- Overview
- Installation
- HTTP Methods
- Resource Objects
- Relationships
- Methods
- HTTP Status Codes
- Endpoint Naming
- Configuration
- More Examples and Use Cases
- Limitations & TODOs
- References
- Thanks
SAFRS is an acronym for SqlAlchemy Flask-Restful Swagger. The purpose of this framework is to help python developers create a self-documenting JSON API for sqlalchemy database objects and relationships. These objects can be serialized to JSON and can be created, retrieved, updated and deleted through the JSON API. Optionally, custom resource object methods can be exposed and invoked using JSON. Class and method descriptions and examples can be provided in yaml syntax in the code comments. The description is parsed and shown in the swagger web interface.
The result is an easy-to-use swagger/OpenAPI and JSON:API compliant API specification.
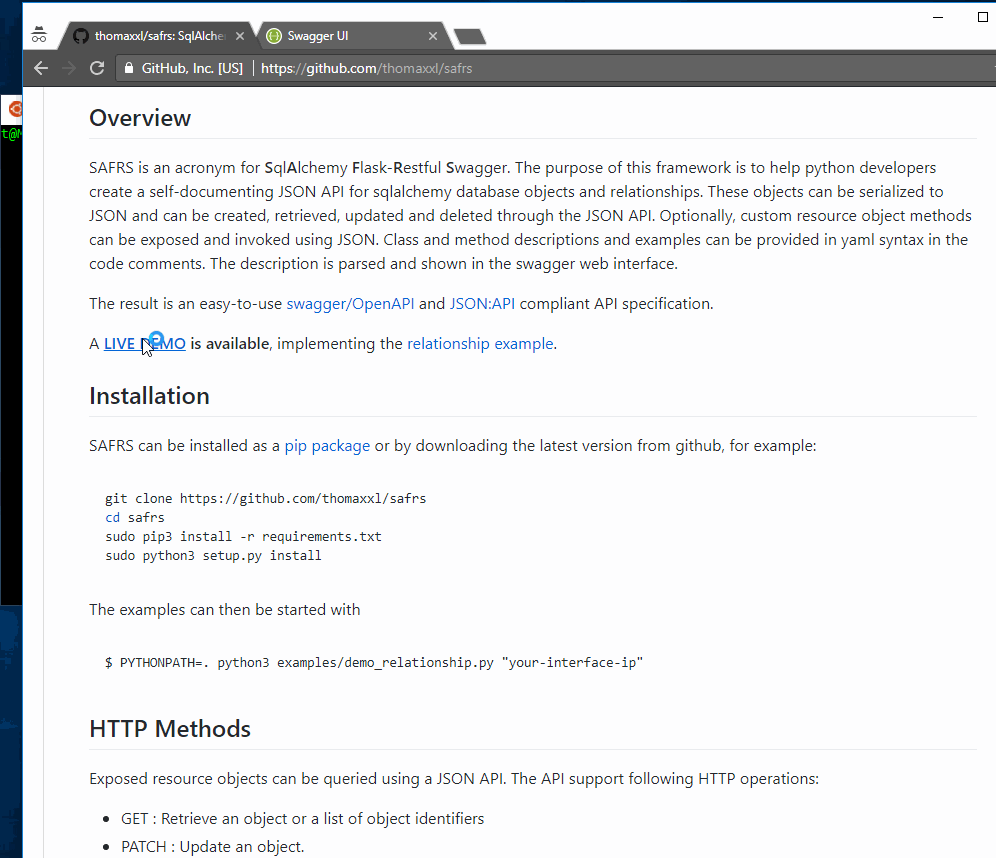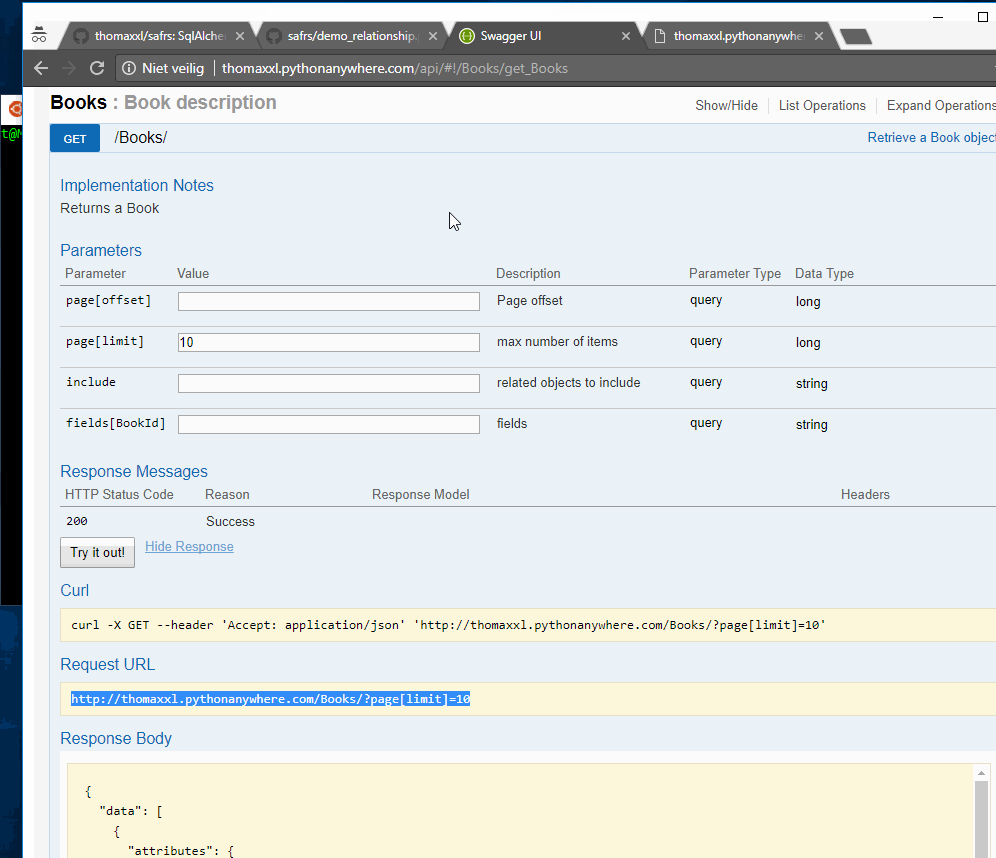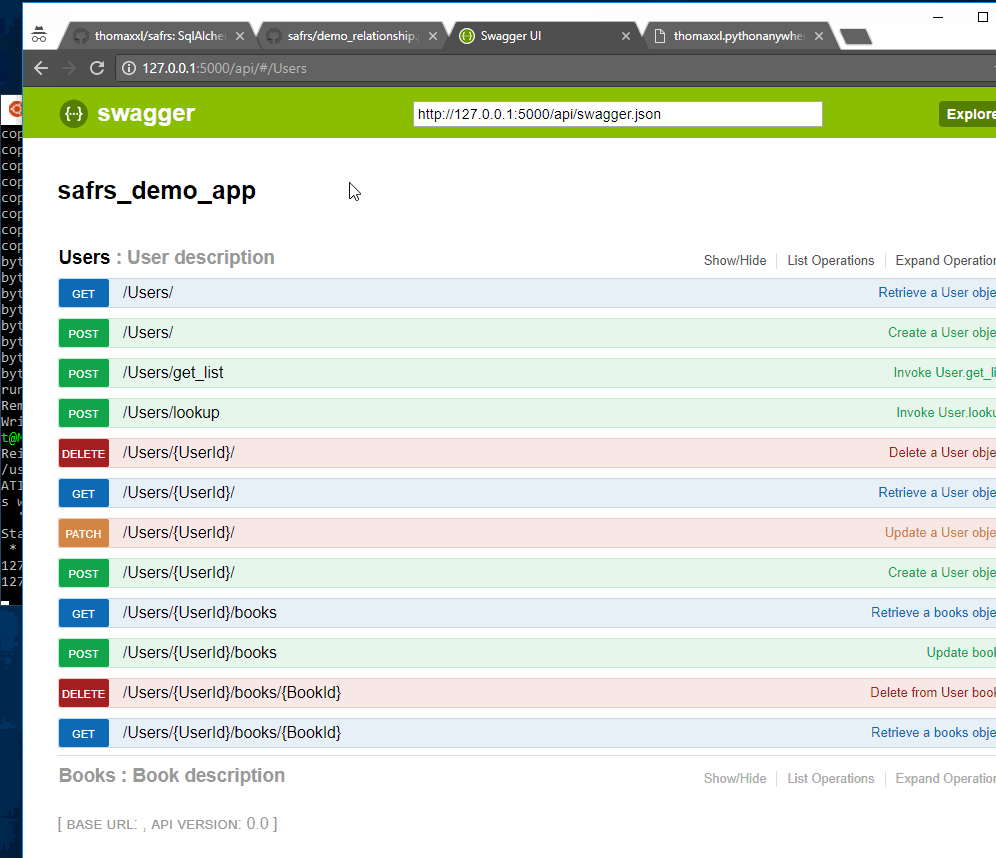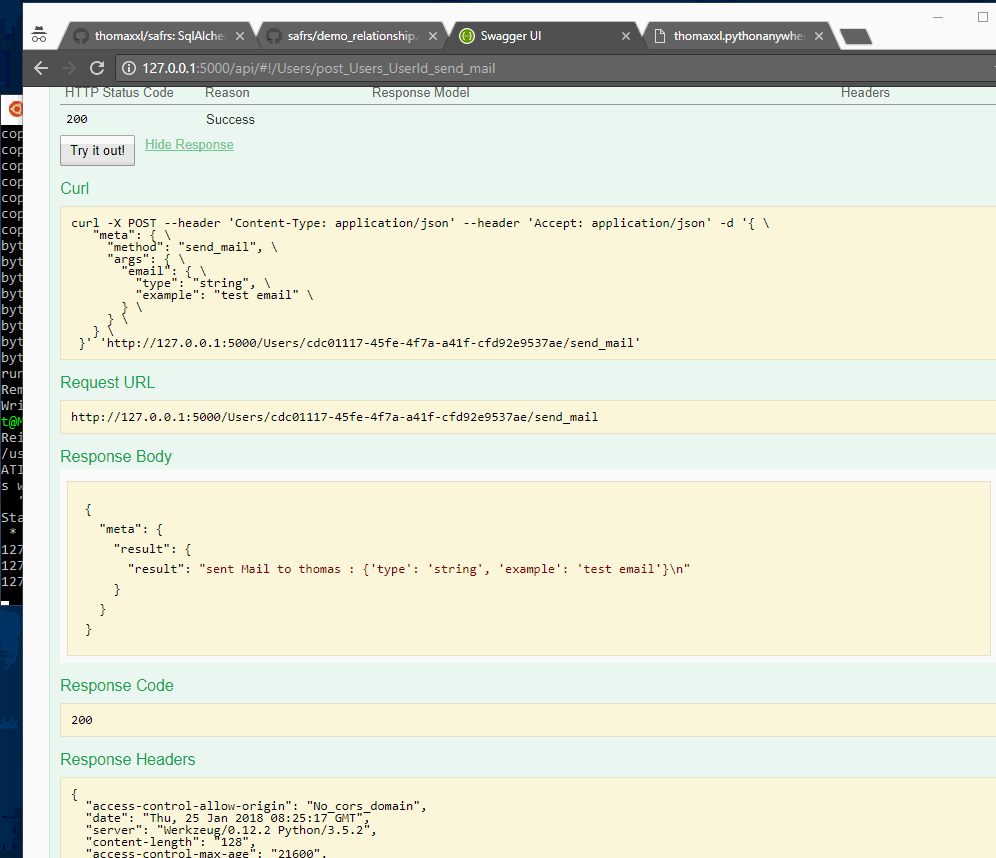
A LIVE DEMO is available, implementing the relationship example.
SAFRS can be installed as a pip package or by downloading the latest version from github, for example:
git clone https://github.com/thomaxxl/safrs
cd safrs
pip3 install -r requirements.txt --user
python3 setup.py install --userThe examples can then be started with
python3 examples/demo_relationship.py "your-interface-ip"
Exposed resource objects can be queried using a JSON API. The API support following HTTP operations:
- GET : Retrieve an object or a list of object identifiers
- PATCH : Update an object.
- DELETE: Delete an object.
- POST : Create an object.
Database objects are implemented as subclasses of the SAFRSBase and SQLAlchemy model classes. The SQLAlchemy columns are serialized to JSON when the corresponding REST API is invoked.
Following example from demo.py illustrates how the API is built and documented:
class User(SAFRSBase, db.Model):
'''
description: User description
'''
__tablename__ = 'Users'
id = Column(String, primary_key=True)
name = Column(String, default = '')
email = Column(String, default = '')The User class is implemented as a subclass of
- db.Model: SQLAlchemy base
- SAFRSBase: Implements JSON serialization for the object and generates (swagger) API documentation
This User object is then exposed through the web interface using the Api object
api.expose_object(User)The User object REST methods are available on /User, the swagger schema is available on /api/swagger.json and the UI is available on /api/:
Database object such as the User class from the demo.py example can be extended to include relationships with other objects. The demo_relationship.py contains following extension of the User class where a relationship with the Book class is implemented:
class User(SAFRSBase, db.Model):
'''
description: User description
'''
__tablename__ = 'Users'
id = db.Column(db.String, primary_key=True)
name = db.Column(db.String, default = '')
email = db.Column(db.String, default = '')
books = db.relationship('Book', back_populates = "user")
...A many-to-one database association is declared by the back_populates relationship argument. The Book class is simply another subclass of SAFRSBase and db.Model, similar to the previous User class:
class Book(SAFRSBase, db.Model):
'''
description: Book description
'''
__tablename__ = 'Books'
id = db.Column(db.String, primary_key=True)
name = db.Column(db.String, default = '')
user_id = db.Column(db.String, db.ForeignKey('Users.id'))
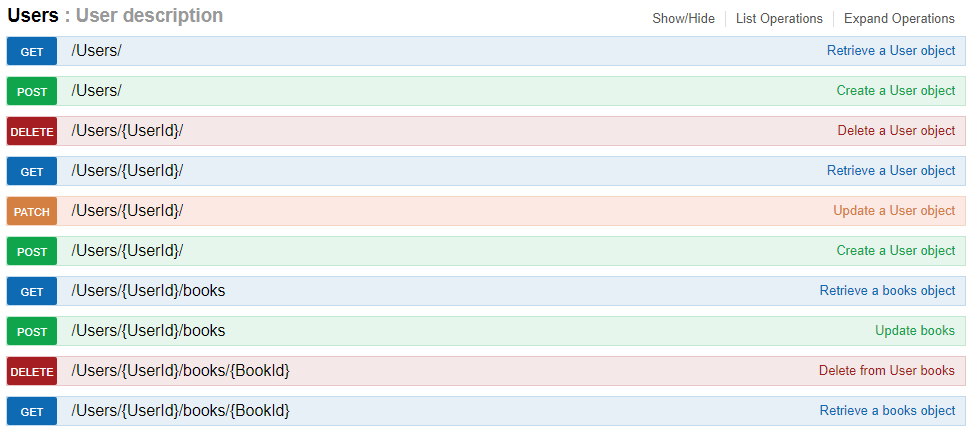
user = db.relationship('User', back_populates='books')The User.book relationship can be queried in the API through the following endpoints:

- POST adds an item to the relationship
- DELETE removes an item from the relationship
- GET retrieves a list of item ids
The relationship REST API works similarly for one-to-many relationships.
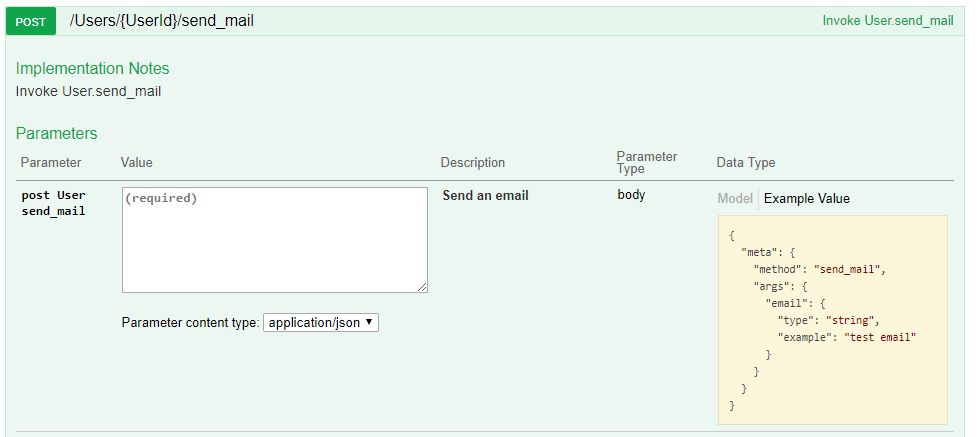
Safrs allows the user to implement custom methods on the exposed objects. This methods can be invoked through the json API by sending an HTTP POST request to the method endpoint The following example implements a "send_mail" method fro example:
class User(SAFRSBase, db.Model):
'''
description: User description
'''
__tablename__ = 'Users'
id = Column(String, primary_key=True)
name = Column(String, default = '')
email = Column(String, default = '')
# Following method is exposed through the REST API
# This means it can be invoked with a HTTP POST
@documented_api_method
def send_mail(self, email):
'''
description : Send an email
args:
email:
type : string
example : test email
'''
content = 'Mail to {} : {}\n'.format(self.name, email)
return { 'result' : 'sent {}'.format(content)}This method shows up in the swagger interface:
The send_mail method is documented with the documented_api_method decorator.
This decorator generates a schema based on the function documentation. This documentation contains yaml specification of the API which is used by the swagger UI.
The yaml specification has to be in the first part of the function and class comments. These parts are delimited by four dashes ("----") . The rest of the comment may contain additional documentation.
Two class-level methods have been defined to facilitate object retrieval:
- lookup : retrieve a list of objects that match the argument list. For example, following HTTP POST request to a container will retrieve a list of itemswhere the name is "thomas"
{
"method": "lookup",
"args": {
"name": "thomas"
}
}- get_list : retrieve a list of the items with the specified ID's
HTTP status codes are used to signal success or failure of a REST operation:
- 200 : OK
- 201 : The request has been fulfilled and resulted in a new resource being created.
- 204 : No Content, DELETE operation was successful
- 400 : The services raised an exception, for example in case of invalid input
- 500 : Internal Server Error
In case of errors( status codes 400+ ), the log file contains a stacktrace. Two custom exceptions are defined in errors.py: ValidationError and GenericError. In case of errors, the webservice will return a default HTTP status code 500 and a customizable error message, for example
{
"error": "Failed to execute query Entity '<class 'C2_server.Image'>' has no property 'namex'"
}
As can be seen in the swagger UI:
- the endpoint collection path names are the SQLAlchemy __tablename__ properties (e.g. /Users )
- the parameter names are derived from the SAFRSBase class names (e.g. {UserId} )
- the the relationship names are the SAFRSBase class relationship names (e.g /books ) The URL path format is configurable
Some configuration parameters can be set in config.py:
- USE_API_METHODS: set this to false in case you want to disable the documented_api_method functionality
- INSTANCE_URL_FMT: This parameter declares the instance url path format
- RELATIONSHIP_URL_FMT: This parameter declares the relationship endpoint path format
The examples folder contains more example scripts:
- Exposing an exisitng sqlite database as a REST service
- Using a sha hash as primary key (id)
- CORS usage
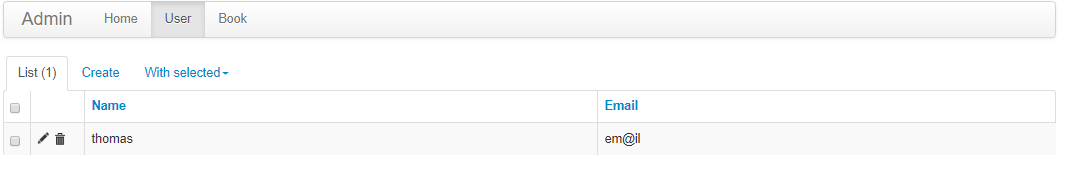
- Flask-Admin integration example, eg.:
This code was developed for a specific use-case and may not be flexible enough for everyone's needs.
- Composite keys might not work well.
- Includes are disabled by default for performance reasons and I haven't worked out how to handle recursive relations.
- I am not a big fan of the multiple inheritance needed to declare SAFRSBase instances but I couldn't subclass sqla's db.Model and I think inheritance is more clear than class decorators.
- Not all of the documentation available in swagger1 is shown with swagger2
- I tried to keep this readme short for the sake of brevity. More details can be found in the README's of the subdirectories. Feel free to drop me an email if something isn't clear!
- By default, SAFRSBase objects are commited to the database in
__init__, as specified by the SAFRSBase.db_commit boolean. When using SAFRSBase in combination with other frameworks (eg. flask-admin), care should be taken of how and when objects are added to the session and commited. An example of flask-admin integration can be found in the examples directory.
I developed this code when I worked at Excellium Services. They allowed me to open source it when I stopped working there.