IGM-Vis: Analyzing Intergalactic and Circumgalactic Medium Absorption Using Quasar Sightlines in a Cosmic Web Context
The Intergalactic Media Visualization, or IGM-Vis, is a novel visualization and data analysis platform for investigating galaxies and the gas that surrounds them in context with their larger scale environment, the Cosmic Web. Environment is an important factor in the evolution of galaxies from actively forming stars to a quiescent state with little, if any, discernible star formation activity. The gaseous halos of galaxies (the circumgalactic medium, or CGM) play a critical role in their evolution, because the gas necessary to fuel star formation and any gas expelled from widely observed galactic winds must encounter this interface region between galaxies and the intergalactic medium (IGM).
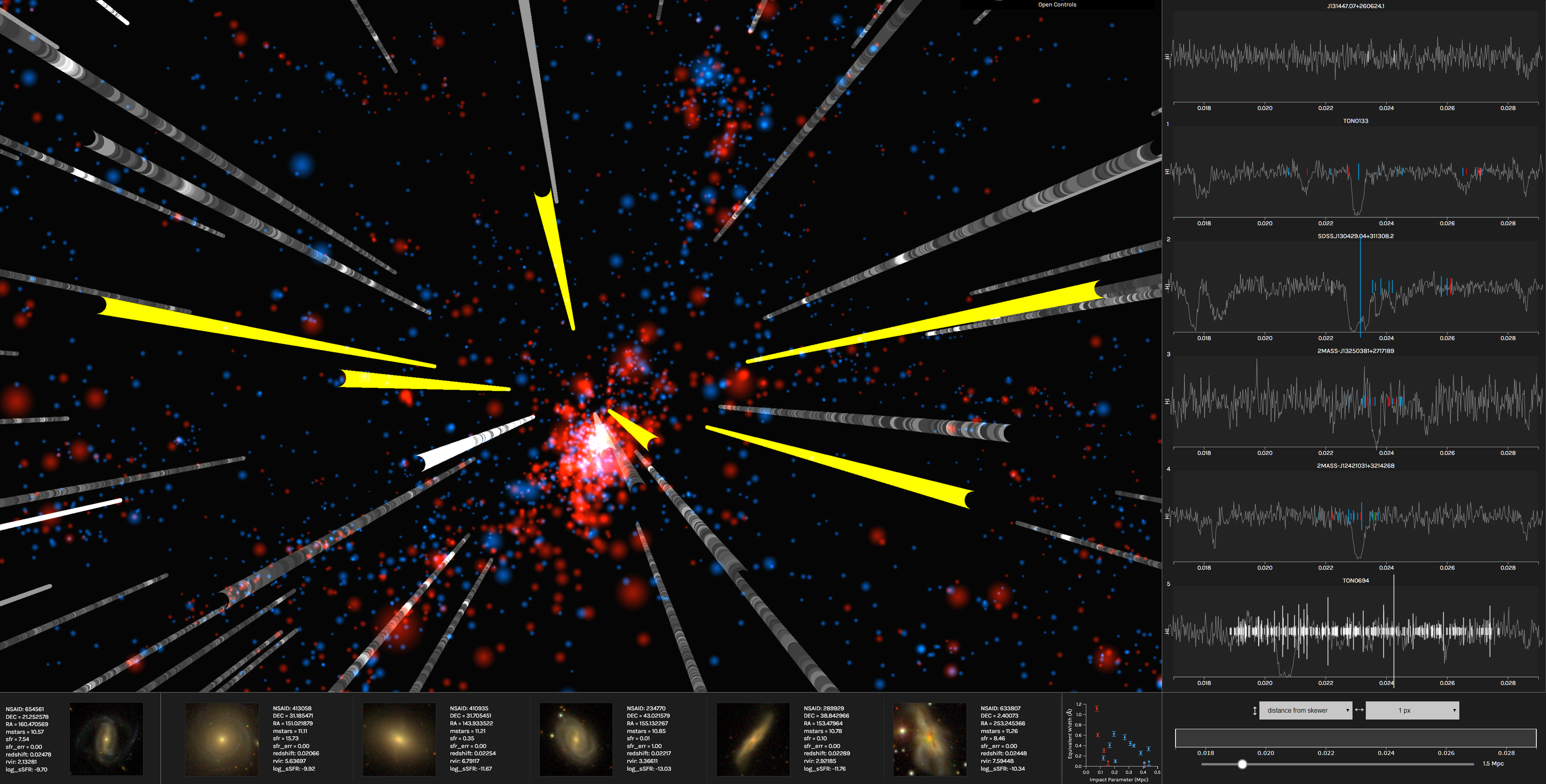
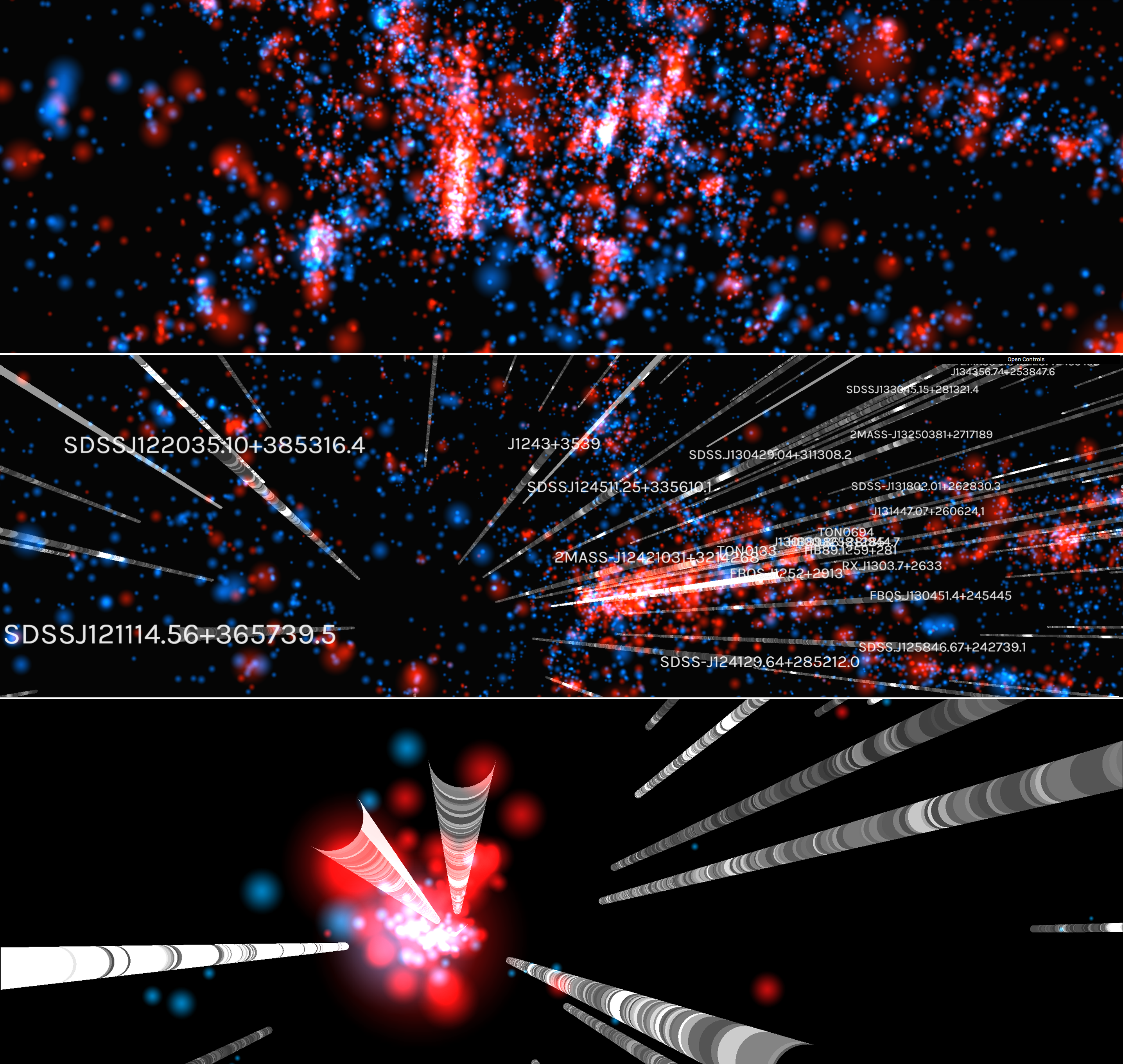
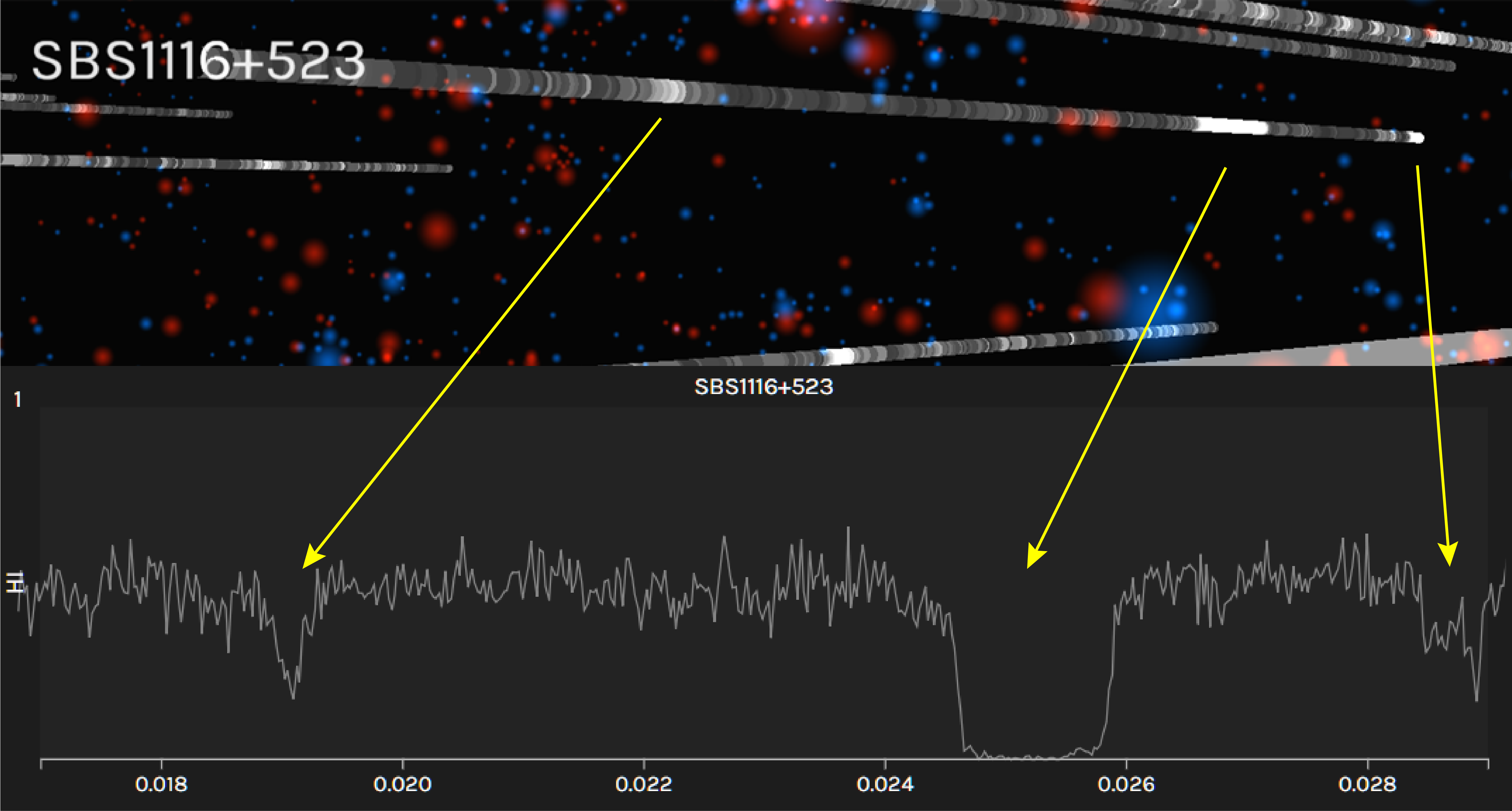
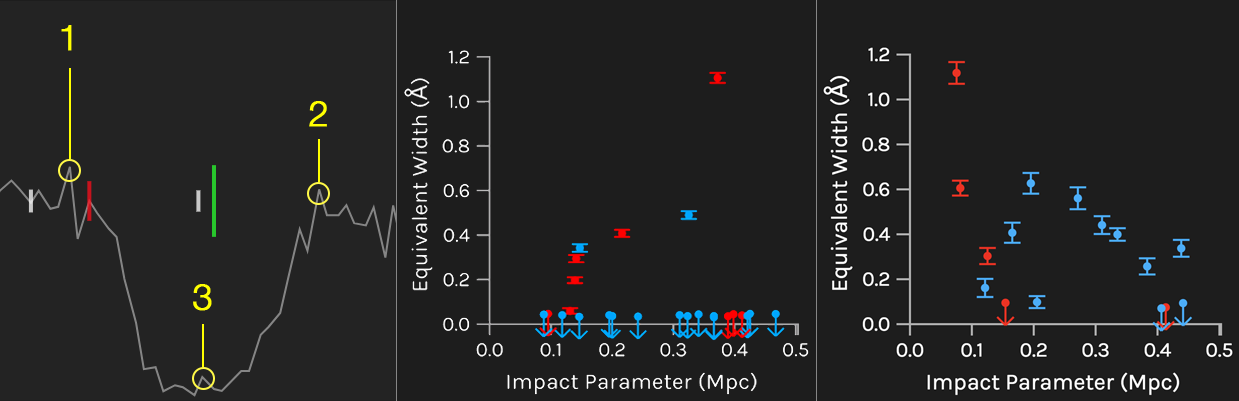
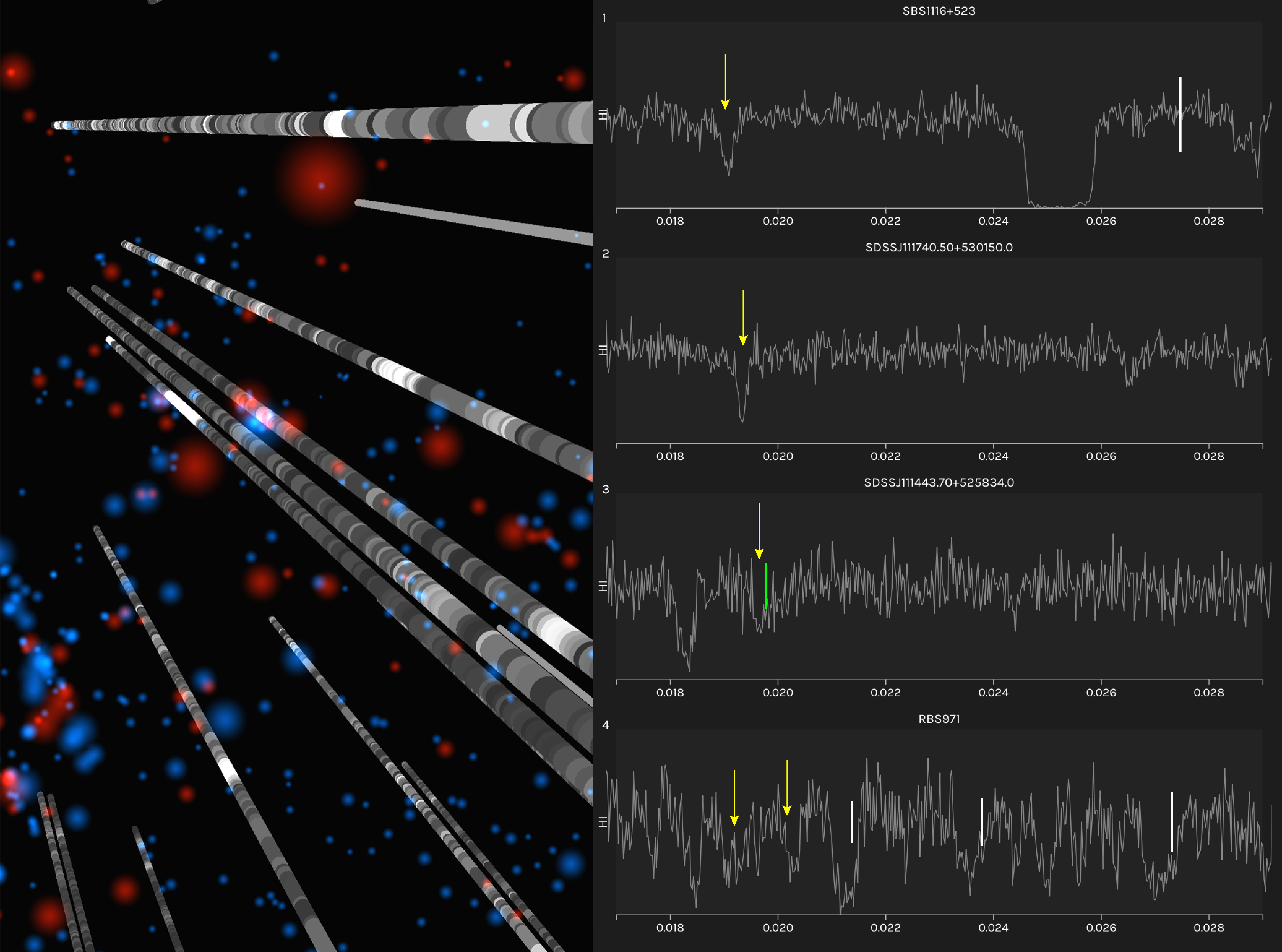
The blue and red spheres represent star-forming and quiescent galaxies, respectively, and the 'skewers' piercing the volume are QSO sightlines. Mouse over a galaxy to see an image and a few of its properties in the lower panel. Mouse over a skewer and the right-hand panels show the spectral region where H I or C IV (or other available sperctra) fall within a specified redshift range. If a galaxy has an impact parameter within the range indicated by the bottom-right slider, a vertical line will appear at its redshift in the spectral window. Use the two drop-down boxes to control the height and thickness of these lines according to different properties. Lastly, control the range of redshift shown in the spectral windows with the sizing bar between the drop-downs and the slider.
Galaxy/absorber pairs can be tracked using the numeric keys '0' through '9' (skghtlines) and 'G' (galaxies), and then saved to disk for further analysis by pressing 'D'.
A video tutorial with an example use case can be seen here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3ZVaExEVZOk
The Web demo of IGM-Vis is located at: https://creativecodinglab.github.io/Intergalactic/intergalactic.html
Arrow keys: move reference point (in 3D view)
0 - 9 : store selected skewer to Spectrum Panel
E : obtain equivalent width measurements (see video tutorial)
G : store selected galaxy in Galaxy Panel
D : download json file of all stored skewers with galaxy neighbor pairs
S : show / hide skewers in 3D view
T : show / hide text in 3D view
Z : zoom camera to selected galaxy in 3D view
Galaxies positions and metadata are loaded from data/galaxies.json file using the loadGalaxyData() function. Once this file has been read, the function loadSkewerData() is called and reads the list of QSOs qsosInSdssSlice_viz.dat for their name, Right Ascension (RA) and Declination (DEC). The HI and CIV spectra for each QSO listed in qsosInSdssSlice_viz.dat is loaded from these folders respectively: data/spectra_HI_norm and data/spectra_CIV_norm. Calculating the projected distance between every skewer and galaxy can be done using the function computeProjections(), which uses the haversine() function to calculate an angular distance (impact parameter) between the two objects. In order to do this calculation, redshift must converted to physical units, which is done with the cosmcalc() function. In order to save time, a lookup table stored in data/projections/lookUp.json is referenced, which was created using the cosmcalc() function. If values outside of the range contained in the lookup table are needed, the computation is done on demand. In order to quicken the initial loading time even further, the impact parameter values for this dataset were precomputed in Megaparsecs using the steps outlined above and are stored in the folder data/projections as a separate file for each quasar with the function loadP(). Data can be downloaded into a .json file using the function exportData('example.json',JSON.stringify([an array])). The data object that is downloaded on the "D" key press can be modified in the onKeyDown(event) event handler.
IGM-Vis was created by an interdisciplinary team of researchers at University of California, Santa Cruz.
- Dept. of Astronomy & Astrophysics: Joseph N. Burchett, J. X. Prochaska;
- Dept. of Computational Media: David Abramov, Cassia Artanegara, Jasmine Otto, and Angus G. Forbes
An article describing IGM-Vis is accepted to EuroVis’19, and a pre-print is available on ArXiv at https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.07092