Wildlife Licencing Services
For Natural England
Getting started
To run the application in a local docker stack
First edit the docker secret environment files to add the secret keys
- docker/env/aqp-secrets.env
(The secrets for the test environment may be obtained from graham.willis@defra.gov.uk)
Extra step for M1 Mac users
Unfortunately the virus check package does not run on macs. This prevents the web-service container from running. To get around this you need to add the following environment variable to docker/env/web.env
NO_SCANNING_REQUIRED=true
Now run the following shell commands;
cd wildlife-licencing
npm i
npm run docker:build
npm run docker:start
docker service ls
npm run docker:stopThe docker services running should be as follows:
-
wls_api
-
wls_aqp
-
wls_aep
-
wls_rep
-
wls_fqp
-
wls_web
-
wls_postgres
-
wls_redis
-
wls_rediscommander
-
wls_localstack
-
wls_clamav
-
wls_adminer
To run locally
To run the microservices locally you need to start the supporting cloud services in the docker swarm.
Run the following shell commands;
cd wildlife-licencing
npm run docker:start-cloud
docker service lsThe docker services running should be as follows:
- wls_postgres
- wls_redis
- wls_rediscommander
- wls_localstack
- wls_clamav
- wls_adminer
Ensure you have node version 16.13.0 or greater installed; node --version
Localstack
The AWS S3 interface is simulated in the local docker stack using the localstack image. 4566 is the port for the localstack interface.
S3
In order to run S3 operations locally the AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY environment variables must be set in the local shell - the value is arbitrary.
Alternatively you can install the AWS CLI.
Instructions to do this are here
Then run aws configure to generate a fake set of credentials. (Localstack does not support IAM)
The service stores files in an S3 bucket before moving them into sharepoint. It is necessary to set up a bucket in local stack as follows
aws --endpoint-url=http://localhost:4566 s3api create-bucket --bucket local-bucket --region eu-west-2
aws --endpoint-url=http://localhost:4566 s3 ls
Note: Be sure to double check that the region also matches the one in the environment variables under AWS_REGION
Secrets Manager
The service uses the Secrets Manager to hold the address lookup certificates. These should be uploaded into the localstack secrets manager as follows
aws --endpoint-url=http://localhost:4566 secretsmanager create-secret \
--name /tst/ldn/new/devops/web_service/address-lookup-certificate \
--secret-string file://<Certificate File> \
--region eu-west-2
aws --endpoint-url=http://localhost:4566 secretsmanager create-secret \
--name /tst/ldn/new/devops/web_service/address-lookup-key \
--secret-string file://<Key File> \
--region eu-west-2
This requires the following corresponding environment variables to be set
ADDRESS_LOOKUP_CERTIFICATE_PARAMETER=/tst/ldn/new/devops/web_service/address-lookup-certificate;
ADDRESS_LOOKUP_KEY_PARAMETER=/tst/ldn/new/devops/web_service/address-lookup-key;
AWS_REGION=eu-west-2;
The address lookup certificates are provided to us as a pfx file combined format. In order to extract the certificate and key from the pxf file follow the procedure shown at the end of this README
To run any package locally
To be able to run a package locally it has to be taken out of the docker swarm To find the process id for the package you want to take out of the swarm you need to run
docker service lsFor example, we'll remove wls_web, but this will work for any package
docker service rm wls_webYou'll need to cd into your package
cd packages/web-serviceIf you were to run this you should get to a point where your server is running, but you get a status 500 error.
The file env.example in the web-service directory needs to be copied and renamed
cp .env.example .env
still inside the web-service, you need on windows to run
node_modules/gulp/bin/gulp.js build
Problems have been faced running this in node, but git bash has been successful.
Running npm run start from the web-service directory should now work.
Start the API locally
cd wildlife-licencing/packages/api
cp env.example .env
npm run devHow to restart your Docker swarm
Sometimes, changes may go into master that will break your Docker swarm if you don't rebuild it. This isn't true for every change, but it's important to know how to bring your swarm down, rebuild it - and then start it again.
The process is pretty simple:
- Pull from
masterand ensure you're upto date - You need to drop all your database tables inside
wls. You'll need your database container to be up, for this to work. Sometimes you may face with some issues with tables having a foreign key that's used elsewhere so it can't be deleted. You'll just have to delete the tables relying on the key first. You can always do this step via calling the delete script that the Jenkins pipelines use: https://gitlab-dev.aws-int.defra.cloud/new/new-jenkins-scripts/-/blob/master/drop_db_tables.sql - Ensure you haven't lost your Docker .env variables, as pulling will often overwrite them
- Stop your swarm with
npm run docker:stop - Double check you don't need to run
npm ifrom the top level of the repo, if the dependencies have changed. Often doesn't happen, just worth a check - Build your swarm again with
npm run docker:build - Start your swarm again with
npm run docker:start
To start the queue processor locally
cd wildlife-licencing/packages/application-queue-processor
cp env.example .env
npm run devEdit the .env files to add secrets
(The secrets for the test environment may be obtained from graham.willis@defra.gov.uk)
If you receive the secrets, please remember to ignore them in git, by running
git update-index --assume-unchanged docker/env/*.env
If changes are required to be made then set git update-index --no-assume-unchanged docker/env/.env`
Alternatively set the environment variables in the running shell or your IDE
Packages
| Package | Description | Runnable | Docker Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| api | The application program interface to support the UI and manage data transfers from the middleware to Power Platform | Y | wildlife-licencing/api |
| application-queue-processor | Consumes jobs from the application-queue and submits them to Power Platform as ODATA batch updates. | Y | wildlife-licencing/aqp |
| application-extract-processor | Extracts data application data from Power Platform and updates the postgres database | Y | wildlife-licencing/ep |
| refdata-extract-processor | Extracts reference data from Power Platform and updates the postgres database | Y | wildlife-licencing/ep |
| web-service | Public facing web server | Y | wildlife-licencing/web-service |
| file-queue-processor | Write files to sharepoint | Y | wildlife-licencing/web-service |
| connectors-lib | Encapsulates connector logic. Currently supports AWS, Postgres, Redis, Power Platform & Bull-Queue | N | |
| database-model | Extracts the sequelize database model in order to share it between multiple processes | N | |
| powerapps-lib | Supports operations against the Power Platform ODATA interface, including transformation | N | |
| powerapps-keys | Record of fixed keys in the power platform | N | |
| queue-defs | Extracts the bull-queue queue definitions | N |
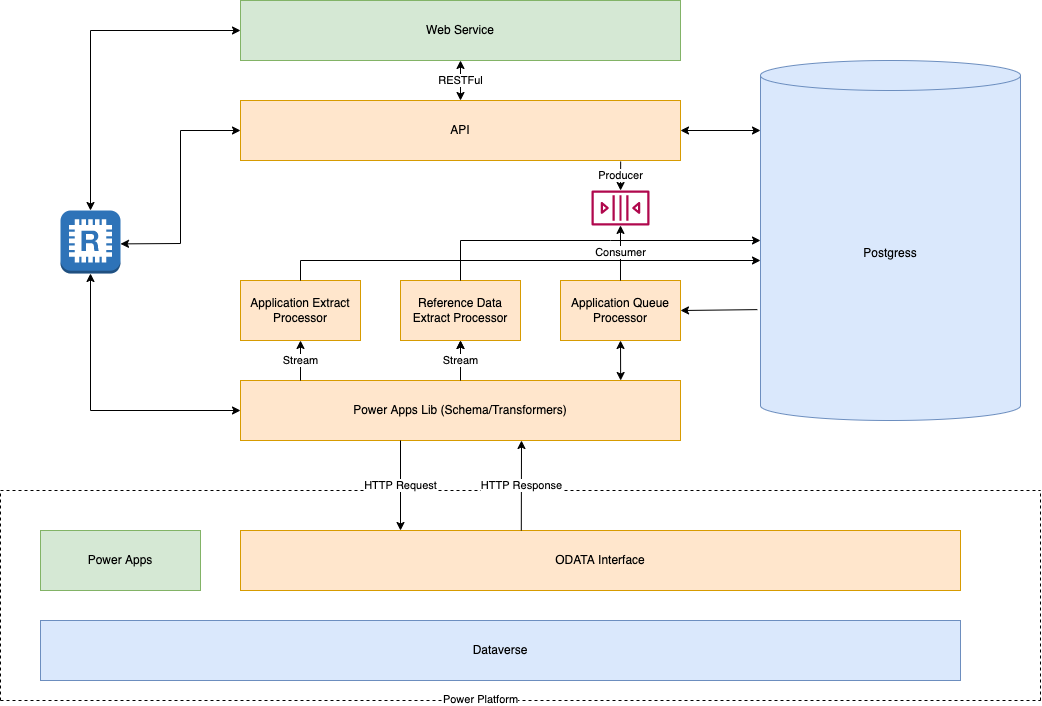
Application Architecture
Overview
A set of API request handlers has been created for the manipulation of the application data in the POSTGRES database. These are
documented via OpenAPI at http://localhost:3000/openapi-ui when running locally.
Requests to the API perform SQL on the postgres tables and populate the JSON structures in the JSONB fields.
Submitted data will be queued using bull-queue. The queues are stored in Redis and can be inspected (locally) using redis-commander http://localhost:8002/
The queues are defined centrally in the package packages/queue-defs/src/defs.js. This enables autonomous processes
that connect to the queues on start-up to ensure they have the same definition.
The queued data is consumed by the Application Queue Processor and wrtiien into the Power Platform using the powerapps-lib package.
The Application Extract Processor and the Reference Data Extract Processor are used to extract data from the Power Platform and write it down to the Postgres tables.
For details of the inbound and outbound processes see powerapps-lib/README.md
Appendix
To extract a certificate and key for the address lookup from the provided pxf file follow these steps:
- Extract .crt file from the .pfx certificate (you will be prompted for the password)
openssl pkcs12 -in BOOMI-SDDS-SND.pfx -clcerts -nokeys -out BOOMI-SDDS-SND.crt
- Extract the private key from the .pfx file
openssl pkcs12 -in BOOMI-SDDS-SND.pfx -nocerts -out temp.key
- Extract the .key file from the encrypted private key openssl rsa -in temp.key -out BOOMI-SDDS-SND.key