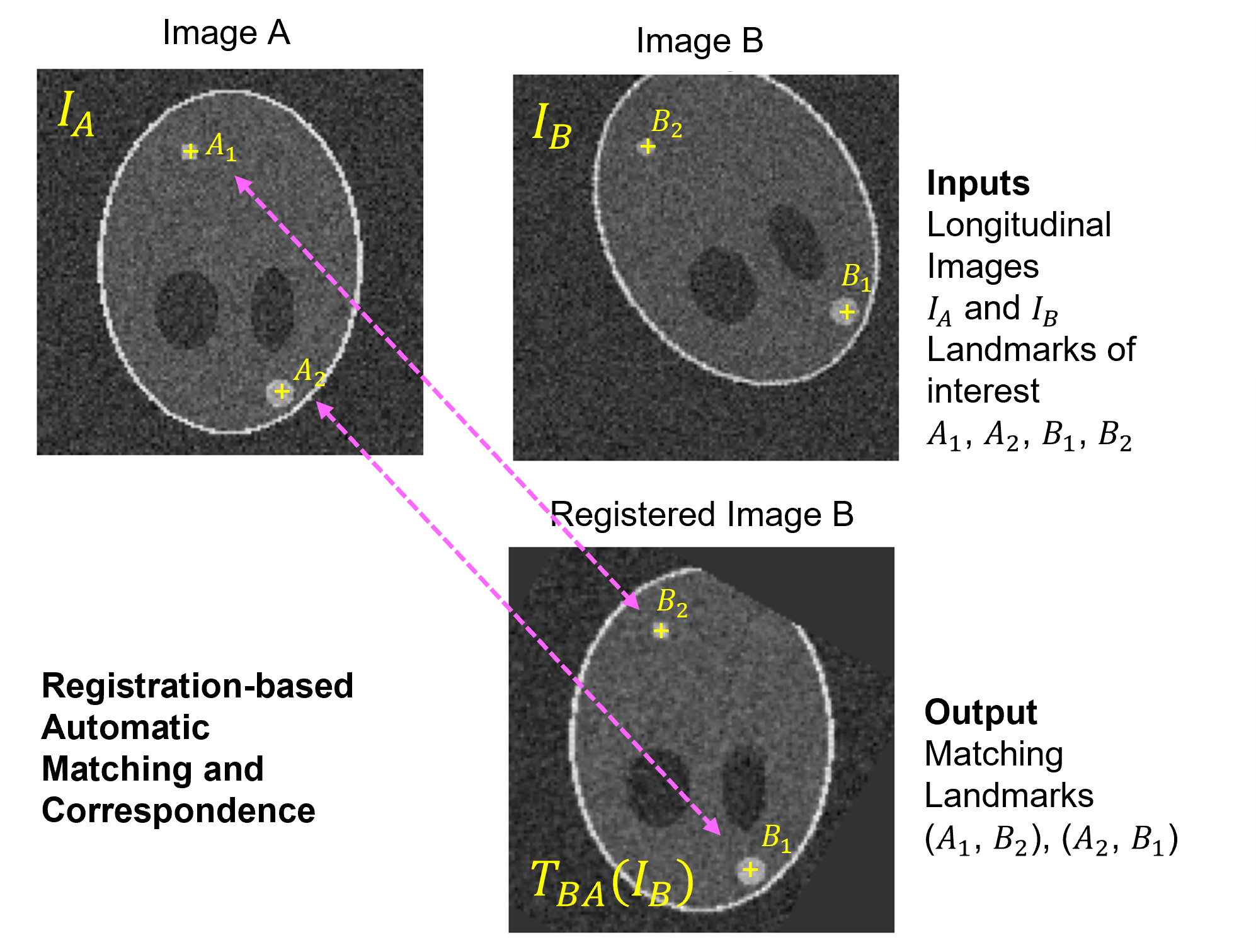
RAMAC is a tool for identifying corresponding annotated regions of interest in a sequence of volumetric images. It is originally developed as part of the FDA-Novartis collaboration to analyze correspondence of metastatic breast lesions in a longitudinal imaging study.
In this guide, we present a comprehensive overview of the Registration-based Automated Matching and Correspondence (RAMAC) package.
RAMAC is a software tool that streamlines the process of automating matching and establishing correspondence between longitudinal medical image datasets. It consists of a two-phase sequential pipeline, combining registration and correspondence algorithms to efficiently analyze and thereby establish correspondence. For example, in a longitudinal imaging study, multiple lesions may be annotated across many DICOM image series. This tool may be used to find corresponding annotations in all image series that correspond to same lesion.
The RAMAC algorithm comprises of a two-phase sequential pipeline:
-
Firstly, the algorithm performs three-dimensional rigid registration to register longitudinal medical images.
-
Correspondence of the regions or landmarks of interest is next established by an adaptive Hungarian algorithm.
The algorithm expects volumetric images and coordinates of landmarks as inputs. The landmark coordinates can be inputted using stored comma-separated values (CSV) files. The tool converts the input images to SimpleITK format and the landmark cooridnates to physical coordinates. Image registration is performed next.
For example, in the Overview figure of RAMAC below, image registration is performed on the input images with one designated as fixed image (Image A) and other as moving (Image B). Currently RAMAC supports rigid registration using stochastic gradient descent as optimzer and linear interpolant. This workflow generates a transform
RAMAC is intended to automate manual work needed to identify corresponding anatomical landmarks in a series of images. The package relies solely on image registration and does not require additional metadata.
You can install RAMAC from source available on GitHub. If you prefer, you can clone it and run the setup.py file. Use the following commands to get a copy from GitHub and install all dependencies:
Once installed, you can run the test_script from the test folder.
git clone https://github.com/DIDSR/RAMAC.git
cd RAMAC
pip install .User manual and examples can be found in the RAMAC Documentation pages.
- Subrata Mukherjee
- Qian Cao
If you use this project in academic work or publications, we appreciate citing it using the following BibTeX entry:
@misc{mukherjee2024image,
title={Image registration based automated lesion correspondence pipeline for longitudinal CT data},
author={Subrata Mukherjee and Thibaud Coroller and Craig Wang and Ravi K. Samala and Tingting Hu and Didem Gokcay and Nicholas Petrick and Berkman Sahiner and Qian Cao},
year={2024},
eprint={2404.16544},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={eess.IV}
}