Detection of pothole using RCNN and Mask-RCNN
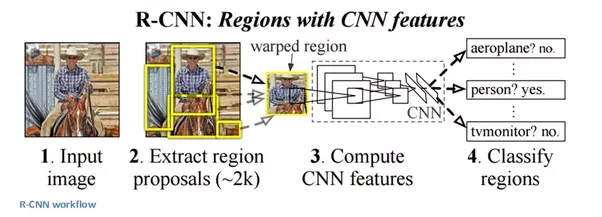
R-CNN is short for “Region-based Convolutional Neural Networks”. The main idea is composed of two steps. First, using selective search, it identifies a manageable number of bounding-box object region candidates (“region of interest” or “RoI”). And then it extracts CNN features from each region independently for classification.
-
Pre-train a CNN network on image classification tasks; for example, VGG or ResNet trained on ImageNet dataset. The classification task involves N classes.
-
Propose category-independent regions of interest by selective search (~2k candidates per image). Those regions may contain target objects and they are of different sizes.
-
Region candidates are warped to have a fixed size as required by CNN.
-
Continue fine-tuning the CNN on warped proposal regions for K + 1 classes; The additional one class refers to the background (no object of interest). In the fine-tuning stage, we should use a much smaller learning rate and the mini-batch oversamples the positive cases because most proposed regions are just background.
-
Given every image region, one forward propagation through the CNN generates a feature vector. It is predicted using VGG16 pre-trained model which is trained on Imagnet dataset.The positive samples are proposed regions with IoU (intersection over union) overlap threshold >= 0.3, and negative samples are irrelevant others.
-
To reduce the localization errors, a regression model is trained to correct the predicted detection window on bounding box correction offset using CNN features.