Spill backend test
This project was bootstrapped via typescript-starter
These instructions will get you a copy of the project up and running on your local machine
NOTE: This is not intended to be used in production.
Some decisions were made (no env variables) and hardcoded secrets to speed up development
I only recommend using docker to setup and run the project and it is super simple
- Docker
- Docker Compose
- pgAdmin - To setup the database
Start the stack
docker-compose up
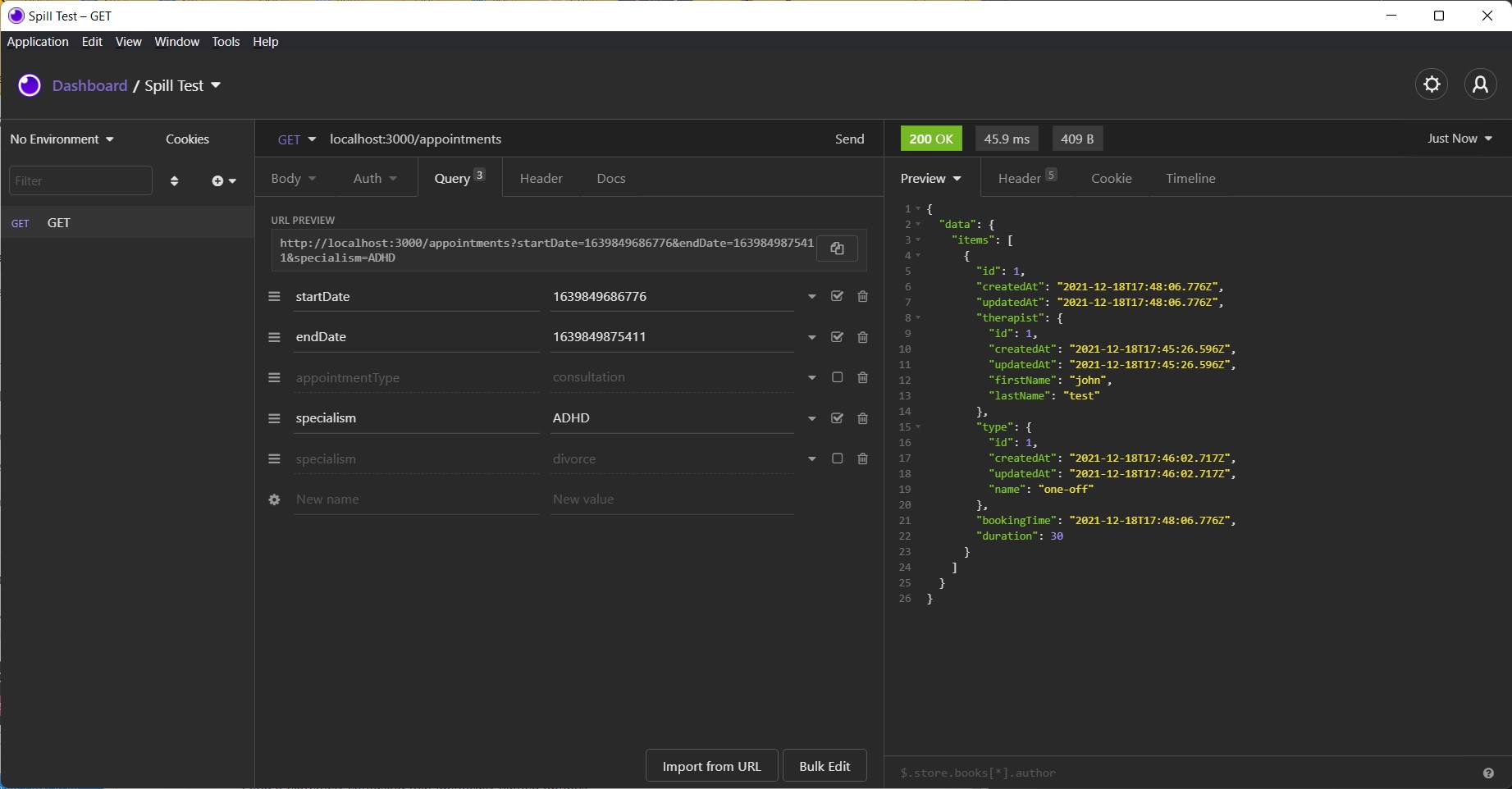
Now connect to the database instance and restore the postgres collection
using spill-backup file
Here I use pgAdmin to connect to the database, the password is password
as defined in docker-compose.yml
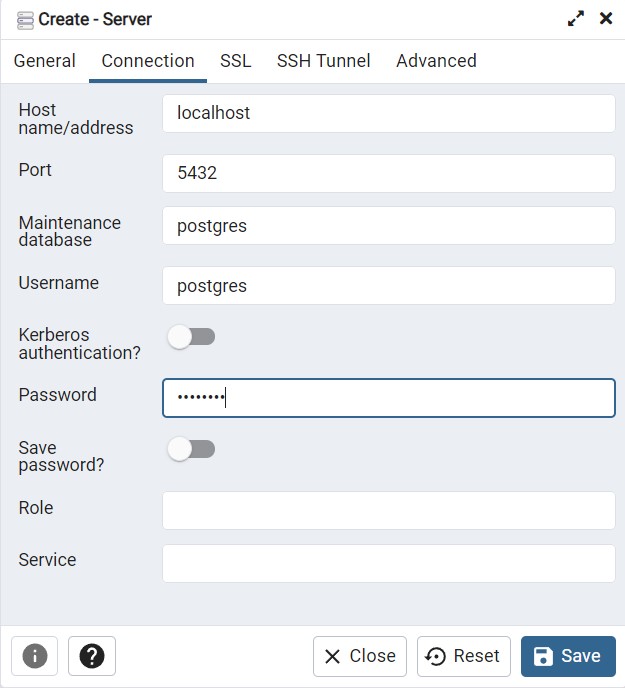
Now restore the database from ./spill-backup file as supplied in the project root.
This creates the tables with the correct schema with some test data
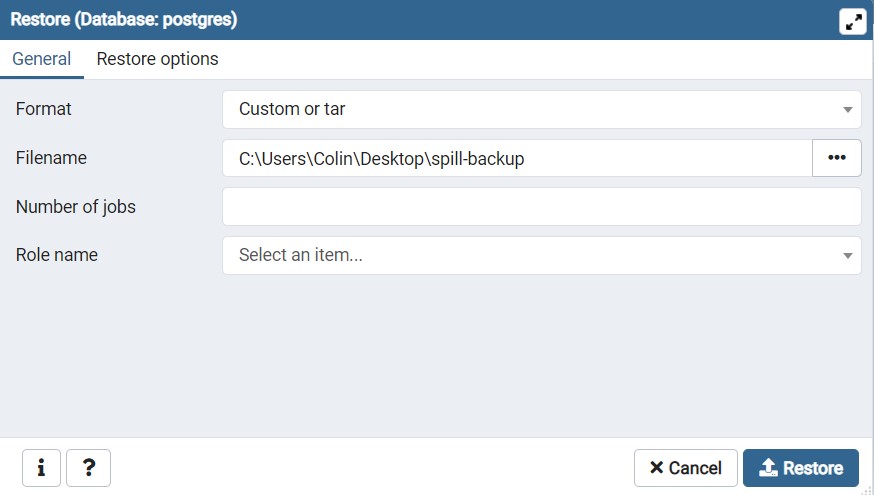
Now you can send a request to localhost:3000/appointments like so
The query params can be any combination of
startDateendDateappointmentTypespecialism
and each have basic validation
Whilst we can also run our tests in docker we might want to run them locally when developing
First install the dependencies locally, you will need node and yarn.
yarn
Then run tests
yarn run test
- Mikro-ORM - Abstraction for the data layer (transactions, SQL queries)
- We're using a typed language, it makes sense to have strong typing on our data models
- Fastify - As the name implies its really fast
- Comes with a tonne of features out of the box (ex. validation)
- Built with docker - Allowing you to easily run the application
- ESLint & Prettier - Standard linting / pretty tooling
Due to a lack of time I'll discuss improvements here that I didn't get to implement
- Testing
- This was limited to two files a unit and integration test
- If given more time I would've like to spend time writing an integration test for the route that hits against a test database
- Observability and Monitoring
- Add Sentry to detect bugs
- Depending on the cloud platform you'd want to log critical parts, example the initial request
- Alerting can be added in depending on what monitoring setup you have (Cloudwatch alarms based off cloudwatch logs)
- Adding appointment slots
- Currently this can only be done by manually inserting into the database via SQL
- Adding an additional POST /appointments route to create the appointment would be trivial
- Extending with PATCH & DELETE completes the CRUD route