Linux:
pynputrequires special keys to be enclosed under angle brackets<&>. Each key is separated by+- Ctrl + Shift + Space is written as
<ctrl>+<shift>+<space> - Ctrl + Alt + X is written as
<ctrl>+<alt>+x
- Ctrl + Shift + Space is written as
- Remapping controls to different hotkeys within the program
- Moving from json storage to a proper db. For a json file with 15 labels with 40k sessions each, average read and write time was 0.6 and 3.0 secs respectively