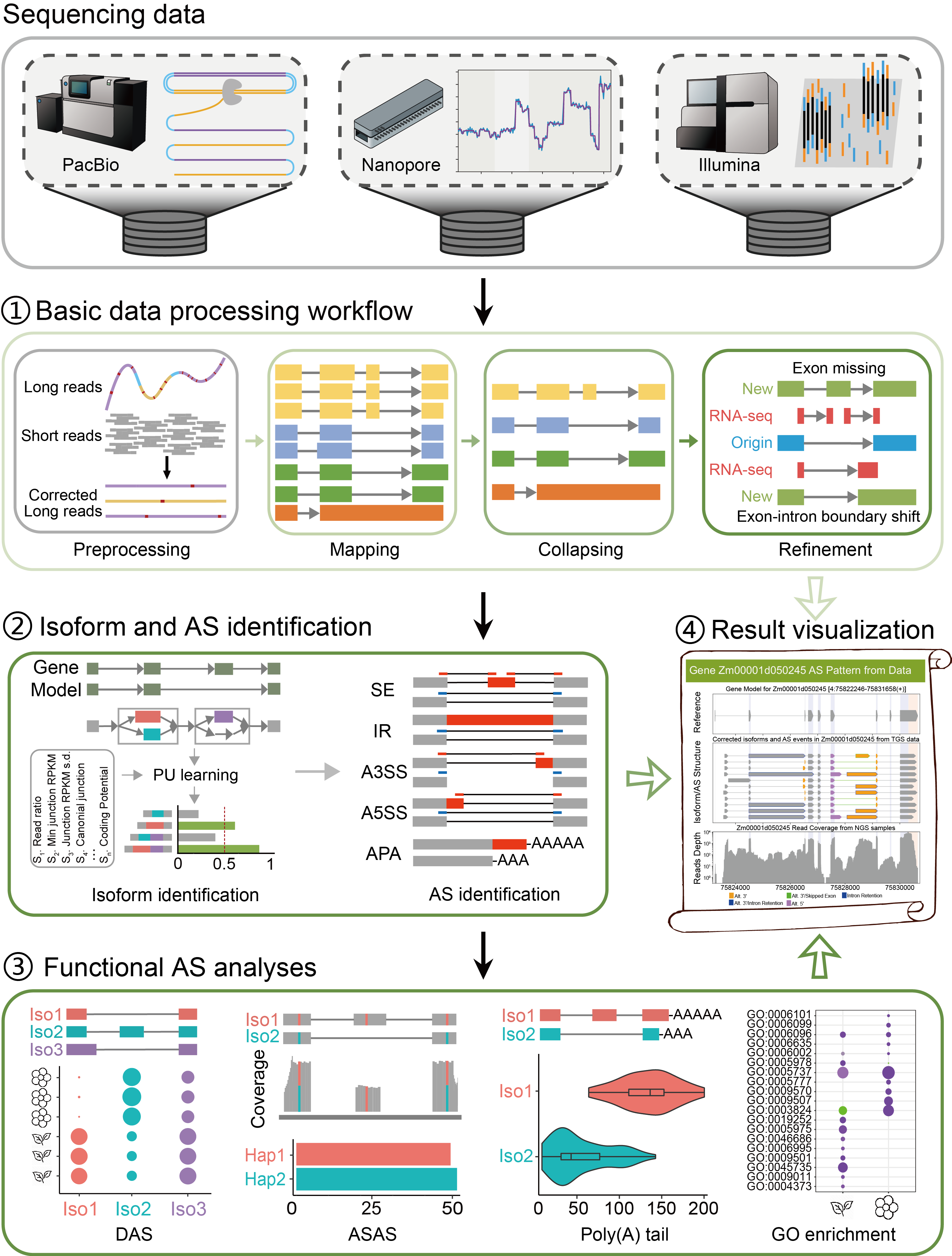
iFLAS is a "one-stop" alternative splicing (AS) analysis tool based on full-length transcriptome, aiming to provide a general analysis framework with diverse functions, accurate results and simple operation for the field of plant full-length AS. In order to achieve this goal, iFLAS integrates a variety of analysis methods and tools for different analysis purposes, and completes comprehensive analysis of alternative splicing through three main modules: 1) basic data processing module, 2) isoform and AS identification module, and 3) functional AS analysis module.
The basic data processing module employs optimized analysis pipelines to handle transcriptome data from different sequencing platforms, including preprocessing of raw data, sequence alignment, isoform redundancy removal, and splice site correction. The high-quality annotation of splice junctions from Illumina RNA-seq ensures the rationality of isoform structures.
The isoform and AS identification module utilizes PU learning for precise isoform identification and accurately characterizes AS events based on a hybrid-sequencing analysis strategies, which alleviates the issue of missing alternative intron commonly met in NGS analysis and provides a more reliable AS analysis results for plants.
The functional AS analysis module performs various functions, including identification of differentially spliced events, characterization of allele-specific splicing events, detection of differential 3' poly(A) tails between splice isoforms, and GO functional enrichment analysis, thereby offering multiple novel insights for plant alternative splicing analysis. Additionally, the visualization and reporting module provides a statistical summary of the analysis results, ensuring the interpretability of the findings.
We recommend using conda to substantially facilitate installation of all Python dependencies. Please follow the steps here to ensure an error-free installation. The installation will be done just once, and all the dependencies will be installed automatically in a conda environment. When the environment has been entirely built, you can print the help prompt. If no errors are thrown, it indicates that iFLAS has been successfully installed.
# Create conda enviroment named iflas
conda create -y -n iflas python=2.7
conda activate iflas
# Install dependencies
conda install -y -c bioconda samtools=1.9 hisat2 bedtools=2.29.2 bamtools subread stringtie minimap2 seqkit fastp
conda install -y -c bioconda ucsc-gtftogenepred ucsc-genepredtogtf fmlrc2=0.1.4 nanopolish=0.11.1 regtools=0.5.2
conda install -y -c bioconda isoseq3=3.3 pbccs=4.2 lima pbcoretools rmats=4.0.2 bax2bam pbbam=1.0.6 pbcopper=1.3.0
conda install -y -c conda-forge r-base=3.6.3 rpy2=2.8.6 r-scales
conda install -y -c bioconda bioconductor-deseq2=1.26.0 bioconductor-clusterprofiler=3.14.0 bioconductor-gviz=1.30.0
conda install -y r-stringi=1.4.6 r-dplyr=1.0.0 r-tibble=3.0.0 r-gridBase
pip install pandas matplotlib==2.2.3 psutil biopython==1.68 pybedtools PyVCF PyPDF2 PyMuPDF-1.17.7 bx-python==0.7.3 networkx==2.2
R -e "install.packages('tidyr')"
R -e "install.packages('valr')"
# install Cupcake
git clone https://github.com/CrazyHsu/cDNA_Cupcake.git
cd cDNA_Cupcake
git checkout Py2_v8.7.x
python setup.py build && python setup.py install
cd ../
# install SpliceGrapher
git clone https://github.com/CrazyHsu/SpliceGrapher_packages.git
cd SpliceGrapher_packages
tar -xf PyML-0.7.14.tar.gz
cd PyML-0.7.14
python setup.py build && python setup.py install
cd ../
tar -xf SpliceGrapher-0.2.7.tgz
cd SpliceGrapher-0.2.7
python setup.py build && python setup.py install
cd ../
cd ../
# clone iFLAS package
git clone https://github.com/CrazyHsu/iFLAS.git
cd iFLAS
python iFLAS.py -hOf course, it is also possible to get iFLAS using Docker image. If you have not installed Docker, you should first install Docker according to the official tutorial (https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/). Then, pull iFLAS Image from DockerHub and print the help prompt. If no errors are thrown, it indicates that iFLAS has been successfully installed.
docker pull CrazyHsu/iFLAS:lastest
docker run CrazyHsu/iFLAS:lastest iflas.py -h$ python iflas.py -h
usage: iflas.py command [options]
iFLAS: integrated Full Length Alternative Splicing analysis
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
command:
preproc Pre-process the raw PacBio/NanoPore/NGS data. When TGS and
NGS data both are provide, This step will use fmlrc2 to
correct the TGS read with the information in NGS
mapping Mapping the TGS/NGS reads to the reference genome with
minimap2
collapse Collapse corrected reads into high-confidence isoforms
refine Refine the splice junction with the information in short
reads
pu_filter Filter Low-Quality novel isoforms using a PU-learning based
method
find_as Identify alternative splicing(AS) type from high-confidence
isoforms. Four common AS type are included: intron retention,
exon skipping, alternative 3 end splicing and alternative 5
end splicing
visual_as Visualize the specific gene structure with details including
isoform mapping, short reads coverage and AS types identified
asas Identify allele-specific AS
palen_as Identify functional poly(A) tail length related to AS
diff_as Carry out differential AS ananlysis among conditions
go Perform GO enrichment analysis and plot results for the
specified gene set or multiple gene sets
report Automatic detect the plots generated in each step, and merge
them into a report file| Function name | Brief descriptions | Primary tools or methods |
|---|---|---|
| preproc | Raw data preprocessing and filtering | ccs (v4.2.0), lima (v2.0.0), isoseq3 (v3.3.0), guppy (v3.4.5), Fastp(v0.20.1), SeqKit (v0.16.0), fmlrc2 (v0.1.4) |
| mapping | Long and short reads alignment | Minimap2 (v2.18-r1015), Hisat2 (v2.2.0), Regtools (v0.5.2) |
| collapse | Collapsing isoforms to reduce redundancy | Cupcake (vPy2_v8.7x) |
| refine | Correction of splicing site bias due to sequencing errors and alignment algorithm preference | In-house scripts |
| Function name | Brief descriptions | Primary tools or methods |
|---|---|---|
| pu_iso | Novel isoform filtration based on PU learning PU-based isoform filtration method | In-house scripts |
| find_as | Identify alternative splicing events at isoform level | In-house scripts |
| Function name | Brief descriptions | Primary tools or methods |
|---|---|---|
| allele_as | Determine allele-specific alternative splicing events | IsoPhase (vPy2_v8.7x) |
| palen_as | Detect isoforms with differential poly(A) tail length in a gene | nanopolish (v0.11.1) |
| diff_as | Identify differential alternative splicing events between samples | rMATS (v3.1.0), DESeq2 (v1.26.0) |
| go | GO enrichment analysis of/between candidate genes (sets) | clusterProfiler (v3.14.0) |
| Function name | Brief descriptions | Primary tools or methods |
|---|---|---|
| visual_as | Visualization of alternative splicing events | SpliceGrapher (v0.2.7), Gviz (v1.30.0) |
| report | Generate HTML format reports for results | Yattag (v1.14.0) |
The operation of iFLAS is simple, and the analysis can be completed by a command similar to 'python iflas.py function -c config.cfg'. In this command, 'function' represents the name of the sub-function, such as preproc function mentioned earlier, which is used for preprocessing and correction of raw data. '-c config.cfg' specifies the configuration file to be used for the run, in which iFLAS adopts the standard format used by Python ConfigParser module, and you only need to modify the configuration file according to your needs. Of course, iFLAS also supports direct parameter setting through the command line, further enhancing the flexibility of the software.
python iflas.py preproc -cfg config.cfgUsage for preproc function
usage: iflas.py preproc [options]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-cfg DEFAULT_CFG The config file used for init setting.
-merge Merge all samples from a same strain.python iflas.py mapping -cfg config.cfg -c -jcs <min_junction_support_count>Usage for mapping function
usage: iflas.py mapping [options]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-cfg DEFAULT_CFG The config file used for init setting.
-merge Merge all samples from a same strain.
-c Correct the flnc reads with fmlrc2.
-jcs JUNCCOMBSUP The number of junction combination supported by flnc
reads. Default: 2.python iflas.py collapse -cfg config.cfgUsage for collapse function
usage: iflas.py collapse [options]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-cfg DEFAULT_CFG The config file used for init setting.
-merge Merge all samples from a same strain.python iflas.py refine -cfg config.cfgUsage for refine function
usage: iflas.py refine [options]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-cfg DEFAULT_CFG The config file used for init setting.
-merge Merge all samples from a same strain.
-adjust Adjust the strand orient by the information of junctions.
-refine Refine the junction position by the reads support.python iflas pu_filter -cfg config.cfg Usage for pu_filter function
usage: iflas.py pu_filter [options]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-cfg DEFAULT_CFG The config file used for init setting.
-merge Merge all samples from a same strain.
-feature_file FEATURE_FILE
Use user provided feature file to train PU learning
model instead of learning from data.
-filter_score FILTER_SCORE
The PU-score that used to filter out low quality novel
isoforms. Default: 0.5.
-draw_auc To draw the AUC plot or not.
-pos_fl_cov POS_FL_COVERAGE
The minimal coverage that get the positive annotated
isoforms. Default: 2.
-pos_min_junc_rpkm POS_MIN_JUNC_RPKM
The minimal rpkm value of the junctions needed for a
postive annotated isoform. Default: 0.05.
-select_best_model Select the best model. If not, iFLAS will use GB.
-auto_filter_score Auto determine pu_score when 'select_best_model' is
selected.python iflas.py find_as -cfg config.cfgUsage for find_as function
usage: iflas.py find_as [options]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-cfg DEFAULT_CFG The config file used for init setting.
-merge Merge all samples from a same strain.
-pa_rpkm PARPKM Filter the pa cluster by RPKM(PAC). Default: 0.
-pa_sup PA_SUPPORT Filter the pa cluster by RPKM(PAC). Default: 5.
-conf_pa CONFIDENTPA The confident PA file used for filtering the results.python iflas.py diff_as -cfg config.cfgUsage for diff_as function
usage: iflas.py diff_as [options]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-cfg DEFAULT_CFG The config file used for init setting.
-merge Merge all samples from a same strain.
-bg GENE2GOFILE The mapping file between gene and go term used for GO
enrichment analysis.
-cutoff CUTOFF The cutoff used to filter the output. Default: 0.05
-filterBy {pvalue,p.adjust}
The value used to filter. Default: p.adjust.
-showCategory SHOWCATEGORY
The number of items to show off. Default: 20.
-d COMPCOND The condition file used to detect differential AS
between samples.
-go Perform GO enrichment analysis for DSGs between
samples.
-pu_filter Get differentially spliced genes containing the
isoforms filtered by PU learning.python iflas.py asas -cfg config.cfgUsage for asas function
usage: iflas.py asas [options]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-cfg DEFAULT_CFG The config file used for init setting.
-merge Merge all samples from a same strain.
-bg GENE2GOFILE The mapping file between gene and go term used for GO
enrichment analysis.
-cutoff CUTOFF The cutoff used to filter the output. Default: 0.05
-filterBy {pvalue,p.adjust}
The value used to filter. Default: p.adjust.
-showCategory SHOWCATEGORY
The number of items to show off. Default: 20.
-go Perform GO enrichment analysis for DSGs between
samples.
-ase Whether to Carry out ASE analysis.
-ref_fa REFFA The reference fasta file used to be quantified in ASE.
-alt_fa ALTFA The alternative fasta file used to be quantified in
ASE.
-fbs Call the heterozygosity SNPs with freebayes in ASE.python iflas.py palen_as -cfg config.cfgUsage for palen_as function
usage: iflas.py palen_as [options]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-cfg DEFAULT_CFG The config file used for init setting.
-merge Merge all samples from a same strain.
-bg GENE2GOFILE The mapping file between gene and go term used for GO
enrichment analysis.
-cutoff CUTOFF The cutoff used to filter the output. Default: 0.05
-filterBy {pvalue,p.adjust}
The value used to filter. Default: p.adjust.
-showCategory SHOWCATEGORY
The number of items to show off. Default: 20.
-go Perform GO enrichment analysis for DSGs between
samples.
-pa_sup PA_SUPPORT The pa cluster coverage supported by flnc reads.
Default: 10.
-conf_pac CONFIDENTPAC
The confident PAC file used for filtering the resultspython iflas.py go -cfg config.cfg -tg <gene_list> -s <> -filterby pvalue -cutoff 0.05Usage for go function
usage: iflas.py go [options]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-cfg DEFAULT_CFG The config file used for init setting.
-merge Merge all samples from a same strain.
-bg GENE2GOFILE The mapping file between gene and go term used for GO
enrichment analysis.
-cutoff CUTOFF The cutoff used to filter the output. Default: 0.05
-filterBy {pvalue,p.adjust}
The value used to filter. Default: p.adjust.
-showCategory SHOWCATEGORY
The number of items to show off. Default: 20.
-tg TARGETGENEFILE The target gene file or file list separated by comma
used for GO enrichment analysis.
-s SAMPLENAME The sample name used plot the track, multi-sample
should be separated by commma used for GO enrichment
analysis.
-o OUTNAME The prefix of the GO enrichment output file.python iflas.py visual_as -cfg config.cfg -g <gene_id>Usage for visual_as function
usage: iflas.py visual_as [options]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-cfg DEFAULT_CFG The config file used for init setting.
-merge Merge all samples from a same strain.
-g GENES The gene list separated by comma or a single file contain
genes one per line used for visualization.python iflas.py report -basic -asp -geneStruc -diff -html -cfg config.cfgUsage for report function
usage: iflas.py report [options]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-cfg DEFAULT_CFG The config file used for init setting.
-merge Merge all samples from a same strain.
-all Generate all the plots.
-basic Generate basic information plots.
-asp Generate AS pattern plots.
-geneStruc Generate gene structure with AS events.
-asas Generate allele-specific AS events.
-palen Generate AS events related differential poly(A) tail
length.
-diff Generate the statistics for differential spliced events.
-html Generate the html report for the results have been
generated.We have uploaded our PacBio full-length transcriptome data for eight maize lines (B73, Chang7-2, Mo17, Huangzao4, PH207, PH4CV, PH6WC and Zheng58) into NCBI database under accession number PRJNA64316.
Here we only use the data of B73 as an example and maize AGPv4.50 annotation files as reference configuration in [refSection] of config.cfg file. The required keys include: 1) ref_genome: maize genome fasta file, and 2) ref_gtf: GTF (General Transfer Format) file describing gene model. In order to simplify the operation, we only need to run prepare.sh to prepare testing files and configurations with one click.
bash prepare.sh
# Pre-processing raw PacBio and Illumina data
python iflas.py preproc -cfg config.cfg
# Map the sequencing data to reference genome
python iflas.py mapping -cfg config.cfg -c -jcs 2
# Collapse isoforms
python iflas.py collapse -cfg config.cfg
# Refine splice junction bias
python iflas.py refine -cfg config.cfg -refine -adjust
# Use PU learning to filter low-confidence isoforms
# Minimal coverage and minimal junction rpkm are set to 2 and 0.05 to define positive isoforms.
python iflas pu_filter -cfg config.cfg -filter_score 0.5 -pos_fl_cov 2 -pos_min_junc_rpkm 0.05
# Find AS events
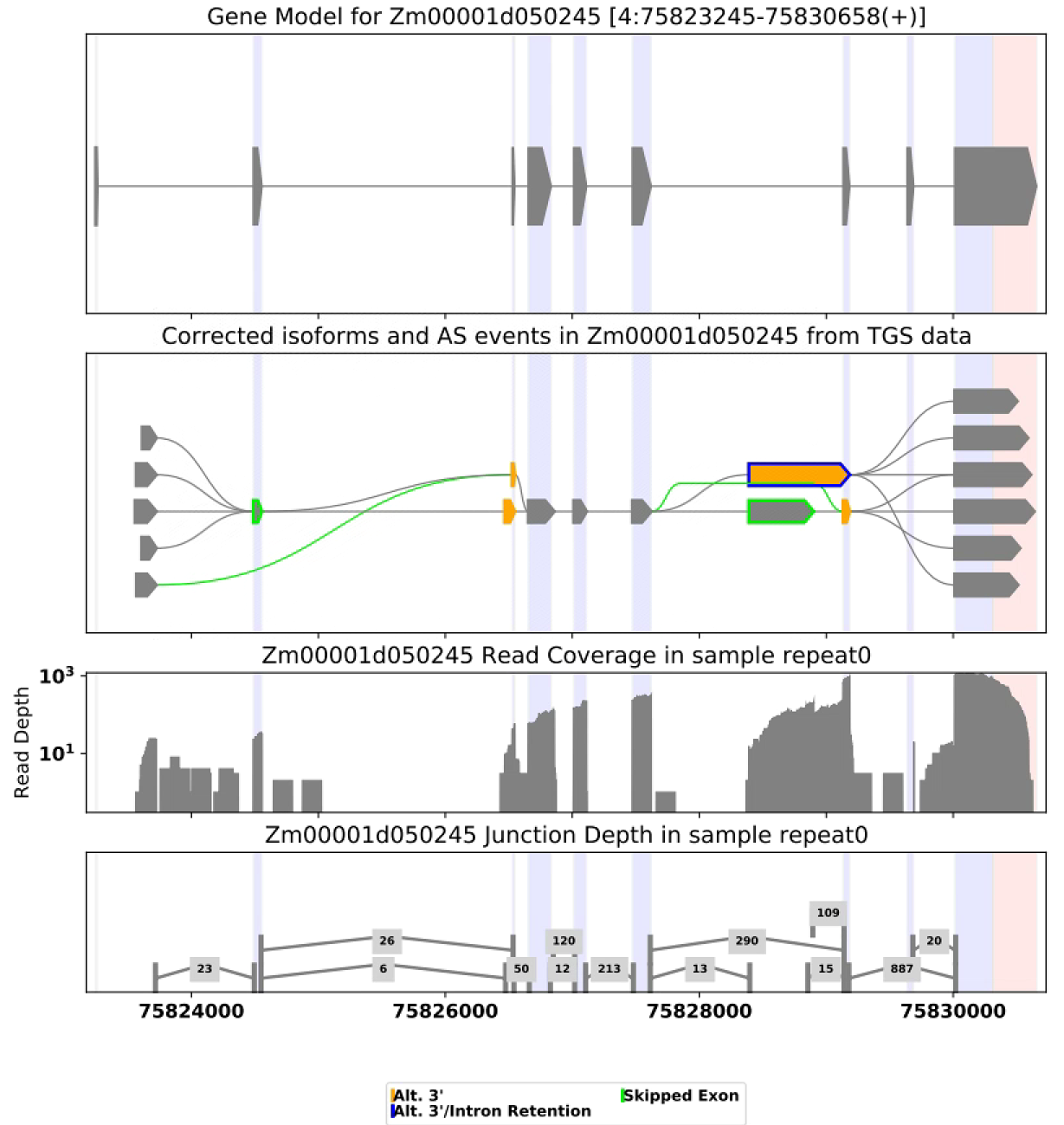
python iflas.py find_as -cfg config.cfg# Visualization the AS events for gene Zm00001d050245
python iflas.py visual_as -cfg config.cfg -g Zm00001d050245# Visualize the GO enrichment result for the target genes
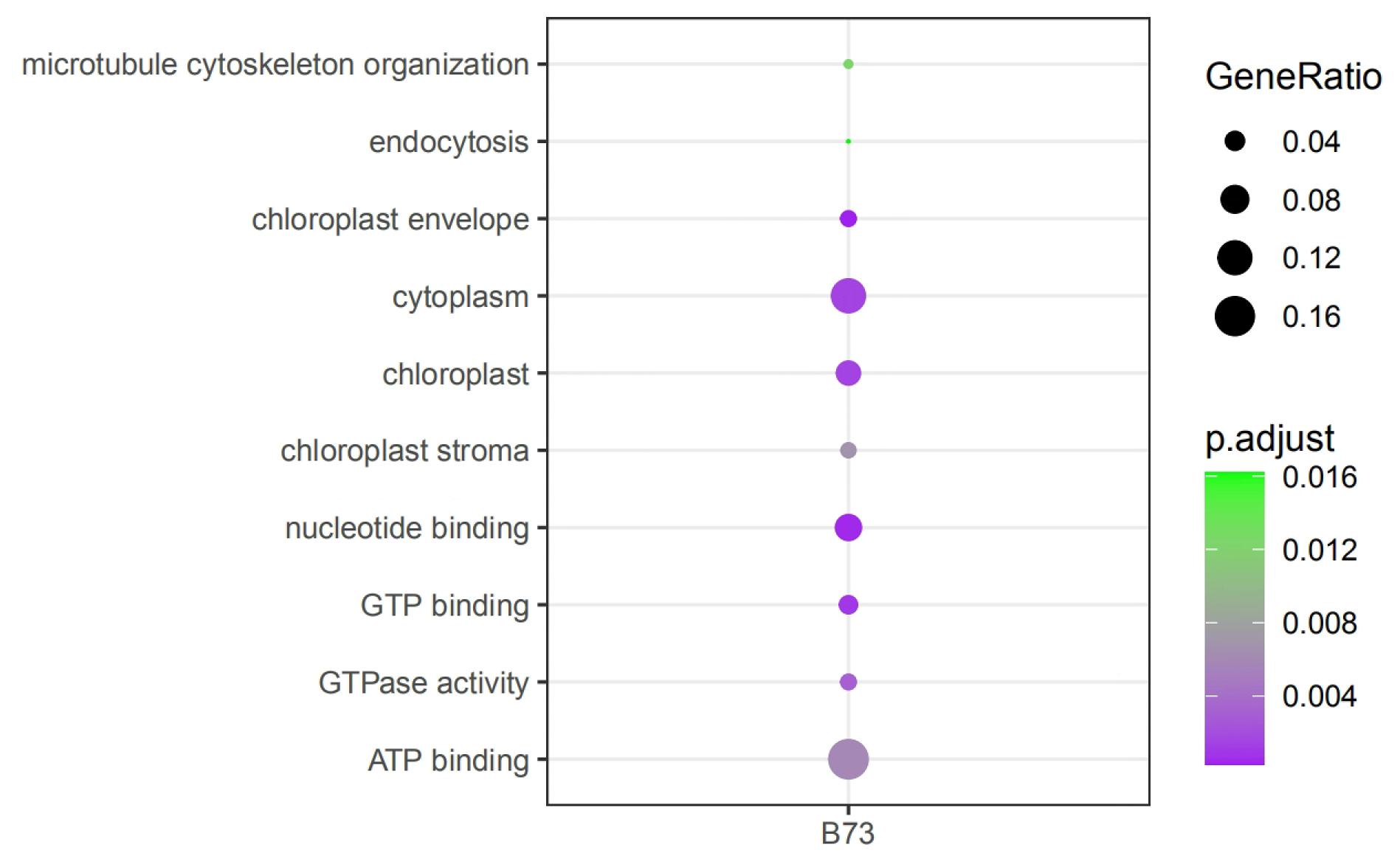
python iflas.py go -cfg config.cfg -td targetGene.lst -s B73The report function can generate the visualization results with HTML files, which can be viewed in browser.
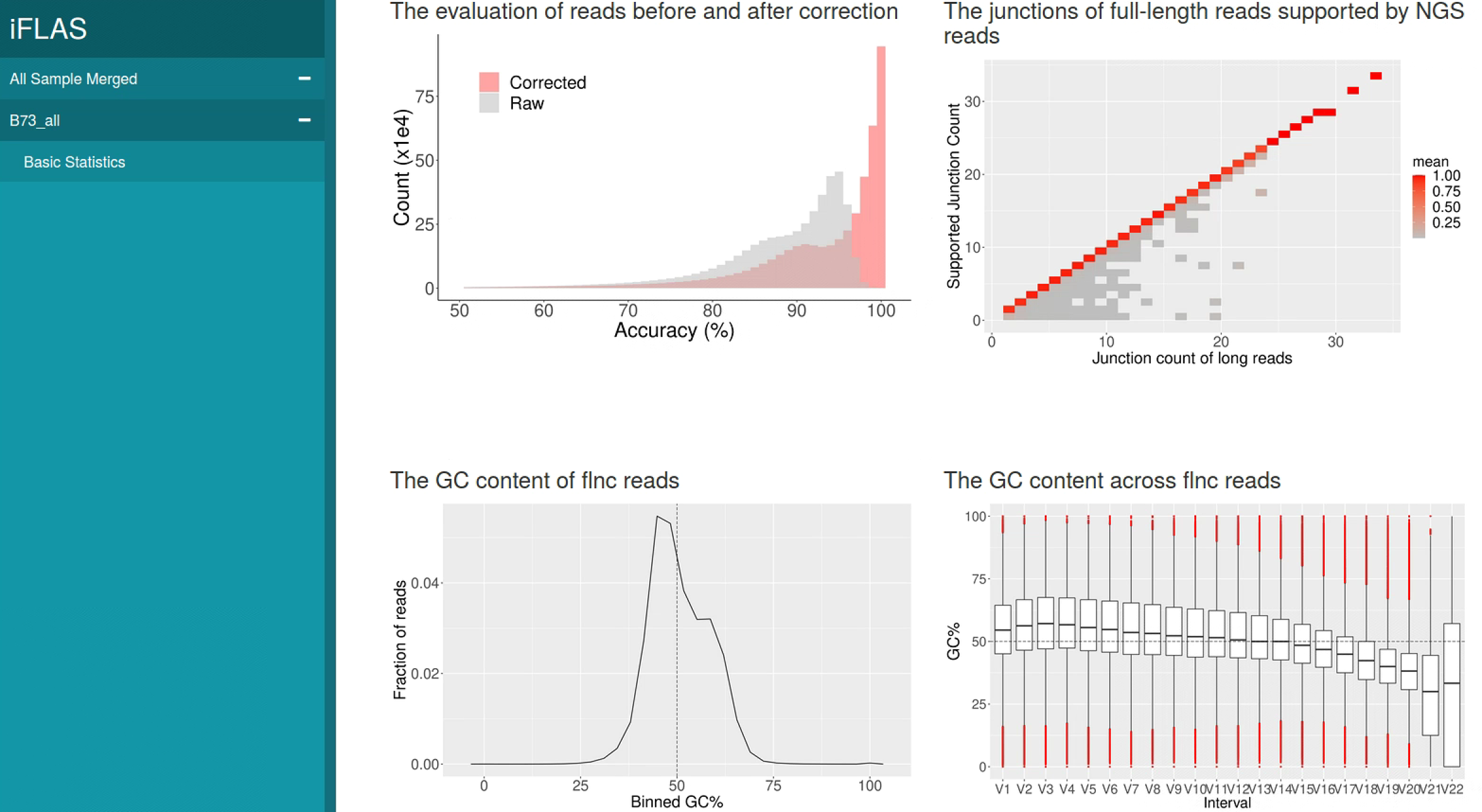
python iflas.py report -cfg config.cfg -basic -htmlPlease feel free to contact us: xufeng9527@cau.edu.cn