-
1.1 Prerequisites
-
1.3 Pre-setup
-
1.6 Install Klayout
-
1.7 Install OpenLANE
-
1.8 Install the PDK
-
2.1 Prerequisites
-
2.2 Pre-setup
-
2.5 Install Klayout
-
2.6 Install OpenLANE
-
2.7 Install the PDK
The goal of this guide is to install the open-source EDA tool-set needed to go through some of the physical design flow stages, and correctly configure the Skywater PDK.
The following packages will be installed:
-
Netgen LVS
-
NGSpice
-
Skywater 130nm PDK
-
Magic VLSI
-
Klayout
-
OpenLANE
The version of the Ubuntu distro should be 18.04+.
In order to install the EDA tool-set within Ubuntu, previously you need to have installed some other required packages. To do so, first update and upgrade packages database and upgrade the packages to avoid version mismatches:
sudo apt -y update && sudo apt -y upgradeNow we can proceed to install required packages:
-
git 2.35+
-
docker 19.03.12+
-
python 3.6* with pip and venv
-
GNU Make
-
Ruby
sudo apt install -y build-essential python3 python3-venv python3-pip make git ruby-full libqt5opengl5Since NGSpice and Netgen-LVS are available as pre-compiled packages, we can install them using apt too.
sudo apt install -y netgen-lvs ngspice ngspice-docRun the following to check it has been correctly installed:
ngspiceexitnetgen-lvsIn order to organize the directory tree for EDA tool-set, let's create a folder to contain every tool needed for the course. To do so, got to your user /home directory.
cd ~/Create the directory eda_tools and move into:
mkdir eda_toolscd eda_tools(WARNING: we will work over eda_tools folder all the time.)
The Skywater PDK requires Magic 8.3.25 or higher, thus we will build the latest version from source.
First install the required dependencies using apt:
-
M4 preprocessor
-
tcsh shell
-
csh shell
-
xlib.h
-
Tcl/Tk
-
Cairo
-
OpenGL
-
ncurses
cd ~/sudo apt install -y m4 tcsh csh libx11-dev tcl-dev tk-dev libcairo2-dev mesa-common-dev libglu1-mesa-devNow, clone Magic VLSI git repository and change the working directory to cloned repository.
cd ~/eda_toolsgit clone git://opencircuitdesign.com/magiccd magic/Finally, run the configuration script, compile and install magic into the default path /usr/local/.
./configuremakesudo make install(Note: by default the installation path is /usr/local/, you can change by adding --prefix=<path> to configure. It takes some time to finish.)
Run the following to check it has been correctly installed:
magic(Note: You should already have installed Magic VLSI)
Even when netgen-lvs usually it is available as precompiled package, typically does not works when installed by the package manager 'apt'. Therefore, we'll install it from source code.
cd ~/eda_toolsgit clone https://github.com/RTimothyEdwards/netgen.gitcd netgen/./configuremakesudo make installRun the following to check it has installed correctly:
netgen-lvsKlayout is an editor that allows to change GDS and OASIS files and create them from scratch.
To install Klayout you should have some dependencies installed.
-
Qt 4.7+
-
gcc 4.6+ or clang 3.8+
-
Ruby
(Note: some of these dependencies were already installed.)
This package should be installed from source code. To do so, first download the most recent .deb file and run:
cd ~/Downloadssudo dpkg -i ./klayout_0.28.6-1_amd64.deb(Note: If getting problems related to libqt dependencies, execute the following and try again sudo dpkg -i ./klayout....)
sh sh sudo apt --fix-broken install
OpenLane requires Docker images, so first of all you shall have installed docker.
To have a more clean installation of docker, do the next steps.
- Uninstall any such older versions before attempting to install a new version:
cd ~/sudo apt remove docker docker-engine docker.io containerd runc- Update the
aptpackage index and install packages to allowaptto use a repository over HTTPS:
sudo apt -y update && sudo apt -y upgradesudo apt install -y ca-certificates curl gnupg- Add Docker’s official GPG key:
sudo mkdir -m 0755 -p /etc/apt/keyringscurl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg- Use the following command to set up the repository:
echo "deb [arch="$(dpkg --print-architecture)" signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
"$(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_CODENAME")" stable" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null- Update the
aptpackage index:
sudo apt update- Install Docker Engine, containerd, and Docker Compose.
sudo apt install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin- Manage Docker as a non-root user
Create the docker group.
sudo groupadd dockerAdd your user to the docker group.
sudo usermod -aG docker $USERActivate the changes to groups.
newgrp docker- Verify that the Docker Engine installation is successful by running the
hello-worldimage:
docker run hello-world(A succesfull instalation of Docker would have the following ouput)
Hello from Docker!
This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
To generate this message, Docker took the following steps:
1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon.
2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub. (amd64)
3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the executable that produces the output you are currently reading.
4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it to your terminal.
To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with:
$ docker run -it ubuntu bash
Share images, automate workflows, and more with a free Docker ID:
https://hub.docker.com/
For more examples and ideas, visit:
https://docs.docker.com/get-started/
OpenLane also requires its own dependencies, some of them were installed previously, but verify them for sanity checks.
- Checking Installation Requirements
In order to check the installation, you can use the following commands:
git --versiondocker --versionpython3 --versionpython3 -m pip --versionmake --versionpython3 -m venv -h- Download OpenLane from GitHub and change the working directory to cloned repository.
cd ~/eda_toolsgit clone https://github.com/The-OpenROAD-Project/OpenLane.gitcd OpenLane- Copy and paste the following commands to add the environment variables to your .bashrc file. (You can either do it manually from any text editor or executing the following.)
echo "export OPENLANE_ROOT=\"/home/\$USER/eda_tools/OpenLane\"" >> ~/.bashrcecho "export PDK_ROOT=\"\$OPENLANE_ROOT/pdks\"" >> ~/.bashrcecho "export PDK_PATH=\"\$PDK_ROOT/sky130A\"" >> ~/.bashrcsource ~/.bashrc- Execute the following command to get the latest docker image for OpenLane.
sudo make all- Build Sky130 PDK.
make pdk- Finally, run a ~5 minute test that verifies that the flow and the PDK were properly installed.
make testAfter installing the needed tools, we can install the Skywater PDK. Since installing the full PDK is slow and requires a lot of storage, we’ll install a minimal version with the needed cells.
First, we have to clone the Skywater repository and initialize the needed submodules.
cd ~/eda_toolsgit clone https://github.com/google/skywater-pdk.gitcd skywater-pdk/git submodule init libraries/sky130_fd_io/latestgit submodule init libraries/sky130_fd_pr/latestgit submodule init libraries/sky130_fd_sc_hd/latestgit submodule update(Note: the next command can take around 15 minutes to finish.)
make timingOnce the previous commands have finished their execution, go to your eda_tools directory:
cd ~/eda_toolsNow, clone the Open PDKs repo to configure and install the repository. Since we already cloned the Skywater PDK repo, we will indicate the configuration script where to find it, instead of pulling the full repo.
git clone https://github.com/RTimothyEdwards/open_pdks.gitcd open_pdks/./configure --enable-sky130-pdk=~/eda_tools/skywater-pdkmakesudo make install(Note: by default the installation path is /usr/local/share/pdk, you can change by adding --prefix=<path>. Remember /opt and /usr/local are paths where you can save your external packages installation. It takes some time to finish.)
The final step is to add environment variables to the .bashrc file, in order to use it in your flows.
(Note: You can add them either manually from any text editor or executing the following.)
PDK env variables
echo "export PDK_ROOT=\"/usr/local/share/pdk\"" >> ~/.bashrcecho "export PDK_PATH=\"\$PDK_ROOT/sky130A\"" >> ~/.bashrcAliases
You can use an alias called magicsky to run magic with the PDK tech file. Also, to use klayout create an alias called klayoutsky.
echo "alias magicsky=\"magic -T \$PDK_PATH/libs.tech/magic/sky130A.tech\"" >> ~/.bashrcecho "alias klayoutsky=\"klayout -e -nn \$PDK_PATH/libs.tech/klayout/tech/sky130A.lyt -l \$PDK_PATH/libs.tech/klayout/tech/sky130A.lyp\"" >> ~/.bashrcOnce, all environment variables were added, load env vars to the system, to do so, run:
source ~/.bashrcIf desired, the installation repos can also be removed to free additional storage.
cd ~/eda_toolsrm -rf magic/rm ~/Downloads/klayout_0.28.6-1_amd64.deb(Note: We do not remove OpenLane repo because it is constantly updating.)
To install the required EDA tools in other non-debian based distros, we first check which is our package manager installed.
uname -a
Or, if you have the lsb_release package installed.
lsb_release -a
Fedora uses dnf as a package manager.
Knowing our package manager go to check if you have already installed the next packages.
-
git 2.35+
-
docker 19.03.12+
-
python 3.6* with pip and venv
-
GNU Make
-
Ruby
git --version
docker --version
python3 --version
python3 -m pip3 --version
make --version
If you do not have one of them, install it, by running:
sudo dnf install <pkg>
In order to organize the directory tree for EDA tool-set, let's create a folder to contain every tool needed for the course. To do so, got to your user /home directory.
cd ~/
Create the directory eda_tools and move into:
mkdir eda_tools
cd eda_tools
(Note: in other linux distros it is recommended to install packages from source code, because there are some packages that are not into databases of your distro.)
Netgen LVS is a netlist generator use to compare Layout vs Schematic.
cd ~/eda_tools
git clone https://github.com/RTimothyEdwards/netgen.git
cd netgen/
./configure --prefix=/opt/netgen
make
sudo make install
NGSpice is an open source simulatori for electric and electronic circuits.
To install NGSpice from source code we keep in mind that the repository is under development, so in this case is better to install an stable version, as we see below.
Magic is a VLSI layout tool to do IC mask design.
To have a good complement with skywater pdk and magic, install the required dependencies before.
sudo dnf install m4 tcsh csh libx11-dev tcl-dev tk-dev libcairo2-dev mesa-common-dev libglu1-mesa-dev
Then, install magic from source code
cd ~/eda_tools
git clone https://github.com/RTimothyEdwards/magic.git
cd magic/
./configure
make
sudo make install
Klayout is an editor that allows to change GDS and OASIS files and create them from scratch.
To install Klayout you should have some dependencies installed.
-
Qt 4.7+
-
gcc 4.6+ or clang 3.8+
-
Ruby
From source code
cd ~/eda_tools
git clone https://github.com/KLayout/klayout.git
cd klayout/
./build.sh
OpenLane is an open source tool to automate RTL to GDSII flow.
To install OpenLane is by using source code. OpenLane will not be install in your PC, instead it uses a docker container.
(Note: you should have installed the prerequisites before to install OpenLane.)
To have a more clean installation of docker, do the next steps.
- First, uninstall any such older versions before attempting to install a new version:
cd ~/
sudo apt remove docker docker-engine docker.io containerd runc
- Update the
dnfpackage index and install packages to allowdnfto use a repository over HTTPS:
sudo dnf update && sudo dnf upgrade
sudo dnf install ca-certificates curl gnupg
- Add Docker’s official GPG key:
sudo mkdir -m 0755 -p /etc/apt/keyrings
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
- Use the following command to set up the repository:
echo "deb [arch="$(dpkg --print-architecture)" signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
"$(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_CODENAME")" stable" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
- Update the
dnfpackage index:
sudo dnf update
- Install Docker Engine, containerd, and Docker Compose.
sudo dnf install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin
- Manage Docker as a non-root user
Create the docker group.
sudo groupadd docker
Add your user to the docker group.
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
Activate the changes to groups.
newgrp docker
- Verify that the Docker Engine installation is successful by running the
hello-worldimage:
docker run hello-world
(A succesfull instalation of Docker would have the following ouput)
Hello from Docker!
This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
To generate this message, Docker took the following steps:
1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon.
2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub. (amd64)
3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the executable that produces the output you are currently reading.
4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it to your terminal.
To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with:
$ docker run -it ubuntu bash
Share images, automate workflows, and more with a free Docker ID:
https://hub.docker.com/
For more examples and ideas, visit:
https://docs.docker.com/get-started/
OpenLane also requires its own dependencies, some of them were installed previously, but verify them for sanity checks.
- Checking Installation Requirements
In order to check the installation, you can use the following commands:
git --version
docker --version
python3 --version
python3 -m pip --version
make --version
python3 -m venv -h
- Download OpenLane from GitHub and change the working directory to cloned repository.
cd ~/eda_tools
git clone https://github.com/The-OpenROAD-Project/OpenLane.git
cd OpenLane
- Copy and paste the following commands to add the environment variables to your .bashrc file. (You can either do it manually from any text editor or executing the following.)
echo "export OPENLANE_ROOT=\"/home/\$USER/eda_tools/OpenLane\"" >> ~/.bashrcecho "export PDK_ROOT=\"\$OPENLANE_ROOT/pdks\"" >> ~/.bashrcecho "export PDK_PATH=\"\$PDK_ROOT/sky130A\"" >> ~/.bashrcsource ~/.bashrc- Execute the following command to get the latest docker image for OpenLane.
sudo make all- Build Sky130 PDK.
make pdk- Finally, run a ~5 minute test that verifies that the flow and the PDK were properly installed.
make test
The PDK is the Process Design Kit where you have information about all standard cells.
First, we have to clone the Skywater repository and initialize the needed submodules.
cd ~/eda_tools
git clone https://github.com/google/skywater-pdk.git
cd skywater-pdk/
git submodule init libraries/sky130_fd_io/latest
git submodule init libraries/sky130_fd_pr/latest
git submodule init libraries/sky130_fd_sc_hd/latest
git submodule update
(Note: the next command can take around 15 minutes to finish.)
make timing
Once the previous commands have finished their execution, go to your eda_tools directory:
cd ~/eda_tools
Now, clone the Open PDKs repo to configure and install the repository. Since we already cloned the Skywater PDK repo, we will indicate the configuration script where to find it, instead of pulling the full repo.
git clone https://github.com/RTimothyEdwards/open_pdks.git
cd open_pdks/
./configure --enable-sky130-pdk=~/eda_tools/skywater-pdk
make
sudo make install
(Note: by default the installation path is /usr/local/share/pdk, you can change by adding --prefix=<path>. Remember /opt and /usr/local are paths where you can save your external packages installation. It takes some time to finish.)
The final step is to add environment variables to the .bashrc file, in order to use it in your flows.
(Note: You can add them either manually from any text editor or executing the following.)
PDK env variables
echo "export PDK_ROOT=\"/usr/local/share/pdk\"" >> ~/.bashrc
echo "export PDK_PATH=\"\$PDK_ROOT/sky130A\"" >> ~/.bashrc
Extra aliases
You can use an alias called magicsky to run magic with the PDK tech file. Also, to use klayout create an alias called klayoutsky.
echo "alias magicsky=\"magic -T \$PDK_PATH/libs.tech/magic/sky130A.tech\"" >> ~/.bashrc
echo "alias klayoutsky=\"klayout -e -nn \$PDK_PATH/libs.tech/klayout/tech/sky130A.lyt -l \$PDK_PATH/libs.tech/klayout/tech/sky130A.lyp\"" >> ~/.bashrc
Once, all environment variables were added, load env vars to the system, to do so, run:
source ~/.bashrc
If desired, the installation repos can also be removed to free additional storage.
cd ~/eda_tools
rm -rf magic/
rm ~/Downloads/klayout_0.28.6-1_amd64.deb
-
In order to verify OpenLANE was correctly installed and the variables needed are pointing to the PDK, move to OpenLane directory and run the following command:
cd ~/eda_tools/OpenLanemake testYou will see a process being executed, and will take around 5 min to finish.
The last lines should look like this:
.
.
.
[INFO]: There are no hold violations in the design at the typical corner.
[INFO]: There are no setup violations in the design at the typical corner.
[SUCCESS]: Flow complete.
[INFO]: Note that the following warnings have been generated:
[WARNING]: Current core area is too small for the power grid settings chosen. The power grid will be scaled down.
Basic test passed
(Note: This test requires that OpenLANE test has been succesfully completed.)
- In order to verify
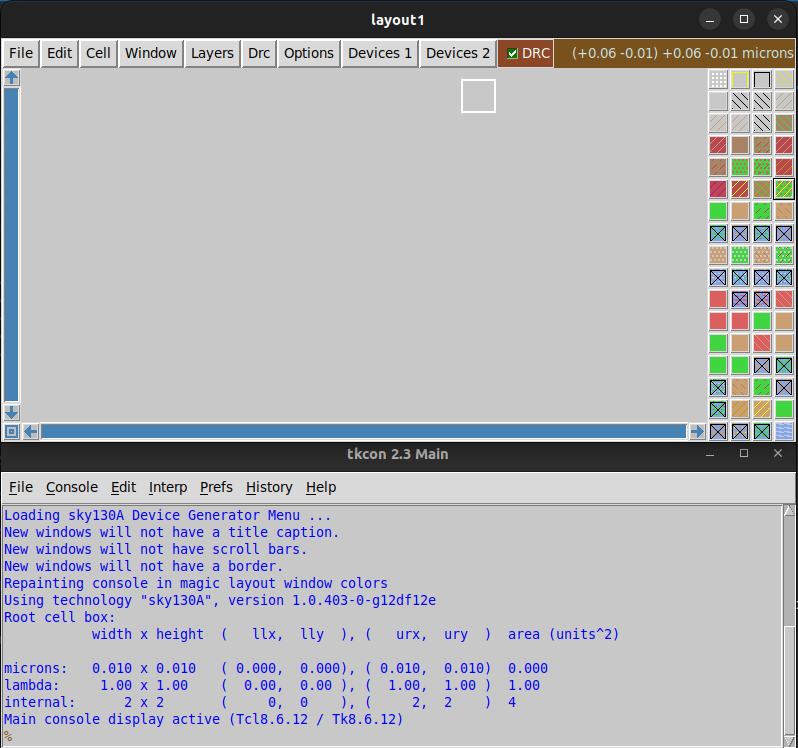
magicwas correctly installed and the alias was correctly set, move to /..../results/signoff/ :
cd ~/eda_tools/OpenLane/designs/spm/runs/openlane_test/results/signoffand run the following command:
magicsky- The following two windows should appear:
-
If Magic is correctly installed and pointing to the PDK, the right-side layer pallet, will be displayed.
(Note: This test requires that OpenLANE test has been succesfully completed.)
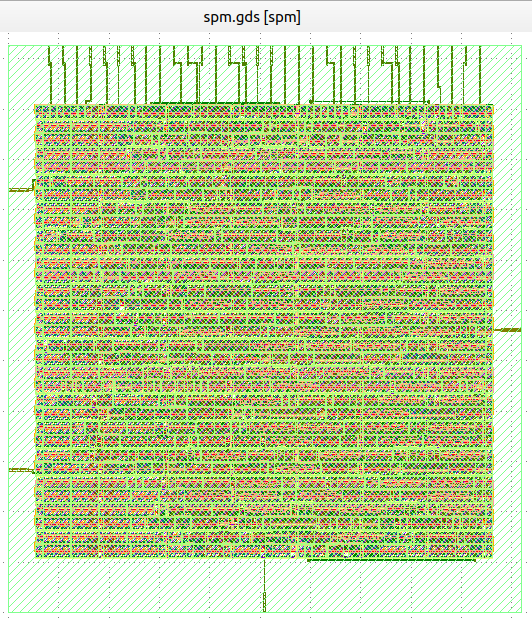
- In order to verify Klayout was correctly installed and the alias was correctly set, move to /..../results/signoff/ :
cd ~/eda_tools/OpenLane/designs/spm/runs/openlane_test/results/signoffand run the following command:
klayoutsky spm.gds- You should be able to watch the following GDS:
- OpenLANE Official Documentation: OpenLane Documentation
-
config.tcl Variables description OpenLane config.tcl Variables
-
Open_PDKs - open_pdks Download : open_pdks
-
Open_PDKs - skywater-pdk Install : skywater-pdk_installation